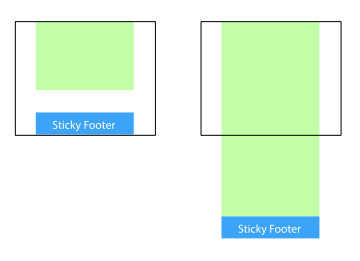
页脚置底(Sticky footer)就是让网页的footer部分始终在浏览器窗口的底部。
当网页内容足够长以至超出浏览器可视高度时,页脚会随着内容被推到网页底部;
但如果网页内容不够长,置底的页脚就会保持在浏览器窗口底部。
方法一:将内容部分的margin-bottom设为负数
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
min-height: 100%;
margin-bottom: -50px; /* 等于footer的高度 */
}
.footer, .push {
height: 50px;
}
这个方法需要容器里有额外的占位元素(div.push)。
div.wrapper的margin-bottom需要和div.footer的-height值一样,注意是负height。
方法二:将页脚的margin-top设为负数
给内容外增加父元素,并让内容部分的padding-bottom与页脚的height相等。
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.content {
min-height: 100%;
}
.content-inside {
padding: 20px;
padding-bottom: 50px;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
margin-top: -50px;
}
方法三:使用calc()设置内容高度
.content {
min-height: calc(100vh - 70px);
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
}
这里假设div.content和div.footer之间有20px的间距,所以70px=50px+20px
方法四:使用flexbox弹性盒布局
以上三种方法的footer高度都是固定的,如果footer的内容太多则可能会破坏布局。
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
min-height: 100%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.content {
flex: 1;
}
方法五:使用Grid网格布局
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
min-height: 100%;
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr auto;
}
.footer {
grid-row-start: 2;
grid-row-end: 3;
}

)
...)
















