一、基本命令
1、启动服务器
cmd
net start [服务器名称]
net start mysql57
2、停止服务器
cmd
net stop [服务器名称]
net stop mysql57
3、链接数据库
mysql -u 用户名 -p 登录密码
mysql -u root -p
4、退出登录
quit
exit
\q
5、查看版本(连接后执行)
select version();
6、查看当前时间(连接后执行)
select now();
7、远程链接
mysql -h ip地址 -u 用户名 -p密码 -P服务器端口号(默认3306)
二、数据库操作
1、创建数据库
格式: create database 【数据库名】 charset=utf8;
示例:create database sunck charset=utf8;
2、删除数据库
格式: drop database 【数据库名】;
示例:drop database sunck;
3、切换数据库
格式:use [数据库名]
示例:use sunck;
4、查看当前选择的数据库
select database();
三、表操作(切换到当前数据库后使用)
1、查看当前数据库中所有表
show tables;
2、创建表
格式:create table 表名(列及类型)
说明:auto_increment 表明自增长 primary key 表示主键
not null 表示不为空
示例:create table student(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
age int not null,
gender bit default 1,
address varchar(20),
isDelete bit default 0
);
3、删除表
格式:drop table 【表名】;
示例:drop table student;
4、查看表结构
格式:desc 【表名】;
示例:desc student;
5、查看建表语句
格式:show create table 【表名】;
示例:show create table student;
6、重命名表名
格式:rename table 元表名 to 新表名
示例:rename table car to newCar;
7、修改表
格式:alter table [表名] add|change|drop 列名 类型;
示例:alter table newCar add isDelete bit default 0;
四、数据操作
1、增
a、全列插入:
格式:insert into [表名] values(...)
说明:主键列是自动增长的,但是在全列插入时需要占位,通常使用0,
插入数据以后以实际数据为准
示例:insert into student values(0,"韩梅梅",15,0,"北京",0);
b、缺省插入:
格式:insert into tablename(column1,column2,.....) values(value1,value2,.....);
示例:insert into student(name,age,address) values ("lilei",19,"上海");
c、同时插入多条数据:
格式:insert into tablename values values(...),(...),...;
示例:insert into student values (0,"穆桂英",28,0,"河南",0),(0,"杨帅",20,1,"河北",0),(0,"刘秀",35,1,"石家庄",0);
2、删
格式:delete from tablename;全部删除,删除整个表的数据
delete from tablename where 条件;
示例:delete from student where id=7;
注意:没有条件是全部删除,慎用。
3、改
格式:update tablename set 列1=值1,列2=值2,....
update tablename set 列1=值1,列2=值2,.... where 条件
示例:update student set age =16 where id=4;
注意:没有条件是全部修改,慎用。
4、查
格式:select * from [tablename];
说明:查询表中的全部数据
示例:select * from student;
五、查
1、基本语法
格式:select * from [tablename];
说明:查询表中的全部数据 a、from 关键字后面是表名,表示数据来源于这张表
b、select 后面写表中的列名,如果是* 表示结果中集中显示表中的所有列
c、在select后面的列名部分,可以使用as为列名起别名,这个别名显示在结果集中
d、如果要查询多个列,之间用逗号分隔
示例:select * from student;
select name,age from student;
select name as "姓名",age from student;
2、消除重复行
在selecthoumian 列前前面使用 distinct 可以消除重复的行
示例:select distinct name,age from student;
3、条件查询
a、语法
select * from 表名 where 条件
b、比较运算符
操作符描述实例
=等号,检测两个值是否相等,如果相等返回true(A = B) 返回false。
<>, !=不等于,检测两个值是否相等,如果不相等返回true(A != B) 返回 true。
>大于号,检测左边的值是否大于右边的值, 如果左边的值大于右边的值返回true(A > B) 返回false。
>=大于等于号,检测左边的值是否大于或等于右边的值, 如果左边的值大于或等于右边的值返回true(A >= B) 返回false。
<=小于等于号,检测左边的值是否小于于或等于右边的值, 如果左边的值小于或等于右边的值返回true(A <= B) 返回 true。
c、逻辑运算符
and
or
not
d、模糊查询
like
% 表示任意多个任意字符
_ 表示一个任意字符
select * from student where name like "刘%";
select * from student where name like "刘_";
e、范围查询
in 表示在一个非连续性的范围内
between... and ... 表示在一个连续范围内
需求:查询编号为8,10,12的学生
示例:select * from student where id in (8,10,12);
需求:查询编号为6-8的学生
示例:select * from student where id between 6 and 8;
f、空判断
insert into student(name,age) values ("daojun",69);
注意:null 与"" 是不同
判断空: is null
判断非空: is not null
需求:查询没有地址的同学
示例: select * from student where address is null;
g、优先级
小括号, not 比较运算符,逻辑运算符
and 比or 优先级高。
4、聚合
为了快速得到统计数据,提供五个聚合函数
a、 count(*) 表示计算总行数,括号中可以写* 和列名
b、 max(列) 表示求此列的最大值
c、 min(列) 表示求此列的最小值
d、 sum(列) 表示求此列的和
e、 avg(列) 表示求此列的平均值
需求:查询学生总数
示例: select count(*) from student;
需求:查询女生的编号最大值
示例: select max(id) from student where gender=0;
需求:查询女生的编号最小值
示例: select min(id) from student where gender=0;
需求:查询女生的年龄和
示例: select sum(age) from student where gender=0;
需求:查询学生年龄平均值
示例: select avg(age) from student;
5、分组
按照字段分组,表示此字段相同的数据会被放到一个集合中。分组后,只能查询出相同的数据列。
对于有差异的数据列,无法显示在结果集中
可以对分组后的数据进行统计,做聚合运算。
语法:select 列1,列2,聚合... from 表名 group by 列1,列2,列3,.... having 列1,列2,.....,聚合...
需求:查询女生和男生总数
示例:select gender,count(*) from student group by gender;
select name,gender,count(*) from student group by gender,age;
需求:分组后的数据筛选
示例: select gender,count(*) from student group by gender having gender;
select gender,count(*) from student group by gender having gender;
where 与 having的区别
where 对from 后面的制定的表进行筛选,属于对原始数据的筛选
having 是对结果集 group by 的结果进行筛选
6、排序
语法: select * from 表名 order by 列1
asc|desc, 列2 asc|desc,....
说明:
a、将数据按照列1进行排序,如果某些列1的值相同,则按照列2进行排序
b、默认按照从小到大的顺序排序
c、asc升序
d、desc降序
需求:按照年龄排序
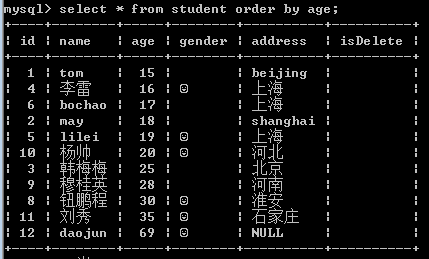
示例: select * from student order by age;
需求:按照没有删除的数据的年龄排序
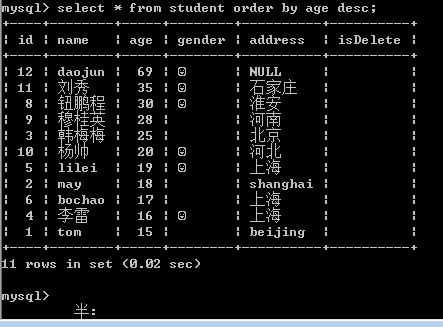
示例: select * from student where isDelete=0 order by age desc,id desc;
7、分页
语法:select * from 表名 limit start,count;
说明: start索引从0开始
示例:select * from student limit 0,3;
select * from student limit 3,3;
select * from student where gender=1 limit 0,3;
六、关联
外键去关联其他表。
建表语句:
create table class(id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(20) not null,stuNum int not null);
create table students(id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(20) not null,gender bit default 1,classid int not null,foreign key(classid) references class(id));
插入数据:
insert into class values(0,"python01",45),(0,"python02",20),(0,"python03",30),(0,"python04",34),(0,"python05",28);
insert into students values(0,"tom",1,1);
insert into students values(0,"lilei",1,1);
insert into students values(0,"jack",1,2);
insert into students values(0,"韩梅梅",0,1);
关联查询
select students.name,class.name from class inner join students on class.id=students.classid;
select students.name,class.name from class left join students on class.id=students.classid;
select students.name,class.name from class right join students on class.id=students.classid;
分类:
1、表A inner join 表B
表示 表A与表B的行会出现在结果集中
2、表A left join 表B
表A与表B的行会出现在结果集中,外加表A中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
3、表A reft join 表B
表A与表B的行会出现在结果集中,外加表B中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充

)













)


)
