不点蓝字,何来故事?
许久之前关于Verilog I/O操作的一篇笔记梳理,再此与诸君共分享。0I/O操作类型verilog中关于文件操作的任务和函数主要分为四类:
(1)打开和关闭文件的任务和函数
(2) 向文件中输入信息的任务
(3) 向变量中输入信息的任务
(4) 从文件中读取数据并写入变量或存储器中
1打开和关闭文件的任务和函数fd=$fopen("file_name",type)
该函数主要用于按照type定义的方式打开"file_name"指定的文件,并返回32比特的文件描述符。type的类型有:
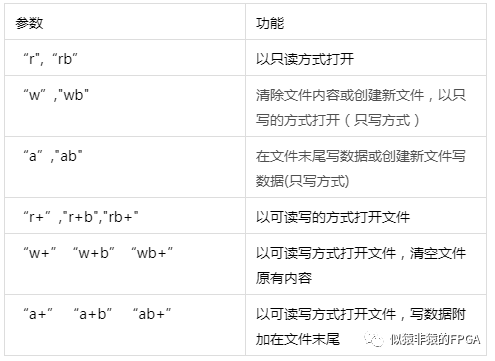
默认方式为以“w”或“wb”方式打开。注意"w","wb","w+","w+b","wb+"打开文件将会清空文件原有数据。其中“b”用于区别文本文件和二进制文件。如果一个文件因为某种无法打开,将会返回0,通过$ferror可用于检测失败原因。
$fclose(fd)
该函数主要用于关闭文件。文件一旦关闭,$fmonitor 、$fstrobe等任务将会自动终止。
2向文件中输入信息file_output_task_name(multi_channel_descriptior|fd,[,list_of_arguments])
file_output_task_name ::=$fdisplay | $fdisplayb | $fdisplayh | $fdisplayo| $fwrite | $fwriteb | $fwriteh | $fwriteo| $fstrobe | $fstrobeb | $fstrobeh | $fstrobeo| $fmonitor | $fmonitorb | $fmonitorh | $fmonitoro
$fmonitor只要有变化就一直记录
$fmonitor(file_id,"%format_char", parameter);
$fmonitor(file_id, "%m:%t in1=%d o1=%h", $time, in1, o1);
只允许有一个$monitor 进程,但同时可以运行任意数量的$fmonitor 进程.
$fwrite需要触发条件才记录,不自动换行
$fwrite(file_id,"%format_char", parameter);
$fdisplay需要触发条件才记录
$fdisplay(file_id,"%format_char", parameter);
$fstrobe();当该时刻的所有事件处理完后,在这个时间步的结尾写入,可以确保所写的数据时无误的。推荐使用。
3向变量中输入信息string_output_tasks ::=string_output_task_name ( output_reg , list_of_arguments ) ;
string_output_task_name ::=$swrite | $swriteb | $swriteh | $swriteo
variable_format_string_output_task ::=
$sformat ( output_reg , format_string , list_of_arguments ) ;
$swrite、$sformat用于以制定格式向寄存器中写入字符串
string s1,s2;$swriteb(s1,"a","b");$sformat(s2,"%s%s","a","b");$display("$sformat: %s ",s2);$display("$swrite: %s ",s1);c=$fgetc(fd)——从文件中一次读取一个字符
如果从文件中读取发生错误时,c将被设为EOF(-1).通过$ferror可获取错误原因,c的位宽应大于8位。采取这种格式读取数据文本文件中的空格、标点符号等也会被读出来。
code=$ungetc(c,fd);
向fd文件的缓冲区内插入字符c,c将会在下次调用$fgetc时返回,调用该函数并不会改变文件本身内容。当发生错误时code为EOF,否则为0。
从文件中读取一行
integer code;
code=$fgets(str,fd);
从fd指定的文件中读取数据到str直至str填满或出现换行符或出现EOF。若str长度不是整数个bytes,则高位部分数据将被舍去。若读取失败,则code返回0,否则code将返回读取的字符数。
按照固定格式从文件中读取数据
integer code;
code=$fscanf(fd,format,args);//从fd文件中按照format制定的格式读取数据到args中
code=$sscanf(fd,format,args);//从寄存器中按照format制定的格式读取数据到args中
空白字符(空格、制表符、换行符)可用于跳过空白符读取非空白字符(对于标点符号等无效)。
%m能够返回当前仿真路径,而不返回文件中的字符
按照二进制格式读取数据
integer code = $fread( myreg,fd);
integer code = $fread( mem, fd);
integer code = $fread( mem, fd, start);
integer code = $fread( mem, fd, start, count);
integer code = $fread( mem, fd, , count);
读取二进制流,将数据从fd读向myreg或mem,不可读x,z.start是指mem的位置,count指待读取的长度。
For start = 12 and the memory up[10:20],the first data would be loaded at up[12]. For the memory down[20:10],the first location loaded would be down[12], then down[13]。
缺省情况下fread将mem填满或读完截止。
文件中的数据逐字节读取。使用一个8位宽的存储器加载一个字节,而使用每个存储器字2个字节宽加载9位宽的存储器。数据是以大尾数方式从文件中读取;第一个字节读取用于填充最重要的位置存储元件。如果内存宽度不能被8(8,16,24,32)整除,则由于截断并不是文件中的所有数据都加载到内存中。
5文件定位integer pos ;
pos = $ftell ( fd );
返回fd文件当前位置距文件首部偏移量(按字节计算),可以用于后续的$fseek使用,以将文件重新定位到此点。重定位将会取消$ungetc操作。
code=$fseek(fd,offest,operation);
code = $rewind ( fd );
$fseek()设置文件fd的下一输入或输出位置。
0:设置位置到偏移地址
1:设置位置到当前位置加偏移量
2:设置位置到文件结束位置加偏移量(向前)
$rewind()等价于$fseek(fd,0,0);
When a file is opened forappend (that is, when type is "a", or "a+"), it isimpossible to overwrite information already in the file.when output is written to the file, the current file pointer is disregarded. All output is written at the end of the file and causes the file pointer to be repositioned at the end of the output.
6缓存区冲刷$fflush ( mcd );
$fflush ( fd );
$fflush ( );
将所有缓冲区的数据写入制定的mcd或fd,若参数缺省,冲刷写入所有打开的文件。
7I/O状态查询I/O error status
integer errno;
errno=$ferror(fd,str);
描述的错误信息字符串将被存放在字符串str中。如果没有错误,errno将为0,str将被清空。
8检测文件结尾integer code;
code=$feof(fd);
当检测到文件结尾时,返回1,否则返回零。
8加载文件到存储区$readmemb ( " file_name ", memory_name [ , start_addr [ , finish_addr ] ] ) ;
$readmemh ( " file_name " , memory_name [ , start_addr [ , finish_addr] ] ) ;
文件应该只包括空白符、注释、二进制或十六进制数据。



 精彩推荐SpinalHDL资料汇总SpinalHDL—优雅地实现总线寄存器读写SpinalHDL代码组织结构之Component换个名字混江湖SpinalHDL—覆盖率收集SpinalHDL—测试平台搭建兄弟,要几段?打个拍,握个手可以么SpinalHDL—柳暗花明又一村FPGA图像处理——老戏新说山水有相逢—和大牛成为同事SpinalHDL——环境搭建乱花渐欲迷人眼—Vivado之SynthesisPCIe之MSI-x中断(一)
精彩推荐SpinalHDL资料汇总SpinalHDL—优雅地实现总线寄存器读写SpinalHDL代码组织结构之Component换个名字混江湖SpinalHDL—覆盖率收集SpinalHDL—测试平台搭建兄弟,要几段?打个拍,握个手可以么SpinalHDL—柳暗花明又一村FPGA图像处理——老戏新说山水有相逢—和大牛成为同事SpinalHDL——环境搭建乱花渐欲迷人眼—Vivado之SynthesisPCIe之MSI-x中断(一)













内部机制的介绍和启动过程)




