最近看到了Brett Beauregard发表的有关PID的系列文章,感觉对于理解PID算法很有帮助,于是将系列文章翻译过来!在自我提高的过程中,也希望对同道中人有所帮助。作者Brett Beauregard的原文网址:http://brettbeauregard.com/blog/2017/06/proportional-on-measurement-the-code/
在上一篇文章中,我把所有的时间都花在解释了比例测量的好处上。在这篇文章中,我将解释代码。人们似乎很欣赏我上次一步一步地解释事情的方式,所以在此我也将采取这样的方式。下面的3个步骤详细介绍了我是如何将 PonM 添加到 PID 库的。
第一阶段–初始输入和比例模式选择
/*working variables*/
unsigned long lastTime;
double Input,Output,Setpoint;
double ITerm,lastInput;
double kp,ki,kd;
int SampleTime = 1000; //1 sec
double outMin,outMax;
bool inAuto = false;#define MANUAL 0
#define AUTOMATIC 1#define DIRECT 0
#define REVERSE 1
int controllerDirection = DIRECT;#define P_ON_M 0
#define P_ON_E 1
bool PonE = true;
double initInput;
void Compute()
{if(!inAuto) return;unsigned long now = millis();int timeChange = (now - lastTime);if(timeChange>=SampleTime){/*Compute all the working error variables*/double error = Setpoint - Input;ITerm+= (ki * error);if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;double dInput = (Input - lastInput);/*Compute P-Term*/if(PonE) Output = kp * error;else Output = -kp * (Input-initInput);/*Compute Rest of PID Output*/Output += ITerm - kd * dInput;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;/*Remember some variables for next time*/lastInput = Input;lastTime = now;}
}void SetTunings(double Kp,double Ki,double Kd,int pOn)
{if (Kp<0 || Ki<0|| Kd<0) return;PonE = pOn == P_ON_E;double SampleTimeInSec = ((double)SampleTime)/1000;kp = Kp;ki = Ki * SampleTimeInSec;kd = Kd / SampleTimeInSec;if(controllerDirection ==REVERSE){kp = (0 - kp);ki = (0 - ki);kd = (0 - kd);}
}void SetSampleTime(int NewSampleTime)
{if (NewSampleTime > 0){double ratio = (double)NewSampleTime/ (double)SampleTime;ki *= ratio;kd /= ratio;SampleTime = (unsigned long)NewSampleTime;}
}void SetOutputLimits(double Min,double Max)
{if(Min > Max) return;outMin = Min;outMax = Max;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;
}void SetMode(int Mode)
{bool newAuto = (Mode == AUTOMATIC);if(newAuto == !inAuto){ /*we just went from manual to auto*/Initialize();}inAuto = newAuto;
}void Initialize()
{lastInput = Input;initInput = Input;ITerm = Output;if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;
}void SetControllerDirection(int Direction)
{controllerDirection = Direction;
}随着输入的变化,测量的比例提供了越来越大的阻力,但如果没有参照系,我们的表现会有些不稳定。如果我们第一次打开控制器时的PID输入是10000,我们真的想从Kp*10000开始抵制吗?不,我们希望使用我们的初始输入作为参考点 (第108行),从那里开始随着输入的变化增加或减少阻力 (第38行)。
我们需要做的另一件事是允许用户选择是要在偏差上做比例或在测量上做比例。在最后一个帖子之后,它看起来像 PonE 是无用的,但重要的是要记住,对于许多回路,它工作的很好。因此,我们需要让用户选择他们想要的模式 ,然后在计算中相应地操作。
第二阶段–动态更改整定参数
虽然上面的代码确实有效,但它有一个我们以前看到的问题。当整定参数在运行时发生更改,我们会得到一个不希望出现的信号。
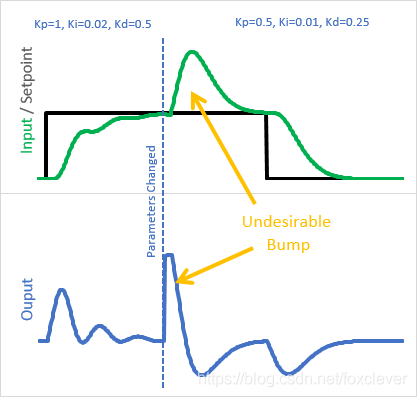
为什么会这样?

上次我们看到这一点时,是积分项被一个新的Ki 重新调整。而这一次,是比例项(输入-初始输入) 被新的Kp所更改。我选择的解决方案类似于我们为 Ki 所做的:我们不再是将(输入-初始输入)作为一个整体乘以当前 Kp,而是我把它分解成单独的步骤乘以当时的Kp:
![]()
/*working variables*/
unsigned long lastTime;
double Input,Output,Setpoint;
double ITerm,lastInput;
double kp,ki,kd;
int SampleTime = 1000; //1 sec
double outMin,outMax;
bool inAuto = false;#define MANUAL 0
#define AUTOMATIC 1#define DIRECT 0
#define REVERSE 1
int controllerDirection = DIRECT;#define P_ON_M 0
#define P_ON_E 1bool PonE = true;
double PTerm;
void Compute()
{if(!inAuto) return;unsigned long now = millis();int timeChange = (now - lastTime);if(timeChange>=SampleTime){/*Compute all the working error variables*/double error = Setpoint - Input;ITerm+= (ki * error);if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;double dInput = (Input - lastInput);/*Compute P-Term*/if(PonE) Output = kp * error;else{PTerm -= kp * dInput;Output = PTerm;}/*Compute Rest of PID Output*/Output += ITerm - kd * dInput;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;/*Remember some variables for next time*/lastInput = Input;lastTime = now;}
}void SetTunings(double Kp,double Ki,double Kd,int pOn)
{if (Kp<0 || Ki<0|| Kd<0) return;PonE = pOn == P_ON_E;double SampleTimeInSec = ((double)SampleTime)/1000;kp = Kp;ki = Ki * SampleTimeInSec;kd = Kd / SampleTimeInSec;if(controllerDirection ==REVERSE){kp = (0 - kp);ki = (0 - ki);kd = (0 - kd);}
}void SetSampleTime(int NewSampleTime)
{if (NewSampleTime > 0){double ratio = (double)NewSampleTime / (double)SampleTime;ki *= ratio;kd /= ratio;SampleTime = (unsigned long)NewSampleTime;}
}void SetOutputLimits(double Min,double Max)
{if(Min > Max) return;outMin = Min;outMax = Max;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;
}void SetMode(int Mode)
{bool newAuto = (Mode == AUTOMATIC);if(newAuto == !inAuto){ /*we just went from manual to auto*/Initialize();}inAuto = newAuto;
}void Initialize()
{lastInput = Input;PTerm = 0;ITerm = Output;if(ITerm > outMax) ITerm= outMax;else if(ITerm < outMin) ITerm= outMin;
}void SetControllerDirection(int Direction)
{controllerDirection = Direction;
}我们现在保留一个有效的和组成的P项,而不是将输入-初始输入作为一个整体乘以Kp。在每一步中,我们只需将当前输入变化乘以当时的Kp,并从P项(第41行) 中减去它。在这里,我们可以看到变化的影响:
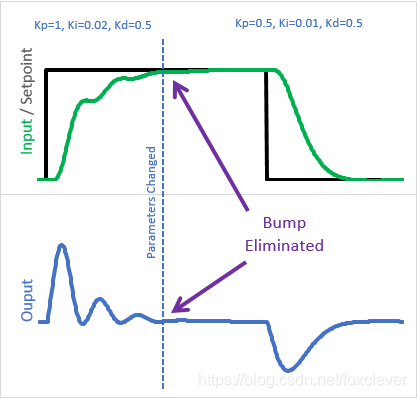

因为旧的Kp是已经存储,调整参数的变化只会影响我们后续的过程。
最终阶段–求和问题。
我不会进入完整的细节 (花哨的趋势等) 以及上述代码有什么问题。这相当不错,但仍有重大问题。例如:
类式积分饱和:虽然最终的输出限制在OUTmin和OUTmax之间。当PTerm不应该增长时,它有可能增长。它不会像积分饱和那样糟糕,但仍然是不可接受的。
动态更改:在运行时,如果用户想从P _ On _ M 更改为P_ ON _E,并在一段时间后返回,那么P项将不会被初始化,这会导致输出振荡。
还有更多,但仅仅这些就足以让人看到真正的问题是什么。早在我们创建I项的时候,我们已经处理过所有这些问题。我没有对P项重新执行相同的解决方案,而是选择了一个更美观的解决方案。
通过将P项和I项合并到一个名为“outputSum”的变量中,P _ ON _ M 代码将受益于已存在的所有上下文修补程序,并且由于代码中没有两个总和,因此不会出现不必要的冗余。
/*working variables*/
unsigned long lastTime;
double Input,Output,Setpoint;
double outputSum,lastInput;
double kp,ki,kd;
int SampleTime = 1000; //1 sec
double outMin,outMax;
bool inAuto = false;#define MANUAL 0
#define AUTOMATIC 1#define DIRECT 0
#define REVERSE 1
int controllerDirection = DIRECT;#define P_ON_M 0
#define P_ON_E 1
bool PonE = true;
void Compute()
{if(!inAuto) return;unsigned long now = millis();int timeChange = (now - lastTime);if(timeChange>=SampleTime){/*Compute all the working error variables*/double error = Setpoint - Input;double dInput = (Input - lastInput);outputSum+= (ki * error);/*Add Proportional on Measurement,if P_ON_M is specified*/if(!PonE) outputSum-= kp * dInput;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;/*Add Proportional on Error,if P_ON_E is specified*/if(PonE) Output = kp * error;else Output = 0;/*Compute Rest of PID Output*/Output += outputSum - kd * dInput;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;/*Remember some variables for next time*/lastInput = Input;lastTime = now;}
}void SetTunings(double Kp,double Ki,double Kd,int pOn)
{if (Kp<0 || Ki<0|| Kd<0) return;PonE = pOn == P_ON_E;double SampleTimeInSec = ((double)SampleTime)/1000;kp = Kp;ki = Ki * SampleTimeInSec;kd = Kd / SampleTimeInSec;if(controllerDirection ==REVERSE){kp = (0 - kp);ki = (0 - ki);kd = (0 - kd);}
}void SetSampleTime(int NewSampleTime)
{if (NewSampleTime > 0){double ratio = (double)NewSampleTime / (double)SampleTime;ki *= ratio;kd /= ratio;SampleTime = (unsigned long)NewSampleTime;}
}void SetOutputLimits(double Min,double Max)
{if(Min > Max) return;outMin = Min;outMax = Max;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
}void SetMode(int Mode)
{bool newAuto = (Mode == AUTOMATIC);if(newAuto == !inAuto){ /*we just went from manual to auto*/Initialize();}inAuto = newAuto;
}void Initialize()
{lastInput = Input;outputSum = Output;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
}void SetControllerDirection(int Direction)
{controllerDirection = Direction;
}现在你可以获得它。因为上述功能现在已存在于 V1.2.0版的Arduino PID库中。
但等等,还有更多:设定点加权。
我没有将下面的代码添加到Arduino库代码中,但是如果您想滚动自己的代码,这个特性可能会很有趣。设置点权重的核心是同时拥有PonE和PonM。通过指定0和1之间的比值,可以得到100% PonM、100% PonE(分别)或介于两者之间的某个比值。如果您的流程不是完全集成的(比如回流炉),并且希望解释这一点,那么这将非常有用。
最终,我决定不在这个时候将它添加到库中,因为它最终会成为另一个需要调整/解释的参数,而且我不认为这样做的好处是值得的。无论如何,如果你想修改代码,使其具有设定值权重,而不仅仅是纯PonM/PonE选择,下面是代码:
/*working variables*/
unsigned long lastTime;
double Input,Output,Setpoint;
double outputSum,lastInput;
double kp,ki,kd;
int SampleTime = 1000; //1 sec
double outMin,outMax;
bool inAuto = false;#define MANUAL 0
#define AUTOMATIC 1#define DIRECT 0
#define REVERSE 1
int controllerDirection = DIRECT;#define P_ON_M 0
#define P_ON_E 1
bool PonE = true,pOnM = false;
double PonEKp,pOnMKp;
void Compute()
{if(!inAuto) return;unsigned long now = millis();int timeChange = (now - lastTime);if(timeChange>=SampleTime){/*Compute all the working error variables*/double error = Setpoint - Input;double dInput = (Input - lastInput);outputSum+= (ki * error);/*Add Proportional on Measurement,if P_ON_M is specified*/if(pOnM) outputSum-= pOnMKp * dInput;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;/*Add Proportional on Error,if P_ON_E is specified*/if(PonE) Output = PonEKp * error;else Output = 0;/*Compute Rest of PID Output*/Output += outputSum - kd * dInput;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;/*Remember some variables for next time*/lastInput = Input;lastTime = now;}
}void SetTunings(double Kp,double Ki,double Kd,double pOn)
{if (Kp<0 || Ki<0|| Kd<0 || pOn<0 || pOn>1) return;PonE = pOn>0; //some p on error is desired;pOnM = pOn<1; //some p on measurement is desired;double SampleTimeInSec = ((double)SampleTime)/1000;kp = Kp; ki = Ki * SampleTimeInSec;kd = Kd / SampleTimeInSec;if(controllerDirection ==REVERSE){kp = (0 - kp);ki = (0 - ki);kd = (0 - kd);}PonEKp = pOn * kp;pOnMKp = (1 - pOn) * kp;
}void SetSampleTime(int NewSampleTime)
{if (NewSampleTime > 0){double ratio = (double)NewSampleTime / (double)SampleTime;ki *= ratio;kd /= ratio;SampleTime = (unsigned long)NewSampleTime;}
}void SetOutputLimits(double Min,double Max)
{if(Min > Max) return;outMin = Min; outMax = Max;if(Output > outMax) Output = outMax;else if(Output < outMin) Output = outMin;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
}void SetMode(int Mode)
{bool newAuto = (Mode == AUTOMATIC);if(newAuto == !inAuto){ /*we just went from manual to auto*/Initialize();}inAuto = newAuto;
}void Initialize()
{lastInput = Input;outputSum = Output;if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
}void SetControllerDirection(int Direction)
{controllerDirection = Direction;
}没有将pOn设置为整数,而是以双精度输入,允许使用一个比率(第58行)。除了一些标记(第62行和第63行)外,第77-78行计算了加权Kp项。然后在第37行和第43行,将加权后的PonM和PonE贡献添加到整个PID输出中。
欢迎关注:




















