一.深度学习可视化的一些工具
1.深度学习网络结构画图工具:https://cbovar.github.io/ConvNetDraw/
2.将.onnx放入即可,可视化网络结构:https://lutzroeder.github.io/netron/
3.结构可视化工具:https://github.com/HarisIqbal88/PlotNeuralNet
二.回归
线性回归的损失函数和梯度更新如下图:
一,numpy实现线性回归梯度下降
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_fake_data(batch_size=8):''' 产生随机数据:y=x*2+3,加上了一些噪声'''x = np.random.rand(batch_size, 1) * 5y = x * 2 + 3 + np.random.rand(batch_size, 1)*2return x, ydef get_gradient(theta,x,y):m=x.shape[0]Y_estimate=np.dot(x,theta)assert (Y_estimate.shape==(m,))error=Y_estimate-yassert (error.shape==(m,))cost =1.0/(2*m)*np.sum(error**2)#grad=(1.0/m)*np.dot(x.T,error).reshape(-1)#(2,)grad = (1.0 / m) * np.dot(error,x) # (2,)return grad,cost
def gradient_descent(x,y,iterations,alpha):theta=np.random.randn(2)costs=[]for i in range(iterations):grad,cost=get_gradient(theta,x,y)new_theta=theta-alpha*gradif i%100==0:print('{} iterations cost={}'.format(i,cost))costs.append(cost)theta=new_thetareturn costs,thetadef vis_data():# 来看看产生的x-y分布x, y = get_fake_data(batch_size=16)print(x.shape)print(y.shape)plt.scatter(np.squeeze(x), np.squeeze(y))plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':batch_size=32data_x, data_y = get_fake_data(batch_size=batch_size)#添加一列为1的向量 实际上就是乘以 theta 就是bdata_x=np.hstack((data_x,np.ones_like(data_x)))#(m,2)print(data_x)print(data_x.shape)costs,theta=gradient_descent(data_x,np.squeeze(data_y),iterations=50000,alpha=0.002)print(data_y.shape)#print(theta)y_predict=np.dot(data_x,theta)#theta[0]+theta[1]*data_x[:,1]print(y_predict.shape)plt.figure()#样本图print(data_x[:2])plt.scatter(data_x[:,0],np.squeeze(data_y),c='red')plt.plot(data_x[:,0],y_predict)plt.show()
红色的是散列点,蓝色的线是拟合的直线。
二,pytorch实现线性回归梯度下降
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch as tdevice=t.device('cpu')def get_fake_data(batch_size=8):''' 产生随机数据:y=x*2+3,加上了一些噪声'''x = t.rand(batch_size, 1,device=device) * 5y = x * 2 + 3 + t.rand(batch_size, 1)*2return x, ydef vis_data():# 来看看产生的x-y分布x, y = get_fake_data(batch_size=16)print(x.shape)print(y.shape)plt.scatter(np.squeeze(x), np.squeeze(y))plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':# vis_data()m=batch_size=32data_x, data_y = get_fake_data(batch_size=batch_size)#添加一列为1的向量 实际上就是乘以 theta 就是bdata_x=t.from_numpy(np.hstack((data_x,np.ones_like(data_x))))#(m,2)print(data_x.shape)theta = t.randn((2, 1),requires_grad=True)iterations=500lr = 0.005 # 学习率losses=[]for i in range(iterations):# forward:计算lossy_pred = data_x.mm(theta)print('y_pred',y_pred.shape)loss = 1/(2*m) * (y_pred - data_y) ** 2print('loss',loss.shape)loss = loss.sum()print('loss', loss.shape)losses.append(loss.item())# backward:手动计算梯度loss.backward()# 更新参数theta.data.sub_(lr * theta.grad.data)# 梯度清零theta.grad.data.zero_()print('losses=',losses)# 画图plt.scatter(np.squeeze(data_x[:,0]), np.squeeze(data_y),c='red')y_predict=data_x.mm(theta)print('y_predict.shape',y_predict.shape)print(data_x.detach().numpy())plt.plot(data_x.detach().numpy()[:,0], y_predict.detach().numpy()) # predictedplt.show()
三.实现ResNet34
from torch import nn
import torch as t
from torch.nn import functional as Fclass ResidualBlock(nn.Module):'''实现子module: Residual Block'''def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1, shortcut=None):super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()self.left = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel))self.right = shortcutdef forward(self, x):out = self.left(x)residual = x if self.right is None else self.right(x)out += residualreturn F.relu(out)class ResNet(nn.Module):'''实现主module:ResNet34ResNet34 包含多个layer,每个layer又包含多个residual block用子module来实现residual block,用_make_layer函数来实现layer'''def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):super(ResNet, self).__init__()# 前几层图像转换self.pre = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, 3, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1))# 重复的layer,分别有3,4,6,3个residual blockself.layer1 = self._make_layer(64, 64, 3)self.layer2 = self._make_layer(64, 128, 4, stride=2)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(128, 256, 6, stride=2)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(256, 512, 3, stride=2)# 分类用的全连接self.fc = nn.Linear(512, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, inchannel, outchannel, block_num, stride=1):'''构建layer,包含多个residual block'''shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, 1, stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel))layers = []layers.append(ResidualBlock(inchannel, outchannel, stride, shortcut))for i in range(1, block_num):layers.append(ResidualBlock(outchannel, outchannel))return nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):x = self.pre(x)x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 7)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)return self.fc(x)
model = ResNet()
input = t.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
o = model(input)
print(o.shape)![]()
四,卷积可视化
1.可视化滤波器
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
def get_filters():filter_vals = np.array([[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1]])print('Filter shape: ', filter_vals.shape)# Defining the Filtersfilter_1 = filter_valsfilter_2 = -filter_1filter_3 = filter_1.Tfilter_4 = -filter_3filters = np.array([filter_1, filter_2, filter_3, filter_4])return filtersdef vis_filter(filters):# Check the Filtersfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))for i in range(4):ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i + 1, xticks=[], yticks=[])ax.imshow(filters[i], cmap='gray')ax.set_title('Filter %s' % str(i + 1))# width, height = filters[i].shape# for x in range(width):# for y in range(height):# ax.annotate(str(filters[i][x][y]), xy=(y, x),# color='white' if filters[i][x][y] < 0 else 'black')plt.show()filters=get_filters()
print(filters.shape)
vis_filter(filters)
2.将自定义的滤波核作为卷积核对狗狗进行卷积,并可视化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
def get_filters():filter_vals = np.array([[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1],[-1, -1, 1, 1]])print('Filter shape: ', filter_vals.shape)# Defining the Filtersfilter_1 = filter_valsfilter_2 = -filter_1filter_3 = filter_1.Tfilter_4 = -filter_3filters = np.array([filter_1, filter_2, filter_3, filter_4])return filtersdef vis_filter(filters):# Check the Filtersfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))for i in range(4):ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i + 1, xticks=[], yticks=[])ax.imshow(filters[i], cmap='gray')ax.set_title('Filter %s' % str(i + 1))# width, height = filters[i].shape# for x in range(width):# for y in range(height):# ax.annotate(str(filters[i][x][y]), xy=(y, x),# color='white' if filters[i][x][y] < 0 else 'black')plt.show()import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self, weight):super(Net, self).__init__()# initializes the weights of the convolutional layer to be the weights of the 4 defined filtersk_height, k_width = weight.shape[2:]# assumes there are 4 grayscale filtersself.conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=(k_height, k_width), bias=False)# initializes the weights of the convolutional layerself.conv.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(weight)print(self.conv.weight.shape)# define a pooling layerself.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)def forward(self, x):# calculates the output of a convolutional layer# pre- and post-activationconv_x = self.conv(x)activated_x = F.relu(conv_x)# applies pooling layerpooled_x = self.pool(activated_x)# returns all layersreturn conv_x, activated_x, pooled_xif __name__ == '__main__':img_path = 'dog.png'bgr_img = cv2.imread(img_path)gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)print(gray_img.shape)# Normalisegray_img = gray_img.astype("float32") / 255filters=get_filters()print(filters.shape)vis_filter(filters)# instantiate the model and set the weightsweight = torch.from_numpy(filters).unsqueeze(1).type(torch.FloatTensor)print(weight.shape)model = Net(weight)# print out the layer in the networkprint(model)gray_img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(gray_img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(1)print(gray_img_tensor.shape)conv_img,relu_img,pool_img=model(gray_img_tensor)print(conv_img.shape)print(relu_img.shape)print(pool_img.shape)conv_img=conv_img.detach().numpy().squeeze()relu_img=relu_img.detach().numpy().squeeze()pool_img=pool_img.detach().numpy().squeeze()print(conv_img.shape)vis_filter(conv_img)vis_filter(relu_img)vis_filter(pool_img)

conv输出
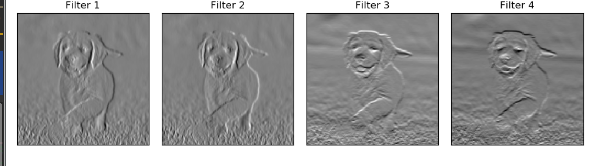
relu输出

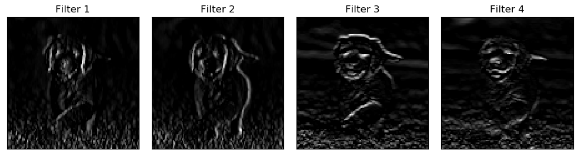
pool输出
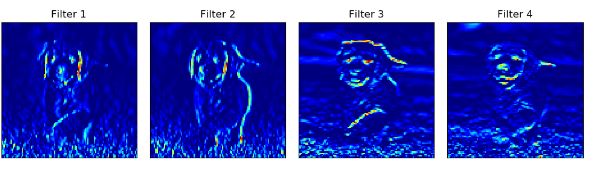
绘图形式换成:cmap=plt.cm.jet
conv输出结果
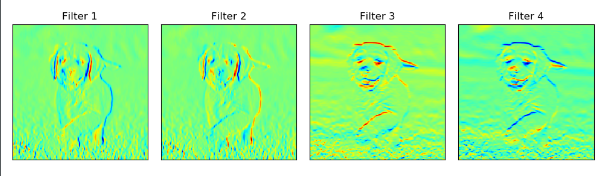
relu输出结果
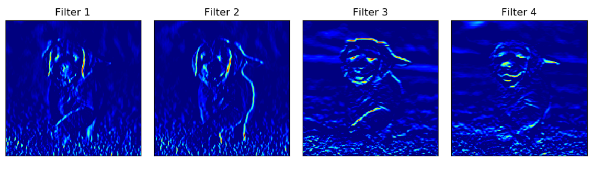
pool输出结果