文章目录
- 1.线性探测 哈希表代码
- 2.拉链法 哈希表代码
- 1. 散列表用的是数组支持按照下标随机访问数据的特性,所以散列表其实就是数组的一种扩展,由数组演化而来。可以说,如果没有数组,就没有散列表。
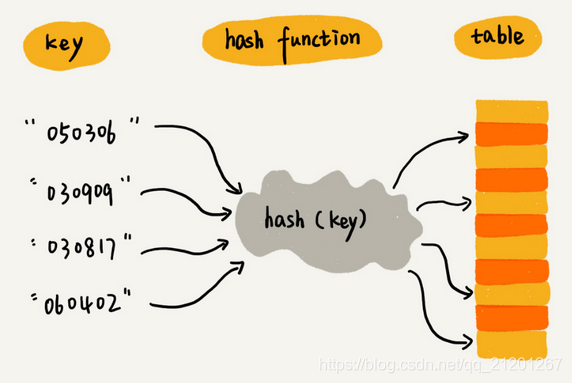
- 2. 散列函数,设计的基本要求
- 散列函数计算得到的散列值是一个非负整数( 因为数组下标从0开始)
- 如果 key1 = key2,那 hash(key1)== hash(key2)
- 如果 key1 != key2,那 hash(key1)!= hash(key2)
第3条是很难完全满足的,不满足称之,散列冲突。
- 3. 散列冲突 解决方法:
- 开放寻址法
a.线性探测
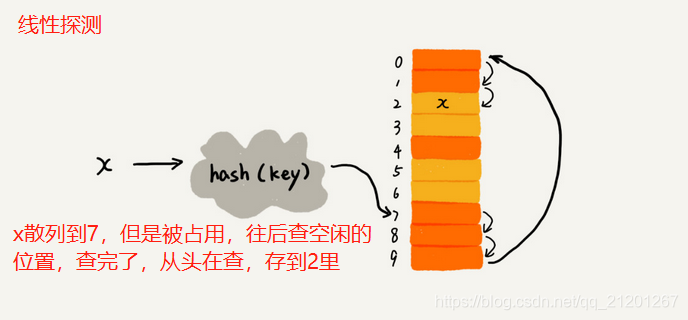
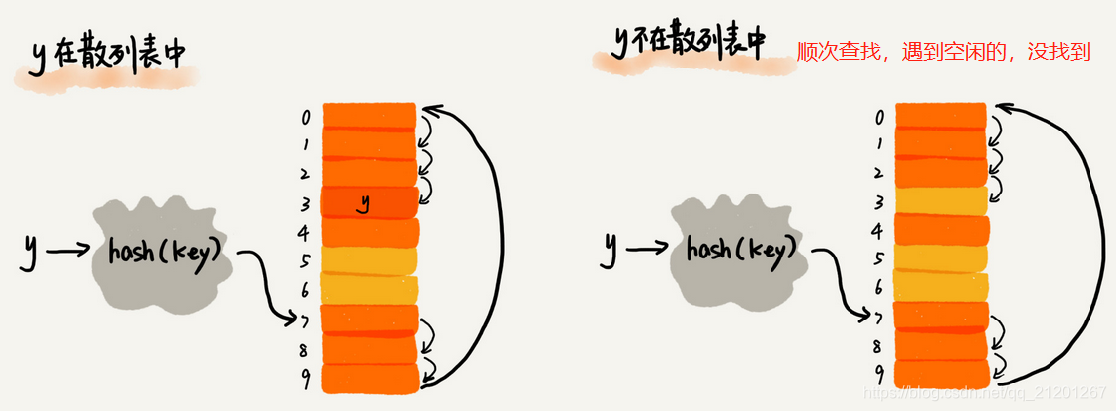

线性探测法,当空闲位置越来越少时,几乎要遍历整个散列表,接近O(n)复杂度
b. 二次探测:每次的步长是 1, 2, 4, 8, 16,…
c. 双重散列:使用多个散列函数,先用第一个,如果位置被占,再用第二个散列函数。。。直到找到空闲位置
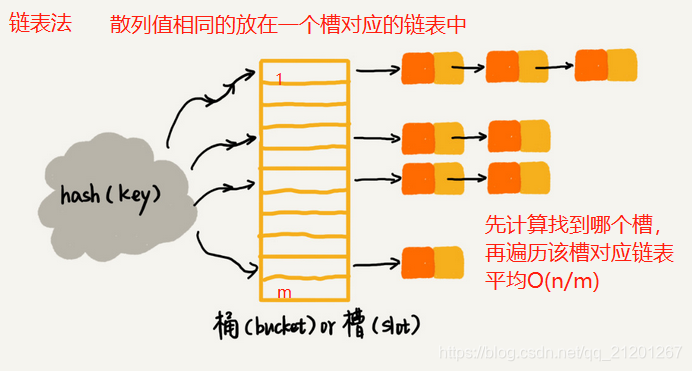
不管哪种方法,空闲位置不多了,冲突概率会大大提高,尽量保证有一定比例的空闲(用装载因子表示,因子越大,空位越少,冲突越多,散列表性能下降) - 链表法(更常用的解决冲突的办法)
- 4. 如何设计散列函数
a. 散列函数的设计不能太复杂。过于复杂的散列函数,势必会消耗很多计算时间,也就间接的影响到散列表的性能。
b. 散列函数生成的值要尽可能随机并且均匀分布,这样才能避免或者最小化散列冲突,即便出现冲突,散列到每个槽里的数据也会比较平均,不会出现某个槽内数据特别多的情况。
c. 装载因子超过阈值,自动扩容,避免累积到最后一次性搬移数据,分批多次搬移,O(1)复杂度
d. 数据量比较小,装载因子小的时候,适合采用开放寻址法
e. 基于链表的散列冲突处理方法比较适合存储大对象、大数据量的散列表,而且,比起开放寻址法,它更加灵活,支持更多的优化策略,比如用红黑树代替链表。
1.线性探测 哈希表代码
hashtable1.h
/*** @description: 哈希表,开放寻址--线性探测法* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/5/6 10:26* @modified by: */
#ifndef SEARCH_HASHTABLE1_H
#define SEARCH_HASHTABLE1_H
#include <iostream>
enum KindOfItem {Empty, Active, Deleted};
template <class DataType>
struct HashItem
{DataType data;KindOfItem info;HashItem<DataType>(KindOfItem i = Empty):info(i){}HashItem<DataType>(const DataType &d, KindOfItem i = Empty):data(d), info(i){}int operator== (HashItem<DataType> &a){return data == a.data;}int operator!= (HashItem<DataType> &a){return data != a.data;}
};
template <class DataType>
class hashtable1
{
private:HashItem<DataType> *ht; //散列表数组int TableSize; //散列表长度int currentSize; //当前表项个数int deletedSize; //删除标记的元素个数
public:hashtable1<DataType>(int m){TableSize = m;ht = new HashItem<DataType> [TableSize];currentSize = 0;deletedSize = 0;}~hashtable1<DataType>(){delete [] ht;}int hash(const DataType &newData) const{return newData%TableSize; //留余数法}int find(const DataType &x) const;int find_de(const DataType &x) const; //当有deleted标记的元素时,插入函数调用此查找int insert(const DataType &x);int delete_elem(const DataType &x);void print() const{for(int i = 0; i < TableSize; ++i){std::cout << ht[i].data << " " << ht[i].info << "->";}std::cout << std::endl;}int isInTable(const DataType &x){int i = find(x);return i >= 0 ? i : -1;}DataType getValue(int i) const{return ht[i].data;}
};
#endif //SEARCH_HASHTABLE1_H
hashtable1.cpp
/*** @description: 哈希表,开放寻址--线性探测法* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/5/6 10:26* @modified by: */
#include "hashtable1.h"
template <class DataType>
int hashtable1<DataType>::find(const DataType &x) const
{int i = hash(x);int j = i;while(ht[j].info == Deleted || (ht[j].info == Active && ht[j].data != x)) //说明存在冲突{j = (j+1)%TableSize; //用解决冲突的方法继续查找(开放定址法)if(j == i)return -TableSize; //遍历整个散列表,未找到}if(ht[j].info == Active)return j; //找到,返回正值elsereturn -j; //没找到,返回负值
}
template <class DataType>
int hashtable1<DataType>::find_de(const DataType &x) const //当有deleted标记的元素时,插入函数调用此查找
{int i = hash(x);int j = i;while(ht[j].info == Active) //说明存在冲突{j = (j+1)%TableSize; //用解决冲突的方法继续查找(开放定址法)if(j == i)return -TableSize; //遍历整个散列表,没有空位}return j; //返回标记为Empty或者Deleted的位置
}
template <class DataType>
int hashtable1<DataType>::insert(const DataType &x)
{int i = find(x);if(i > 0)return 0; //元素x已存在else if(i != -TableSize && !deletedSize) //元素x不存在,且散列表未满(且没有deleted标记){ht[-i].data = x; //元素赋值ht[-i].info = Active; //占用了,标记一下currentSize++;return 1;}else if(i != -TableSize && deletedSize) //元素x不存在,且散列表未满(且有deleted标记){int j = find_de(x);if(j >= 0){if(ht[j].info == Deleted)deletedSize--;ht[j].data = x; //元素赋值ht[j].info = Active; //占用了,标记一下(删除标记改成占用标记 )currentSize++;return 1;}elsereturn 0;}else return 0;
}
template <class DataType>
int hashtable1<DataType>::delete_elem(const DataType &x)
{int i = find(x);if(i >= 0){ht[i].info = Deleted; //找到了要删除的,标记删除currentSize--;deletedSize++;return 1;}else return 0;
}
hashtable1_test.cpp 测试程序
/*** @description: * @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/5/6 10:42* @modified by: */
#include "hashtable1.cpp"
#include <iostream>
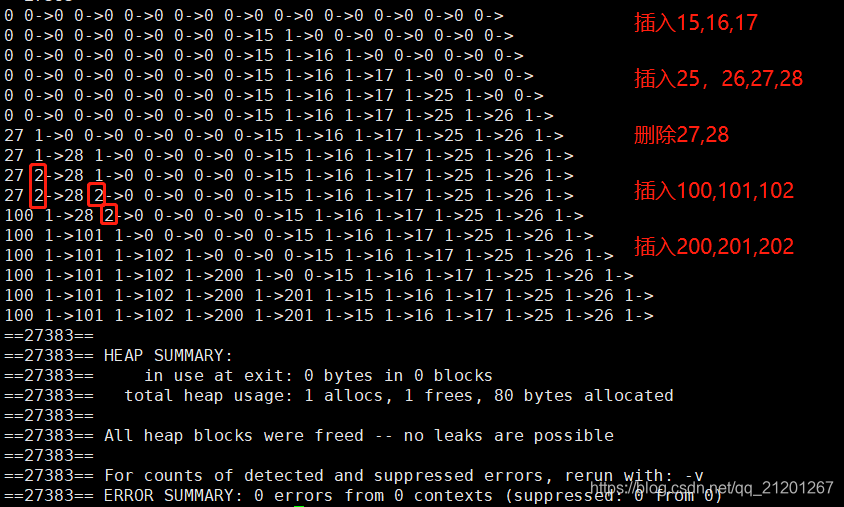
int main()
{hashtable1<int> ht1(10);ht1.print();for(int i = 15; i < 18; ++i){ht1.insert(i);ht1.print();}for(int i = 25; i < 29; ++i){ht1.insert(i);ht1.print();}for(int i = 27; i < 29; ++i){ht1.delete_elem(i);ht1.print();}for(int i = 100; i < 103; ++i){ht1.insert(i);ht1.print();}for(int i = 200; i < 203; ++i){ht1.insert(i);ht1.print();}if(ht1.isInTable(109) >= 0)std::cout << ht1.getValue(ht1.isInTable(109));return 0;
}
测试结果:(data,标记位)标记 empty = 0,active = 1, deleted = 2
2.拉链法 哈希表代码
linkedHash.h
/*** @description: 拉链法散列表* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/5/6 17:56* @modified by: */#ifndef SEARCH_LINKEDHASH_H
#define SEARCH_LINKEDHASH_H
#include <iostream>
template <class DataType>
struct linkedNode //链表节点
{DataType data;linkedNode *next;linkedNode():next(NULL){}linkedNode(const DataType &d):next(NULL), data(d){}
};
template <class DataType>
class linkedList //链表
{
public:linkedNode<DataType> *head;linkedList(){head = new linkedNode<DataType>(); //表头哨兵}~linkedList(){delete head;}
};
template <class DataType>
class linkedHash
{
private:linkedList<DataType> *htList; //散列表链表数组int bucket; //散列表桶个数
public:linkedHash<DataType>(int m):bucket(m){htList = new linkedList<DataType> [bucket] ();}~linkedHash<DataType>(){for(int i = 0; i < bucket; ++i){linkedNode<DataType> *p = htList[i].head->next, *q = p;while(q != NULL){p = q;q = q->next;delete p;}}delete [] htList;}int hash(const DataType &newData) const{return newData%bucket; //留余数法}linkedNode<DataType>* find(const DataType &x) const{int i = hash(x);linkedNode<DataType> *p = htList[i].head->next, *q = htList[i].head;while(p && p->data != x){q = p;p = p->next;}return q; //返回找到元素的前一个节点,或者没有找到,返回最后一个元素}linkedNode<DataType>* insert(const DataType &x){int i = hash(x);linkedNode<DataType> *p = htList[i].head, *q = p;while(q != NULL){p = q;q = q->next;}p->next = new linkedNode<DataType>(x);return p->next;}void delete_elem(const DataType &x){linkedNode<DataType> *q = find(x), *p;if(q->next){p = q->next;q->next = q->next->next;delete p;}}void print() const{for(int i = 0; i < bucket; ++i){std::cout << i << "[ ]";linkedNode<DataType> *p = htList[i].head->next;while(p){std::cout << p->data << "->";p = p->next;}std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << "----------------------" << std::endl;}
};
#endif //SEARCH_LINKEDHASH_H
linkedHash_test.cpp 测试程序
/*** @description: 拉链法散列表 测试* @author: michael ming* @date: 2019/5/6 17:57* @modified by: */
#include "linkedHash.h"
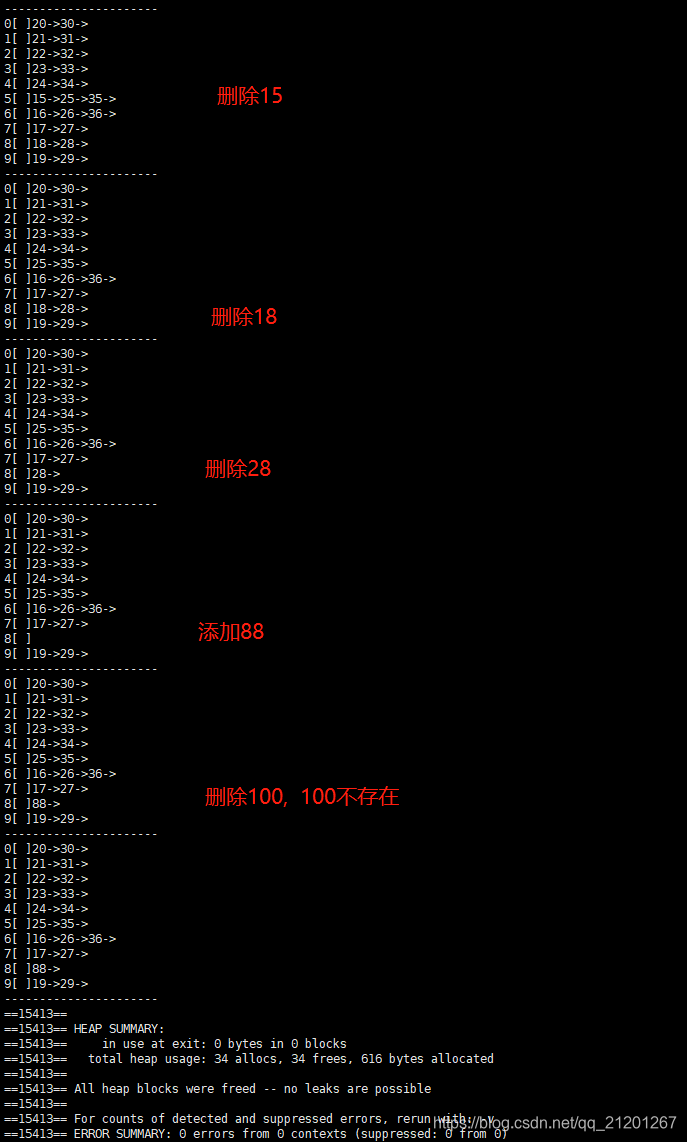
int main()
{linkedHash<int> ht2(10);for(int i = 15; i < 37; ++i){ht2.insert(i);ht2.print();}ht2.delete_elem(15);ht2.print();ht2.delete_elem(18);ht2.print();ht2.delete_elem(28);ht2.print();ht2.insert(88);ht2.print();ht2.delete_elem(100);ht2.print();return 0;
}
测试结果:


:线程池+并发编程+分布式设计+中间件)




————用户画像)




)






