文章目录
- 1. 读取数据
- 2. 处理label
- 3. 添加特征
- 4. 数据集切片
- 5. 训练
- 6. 预测
learn from https://www.kaggle.com/learn/feature-engineering
下一篇:Feature Engineering 特征工程 2. Categorical Encodings
1. 读取数据
预测任务:用户是否会下载APP,当其点击广告以后
数据集:ks-projects-201801.csv
- 读取数据,指定两个特征
'deadline','launched',parse_dates解析为时间
ks = pd.read_csv('ks-projects-201801.csv',parse_dates=['deadline','launched'])
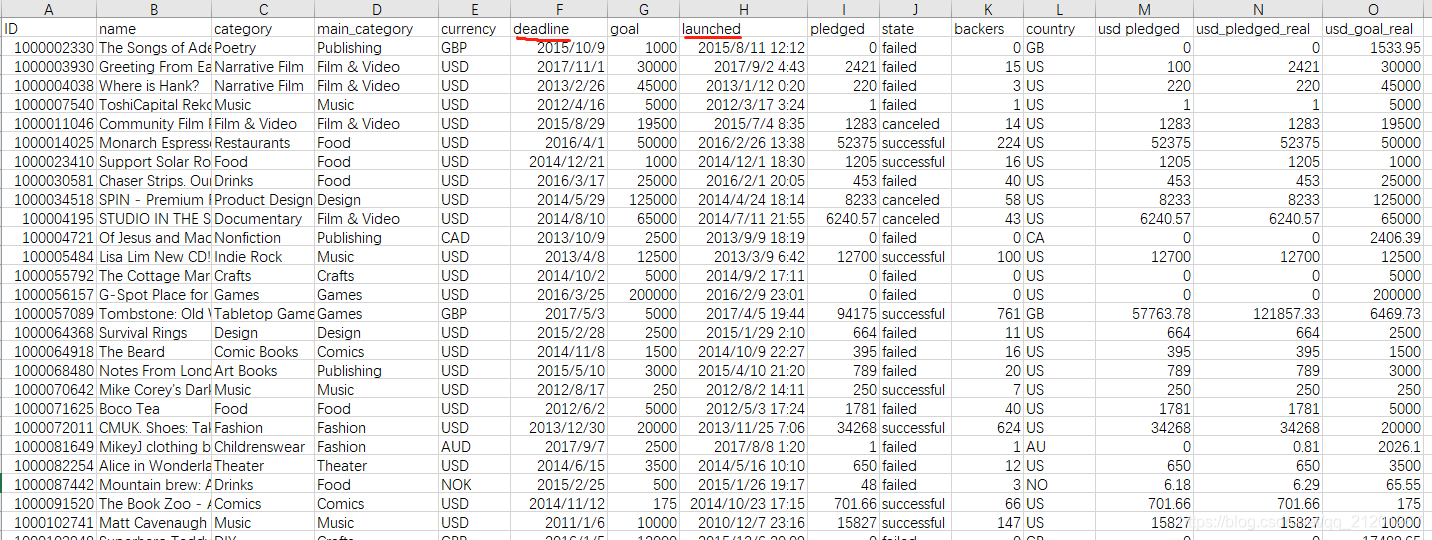
预测Kickstarter项目是否会成功。state作为结果label
可以使用类别category,货币currency,资金目标funding goal,国家country以及启动时间launched等特征
2. 处理label
- 准备标签列,看看有哪些值,转换成可用的数字格式
pd.unique(ks.state)
有6种数值
array(['failed', 'canceled', 'successful', 'live', 'undefined','suspended'], dtype=object)
每种多少个?按state分组,每组中ID行数有多少
ks.groupby('state')['ID'].count()
state
canceled 38779
failed 197719
live 2799
successful 133956
suspended 1846
undefined 3562
Name: ID, dtype: int64
- 简单处理下标签列,正在进行的项目
live丢弃,successful的标记为1,其余的为0
ks = ks.query('state != "live"') # live行不要
ks = ks.assign(outcome=(ks['state']=='successful').astype(int))
# label 转成1,0,int型
3. 添加特征
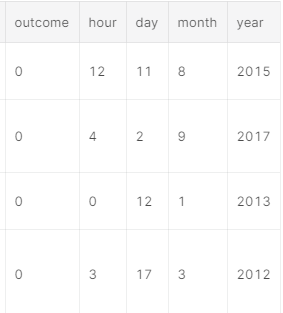
- 把
launched时间拆分成,年月日小时,作为新的特征
ks = ks.assign(hour=ks.launched.dt.hour,day=ks.launched.dt.day,month=ks.launched.dt.month,year=ks.launched.dt.year)
ks.head()
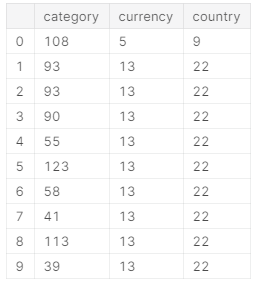
- 转换文字特征
category, currency, country为数字
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncodercat_features = ['category','currency','country']
encoder = LabelEncoder()encoded = ks[cat_features].apply(encoder.fit_transform)
encoded.head(10)
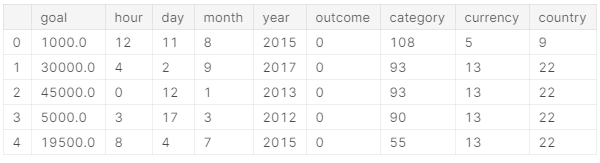
- 将选择使用的特征合并在一个数据里
X = ks[['goal', 'hour', 'day', 'month', 'year', 'outcome']].join(encoded)
X.head()
4. 数据集切片
- 数据切片,按比例分成训练集、验证集、测试集(0.8,0.1,0.1)
- 更高级的简单做法
sklearn.model_selection.StratifiedShuffleSplit
valid_ratio = 0.1
valid_size = int(len(X)*valid_ratio)
train = X[ : -2*valid_size]
valid = X[-2*valid_size : -valid_size]
test = X[-valid_size : ]
需要关注下,label 在每个数据集中的占比是否接近
for each in [train, valid, test]:print("Outcome fraction = {:.4f}".format(each.outcome.mean()))
Outcome fraction = 0.3570
Outcome fraction = 0.3539
Outcome fraction = 0.3542
5. 训练
- 使用LightGBM模型进行训练
机器学习算法之LightGBM
feature_cols = train.columns.drop('outcome')dtrain = lgb.Dataset(train[feature_cols], label=train['outcome'])
dvalid = lgb.Dataset(valid[feature_cols], label=valid['outcome'])param = {'num_leaves': 64, 'objective': 'binary'}
param['metric'] = 'auc'
num_round = 1000
bst = lgb.train(param, dtrain, num_round, valid_sets=[dvalid],early_stopping_rounds=10, verbose_eval=False)
6. 预测
- 对测试集进行预测
from sklearn import metrics
ypred = bst.predict(test[feature_cols])
score = metrics.roc_auc_score(test['outcome'], ypred)print(f"Test AUC score: {score}")
下一篇:Feature Engineering 特征工程 2. Categorical Encodings
![[转载] 湖北:星空团队——海燕计划](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[转载] 湖北:星空团队——海燕计划)


之核心技术)







)

)
)




