文章目录
- 1. 安装 PyMySQL
- 2. 连接对象
- 3. 游标对象
- 4. 增删改操作
- cursor.execute(sql)
- cursor.executemany(sql, seq_of_params)
- 5. 查询操作
- 6. ORM编程
- 常用 python ORM 库
learning from 《python web开发从入门到精通》
1. 安装 PyMySQL
conda 虚拟环境下安装 pip install pymysql
2. 连接对象
- 创建连接的一个 object
import pymysqltry:connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='michaeldata',charset='utf8',cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # 游标类型)print("连接成功:", connection)
except Exception as e:print("连接失败:", e)
输出:连接成功: <pymysql.connections.Connection object at 0x00000205AC8E96D0>
成功连接后,获取的连接对象,有很多方法,常用的如下:
cursor()获取游标对象,操作数据库commit()提交事务rollback()回滚事务close()关闭数据库连接
3. 游标对象
cursor = connection.cursor()
游标对象的常用方法:
execute(operation, [, param])执行数据库操作,SQL语句executemany(operation, 参数序列)批量执行操作fetchone()获取查询结果集里的下一条fetchmany(size)获取指定数量的记录fetchall()获取所有记录close()关闭游标
操作流程实例:
import pymysqltry:connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='michaeldata',charset='utf8',cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # 游标类型)print("连接成功:", connection)
except Exception as e:print("连接失败:", e)# sql 语句
sql = '''
create table books(id int not null auto_increment,name varchar(255) not null,category varchar(50) not null,price decimal(10, 2) default '0',publish_time date default null,primary key (id)
) engine = InnoDB auto_increment=1
default charset = utf8mb4 collate = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
'''cursor = connection.cursor() # 获取游标对象
cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句
cursor.close() # 先关闭游标
connection.close() # 再关闭连接,或者使用 with as
4. 增删改操作
-
对于 增删改 ,使用
cursor.execute()执行 SQL 语句后,默认不会自动提交,要使用connection.commit()提交 -
insert语句使用%s作为占位符,可以防止SQL注入
cursor.execute(sql)
import pymysqltry:connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='michaeldata',charset='utf8',cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # 游标类型)print("连接成功:", connection)
except Exception as e:print("连接失败:", e)# sql 语句
sql = '''
create table if not exists books(id int not null auto_increment,name varchar(255) not null,category varchar(50) not null,price decimal(10, 2) default '0',publish_time date default null,primary key (id)
) engine = InnoDB auto_increment=1
default charset = utf8mb4 collate = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
'''cursor = connection.cursor() # 获取游标对象
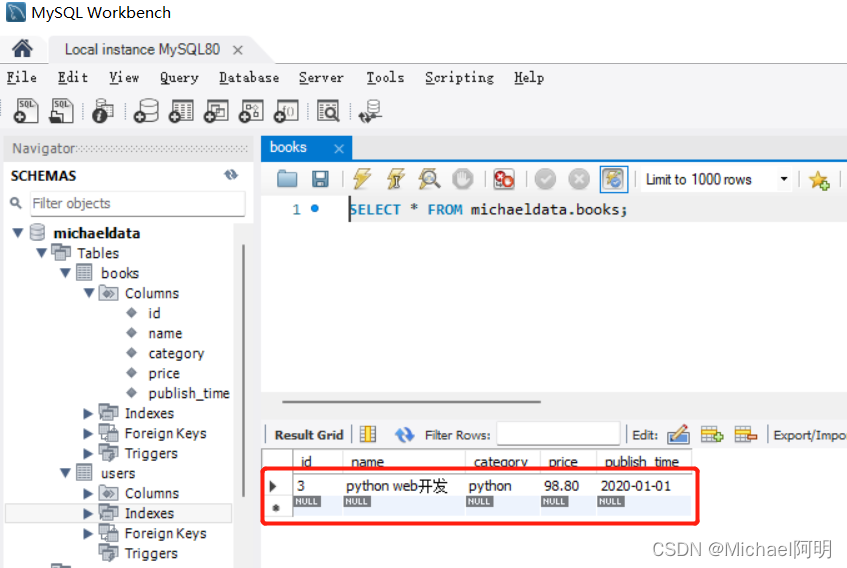
cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句sql1 = 'insert into books(name, category, price, publish_time) values("python web开发", "python", "98.8", "2020-01-01")'
cursor.execute(sql1) # 执行sql语句
connection.commit() # connection 提交才能生效cursor.close() # 先关闭游标
connection.close() # 再关闭连接,或者使用 with as
cursor.executemany(sql, seq_of_params)
批量操作
import pymysqltry:connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='michaeldata',charset='utf8',cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # 游标类型)print("连接成功:", connection)
except Exception as e:print("连接失败:", e)# sql 语句
sql = '''
create table if not exists books(id int not null auto_increment,name varchar(255) not null,category varchar(50) not null,price decimal(10, 2) default '0',publish_time date default null,primary key (id)
) engine = InnoDB auto_increment=1
default charset = utf8mb4 collate = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
'''cursor = connection.cursor() # 获取游标对象
cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句# sql1 = 'insert into books(name, category, price, publish_time) values("python web开发", "python", "98.8", "2020-01-01")'
# cursor.execute(sql1) # 执行sql语句
# connection.commit() # connection 提交才能生效# 数据列表
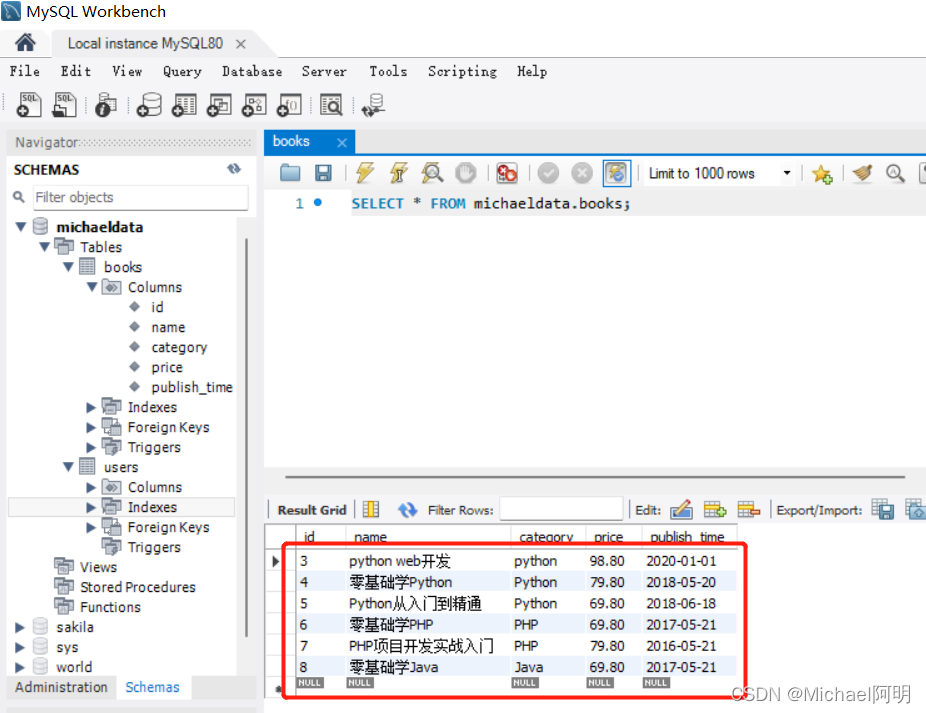
data = [("零基础学Python", 'Python', '79.80', '2018-5-20'),("Python从入门到精通", 'Python', '69.80', '2018-6-18'),("零基础学PHP", 'PHP', '69.80', '2017-5-21'),("PHP项目开发实战入门", 'PHP', '79.80', '2016-5-21'),("零基础学Java", 'Java', '69.80', '2017-5-21'),]
try:cursor.executemany('insert into books(name, category, price, publish_time) values(%s, %s, %s, %s)', data)connection.commit() # connection 提交才能生效
except Exception as e:connection.rollback() # 回滚cursor.close() # 先关闭游标
connection.close() # 再关闭连接,或者使用 with as
5. 查询操作
- 执行
select查询,生成结果集,然后使用fetchone/fetchmany/fetchall ()相关语句获取记录
import pymysqltry:connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='michaeldata',charset='utf8',cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # 游标类型)print("连接成功:", connection)
except Exception as e:print("连接失败:", e)# sql 语句
sql = "select * from books order by price"
with connection.cursor() as cursor:cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句result1 = cursor.fetchone() # 获取查询结果result2 = cursor.fetchall() # 获取查询结果print(result1)
print("*" * 10)
for res in result2:print(res)connection.close() # 关闭连接
输出结果:
连接成功: <pymysql.connections.Connection object at 0x00000216C72696D0>
{'id': 5, 'name': 'Python从入门到精通', 'category': 'Python', 'price': Decimal('69.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2018, 6, 18)}
**********
{'id': 6, 'name': '零基础学PHP', 'category': 'PHP', 'price': Decimal('69.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2017, 5, 21)}
{'id': 8, 'name': '零基础学Java', 'category': 'Java', 'price': Decimal('69.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2017, 5, 21)}
{'id': 4, 'name': '零基础学Python', 'category': 'Python', 'price': Decimal('79.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2018, 5, 20)}
{'id': 7, 'name': 'PHP项目开发实战入门', 'category': 'PHP', 'price': Decimal('79.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2016, 5, 21)}
{'id': 3, 'name': 'python web开发', 'category': 'python', 'price': Decimal('98.80'), 'publish_time': datetime.date(2020, 1, 1)}
6. ORM编程
ORM Object Relational Mapping 对象关系映射
它把 数据库 映射为 对象
- table - class
- record - object
- field - attribute
ORM 示例写法 data = Book.query.all()
好处:
- 数据模型利于重用代码
- 有很多现成工具完成预处理,事物等
- 基于 ORM 的业务代码简单语义好,易理解
- 不必编写性能不佳的 sql
缺点:
- ORM 库不是轻量级工具,学习成本高
- 复杂的查询,无法表达 或者 性能不如原生SQL
- ORM 抽象掉了数据库层,无法了解底层操作,也就无法定制特殊的SQL
常用 python ORM 库
Django ORM,跟Django结合紧密SQLAlchemy比较成熟Peewee轻量级,基于SQLAlchemy开发Storm中型,允许跨数据库查询
:第一个go程序-hello word)






+睡眠等待(--------------------))




)
)


)


)