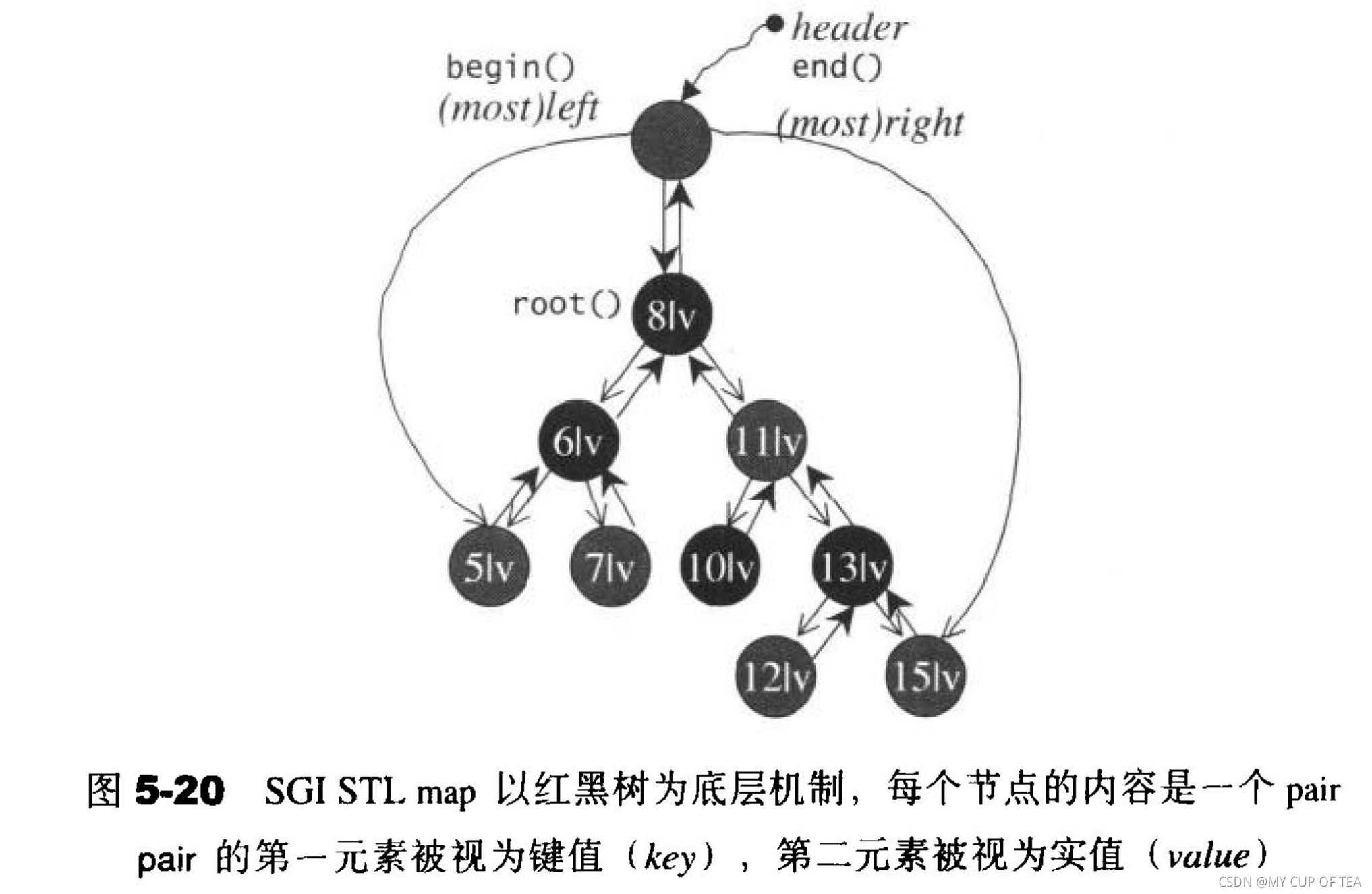
所有元素会根据元素的键值自动被排序
- 元素的类型是pair,同时拥有键值和实值;map不允许两个元素出现相同的键值
- pair 代码
template <class T1,class T2>
struct pair{typedef T1 first_type;typedef T2 second_type;T1 first; //publicT2 second; //publicpair():first(T1()),second(T2()){};pair(const T1& a,const T2& b):first(a),second(b){};
};- 不可以修改map的键值 但是可以修改实值
- map基于红黑树实现对应的函数
#include <iostream>#ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
#define __STL_TRY try
#define __STL_UNWIND(action) catch(...) { action; throw; }
#else
#define __STL_TRY
#define __STL_UNWIND(action)
#endif# ifdef __STL_EXPLICIT_FUNCTION_TMPL_ARGS
# define __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS <>
# else
# define __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS
# endiftypedef bool __rb_tree_color_type;
const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_red = false; //红色为0
const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_black = true; //黑色为1struct __rb_tree_node_base{typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;color_type color; //节点颜色 非红即黑base_ptr parent; //RB-Tree的许多操作 都是需要父节点的参与base_ptr left; //指向左节点base_ptr right; //指向右节点static base_ptr minimum(base_ptr x){while (x->left != 0){//二叉搜索树的特性//一直向左走 就会找到最小值x = x->left;}return x;}static base_ptr maximum(base_ptr x){while(x->right != 0){//二叉搜索树的特性//一直向右走 就会找到最大值x = x->right;}return x;}
};template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base{typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;Value value_field; //节点值
};//基层迭代器
struct __rb_tree_base_iterator{typedef __rb_tree_node_base::base_ptr base_ptr;typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;base_ptr node; //用于和容器之间产生一个连接关系(make a reference)//以下实现于operator++内,因为再无其他地方会调用这个函数了void increment(){if (node->right != 0){ //如果有右节点,状况一node = node->right; //就向右走while(node->left != 0){ //然后一直往左子树前进node = node->left; //即为答案}} else{ //没有右节点 状况二base_ptr y = node->parent;//找出父节点while(node == y->right){ //如果现行节点本身是个右子节点node = y; //需要一直上溯 直到不为右子节点为止y = y->parent;}if (node->right != y){ //如果此时node的右子节点不等于此时的父节点node = y; //状况三 此时的父节点即为解答} //否则 此时的node即为解答 状况四}/*以上判断 "若此时的右子节点不等于此时的父节点"是为了应对一种特殊的情况* 即:欲寻找的根节点的下一个节点,而此时根节点恰好没有右子节点* 当然,上述的特殊做法需要配合RB-Tree根节点和特殊的header之间的特殊的关系*/}//以下实现于operator--内,因为再无其他地方会调用这个函数了void decrement(){//状况一//如果是红节点 且 父节点的父节点等于自己 右子节点即为答案//状况一 发生于node为header的时候(亦即node为end()时)//注意:header的右子节点 即 mostright指向整棵树的max节点if (node->color == __rb_tree_red && node->right->right == node){node = node->right;}//状况二//如果有左子节点 令y指向左子节点;只有当y有右子节点的时候 一直往右走 到底,最后即为答案else if (node->left!=0){base_ptr y = node->left;while (y->right != 0){y = y->right;}node = y;} else{//状况三//既不是根节点 也没有左节点//找出父节点,当现行的节点身为左子节点时,一直交替往上走,直到现行节点不是左节点为止base_ptr y = node->parent;while(node == y->left){node = y;y = y->right;}node = y; //此时父节点即为答案}}
};//RB-Tree的正规迭代器
template <class Value,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __rb_tree_iterator : public __rb_tree_base_iterator{typedef Value value_type;typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value,Value&,Value*> iterator;typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value,const Value&,const Value*> const_iterator;typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value,Value&,Value*> self;typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;__rb_tree_iterator(){}__rb_tree_iterator(link_type x){node = x;}__rb_tree_iterator(const iterator& it){node = it.node;}reference operator* () const {return link_type(node)->value_field; }#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATORreference operator->()const {return &(operator*());}
#endif //__SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATORself& operator++(){increment();return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp = *this;increment();return tmp;}self& operator--(){decrement();return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp = *this;decrement();return tmp;}};template<class T,class Alloc>
class simple_alloc{
public:static T* allocate(std::size_t n){return 0==n?0:(T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof (T));}static void deallocate(T* p,size_t n){if (n!=0){Alloc::deallocate(p,n * sizeof(T));}}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p,sizeof(T));}
};namespace Chy{template <class T>inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size,T*){std::set_new_handler(0);T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((std::size_t)(size * sizeof (T))));if (tmp == 0){std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl;exit(1);}return tmp;}template<class T>inline void _deallocate(T* buffer){::operator delete (buffer);}template<class T1,class T2>inline void _construct(T1 *p,const T2& value){new(p) T1 (value); //没看懂}template <class T>inline void _destroy(T* ptr){ptr->~T();}template <class T>class allocator{public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef const T* const_pointer;typedef T& reference;typedef const T& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;template<class U>struct rebind{typedef allocator<U>other;};pointer allocate(size_type n,const void * hint = 0){return _allocate((difference_type)n,(pointer)0);}void deallocate(pointer p,size_type n){_deallocate(p);}void construct(pointer p,const T& value){_construct(p,value);}void destroy(pointer p){_destroy(p);}pointer address(reference x){return (pointer)&x;}const_pointer const_address(const_reference x){return (const_pointer)&x;}size_type max_size()const{return size_type(UINT_MAX/sizeof (T));}};
}template <class Key,class Value,class KeyOfValue,class Compare,class Alloc>
class rb_tree{
protected:typedef void* void_pointer;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;typedef simple_alloc<rb_tree_node,Alloc>rb_tree_node_allocator;typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
public:typedef Key key_type;typedef Value value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef std::ptrdiff_t difference_type;
protected:link_type get_node(){return rb_tree_node_allocator::allocate();}void put_node(link_type p){return rb_tree_node_allocator::deallocate(p);}link_type create_node(const value_type& x){link_type tmp = get_node(); //配置空间__STL_TRY{Chy::allocator<Key>::construct(&tmp->value_field,x);//构造内容};__STL_UNWIND(put_node(tmp));return tmp;}link_type clone_node(link_type x){//复制一个节点的颜色和数值link_type tmp = create_node(x->value_field);tmp->color = x->color;tmp->left = 0;tmp->right = 0;return tmp;}void destroy_node(link_type p){Chy::allocator<Key>::destroy(&p->value_field); //析构内容put_node(p); //释放内存}
protected://RB-tree只使用三笔数据表现size_type node_count; //追踪记录树的大小 (节点的数量)link_type header; //实现上的小技巧Compare key_compare; //节点之间的键值大小的比较准则. 应该会是一个function object//以下三个函数用于方便获取header的成员link_type& root() const{return (link_type&)header->parent;}link_type& left_most() const{return (link_type&)header->left;}link_type& right_most() const{return (link_type&)header->right;}//以下六个函数用于方便获得节点x的成员static link_type& left(link_type x){ return(link_type&)x->left;}static link_type& right(link_type x){ return(link_type&)x->right;}static link_type& parent(link_type x){ return(link_type&)x->parent;}static reference value(link_type x){ return x->value_field;}static const Key& key(link_type x){ return KeyOfValue()(value(x));}static color_type& color(link_type x){return (color_type&) (x->color);}//获取极大值和极小值 node class有实现此功能static link_type minimum(link_type x){return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::minimum(x);}static link_type maximum(link_type x){return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::maximum(x);}//迭代器typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type,reference,pointer>iterator;
public:iterator __insert(base_ptr x,base_ptr y,const value_type& v);link_type __copy(link_type x,link_type p);void __erase(link_type x);void clear() {if (node_count != 0) {__erase(root());left_most() = header;root() = 0;right_most() = header;node_count = 0;}}void init(){header = get_node(); //产生一个节点空间 令header指向它color(header) = __rb_tree_red;//令header为红色 用于区分header和root,在iterator的operator++中root() == 0;left_most() = header; //令header的左子节点等于自己right_most() = header; //令header的右子节点等于自己}
public://allocation / deallocationrb_tree(const Compare& comp = Compare()): node_count(0),key_compare(comp){init();}~rb_tree(){clear();put_node(header);}rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>&operator==(const rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>&x);
public://accessorsCompare key_comp() const {return key_compare;}iterator begin() {return left_most();} //RB树的起头为最左(最小)节点处iterator end(){return header;} //RB树的终点为header所指处bool empty() const {return node_count == 0;}size_type size() const {return node_count;}size_type max_size() const {return size_type (-1);}
public://insert/erase//将x插入到RB-Tree中 (保持节点的独一无二)std::pair<iterator,bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);//将x插入到RB-Tree中 (允许节点数值重复)iterator insert_equal(const value_type& x);//寻找键值为k的节点iterator find(const value_type& k);
};//插入新的数值 节点键值允许重复
//注意:返回的是一个RB-Tree的迭代器,指向的是新增的节点
template <class Key,class Value,class KeyOfValue,class Compare,class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::insert_equal(const value_type &v) {link_type y = header;link_type x = root(); //根节点开始while(x != 0){ //根节点开始 从上往下寻找适当的插入节点y = x;//如果当前根节点比 输入的v大,则转向左边,否则转向右边x = key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(x)) ? left(x) : right(x);}//x为新值插入点 y为插入点的父节点 v为新值return __insert(x,y,v);
}//插入新的数值 节点键值不允许重复
//注意:返回结果是pair类型,第一个元素是一个RB-Tree的迭代器,指向的是新增的节点;第二个参数表示插入成功与否
template <class Key,class Value,class KeyOfValue,class Compare,class Alloc>
std::pair<typename rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::iterator,bool>
rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::insert_unique(const value_type &v) {link_type y = header;link_type x = root(); //从根节点开始bool comp = true;while(x != 0){ //从根节点开始 往下寻找适当的插入点y = x;comp = key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(x)); //v键值小于目前节点的键值x = comp ? left(x) : right(x); //遇"大"则向左 遇"小"则向右}//离开while循环之后 y所指的即 插入点之父节点(此时它必为叶子结点)iterator j = iterator(y); //迭代器j指向插入点的父节点yif (comp){//如果while循环时候,判定comp的数值,如果comp为真(表示遇到大的元素,将插入左侧)//如果插入节点的父节点是最左侧的节点//x为插入点,y为插入节点的父节点,v表示新值if (j == begin()){return std::pair<iterator,bool>(__insert(x,y,v), true);} else{//插入节点的父节点不是最左侧的节点//调整j 回头准备测试--j;}if (key_compare(key(j.node),KeyOfValue()(v))){//小于新值(表示遇到小的数值,将插在右侧)return std::pair<iterator,bool>(__insert(x,y,v), true);}}//至此 表示新值一定和树中的键值重复 就不应该插入新的数值return std::pair<iterator,bool>(j, false);
}//真正的插入执行程序 __insert()
template <class Key,class Value,class KeyOfValue,class Compare,class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::__insert(base_ptr x_, base_ptr y_, const value_type &v) {//参数x_为新的插入点 参数y_为插入点的父节点 参数v为新值link_type x = (link_type)x_;link_type y = (link_type)y_;link_type z ;//key_compare 是键值大小的比较准则,应该是一个function objectif (y == header||x != 0||key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v),key(x))){z = create_node(v); //产生一个新的节点//当y即为header的时候,leftmost = z;if (y == header){root() = z;right_most() = z;} else if (y == left_most()){//y为最左节点//维护leftmost() 使其永远指向最左节点left_most() = z;} else{z = create_node(v);//产生一个新的节点//让新节成为插入点的父节点y的右子节点right(y) = z;if (y == right_most()){ //维护rightmost()让其永远指向最右的节点right_most() = z;}}parent(z) = y; //设定新节点的父节点left(z) = 0; //设定新节点的左子节点right(z) = 0; //设定新节点的右子节点//修改颜色//参数一为新增节点 ;参数二 为root__rb_tree_rebalance(z,header->parent);++node_count;//返回一个迭代器 指向新的节点return iterator(z);}
}//全局函数
//新节点必须为红色,如果插入出父节点同样为红色,就需要进行树形旋转
inline void __rb_tree_rotate_left(__rb_tree_node_base* x,__rb_tree_node_base*& root){//x为旋转点__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->right;//令y为旋转点的右子节点x->right = y->left;if (y->left != 0){//回马枪设定父亲节点y->left->parent = x;}y->parent = x->parent;//令y完全替代x的地位 (需要将x对其父节点的关系完全接收回来)if (x == root){root = y; //x为根节点} else if (x == x->parent->left){x->parent->left = y; //x为其父节点的左子节点} else{x->parent->right = y; //x为其父节点的右子节点}y->left = x;x->parent = y;
}//全局函数
//新节点必须为红色,如果插入出父节点同样为红色,就需要进行树形旋转
inline void __rb_tree_rotate_right(__rb_tree_node_base* x,__rb_tree_node_base*& root){//x为旋转点__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->left; //y为旋转点的左子节点x->left = y->right;if (y->right != 0){y->right->parent = x;}y->parent = x->parent;//令y完全替代x的地位if(x == root){root = y;} else if (x == x->parent->right){x->parent->right = y;} else{x->parent->left = y;}y->parent = x;x->parent = y;
}//调整RB_tree 插入节点之后,需要进行调整(颜色/翻转)从而满足要求
inline void __rb_tree_balance(__rb_tree_node_base* x,__rb_tree_node_base*& root){x->color = __rb_tree_red; //新节点的颜色必须是红色的while(x!=root && x->parent->color == __rb_tree_red){//父节点为红色的//父节点为祖父节点的左子节点if (x->parent == x->parent->parent->left){//令y为伯父节点__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->parent->right;if (y && y->color == __rb_tree_red){ //伯父节点存在 且为红x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black;//更改父节点的颜色为黑y->color = __rb_tree_black;//更改父节点的颜色为黑x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red;//更改祖父节点的颜色为红x = x->parent->parent;} else{//无伯父节点 或者伯父节点的颜色为黑if (x == x->parent->right){//新节点为父节点的右子节点x = x->parent;//第一次参数为左旋节点__rb_tree_rotate_left(x,root);}x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black;//改变颜色x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red;//第一次参数为右旋节点__rb_tree_rotate_right(x->parent->parent,root);}} else{//父节点为祖父节点的右子节点__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->parent->parent->left; //令y为伯父节点if (y && y->color == __rb_tree_red){ //存在伯父节点,且为红x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black;//更改父节点为黑y->color = __rb_tree_black;//更改伯父节点为黑x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red; //更改祖父节点为红x = x->parent->parent; //准备继续往上层检查} else{//无伯父节点 或者伯父节点 为黑if (x == x->parent->left){//新节点 为 父节点的左子节点x = x->parent;__rb_tree_rotate_right(x,root); //第一参数为右旋转点}x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black;//改变颜色x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red;//第一参数为左旋点__rb_tree_rotate_left(x->parent->parent,root);}}} //while结束root->color = __rb_tree_black;
}//元素查找程序
template <class Key,class Value,class KeyOfValue,class Compare,class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>::find(const value_type &k) {link_type y = header; //last node which is not less than klink_type x = root(); //current nodewhile(x != 0){//key_compare 是节点大小的比较准则 function objectif (!key_compare(key(x),k)){//进行到这里 表示x的数值大于k 。遇到大的数值向左走y = x,x = left(x);} else{x = right(x);}}iterator j = iterator (y);return (j == end() || key_compare(k,key(j.node))) ? end() : j;
}/************************************************************************************************************************/
//注意:以下的identify定义于
template <class T>
struct identify : public std::unary_function<T,T>{const T& operator()(const T& x) const {return x;}
};template<typename _Pair>
struct _Select1st: public std::unary_function<_Pair, typename _Pair::first_type>
{typename _Pair::first_type&operator()(_Pair& __x) const{ return __x.first; }
};template <class Key,class T,class Alloc,class Compare = std::less<Key>>
class map{
public:typedef Key key_type;//键值型别typedef T data_type;//数据(实值)型别typedef T mapped_type;typedef std::pair<const Key,T>value_type; //元素型别(键值/实值)//键值比较函数typedef Compare key_compare;//以下定义一个functor 其作用就是调用"元素比较函数"class value_compare : public std::binary_function<value_type,value_type,bool>{friend class map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>;protected:Compare comp;value_compare(Compare c):comp(c){}public:bool operator()(const value_type& x,const value_type& y)const{return comp(x.first,y.first);}};
private://定义表述型别 使用map元素的型别(pair)作为第一性别,作为红黑树节点的键值型别typedef rb_tree<key_type,value_type,_Select1st<value_type>,key_compare,Alloc>rep_type;rep_type t; //使用红黑树(RB-Tree)实现map
public:typedef typename rep_type::pointer pointer;typedef typename rep_type::const_pointer const_pointer;typedef typename rep_type::reference reference;typedef typename rep_type::const_reference const_reference;//map迭代器无法执行写入操作,因为map的元素有一定的次序安排,不允许用户在任意处进行写入操作typedef typename rep_type::iterator iterator;typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;typedef typename rep_type::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;typedef typename rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;typedef typename rep_type::size_type size_type;typedef typename rep_type::difference_type difference_type;//allocation/deallocation//map使用RB-Tree的insert_unique() 要求插入的元素都不可以重复//multimap 使用 insert_equal() 允许相同键值的存在//构造函数map():t(Compare()){}explicit map(const Compare& comp) : t(comp){}template<class InputIterator>map(InputIterator first,InputIterator last) : t(Compare()){t.insert_unique(first,last);}template<class InputIterator>map(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,const Compare& comp) : t(comp){t.insert_unique(first,last);}map(const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&x):t(x.t){}map<Key,Compare,Alloc>& operator=(const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&x){t = x.t;return *this;}//map进行函数的包装//accessorskey_compare key_comp()const{ return t.key_comp();}//需要注意 map使用的value_comp 事实上为RB-Tree的key_comp()value_compare value_comp() const {return value_compare(t.key_comp());}iterator begin() {return t.begin();}const_iterator begin() const {return t.begin();}iterator end() {return t.end();}const_iterator end() const {return t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin() {return t.rbegin();}const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const {return t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend() {return t.rend();}const_reverse_iterator rend() const{return t.rend();}bool empty() const {return t.empty();}size_type size() const {return t.size();}size_type max_size() const {return t.max_size();}//注意以下 下标操作符号T& operator[](const key_type& k){return (*((insert(value_type(k,T()))).first)).second;}void swap(map<Key,Compare,Alloc>& x){t.swap(x.t);}//insert / erase
// typedef std::pair<iterator,bool>pair_iterator_bool;std::pair<iterator,bool>insert(const value_type& x){return t.insert_unique(x);}iterator insert(iterator position,const value_type& x){return t.insert_unique(position,x);}template <class InputIterator>void insert(InputIterator first,InputIterator last){t.insert_unique(first,last);}void erase(iterator position){t.erase(position);}size_type erase(const key_type& x){return t.erase(x);}void erase(iterator first,iterator last){t.erase(first,last);}void clear(){t.clear();}//map operationsiterator find(const key_type& x)const {return t.find(x);}const_iterator find(const key_type& x) {return t.find(x);}size_type count(const key_type& x)const {return t.count(x);}iterator lower_bound(const key_type&x) { return t.lower_bound(x);}const_iterator lower_bound(const key_type&x) const{ return t.lower_bound(x);}iterator upper_bound(const key_type&x) { return t.upper_bound(x);}const_iterator upper_bound(const key_type&x) const{ return t.upper_bound(x);}std::pair<iterator,iterator>equal_range(const key_type&x){return t.equal_range(x);}std::pair<const_iterator,const_iterator>equal_range(const key_type&x)const{return t.equal_range(x);}//以下的__STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS 被定义为<>friend bool operator== __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const map&,const map&);friend bool operator< __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const map&,const map&);
};template <class Key,class Compare,class Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&x,const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&y){return x.t == y.t;
}template <class Key,class Compare,class Alloc>
inline bool operator<(const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&x,const map<Key,Compare,Alloc>&y){return x.t < y.t;
}#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>int main(){std::map<std::string,int>s_i_map;s_i_map[std::string("number1")] = 1;s_i_map[std::string("number2")] = 2;s_i_map[std::string("number3")] = 3;s_i_map[std::string("number4")] = 4;std::pair<std::string,int>value(std::string("david"),5);s_i_map.insert(value);std::map<std::string,int>::iterator map_iterator = s_i_map.begin();for ( ;map_iterator != s_i_map.end();++map_iterator) {std::cout << map_iterator->first << ' ';std::cout << map_iterator->second << std::endl;}int number = s_i_map[std::string("number2")];std::cout << number << std::endl;map_iterator = s_i_map.find(std::string("number2"));if (map_iterator == s_i_map.end()){std::cout << "number2 not found!" << std::endl;}//通过map迭代器修改value 但是不可以修改keyint number2 = s_i_map[std::string("12344555")];std::cout << number2 << std::endl;}- 下标操作符用法有两种:1,作为左值使用(内容可以被改变);2,作为右值使用(内容不可以被修改)
- 左值和右值都适用的关键在于,返回数值采用 by reference 传递的形式
- 无论如何,下标操作符都根据键值找到与之对应的实值
std::map<std::string,int>simap; //以string作为键值,以int作为实值simap[std::string("jjhou")] = 1; //左值运用int right_value = simap[std::string("jjhou")]; //右值运用#include <iostream>template<class Key,class T,class Alloc,class Compare = std::less<Key>>
class map{
public:typedef Key key_type; //键值类型typedef std::pair<const Key,T>value_type;//元素类型 (键值/实值)public:T& operator[] (const key_type& k){return (*((inserter(value_type(k,T()))).first)).second;}
}; - 对于上式operator[] 讲解,首先根据键值和实值做出一个元素,但是考虑到实值是未知的,所以调用实值的构造函数,产生一个和实值型别相同的暂时对象,这也就是value_type(k,T())这一句的含义。再将这个元素插入到map里面,inserter(value_type(k,T()),insert返回的是一个pair类型的结构,第一个元素是第一个迭代器,指向的是插入妥当的新元素或者指向的是插入失败点(键值重复的)旧的元素
- 注意如果下标操作符作为左值使用(通常表示要添加的元素),我们正好以此"实值待填"的元素将位置卡号;
- 如果下标操作符号作为右值使用(通常代表需要根据键值得到与之对应的实值),此时的插入操作所返回的pair的第一个元素(迭代器)指向的是键值符合的旧元素
- 取得操作操作所返回的pair的第一元素,inserter(value_type(k,T())).first 是一个迭代器
- 提领迭代器 *(inserter(value_type(k,T())).first) 得到一个map元素,取其第二个元素,即得到实值 *(inserter(value_type(k,T())).first).second
- 注意这个实值是通过by reference的方式传递的,因此它作为左值和右值都可以
参考链接
- C++ STL源码剖析之map、multimap、initializer_list - 知乎









文本文件中每一行的...)









