摘要: 活体检测在各行各业应用比较广泛,如何实现一个活体检测系统呢?早期实现很困难,现在仅使用opencv即可实现,快来尝试一下吧。
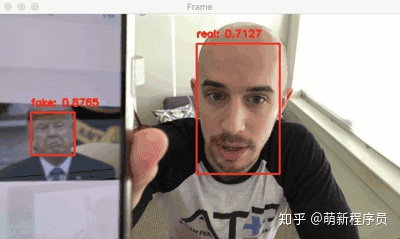
什么是活体检测,为什么需要它?
随着时代的发展,人脸识别系统的应用也正变得比以往任何时候都更加普遍。从智能手机上的人脸识别解锁、到人脸识别打卡、门禁系统等,人脸识别系统正在各行各业得到应用。然而,人脸识别系统很容易被“非真实”的面孔所欺骗。比如将人的照片放在人脸识别相机,就可以骗过人脸识别系统,让其识别为人脸。
为了使人脸识别系统更安全,我们不仅要识别出人脸,还需要能够检测其是否为真实面部,这就要用到活体检测了。
目前有许多活体检测方法,包括:
- 纹理分析(Texture analysis),包括计算面部区域上的局部二进制模式(LBP)并使用SVM将面部分类为真脸或假脸;
- 频率分析(Frequency analysis),例如检查面部的傅里叶域;
- 可变聚焦分析(ariable focusing analysis),例如检查两个连续帧之间的像素值的变化。
- 基于启发式的算法(Heuristic-based algorithms),包括眼球运动、嘴唇运动和眨眼检测;
- 光流算法(Optical Flow algorithms),即检查从3D对象和2D平面生成的光流的差异和属性;
- 3D脸部形状,类似于Apple的iPhone脸部识别系统所使用的脸部形状,使脸部识别系统能够区分真人脸部和其他人的打印输出的照片图像;
面部识别系统工程师可以组合上述方法挑选和选择适合于其特定应用的活体检测模型。但本教程将采用图像处理中常用方法——卷积神经网络(CNN)来构建一个能够区分真实面部和假面部的深度神经网络(称之为“LivenessNet”网络),将活体检测视为二元分类问题。
首先检查一下数据集。
活动检测视频

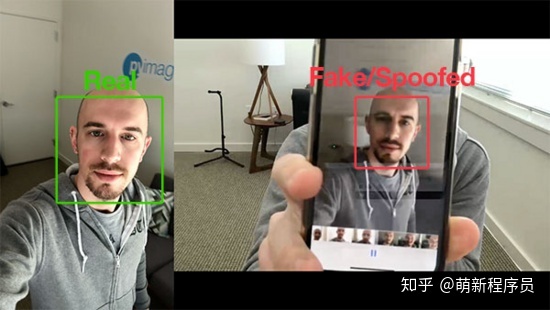
为了让例子更加简单明了,本文构建的活体检测器将侧重于区分真实面孔与屏幕上的欺骗面孔。且该算法可以很容易地扩展到其他类型的欺骗面孔,包括打印输出、高分辨率打印等。
活体检测数据集来源:
- iPhone纵向/自拍;
- 录制了一段约25秒在办公室里走来走去的视频;
- 重播了相同的25秒视频,iPhone重录视频;
- 获得两个示例视频,一个用于“真实”面部,另一个用于“假/欺骗”面部。
- 最后,将面部检测应用于两组视频,以提取两个类的单个面部区域。
项目结构
$ tree --dirsfirst --filelimit 10
.
├── dataset
│ ├── fake [150 entries]
│ └── real [161 entries]
├── face_detector
│ ├── deploy.prototxt
│ └── res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel
├── pyimagesearch
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── livenessnet.py
├── videos
│ ├── fake.mp4
│ └── real.mov
├── gather_examples.py
├── train_liveness.py
├── liveness_demo.py
├── le.pickle
├── liveness.model
└── plot.png6 directories, 12 files项目中主要有四个目录:
* dataset / :数据集目录,包含两类图像:
在播放脸部视频时,手机录屏得到的假脸;
face_detector /
pyimagesearch /
video/
另外还有三个Python脚本:
gather_examples.py:此脚本从输入视频文件中获取面部区域,并创建深度学习面部数据集;train_liveness.py:此脚本将训练LivenessNet分类器。训练会得到以下几个文件:
le .pickle liveness.model plot.pngliveness_demo.py:该演示脚本将启动网络摄像头以进行面部实时活体检测;
从训练数据集中检测和提取面部区域
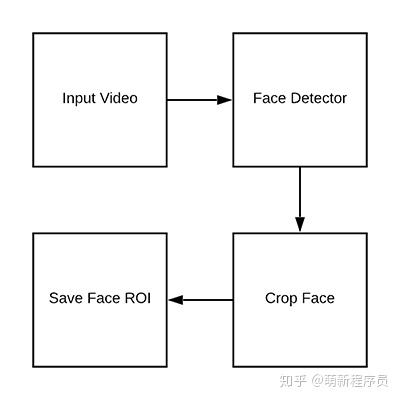
数据目录:
dataset / fake /
dataset / real /
打开 gather_examples.py 文件并插入以下代码:
# import the necessary packages
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
import os# construct the argument parse and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--input", type=str, required=True,help="path to input video")
ap.add_argument("-o", "--output", type=str, required=True,help="path to output directory of cropped faces")
ap.add_argument("-d", "--detector", type=str, required=True,help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face detector")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
ap.add_argument("-s", "--skip", type=int, default=16,help="# of frames to skip before applying face detection")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())首先导入所需的包:
第8-19行解析命令行参数:
input
output
detector
confidence
skip
之后加载面部检测器并初始化视频流:
# load our serialized face detector from disk
print("[INFO] loading face detector...")
protoPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"], "deploy.prototxt"])
modelPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"],"res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel"])
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoPath, modelPath)# open a pointer to the video file stream and initialize the total
# number of frames read and saved thus far
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["input"])
read = 0
saved = 0此外还初始化了两个变量,用于读取的帧数以及循环执行时保存的帧数。
创建一个循环来处理帧:
# loop over frames from the video file stream
while True:# grab the frame from the file(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()# if the frame was not grabbed, then we have reached the end# of the streamif not grabbed:break# increment the total number of frames read thus farread += 1# check to see if we should process this frameif read % args["skip"] != 0:continue下面进行面部检测:
# grab the frame dimensions and construct a blob from the frame(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300)), 1.0,(300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0))# pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and# predictionsnet.setInput(blob)detections = net.forward()# ensure at least one face was foundif len(detections) > 0:# we're making the assumption that each image has only ONE# face, so find the bounding box with the largest probabilityi = np.argmax(detections[0, 0, :, 2])confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]为了执行面部检测,需要从图像中创建一个区域,该区域有300×300的宽度和高度,以适应Caffe面部检测器。
此外脚本假设视频的每一帧中只有一个面部,这有助于防止误报。获得最高概率的面部检测指数,并使用索引提取检测的置信度,之后将低概率的进行过滤,并将结果写入磁盘:
# ensure that the detection with the largest probability also# means our minimum probability test (thus helping filter out# weak detections)if confidence > args["confidence"]:# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for# the face and extract the face ROIbox = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")face = frame[startY:endY, startX:endX]# write the frame to diskp = os.path.sep.join([args["output"],"{}.png".format(saved)])cv2.imwrite(p, face)saved += 1print("[INFO] saved {} to disk".format(p))# do a bit of cleanup
vs.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()提取到面部区域后,就可以得到面部的边界框坐标。然后为面部区域生成路径+文件名,并将其写入磁盘中。
构建活体检测图像数据集

打开终端并执行以下命令来提取“假/欺骗”类别的面部图像:
$ python gather_examples.py --input videos/real.mov --output dataset/real --detector face_detector --skip 1
[INFO] loading face detector...
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/0.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/1.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/2.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/3.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/4.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/5.png to disk
...
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/145.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/146.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/147.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/148.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/fake/149.png to disk同理也可以执行以下命令获得“真实”类别的面部图像:
$ python gather_examples.py --input videos/fake.mov --output dataset/fake --detector face_detector --skip 4
[INFO] loading face detector...
[INFO] saved datasets/real/0.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/1.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/2.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/3.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/4.png to disk
...
[INFO] saved datasets/real/156.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/157.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/158.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/159.png to disk
[INFO] saved datasets/real/160.png to disk注意,这里要确保数据分布均衡。
执行脚本后,统计图像数量:
- 假:150张图片
- 真:161张图片
- 总计:311张图片
实施“LivenessNet”深度学习活体检测模型

LivenessNet实际上只是一个简单的卷积神经网络,尽量将这个网络设计的尽可能浅,参数尽可能少,原因有两个:
- 减少过拟合可能性;
- 确保活体检测器能够实时运行;
打开 livenessnet .py 并插入以下代码:
# import the necessary packages
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv2D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling2D
from keras.layers.core import Activation
from keras.layers.core import Flatten
from keras.layers.core import Dropout
from keras.layers.core import Dense
from keras import backend as Kclass LivenessNet:@staticmethoddef build(width, height, depth, classes):# initialize the model along with the input shape to be# "channels last" and the channels dimension itselfmodel = Sequential()inputShape = (height, width, depth)chanDim = -1# if we are using "channels first", update the input shape# and channels dimensionif K.image_data_format() == "channels_first":inputShape = (depth, height, width)chanDim = 1# first CONV => RELU => CONV => RELU => POOL layer setmodel.add(Conv2D(16, (3, 3), padding="same",input_shape=inputShape))model.add(Activation("relu"))model.add(BatchNormalization(axis=chanDim))model.add(Conv2D(16, (3, 3), padding="same"))model.add(Activation("relu"))model.add(BatchNormalization(axis=chanDim))model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))model.add(Dropout(0.25))# second CONV => RELU => CONV => RELU => POOL layer setmodel.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding="same"))model.add(Activation("relu"))model.add(BatchNormalization(axis=chanDim))model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding="same"))model.add(Activation("relu"))model.add(BatchNormalization(axis=chanDim))model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))model.add(Dropout(0.25))# first (and only) set of FC => RELU layersmodel.add(Flatten())model.add(Dense(64))model.add(Activation("relu"))model.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.5))# softmax classifiermodel.add(Dense(classes))model.add(Activation("softmax"))# return the constructed network architecturereturn model创建活体检测器训练脚本

打开 train_liveness .py 文件并插入以下代码:
# set the matplotlib backend so figures can be saved in the background
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Agg")# import the necessary packages
from pyimagesearch.livenessnet import LivenessNet
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.utils import np_utils
from imutils import paths
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import argparse
import pickle
import cv2
import os# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-d", "--dataset", required=True,help="path to input dataset")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", type=str, required=True,help="path to trained model")
ap.add_argument("-l", "--le", type=str, required=True,help="path to label encoder")
ap.add_argument("-p", "--plot", type=str, default="plot.png",help="path to output loss/accuracy plot")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())此脚本接受四个命令行参数:
dataset
model
le
plot
下一个代码块将执行初始化并构建数据:
# initialize the initial learning rate, batch size, and number of
# epochs to train for
INIT_LR = 1e-4
BS = 8
EPOCHS = 50# grab the list of images in our dataset directory, then initialize
# the list of data (i.e., images) and class images
print("[INFO] loading images...")
imagePaths = list(paths.list_images(args["dataset"]))
data = []
labels = []for imagePath in imagePaths:# extract the class label from the filename, load the image and# resize it to be a fixed 32x32 pixels, ignoring aspect ratiolabel = imagePath.split(os.path.sep)[-2]image = cv2.imread(imagePath)image = cv2.resize(image, (32, 32))# update the data and labels lists, respectivelydata.append(image)labels.append(label)# convert the data into a NumPy array, then preprocess it by scaling
# all pixel intensities to the range [0, 1]
data = np.array(data, dtype="float") / 255.0之后对标签进行独热编码并对将数据划分为训练数据(75%)和测试数据(25%):
# encode the labels (which are currently strings) as integers and then
# one-hot encode them
le = LabelEncoder()
labels = le.fit_transform(labels)
labels = np_utils.to_categorical(labels, 2)# partition the data into training and testing splits using 75% of
# the data for training and the remaining 25% for testing
(trainX, testX, trainY, testY) = train_test_split(data, labels,test_size=0.25, random_state=42)之后对数据进行扩充并对模型进行编译和训练:
# construct the training image generator for data augmentation
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=20, zoom_range=0.15,width_shift_range=0.2, height_shift_range=0.2, shear_range=0.15,horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")# initialize the optimizer and model
print("[INFO] compiling model...")
opt = Adam(lr=INIT_LR, decay=INIT_LR / EPOCHS)
model = LivenessNet.build(width=32, height=32, depth=3,classes=len(le.classes_))
model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=opt,metrics=["accuracy"])# train the network
print("[INFO] training network for {} epochs...".format(EPOCHS))
H = model.fit_generator(aug.flow(trainX, trainY, batch_size=BS),validation_data=(testX, testY), steps_per_epoch=len(trainX) // BS,epochs=EPOCHS)模型训练后,可以评估效果并生成仿真曲线图:
# evaluate the network
print("[INFO] evaluating network...")
predictions = model.predict(testX, batch_size=BS)
print(classification_report(testY.argmax(axis=1),predictions.argmax(axis=1), target_names=le.classes_))# save the network to disk
print("[INFO] serializing network to '{}'...".format(args["model"]))
model.save(args["model"])# save the label encoder to disk
f = open(args["le"], "wb")
f.write(pickle.dumps(le))
f.close()# plot the training loss and accuracy
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(0, EPOCHS), H.history["loss"], label="train_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, EPOCHS), H.history["val_loss"], label="val_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, EPOCHS), H.history["acc"], label="train_acc")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, EPOCHS), H.history["val_acc"], label="val_acc")
plt.title("Training Loss and Accuracy on Dataset")
plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
plt.ylabel("Loss/Accuracy")
plt.legend(loc="lower left")
plt.savefig(args["plot"])训练活体检测器
执行以下命令开始模型训练:
$ python train.py --dataset dataset --model liveness.model --le le.pickle
[INFO] loading images...
[INFO] compiling model...
[INFO] training network for 50 epochs...
Epoch 1/50
29/29 [==============================] - 2s 58ms/step - loss: 1.0113 - acc: 0.5862 - val_loss: 0.4749 - val_acc: 0.7436
Epoch 2/50
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.9418 - acc: 0.6127 - val_loss: 0.4436 - val_acc: 0.7949
Epoch 3/50
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.8926 - acc: 0.6472 - val_loss: 0.3837 - val_acc: 0.8077
...
Epoch 48/50
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2796 - acc: 0.9094 - val_loss: 0.0299 - val_acc: 1.0000
Epoch 49/50
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.3733 - acc: 0.8792 - val_loss: 0.0346 - val_acc: 0.9872
Epoch 50/50
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2660 - acc: 0.9008 - val_loss: 0.0322 - val_acc: 0.9872
[INFO] evaluating network...precision recall f1-score supportfake 0.97 1.00 0.99 35real 1.00 0.98 0.99 43micro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 78macro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 78
weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 78[INFO] serializing network to 'liveness.model'...
从上述结果来看,在测试集上获得99%的检测精度!
合并起来:使用OpenCV进行活体检测

最后一步是将所有部分组合在一起:
- 访问网络摄像头/视频流;
- 对每个帧应用面部检测;
- 对于检测到的每个脸部,应用活体检测器模型;
打开`liveness_demo.py并插入以下代码:
# import the necessary packages
from imutils.video import VideoStream
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.models import load_model
import numpy as np
import argparse
import imutils
import pickle
import time
import cv2
import os# construct the argument parse and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", type=str, required=True,help="path to trained model")
ap.add_argument("-l", "--le", type=str, required=True,help="path to label encoder")
ap.add_argument("-d", "--detector", type=str, required=True,help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face detector")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())上述代码导入必要的包,并加载模型。
下面初始化人脸检测器、LivenessNet模型以及视频流:
# load our serialized face detector from disk
print("[INFO] loading face detector...")
protoPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"], "deploy.prototxt"])
modelPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"],"res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel"])
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoPath, modelPath)# load the liveness detector model and label encoder from disk
print("[INFO] loading liveness detector...")
model = load_model(args["model"])
le = pickle.loads(open(args["le"], "rb").read())# initialize the video stream and allow the camera sensor to warmup
print("[INFO] starting video stream...")
vs = VideoStream(src=0).start()
time.sleep(2.0)之后开始循环遍历视频的每一帧以检测面部是否真实:
# loop over the frames from the video stream
while True:# grab the frame from the threaded video stream and resize it# to have a maximum width of 600 pixelsframe = vs.read()frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=600)# grab the frame dimensions and convert it to a blob(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300)), 1.0,(300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0))# pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and# predictionsnet.setInput(blob)detections = net.forward()使用OpenCV blobFromImage函数生成一个面部数据,然后将其传递到面部检测器网络继续进行推理。核心代码如下:
# loop over the detectionsfor i in range(0, detections.shape[2]):# extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with the# predictionconfidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]# filter out weak detectionsif confidence > args["confidence"]:# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for# the face and extract the face ROIbox = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")# ensure the detected bounding box does fall outside the# dimensions of the framestartX = max(0, startX)startY = max(0, startY)endX = min(w, endX)endY = min(h, endY)# extract the face ROI and then preproces it in the exact# same manner as our training dataface = frame[startY:endY, startX:endX]face = cv2.resize(face, (32, 32))face = face.astype("float") / 255.0face = img_to_array(face)face = np.expand_dims(face, axis=0)# pass the face ROI through the trained liveness detector# model to determine if the face is "real" or "fake"preds = model.predict(face)[0]j = np.argmax(preds)label = le.classes_[j]# draw the label and bounding box on the framelabel = "{}: {:.4f}".format(label, preds[j])cv2.putText(frame, label, (startX, startY - 10),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 2)cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),(0, 0, 255), 2)首先过滤掉弱检测结果,然后提取面部图像并对其进行预处理,之后送入到活动检测器模型来确定面部是“真实的”还是“假的/欺骗的”。最后,在原图上绘制标签和添加文本以及矩形框,最后进行展示和清理。
# show the output frame and wait for a key presscv2.imshow("Frame", frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loopif key == ord("q"):break# do a bit of cleanup
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.stop()将活体检测器应用到实时视频上
打开终端并执行以下命令:
$ python liveness_demo.py --model liveness.model --le le.pickle --detector face_detector
Using TensorFlow backend.
[INFO] loading face detector...
[INFO] loading liveness detector...
[INFO] starting video stream...
可以看到,活体检测器成功地区分了真实和伪造的面孔。下面的视频作为一个更长时间的演示:视频地址
进一步的工作
本文设计的系统还有一些限制和缺陷,主要限制实际上是数据集有限——总共只有311个图像。这项工作的第一个扩展之一是简单地收集额外的训练数据,比如其它人,其它肤色或种族的人。
此外,活体检测器只是通过屏幕上的恶搞攻击进行训练,它并没有经过打印出来的图像或照片的训练。因此,建议添加不同类型的图像源。
最后,我想提一下,活体检测没有最好的方法,只有最合适的方法。一些好的活体检测器包含多种活体检测方法。
总结
在本教程中,学习了如何使用OpenCV进行活动检测。使用此活体检测器就可以在自己的人脸识别系统中发现伪造的假脸并进行反面部欺骗。此外,创建活动检测器使用了OpenCV、Deep Learning和Python等领域的知识。整个过程如下:
- 第一步是收集真假数据集。数据来源有:
- 智能手机录制自己的视频(即“真”面);
- 手机录播(即“假”面);
- 对两组视频应用面部检测以形成最终数据集。
- 第二步,获得数据集之后,实现了“LivenessNet”网络,该网络设计的比较浅层,这是为了确保:
- 减少了过拟合小数据集的可能性;
- 该模型本身能够实时运行;
总的来说,本文设计的活体检测器能够在验证集上获得99%的准确度。此外,活动检测器也能够应用于实时视频流。



腾讯2011.10.15校园招聘会笔试题)


)


)


A卷)
)





