RT,使用消息队列,信号量和命名管道实现的多人群聊系统。
本学期Linux、unix网络编程的第三个作业。
先上实验要求:
实验三 多进程服务器
【实验目的】
1、熟练掌握进程的创建与终止方法;
2、熟练掌握进程间通信方法;
2、应用套接字函数完成多进程服务器,实现服务器与客户端的信息交互。
【实验学时】
4学时
【实验内容】
通过一个服务器实现最多5个客户之间的信息群发。
服务器显示客户的登录与退出;
客户连接后首先发送客户名称,之后发送群聊信息;
客户输入bye代表退出,在线客户能显示其他客户的登录于退出。
任务分析:
实现提示:
1、服务器端:
服务器进程称之为主进程,主进程创建一个转发子进程和最多5个通信子进程。
主进程与转发子进程之间:
信号量(初值5,主进程接受一个客户连接后执行P操作判断是否超过5,转发子进程有一个客户退出后执行V操作,并发消息队列标识符)
命名管道SERVER(转发子进程将可用的消息队列标识符写入管道,主进程从管道中读取消息队列标识符)
转发子进程与通信子进程之间:
命名管道CLIENT(通信子进程向命名管道写入客户端发来的消息,转发子进程从管道中读取消息并发送给对应的客户端)
消息队列(转发子进程将客户发来的信息通过消息队列发送给每个通信子进程)
(1)主进程:
从转发子进程获取一个可用的消息队列标识符;
接收客户连接请求,如果连接数超过最大连接数,向客户发送退出标志,否则发送OK标志;
每接受一个连接,创建一个通信子进程并将连接socket、消息队列标识符、客户地址传递给通信子进程。
(2)通信子进程:
创建一个子进程负责从消息队列中读取消息,发送给客户。
通信子进程负责接收客户发来信息,通过命名管道CLIENT发送给转发子进程;
若信息为用户名,附带消息队列、客户地址发送给转发子进程;
若信息为退出,终止子进程,程序结束
(3)转发子进程:
创建5个消息队列;
维护客户信息表:消息队列、客户名、客户IP、客户端口、状态。
从命名管道CLIENT中读取通信子进程发来的消息,消息类型为:用户名、退出及一般信息;
若为用户名,依据消息队列在更新客户信息表,状态为可用;
若为一般信息,将信息转换后写入可用客户的消息队列,等待其他通信子进程读取;
若为退出,在客户信息表中状态设为不可用,执行信号量V操作,并将可用客户的消息队列标识符写入到命名管道SERVER;
2、客户端:
根据用户从终端输入的服务器IP地址及端口号连接到相应的服务器;
连接成功后,先发送客户名称;
创建一个子进程负责接收服务器发来的信息,并显示;
主进程循环从终端输入信息,并将信息发送给服务器;
当发送给服务器为bye后,关闭子进程,程序退出。
架构看起来很复杂,我们可以绘制一下流程图方便理清思路。
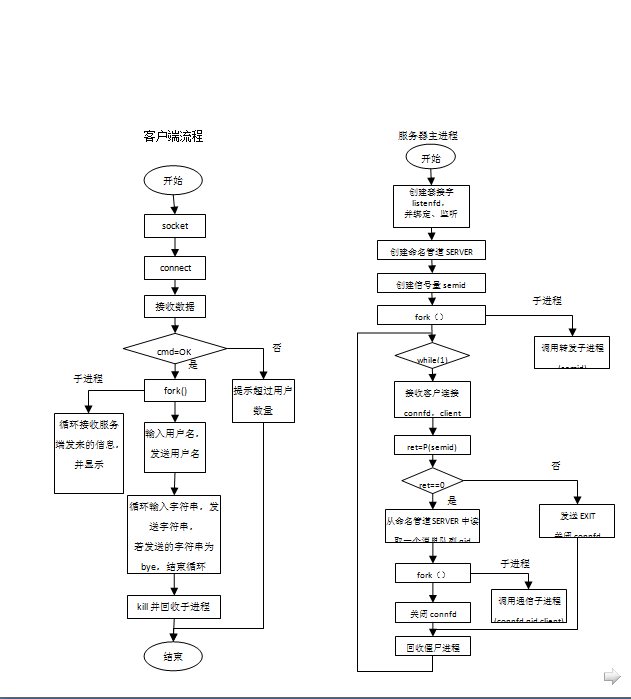
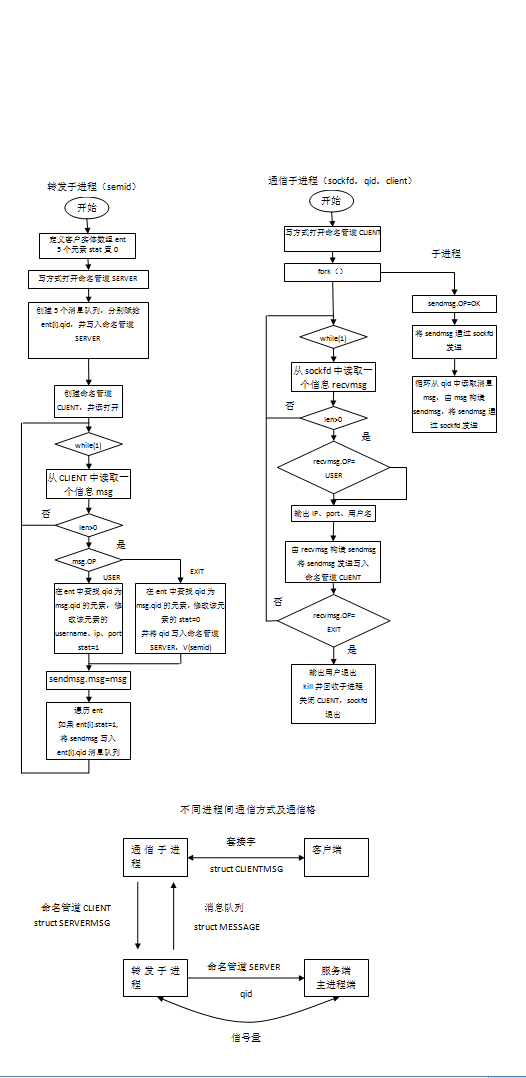
在word里面截图不是很清晰啊。。。
开始写代码吧:首先clientmsg.h,它定义了一些消息的操作符(OP)和CLIENTMSG这个结构体(用于服务器和客户端之间传递消息)
1 //CLIENTMSG between server and client 2 #ifndef _clientmsg 3 #define _clientmsg 4 5 //USER MSG EXIT for OP of CLIENTMSG 6 #define EXIT -1 7 #define USER 1 8 #define MSG 2 9 #define OK 3 10 11 #ifndef CMSGLEN 12 #define CMSGLEN 100 13 #endif 14 15 struct CLIENTMSG{ 16 int OP; 17 char username[20]; 18 char buf[CMSGLEN]; 19 }; 20 21 #endif
然后实现一下servermsg.h,用于服务器内部的转发子进程和通信子进程之间的消息传递。
1 //SERVERMSG for communicate to translate 2 //MESSAGE for translate to communicate 3 #ifndef _servermsg 4 #define _servermsg 5 6 #include <netinet/in.h> 7 #include "clientmsg.h" 8 9 10 #ifndef CMSGLEN 11 #define CMSGLEN 100 12 #endif 13 14 15 struct SERVERMSG{ 16 int OP; 17 char username[20]; 18 char buf[CMSGLEN]; 19 struct sockaddr_in client; 20 int stat; 21 int qid; 22 }; 23 24 struct MESSAGE{ 25 long msgtype; 26 struct SERVERMSG msg; 27 }; 28 29 #endif
由于需要操作信号量,所以将一些信号量的操作做成函数
semaphore.h
1 #ifndef _semaphore 2 #define _semaphore 3 4 union semun 5 { 6 int val; 7 struct semid_ds *buf; 8 unsigned short *array; 9 }; 10 11 int CreateSem(key_t key,int value); 12 int Sem_P(int semid); 13 int Sem_V(int semid); 14 int GetvalueSem(int semid); 15 void DestroySem(int semid); 16 17 18 #endif
对函数的实现:semaphore.c
1 #include <stdlib.h> 2 #include <fcntl.h> 3 #include <sys/sem.h> 4 #include "semaphore.h" 5 6 int CreateSem(key_t key,int value) 7 { 8 union semun sem; 9 int semid; 10 sem.val=value; 11 semid=semget(key,1,IPC_CREAT); 12 if (semid==-1){ 13 perror("semget error"); exit(1); 14 } 15 semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,sem); 16 return semid; 17 } 18 19 int Sem_P(int semid) 20 { 21 struct sembuf sops={0,-1,IPC_NOWAIT}; 22 return (semop(semid,&sops,1)); 23 } 24 25 int Sem_V(int semid) 26 { 27 struct sembuf sops={0,+1,IPC_NOWAIT}; 28 return (semop(semid,&sops,1)); 29 } 30 31 int GetvalueSem(int semid) 32 { 33 union semun sem; 34 return semctl(semid,0,GETVAL,sem); 35 } 36 void DestroySem(int semid) 37 { 38 union semun sem; 39 sem.val=0; 40 41 semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID,sem); 42 }
接下来是非常重要的服务器端实现(里面有很多调试信息,比较懒没有删掉,直接在里面注释掉了。)
server.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <sys/socket.h> 4 #include <netinet/in.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <sys/wait.h> 8 #include <sys/stat.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include <fcntl.h> 11 #include <sys/ipc.h> 12 #include "semaphore.h" 13 #include "servermsg.h" 14 15 16 void trans_process(int semid); 17 void communicate_process(int connetfd,int qid,struct sockaddr_in client); 18 19 int main(){ 20 21 struct sockaddr_in server; 22 struct sockaddr_in client; 23 int listenfd,connetfd; 24 char ip[20]; 25 int port; 26 int addrlen; 27 struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg; 28 int ret,status; 29 /*---------------------socket-------------------*/ 30 if((listenfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))== -1){ 31 perror("socket() error\n"); 32 exit(1); 33 } 34 35 /*----------------------IO-----------------------*/ 36 printf("Please input the ip:\n"); 37 scanf("%s",ip); 38 printf("Please input the port:\n"); 39 scanf("%d",&port); 40 41 /*---------------------bind----------------------*/ 42 bzero(&server,sizeof(server)); 43 server.sin_family = AF_INET; 44 server.sin_port = htons(port); 45 server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip); 46 if(bind(listenfd,(struct sockaddr *)&server,sizeof(server))== -1){ 47 perror("bind() error\n"); 48 exit(1); 49 } 50 51 /*----------------------listen-------------------*/ 52 if (listen(listenfd,5)== -1){ 53 perror("listen() error\n"); 54 exit(1); 55 } 56 57 //创建命名管道 58 unlink("SERVER"); 59 mkfifo("SERVER",O_CREAT); 60 int rd = open("SERVER",O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK); 61 int semid; 62 key_t k = ftok(".",'b'); 63 semid = CreateSem(k,5); 64 pid_t pid_1,pid_2; 65 pid_1 = fork(); 66 if(pid_1 == 0){ 67 trans_process(semid); 68 exit(0); 69 } 70 else if(pid_1 > 0){ 71 while(1){ 72 addrlen = sizeof(client); 73 if((connetfd = accept(listenfd,(struct sockaddr *)&client,&addrlen))== -1){ 74 perror("accept() error\n"); 75 exit(1); 76 } 77 ret = Sem_P(semid); 78 if(ret == 0){ 79 int qid; 80 read(rd,&qid,sizeof(qid)); 81 //printf("qid1:%d\n",qid ); 82 pid_2 = fork(); 83 if (pid_2 > 0){ 84 close(connetfd); 85 waitpid(pid_2,&status,WNOHANG); 86 continue; 87 } 88 else if(pid_2 == 0){ 89 communicate_process(connetfd,qid,client); 90 exit(0); 91 } 92 else { 93 perror("the second fork error\n"); 94 } 95 } 96 else { 97 clientMsg.OP = EXIT; 98 send(connetfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 99 close(connetfd); 100 } 101 waitpid(pid_1,&status,WNOHANG); 102 103 } 104 } 105 else { 106 perror("first time fork error\n"); 107 } 108 /*----------------------close-------------------*/ 109 close(connetfd); 110 close(listenfd); 111 112 return 0; 113 } 114 115 116 /*----------------------------函数实现区----------------------------*/ 117 void trans_process(int semid){ 118 struct SERVERMSG ent[5]; 119 struct MESSAGE sendMsg; 120 struct SERVERMSG msg; 121 int i; 122 for(i=0;i<5;i++){ 123 ent[i].stat = 0; 124 } 125 int wfd = open("SERVER",O_WRONLY|O_NONBLOCK); 126 for(i=0;i<5;i++){ 127 key_t key = ftok(".",(char)i+102); 128 ent[i].qid = msgget(key,IPC_CREAT); 129 write(wfd,&ent[i].qid,sizeof(ent[i].qid)); 130 } 131 unlink("CLIENT"); 132 mkfifo("CLIENT",O_CREAT); 133 int rfd = open("CLIENT",O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK); 134 int len; 135 while(1){ 136 bzero(&msg,sizeof(msg)); 137 len = read(rfd,&msg,sizeof(msg)); 138 //printf(" %d,%s ,%s\n",msg.OP,msg.username,msg.buf ); 139 //sleep(3); 140 if(len > 0){ 141 if(msg.OP == USER){ 142 for(i=0;i<5;i++){ 143 if(ent[i].qid == msg.qid){ 144 bcopy(msg.username,ent[i].username,strlen(msg.username)); 145 ent[i].client = msg.client; 146 ent[i].stat = 1; 147 break; 148 } 149 } 150 } 151 else if(msg.OP == EXIT){ 152 for(i=0;i<5;i++){ 153 if(ent[i].qid == msg.qid){ 154 ent[i].stat = 0; 155 write(wfd,&ent[i].qid,sizeof(ent[i].qid)); 156 Sem_V(semid); 157 break; 158 } 159 } 160 } 161 //bzero(&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg)); 162 sendMsg.msg = msg; 163 for(i=0;i<5;i++){ 164 if(ent[i].stat == 1){ 165 printf("stat 1...\n"); 166 int m_len = sizeof(msg); 167 int sta=msgsnd(ent[i].qid,&sendMsg,len,0); 168 //printf("flag:%d\n",sta ); 169 } 170 } 171 } 172 else { 173 continue; 174 } 175 } 176 177 } 178 179 void communicate_process(int connetfd,int qid,struct sockaddr_in client){ 180 struct CLIENTMSG sendMsg; 181 struct CLIENTMSG recvMsg; 182 struct MESSAGE server_Msg; 183 struct SERVERMSG client_sndMsg; 184 struct SERVERMSG msg; 185 int status; 186 int wfd = open("CLIENT",O_WRONLY|O_NONBLOCK); 187 pid_t pid; 188 pid = fork(); 189 if(pid < 0){ 190 perror("communicate_process fork error\n"); 191 } 192 else if (pid == 0){ 193 bzero(&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg)); 194 sendMsg.OP = OK; 195 send(connetfd,&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg),0); 196 while(1){ 197 int m_len = sizeof(msg); 198 bzero(&server_Msg,sizeof(server_Msg)); 199 int sta=msgrcv(qid,&server_Msg,m_len,0,0); 200 //printf("flag:%d\n",sta ); 201 //printf("send..%d,%s,%s\n",server_Msg.msg.OP,server_Msg.msg.username,server_Msg.msg.buf ); 202 bzero(&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg)); 203 bcopy(server_Msg.msg.username,sendMsg.username,strlen(server_Msg.msg.username)); 204 sendMsg.OP = server_Msg.msg.OP; 205 bcopy(server_Msg.msg.buf,sendMsg.buf,strlen(server_Msg.msg.buf)); 206 //printf("send..%d,%s,%s\n",sendMsg.OP,sendMsg.username,sendMsg.buf ); 207 send(connetfd,&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg),0); 208 } 209 } 210 else{ 211 while(1){ 212 bzero(&recvMsg,sizeof(recvMsg)); 213 int len =recv(connetfd,&recvMsg,sizeof(recvMsg),0); 214 if(len > 0){ 215 if(recvMsg.OP == USER){ 216 printf("user %s login from ip:%s,port:%d\n",recvMsg.username,inet_ntoa(client.sin_addr),ntohs(client.sin_port) ); 217 client_sndMsg.OP = USER; 218 } 219 else if(recvMsg.OP == EXIT){ 220 printf("user %s is logout\n",recvMsg.username ); 221 client_sndMsg.OP = EXIT; 222 write(wfd,&client_sndMsg,sizeof(client_sndMsg)); 223 break; 224 } 225 else if(recvMsg.OP == MSG){ 226 client_sndMsg.OP = MSG; 227 } 228 bzero(&client_sndMsg,sizeof(client_sndMsg)); 229 bcopy(recvMsg.username,client_sndMsg.username,strlen(recvMsg.username)); 230 bcopy(recvMsg.buf,client_sndMsg.buf,strlen(recvMsg.buf)); 231 client_sndMsg.client = client; 232 //printf("qid2:%d\n",qid ); 233 client_sndMsg.qid = qid; 234 client_sndMsg.OP = recvMsg.OP; 235 write(wfd,&client_sndMsg,sizeof(client_sndMsg)); 236 237 } 238 else{ 239 continue; 240 } 241 } 242 kill(pid,SIGKILL); 243 waitpid(pid,&status,WNOHANG); 244 close(wfd); 245 close(connetfd); 246 } 247 }
写出了服务端,就可以非常容易的写出客户端了。
client.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <sys/socket.h> 4 #include <netinet/in.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <sys/wait.h> 8 #include <signal.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include "clientmsg.h" 11 12 int main(){ 13 int sockfd; 14 char ip[20]; 15 int port; 16 int status; 17 pid_t pid; 18 struct sockaddr_in server; 19 struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg; 20 21 /*---------------------socket---------------------*/ 22 if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))== -1){ 23 perror("socket error\n"); 24 exit(1); 25 } 26 27 /*---------------------connect--------------------*/ 28 printf("Please input the ip:\n"); 29 scanf("%s",ip); 30 printf("Please input the port:\n"); 31 scanf("%d",&port); 32 bzero(&server,sizeof(server)); 33 server.sin_family = AF_INET; 34 server.sin_port = htons(port); 35 inet_aton(ip,&server.sin_addr); 36 if(connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&server,sizeof(server))== -1){ 37 perror("connect() error\n"); 38 exit(1); 39 } 40 recv(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 41 if(clientMsg.OP == OK){ 42 int len; 43 pid = fork(); 44 if(pid == 0){ 45 while(1){ 46 bzero(&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg)); 47 len =recv(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 48 if(len > 0){ 49 if(clientMsg.OP ==USER){ 50 printf("the user %s is login.\n",clientMsg.username ); 51 } 52 else if(clientMsg.OP == EXIT){ 53 printf("the user %s is logout.\n",clientMsg.username); 54 } 55 else if(clientMsg.OP == MSG){ 56 printf("%s: %s\n",clientMsg.username,clientMsg.buf ); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 61 } 62 else if(pid > 0){ 63 printf("Please input the username:\n"); 64 scanf("%s",clientMsg.username); 65 clientMsg.OP = USER; 66 send(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 67 while(1){ 68 clientMsg.OP = MSG; 69 scanf("%s",clientMsg.buf); 70 if(strcmp("bye",clientMsg.buf) == 0){ 71 clientMsg.OP = EXIT; 72 send(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 73 break; 74 } 75 send(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),0); 76 77 } 78 kill(pid,SIGKILL); 79 waitpid(pid,&status,WNOHANG); 80 } 81 else{ 82 perror("fork error!\n"); 83 } 84 } 85 else{ 86 printf("以达到最大连接数!\n"); 87 } 88 /*------------------------close--------------------------*/ 89 close(sockfd); 90 91 return 0; 92 }
最后是makefile:
main:server.o client.o semaphore.ogcc server.o semaphore.o -oservergcc client.o -oclient server.o:server.c semaphore.h clientmsg.h servermsg.hgcc -c server.c client.o:client.c clientmsg.hgcc -c client.c semaphore.o:semaphore.h semaphore.cgcc -c semaphore.c clean:rm -rf *.o
下面上一下演示过程:(测试环境,Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 + centos系Linux,ubuntu下可能会有些问题。)
首先先把服务端启动开来,为了方便测试,这里直接使用的是127.0.0.1的localhost。

然后启动两个客户端用来测试,在用户登录的时候客户端会有消息提醒。服务端会有日志打印输出客户端的名字和登录ip、端口。
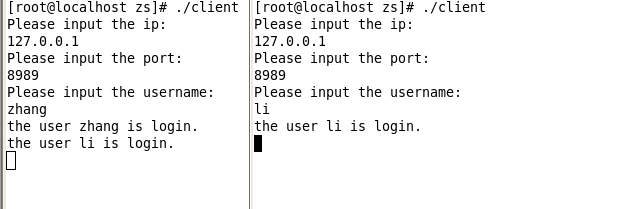
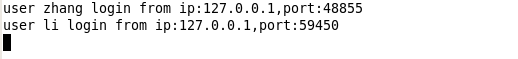
客户可以发送消息了,如图发送与接收均正常。可以同时启动<=5个客户端进行群聊,这里为了简单演示只是启动了2个。(修改信号量代码可以实现n多个客户的同时登陆):
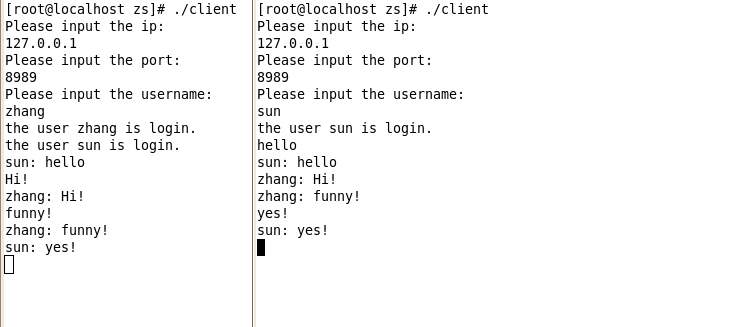
输入bye以后即可退出聊天并下线。当有客户下线的时候,在线的客户端会收到下线提醒,客户端会有日志打印输出。
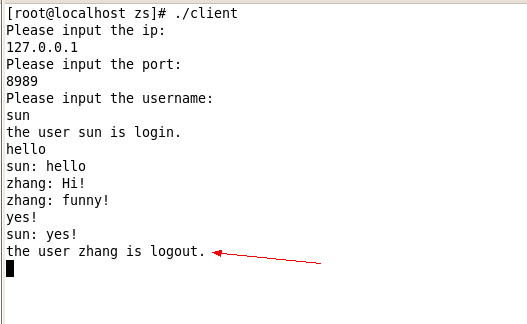
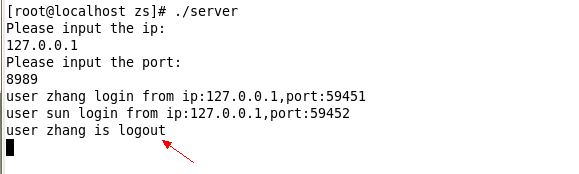
这个实验内容前前后后花了我2天才写完,刚开始没有弄清楚这一整套的工作机制与流程,写起来很是吃力,程序就是各种调不通。本来都想放弃了,但是后来还是咬咬牙坚持了一下来,饭要一口一口吃,程序要一点一点的写,万事不能操之过急,写代码一定要心平气和,头脑清晰。由于gdb调试工具用的不是很熟练,只能在程序里面一段一段的print变量来DEBUG,很是辛苦啊。




上运行python总结)
学习笔记)













)