这次来说一下AFURLResponseSerialization这个HTTP响应类。
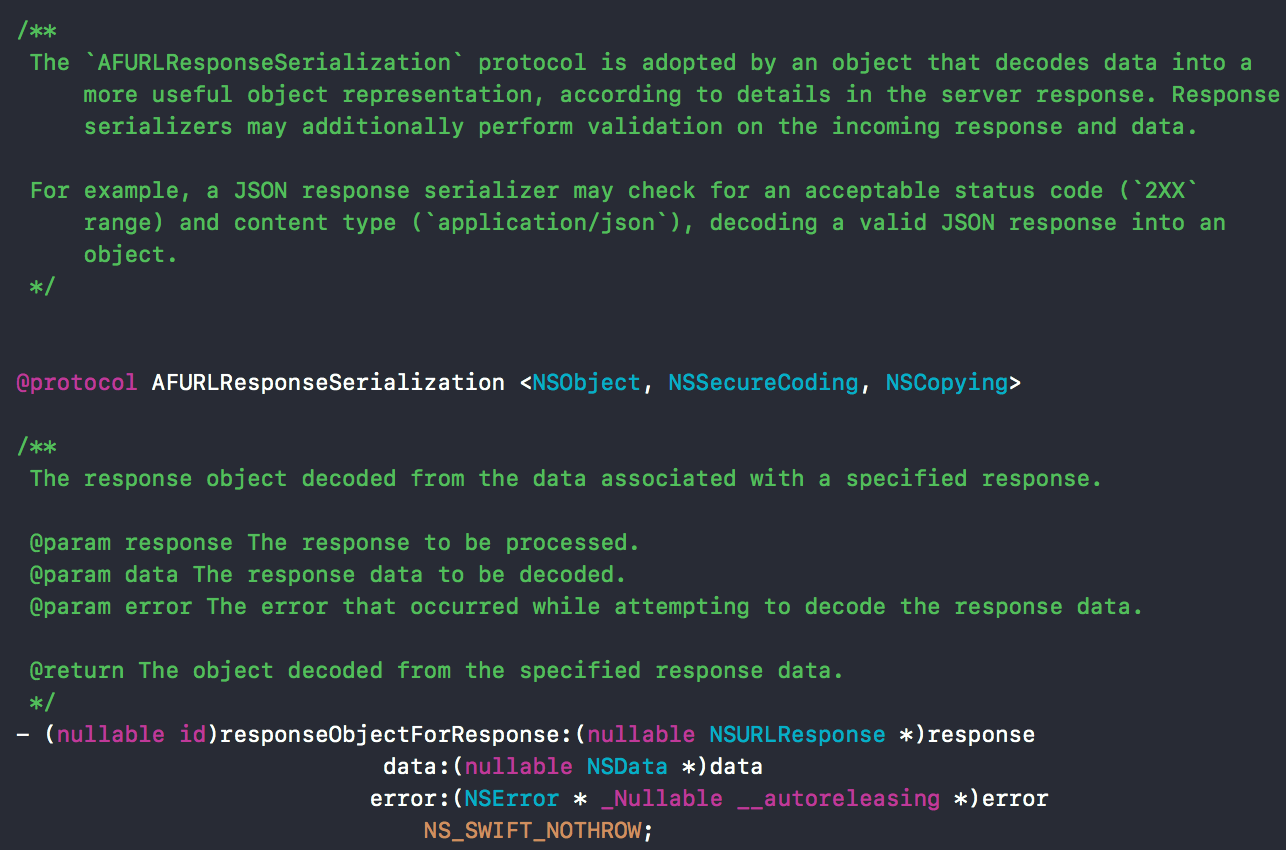
定义了一个协议,该协议返回序列化后的结果。后续的AFHTTPResponseSerializer以及他的子类都遵循了该协议
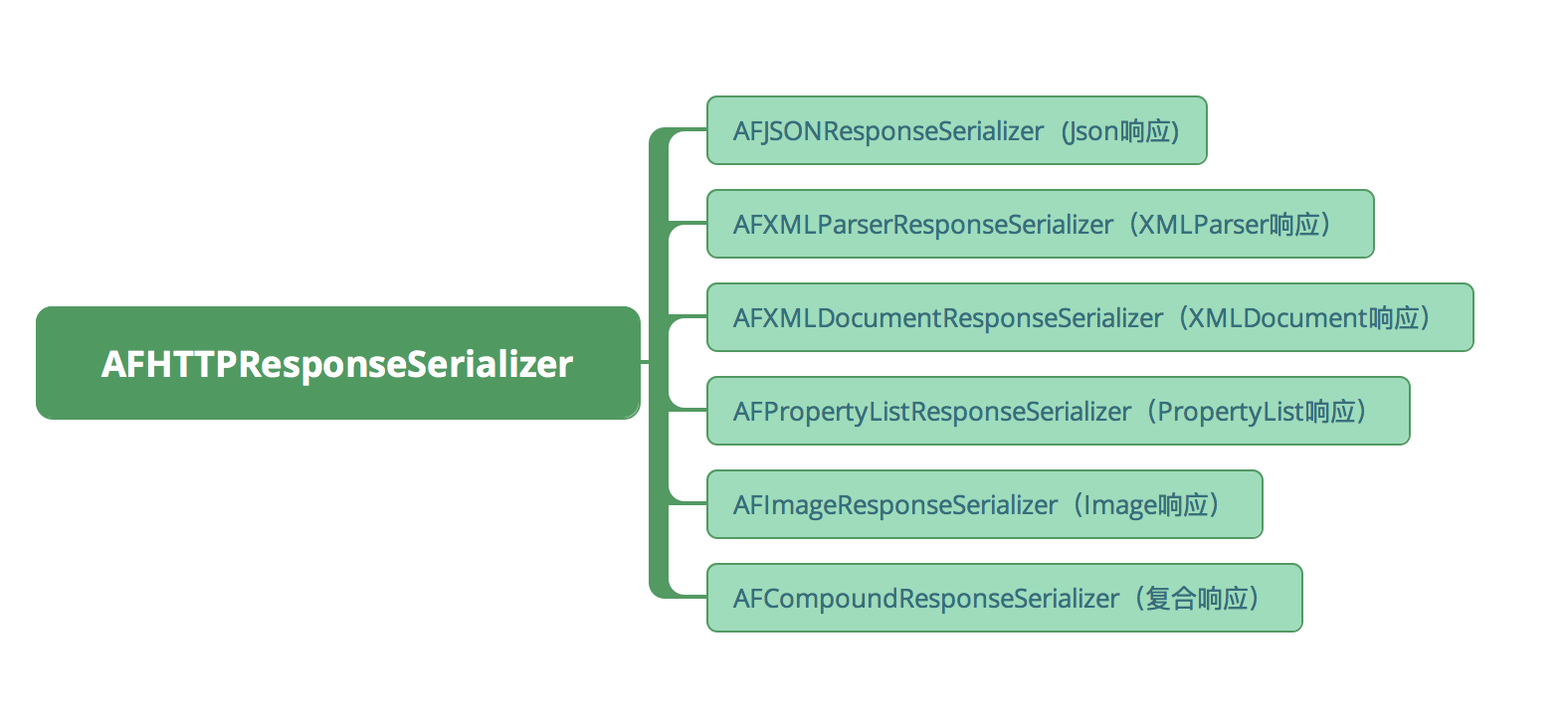
该类内有很多子类定义,这里借用一张图来展示,之后一个一个来说。
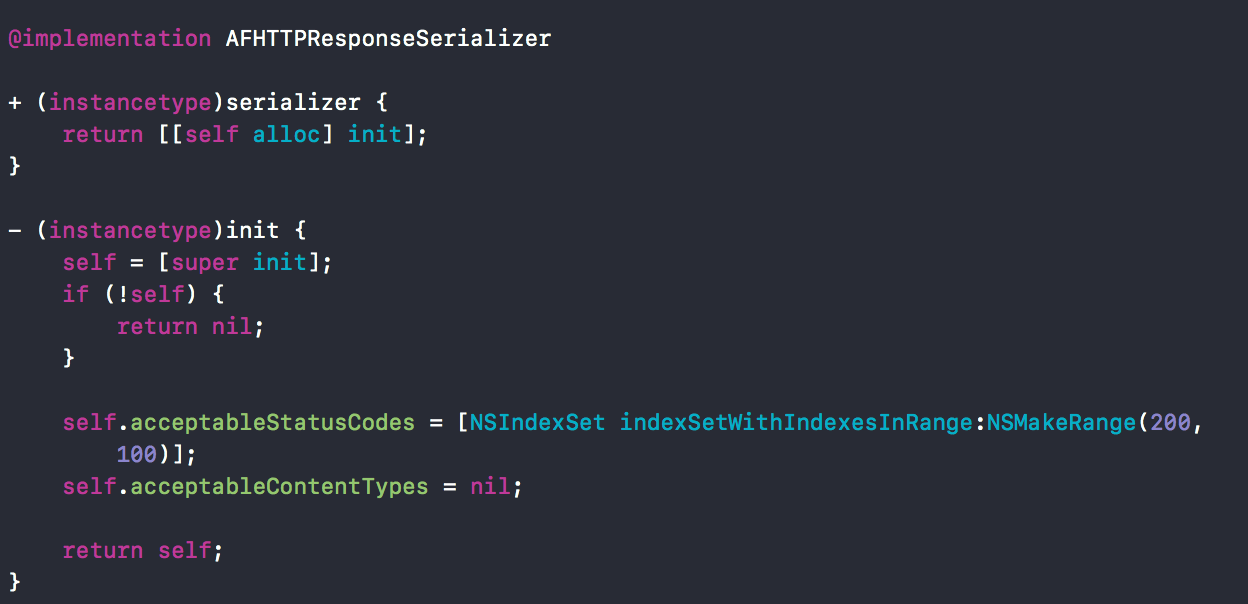
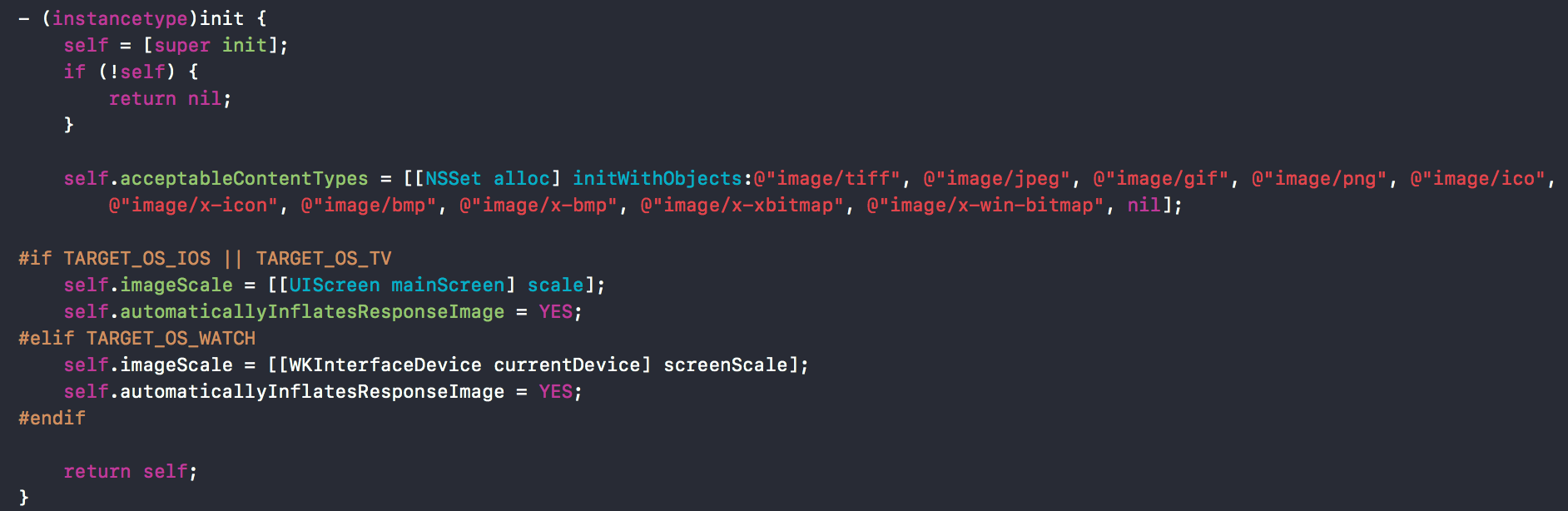
我们先来看下AFHTTPResponseSerializer在头文件中的定义有哪些。
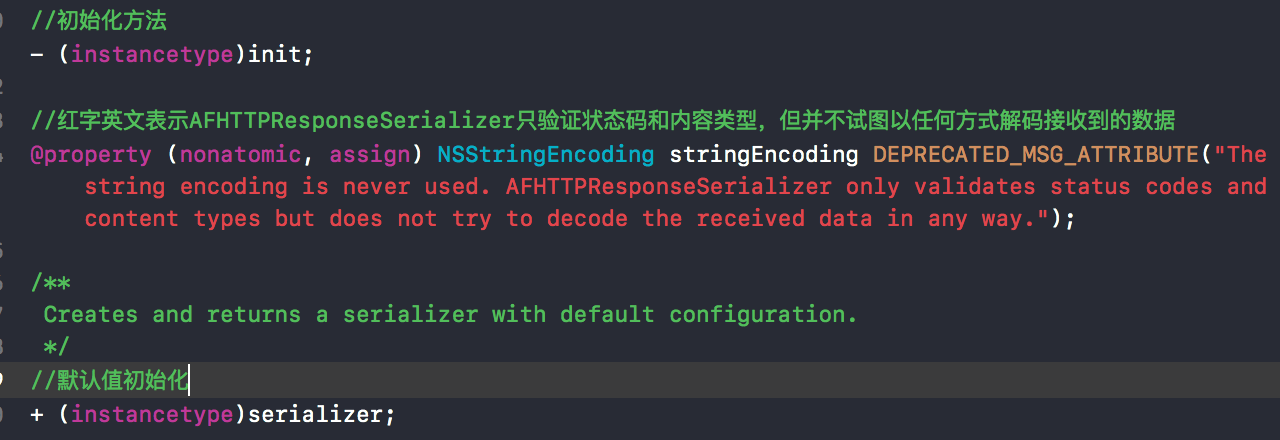
可以看到有两个初始化方法,然后stringEncoding后面有一个宏,这个宏代表这弃用了。
![]()
![]()
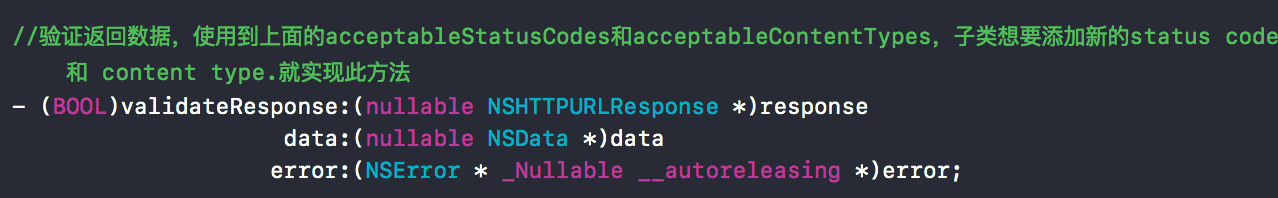
来看实现文件的部分。
这里有一个NSIndexSet。
NSIndexSet:代表一个不可变的独特的无符号整数的集合,称为索引,因为使用它们的方式。这个集合被称为索引集。你不应该使用索引集存储任意集合的整数值,因为索引集按索引排序范围的方式存储的。这使得它们更有效率比存储单个整数的集合。这也意味着每个索引值指数中只能出现一次。通俗点讲NSIndexSet就是一个唯一的,有序的,无符号整数的集合。
self.acceptableStatusCodes = [NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndexesInRange:NSMakeRange(200, 100)];
表示接受状态码范围200~299。
- (BOOL)validateResponse:(NSHTTPURLResponse *)responsedata:(NSData *)dataerror:(NSError * __autoreleasing *)error {BOOL responseIsValid = YES;//默认为yesNSError *validationError = nil;//存在response且为NSHTTPURLResponse类if (response && [response isKindOfClass:[NSHTTPURLResponse class]]) {//条件:1.acceptableContentTypes存在 2.response的MIMEType不在范围内 3.MIMEType和data均不为空if (self.acceptableContentTypes && ![self.acceptableContentTypes containsObject:[response MIMEType]] &&!([response MIMEType] == nil && [data length] == 0)) {//data长度大于0且respone的URL存在if ([data length] > 0 && [response URL]) {//定义错误信息字典NSMutableDictionary *mutableUserInfo = [@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey: [NSString stringWithFormat:NSLocalizedStringFromTable(@"Request failed: unacceptable content-type: %@", @"AFNetworking", nil), [response MIMEType]],NSURLErrorFailingURLErrorKey:[response URL],AFNetworkingOperationFailingURLResponseErrorKey: response,} mutableCopy];if (data) {//错误信息包含datamutableUserInfo[AFNetworkingOperationFailingURLResponseDataErrorKey] = data;}//生成NSerrorvalidationError = AFErrorWithUnderlyingError([NSError errorWithDomain:AFURLResponseSerializationErrorDomain code:NSURLErrorCannotDecodeContentData userInfo:mutableUserInfo], validationError);}responseIsValid = NO;}if (self.acceptableStatusCodes && ![self.acceptableStatusCodes containsIndex:(NSUInteger)response.statusCode] && [response URL]) {NSMutableDictionary *mutableUserInfo = [@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey: [NSString stringWithFormat:NSLocalizedStringFromTable(@"Request failed: %@ (%ld)", @"AFNetworking", nil), [NSHTTPURLResponse localizedStringForStatusCode:response.statusCode], (long)response.statusCode],NSURLErrorFailingURLErrorKey:[response URL],AFNetworkingOperationFailingURLResponseErrorKey: response,} mutableCopy];if (data) {mutableUserInfo[AFNetworkingOperationFailingURLResponseDataErrorKey] = data;}validationError = AFErrorWithUnderlyingError([NSError errorWithDomain:AFURLResponseSerializationErrorDomain code:NSURLErrorBadServerResponse userInfo:mutableUserInfo], validationError);responseIsValid = NO;}}if (error && !responseIsValid) {*error = validationError;}return responseIsValid; }
response有效性验证过程。
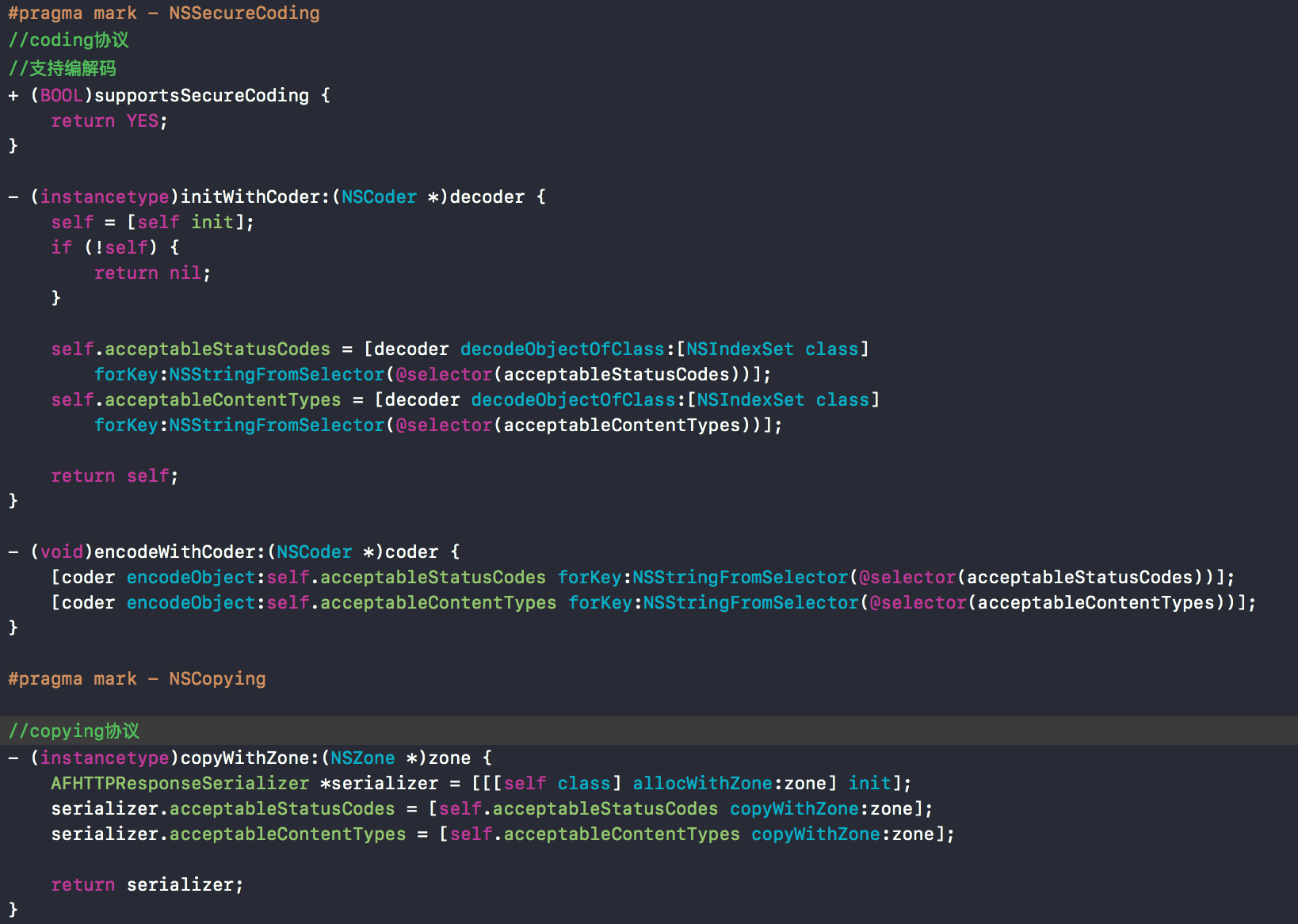
NSSecureCoding, NSCopying协议方法。

![]()
![]()
进入该属性类型NSJSONReadingOptions可以看到是下图这么定义的。

-
NSJSONReadingMutableContainers:返回是可变容器类型如NSMutableArray,NSMutableDictionay。
-
NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves:返回的字符串是NSMutableSting。
-
NSJSONReadingAllowFragments:json结构最外层可以不是NSArray和NSDictionay。
接着来看对应的实现文件部分。
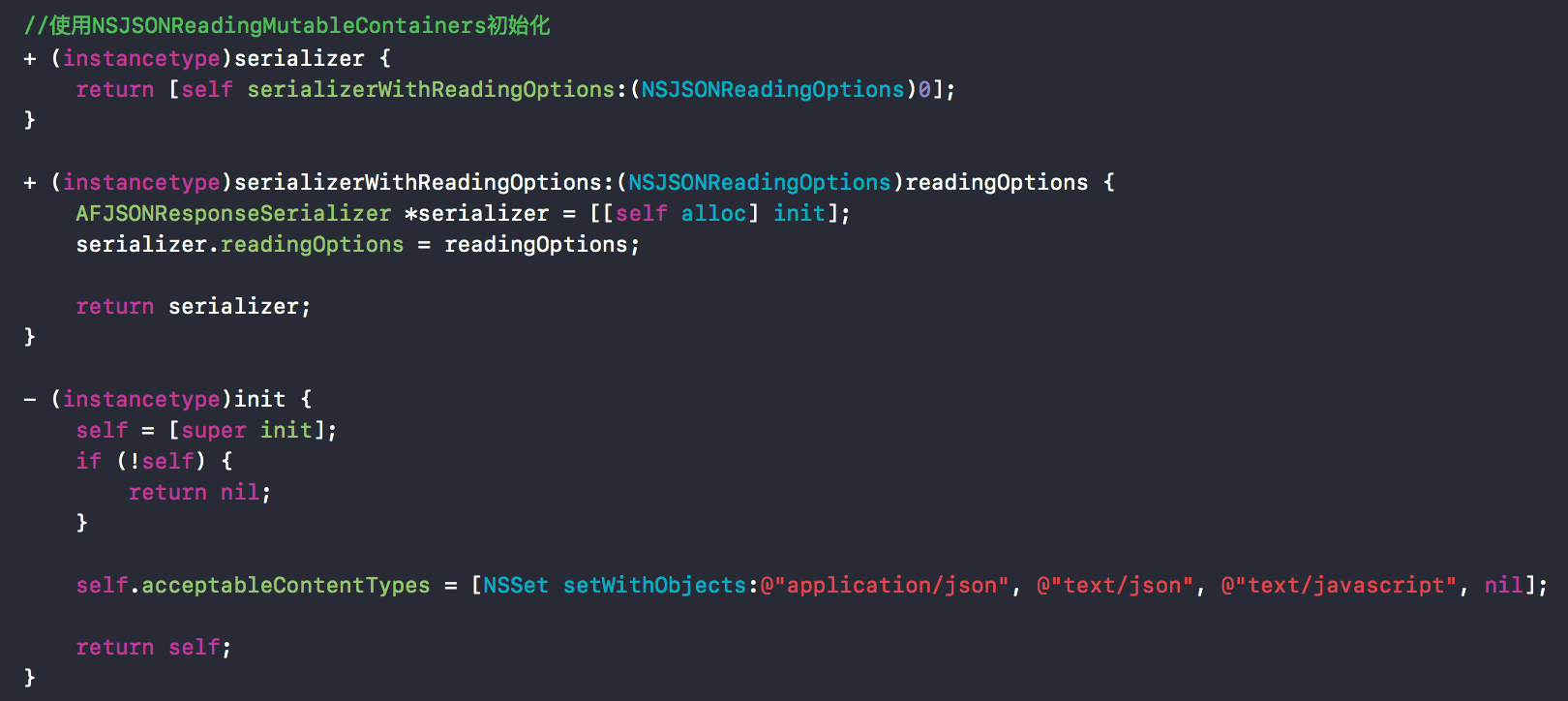
三种初始化方法从init方法中可以看到acceptableContentTypes支持"application/json", "text/json", "text/javascript"三种。
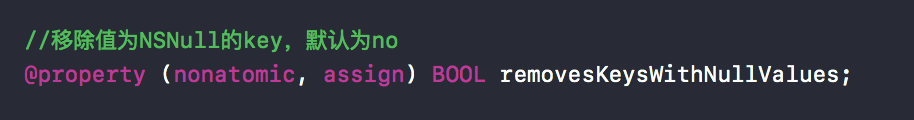
- (id)responseObjectForResponse:(NSURLResponse *)responsedata:(NSData *)dataerror:(NSError *__autoreleasing *)error {//response有效性无效if (![self validateResponse:(NSHTTPURLResponse *)response data:data error:error]) {//无error或者code为NSURLErrorCannotDecodeContentData解析无效,要返回nilif (!error || AFErrorOrUnderlyingErrorHasCodeInDomain(*error, NSURLErrorCannotDecodeContentData, AFURLResponseSerializationErrorDomain)) {return nil;}}// Workaround for behavior of Rails to return a single space for `head :ok` (a workaround for a bug in Safari), which is not interpreted as valid input by NSJSONSerialization.// See https://github.com/rails/rails/issues/1742//data由空格字符构成也需要返回nilBOOL isSpace = [data isEqualToData:[NSData dataWithBytes:" " length:1]];if (data.length == 0 || isSpace) {return nil;}NSError *serializationError = nil;id responseObject = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:self.readingOptions error:&serializationError];if (!responseObject){if (error) {*error = AFErrorWithUnderlyingError(serializationError, *error);}return nil;}if (self.removesKeysWithNullValues) {return AFJSONObjectByRemovingKeysWithNullValues(responseObject, self.readingOptions);}return responseObject; }
转化和解析方法,这里又出现了两个定义的C函数贴在下面。
static BOOL AFErrorOrUnderlyingErrorHasCodeInDomain(NSError *error, NSInteger code, NSString *domain) {//error的domain和code与入参对影响等直接返回yesif ([error.domain isEqualToString:domain] && error.code == code) {return YES;} else if (error.userInfo[NSUnderlyingErrorKey]) {//否则判断userInfo中key为NSUnderlyingErrorKey是否有值,有递归调用自身return AFErrorOrUnderlyingErrorHasCodeInDomain(error.userInfo[NSUnderlyingErrorKey], code, domain);}return NO; }
static id AFJSONObjectByRemovingKeysWithNullValues(id JSONObject, NSJSONReadingOptions readingOptions) {//数组类if ([JSONObject isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {//定义可变数组NSMutableArray *mutableArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:[(NSArray *)JSONObject count]];for (id value in (NSArray *)JSONObject) { [mutableArray addObject:AFJSONObjectByRemovingKeysWithNullValues(value, readingOptions)];}return (readingOptions & NSJSONReadingMutableContainers) ? mutableArray : [NSArray arrayWithArray:mutableArray];} else if ([JSONObject isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {//同上NSMutableDictionary *mutableDictionary = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:JSONObject];for (id <NSCopying> key in [(NSDictionary *)JSONObject allKeys]) {id value = (NSDictionary *)JSONObject[key];
//去除value为NSNull的keyif (!value || [value isEqual:[NSNull null]]) {[mutableDictionary removeObjectForKey:key];} else if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]] || [value isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {mutableDictionary[key] = AFJSONObjectByRemovingKeysWithNullValues(value, readingOptions);}}return (readingOptions & NSJSONReadingMutableContainers) ? mutableDictionary : [NSDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:mutableDictionary];}return JSONObject; }
这里有点好奇为什么不把数组里面的NSNull对象也去掉而只是把字典中value为NSNull的key去掉。

NSSecureCoding, NSCopying协议方法。

![]()
解析XML的子类。
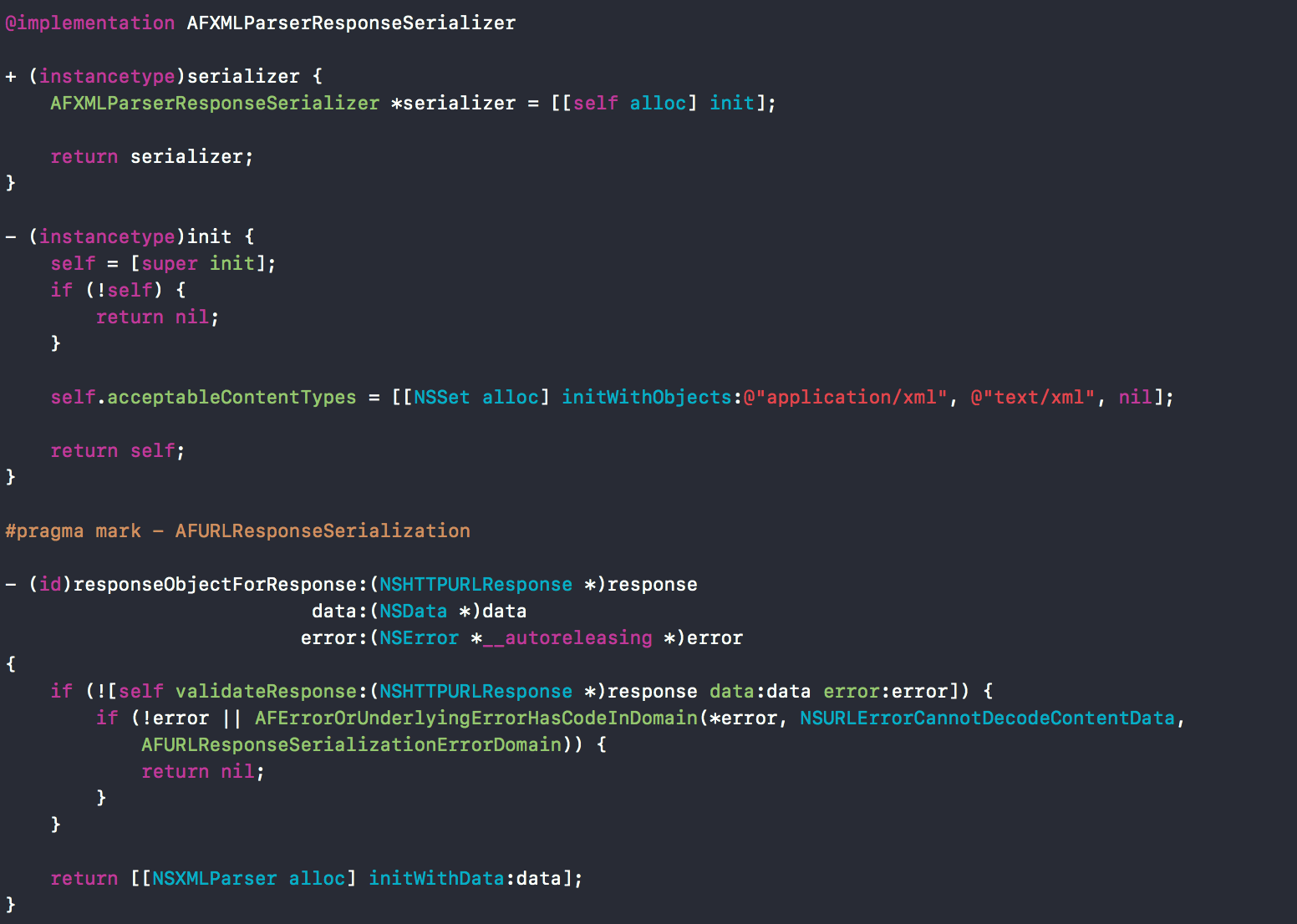
不多说比较好理解。

![]()
将JSON转换为PropertyList用到的子类。
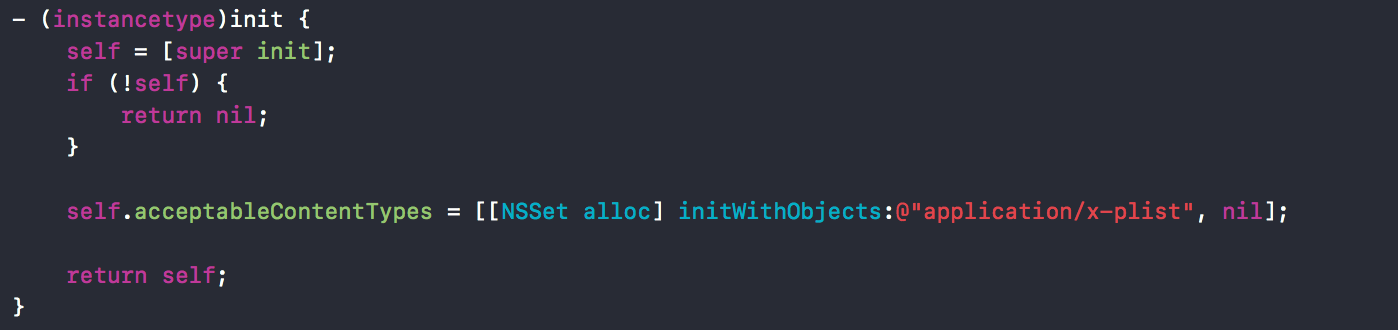
ContentType支持application/x-plist。

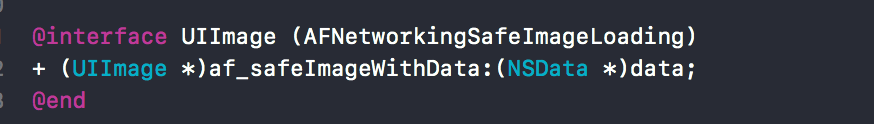
这里是UIImage的一个分类,从方法名字上看可以想到是一个安全的NSData转Image的方法。
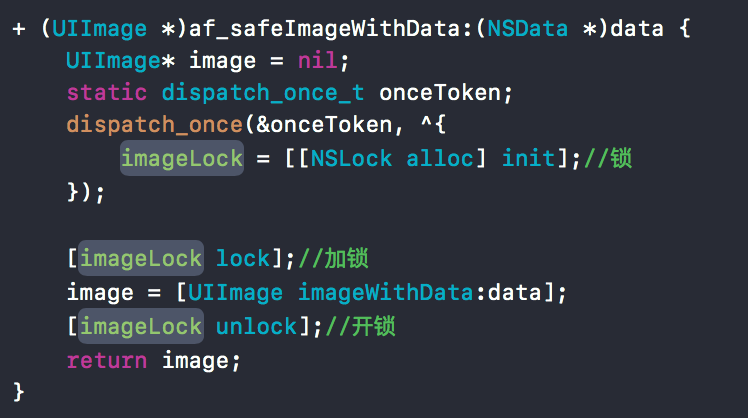
通过NSLock来解决多线程上的一些安全问题。
static UIImage * AFImageWithDataAtScale(NSData *data, CGFloat scale) {UIImage *image = [UIImage af_safeImageWithData:data];if (image.images) {return image;}return [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:[image CGImage] scale:scale orientation:image.imageOrientation]; }static UIImage * AFInflatedImageFromResponseWithDataAtScale(NSHTTPURLResponse *response, NSData *data, CGFloat scale) {if (!data || [data length] == 0) {return nil;}CGImageRef imageRef = NULL;CGDataProviderRef dataProvider = CGDataProviderCreateWithCFData((__bridge CFDataRef)data);if ([response.MIMEType isEqualToString:@"image/png"]) {imageRef = CGImageCreateWithPNGDataProvider(dataProvider, NULL, true, kCGRenderingIntentDefault);} else if ([response.MIMEType isEqualToString:@"image/jpeg"]) {imageRef = CGImageCreateWithJPEGDataProvider(dataProvider, NULL, true, kCGRenderingIntentDefault);if (imageRef) {CGColorSpaceRef imageColorSpace = CGImageGetColorSpace(imageRef);CGColorSpaceModel imageColorSpaceModel = CGColorSpaceGetModel(imageColorSpace);// CGImageCreateWithJPEGDataProvider does not properly handle CMKY, so fall back to AFImageWithDataAtScaleif (imageColorSpaceModel == kCGColorSpaceModelCMYK) {CGImageRelease(imageRef);imageRef = NULL;}}}CGDataProviderRelease(dataProvider);UIImage *image = AFImageWithDataAtScale(data, scale);if (!imageRef) {if (image.images || !image) {return image;}imageRef = CGImageCreateCopy([image CGImage]);if (!imageRef) {return nil;}}size_t width = CGImageGetWidth(imageRef);size_t height = CGImageGetHeight(imageRef);size_t bitsPerComponent = CGImageGetBitsPerComponent(imageRef);if (width * height > 1024 * 1024 || bitsPerComponent > 8) {CGImageRelease(imageRef);return image;}// CGImageGetBytesPerRow() calculates incorrectly in iOS 5.0, so defer to CGBitmapContextCreatesize_t bytesPerRow = 0;CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();CGColorSpaceModel colorSpaceModel = CGColorSpaceGetModel(colorSpace);CGBitmapInfo bitmapInfo = CGImageGetBitmapInfo(imageRef);if (colorSpaceModel == kCGColorSpaceModelRGB) {uint32_t alpha = (bitmapInfo & kCGBitmapAlphaInfoMask); #pragma clang diagnostic push #pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wassign-enum"if (alpha == kCGImageAlphaNone) {bitmapInfo &= ~kCGBitmapAlphaInfoMask;bitmapInfo |= kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst;} else if (!(alpha == kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst || alpha == kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast)) {bitmapInfo &= ~kCGBitmapAlphaInfoMask;bitmapInfo |= kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst;} #pragma clang diagnostic pop}CGContextRef context = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL, width, height, bitsPerComponent, bytesPerRow, colorSpace, bitmapInfo);CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);if (!context) {CGImageRelease(imageRef);return image;}CGContextDrawImage(context, CGRectMake(0.0f, 0.0f, width, height), imageRef);CGImageRef inflatedImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(context);CGContextRelease(context);UIImage *inflatedImage = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:inflatedImageRef scale:scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];CGImageRelease(inflatedImageRef);CGImageRelease(imageRef);return inflatedImage; }
上面的这些个方法涉及图形图像和CoreGraphics,不是很懂。。以后再补吧,先把代码贴在这里。

![]()
![]()

最后还有个AFCompoundResponseSerializer,也比较简单不常用不多说了。
通过该篇记录下之后需要学习的东西
- CoreGraphics
- NSError






![[NOI2014] 起床困难综合症](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[NOI2014] 起床困难综合症)



: 抽象类与接口)






![micropython stm32f407 以太网_[MicroPython]STM32F407开发板DIY声光控开关](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/micropython stm32f407 以太网_[MicroPython]STM32F407开发板DIY声光控开关)

)