介绍Compiler的构造比较无趣,不如先过后面的,在用到compiler的时候再做讲解。
这一节主要讲这行代码:
// 不管这里 compiler = new Compiler(); compiler.context = options.context; compiler.options = options; // 看这里 new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler);
这个构造了一个NodeEnvironmentPlugin对象并调用apply对compiler进行操作。
流程图:
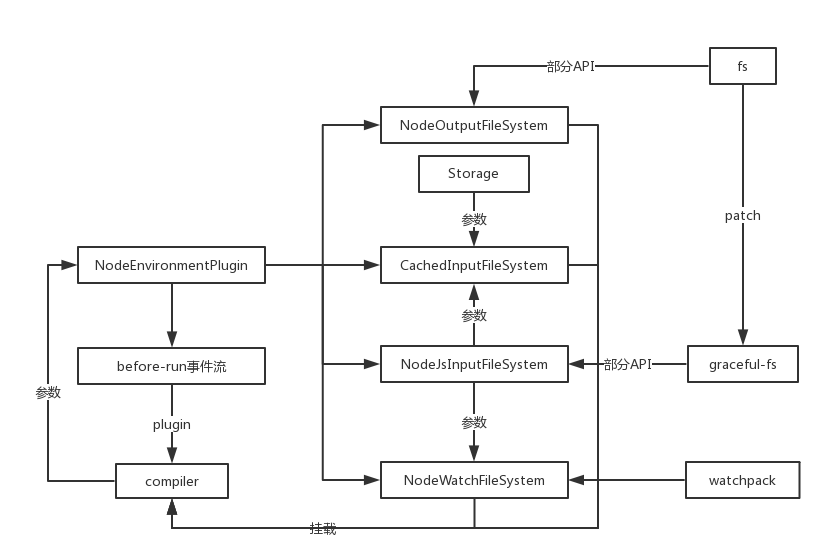
模块源码如下:
"use strict";const NodeWatchFileSystem = require("./NodeWatchFileSystem"); const NodeOutputFileSystem = require("./NodeOutputFileSystem"); const NodeJsInputFileSystem = require("enhanced-resolve/lib/NodeJsInputFileSystem"); const CachedInputFileSystem = require("enhanced-resolve/lib/CachedInputFileSystem");class NodeEnvironmentPlugin {apply(compiler) {// 可以缓存输入的文件系统compiler.inputFileSystem = new CachedInputFileSystem(new NodeJsInputFileSystem(), 60000);const inputFileSystem = compiler.inputFileSystem;// 输出文件系统compiler.outputFileSystem = new NodeOutputFileSystem();// 监视文件系统compiler.watchFileSystem = new NodeWatchFileSystem(compiler.inputFileSystem);// 添加事件流before-runcompiler.plugin("before-run", (compiler, callback) => {if (compiler.inputFileSystem === inputFileSystem)inputFileSystem.purge();callback();});} } module.exports = NodeEnvironmentPlugin;
除去添加事件流,其余几步都是在compiler对象上挂载node的fs文件系统,详细的API用法可以去nodejs官网看文档:https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v8.x/docs/api/
这里只做简介:
NodeJsInputFileSystem
var fs = require("graceful-fs");module.exports = NodeJsInputFileSystem; // 获取文件信息 NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.stat = fs.stat.bind(fs); // 读取目录内容 NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readdir = function readdir(path, callback) {// files 是目录中不包括 '.' 和 '..' 的文件名的数组fs.readdir(path, function(err, files) {callback(err, files && files.map(function(file) {// 对文件名进行NFC格式化return file.normalize ? file.normalize("NFC") : file;}));}); }; // 读取文件 NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readFile = fs.readFile.bind(fs); // 读取链接 NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readlink = fs.readlink.bind(fs); // 同步方法 NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.statSync = fs.statSync.bind(fs); NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readdirSync = function readdirSync(path) {/**/}; NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readFileSync = fs.readFileSync.bind(fs); NodeJsInputFileSystem.prototype.readlinkSync = fs.readlinkSync.bind(fs);
可以看到,这里只是对引入的graceful-js的部分方法进行bind绑定,大概看一下graceful-fs的内容:
var fs = require('fs')// ...工具方法 module.exports = patch(require('./fs.js')) if (process.env.TEST_GRACEFUL_FS_GLOBAL_PATCH) {module.exports = patch(fs) }module.exports.close = fs.close = (function(fs$close) { /*...*/ })(fs.close)module.exports.closeSync = fs.closeSync = (function(fs$closeSync) { /*...*/ })(fs.closeSync)function patch(fs) {// fs方法二次封装return fs }
跟名字一样,内部调用了一个patch对fs模块进行二次封装,变得更加'优雅'。
NodeOutputFileSystem
"use strict";const fs = require("fs"); const path = require("path"); const mkdirp = require("mkdirp");class NodeOutputFileSystem {constructor() {// 新建多层级文件夹this.mkdirp = mkdirp;// 新建单个文件夹this.mkdir = fs.mkdir.bind(fs);// 删除文件夹this.rmdir = fs.rmdir.bind(fs);// 删除文件this.unlink = fs.unlink.bind(fs);// 将内容写进某个文件this.writeFile = fs.writeFile.bind(fs);// 略this.join = path.join.bind(path);} }module.exports = NodeOutputFileSystem;
这个模块就十分亲民,都是原生的nodeAPI,并没有进行包装。
NodeWatchFileSystem
"use strict";const Watchpack = require("watchpack");class NodeWatchFileSystem {constructor(inputFileSystem) {this.inputFileSystem = inputFileSystem;this.watcherOptions = {aggregateTimeout: 0};this.watcher = new Watchpack(this.watcherOptions);}// 对文件进行监视watch(files, dirs, missing, startTime, options, callback, callbackUndelayed) { /*...*/ } }module.exports = NodeWatchFileSystem;
模块内容比较简单,引入一个inputFileSystem进行初始化监视对象,原型上只有一个watch方法。(实际内容非常深入和繁杂,后面再讲)
这个模块主要是为了接下来输出打包文件做准备,主要内容大部分是nodejs相关。
不过没关系,都是用JS写的。






![java js跳出循环_[Java教程]js循环的总结](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/java js跳出循环_[Java教程]js循环的总结)



)



 C】 Dividing the numbers)




,以下选项中描述错误的是_学小易找答案...)