pytorch与tensorflow是两个近些年来使用最为广泛的机器学习模块。开个新坑记录博主学习pytorch模块的过程,不定期更新学习进程。 文章较为适合初学者,欢迎对代码和理解指点讨论,下面进入正题。
import torch
import numpy as npt1 = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4],dtype=torch.float64)
print(t1)
print(type(t1))
print(t1.size())

与numpy基本一致,tensor可以用于创建多维的array(张量)。
c = t1[0] + t1[1]
print(c)
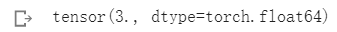
对单元素进行加减乘除运算,得到的结果仍然是一个tensor。
x = torch.tensor(3.)
w = torch.tensor(4.,requires_grad=True) # only calculate the deriative when necessary
b = torch.tensor(5., requires_grad=True)y = w * x + b # 正向传播过程y.backward() # 反向传播,计算梯度的过程
print("dy/dx : "x.grad)
print("dy/dw : ",w.grad)
print("dy/db :"b.grad)
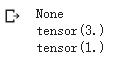
只有requires_grad属性为真的张量,在反向传播的过程中会计算梯度。
与numpy数组之间的转换
因为很多通常使用的数据,使用的是numpy矩阵的形式,pytorch也提供了一些函数用于将numpy数组转换为张量。
一般而言,将numpy ndarray转换为tensor的方法有以下三种 :
np_matrix = np.array([1,3,5,7,9])
test1 = torch.tensor(np_matrix)
test2 = torch.from_numpy(np_matrix)
test3 = torch.as_tensor(np_matrix)
实际测试中会发现,直接使用tensor构建的实例会新分配一个内存,而使用from_numpy与as_tensor两个方法与之前的矩阵是统一个内存,不会重新分配内存。因此在优化内存方面可以优先使用后两个函数。(tips : 在将numpy数组转换为tensor时需要注意精度问题,pytorch一般使用float32)
tensor的数据类型转换
使用 long float short int 等等方法,可以改变张量的数据类型,numpy方法可以将tensor转回numpy矩阵。



















