一.线程池开发框架
我所开发的线程池由以下几部分组成:
1.工作中的线程。也就是线程池中的线程,主要是执行分发来的task。
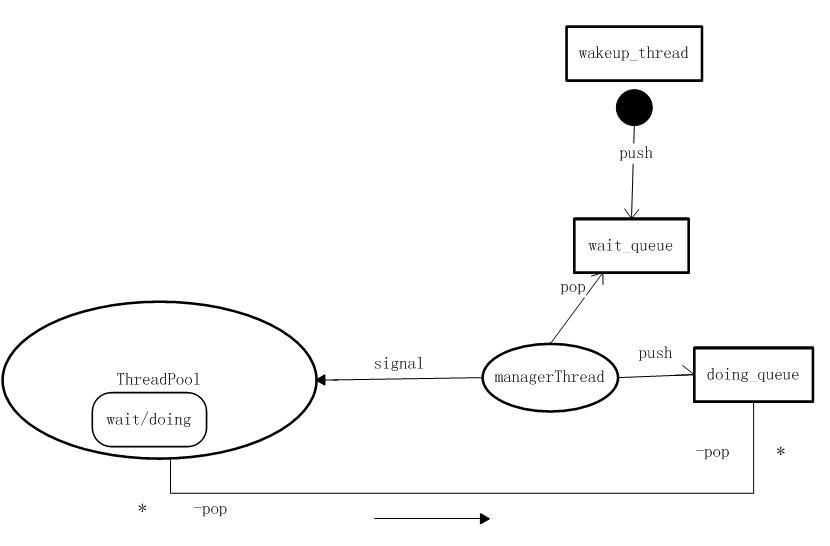
2.管理线程池的监督线程。这个线程的创建独立于线程池的创建,按照既定的管理方法进行管理线程池中的所有线程,主要任务是监听任务的到来,唤醒线程池中的空闲线程,分发任务;如果任务增多,动态的创建一批线程加入原来的线程池中,进行工作;适当的销毁线程,减少系统开销。
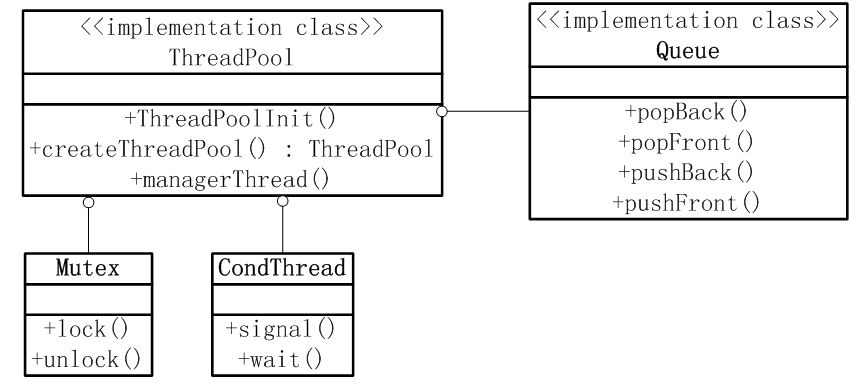
这个线程池的开发涉及了以下几个数据结构、设计模式和软件结构:
1.任务队列。整个框架有两个任务队列,1)等待任务队列(以下简称wait_queue)。2)正在执行中任务队列(以下简称doing_queue)。队列采用先进先出的数据结构。当一个任务来到时,会先被push到wait_queue,监督线程会一直监督wait_queue中的元素,一旦有任务,便会pop wait_queue中的元素,再push到doing_queue中。
2.单例设计模式。线程池的类被设计成单例模式,防止一个程序中多次创建线程池对象,出现紊乱现象,用户只能调用静态方法初始化得到线程池的对象。
3.回调函数。回调函数的设计主要是为了能够把任务接口(也就是需要线程去执行的任务,通常是一个写好的函数方法)提前初始化注册,然后延迟调用。
下图是所用类的的大概结构图:
程序整体结构如下:
二.线程池开发具体实现
1.思路分析。
线程池顾名思义就是同时有数个线程处于待执行状态,编码上的初始化的实现无非就是循环创建指定数量的线程,然后等待任务的到来唤醒空闲线程。以下是ThreadPoll的类:
class ThreadPool
{private:pthread_t *_thread; //线程池pthread_t *_thread_bak; //备用线程池,当任务过多会自动创建pthread_t taskqueue_thread; //管理线程int u4sequence;int wait_time;int CANCEL_SIGNAL;bool F_improve_ThrdPoll; //备用线程池创建标志Mutex *mutex; //互斥锁CondThread *task_cond; //条件变量TaskFuncCallback callback; //声明回调函数,即线程所需要执行的函数int _num_threads; //线程池数量//构造函数的实现为private属性,禁止用户用构造函数初始化对象。ThreadPool(int num_threads):_num_threads(num_threads),F_improve_ThrdPoll(0),wait_time(0),u4sequence(0),CANCEL_SIGNAL(0){init(); //一些变量的创建ManagerThreadInit(); //创建管理线程ThreadPoolInit(num_threads);//初始化线程池}public:LVQueue<TASK_QUEUE_T> task_wait_queue;//创建任务等待队列LVQueue<TASK_QUEUE_T> task_doing_queue;//创建任务执行队列~ThreadPool(){delete(mutex);delete(task_cond);delete(_thread);delete(_thread_bak);}//用户通过调用此静态方法得到线程池的对象(单例模式)static ThreadPool* createThreadPool(int num){ static ThreadPool *_pool = new ThreadPool(num);return _pool;}void init(){_thread = new pthread_t[_num_threads];mutex = new Mutex();task_cond = new CondThread();}API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPoolInit(int num_thr);//线程池初始化,核心接口API_RETURN_TYPE_T run(); //线程执行函数API_RETURN_TYPE_T ManagerThreadInit();//管理线程初始化API_RETURN_TYPE_T managerThread();线程执行函数API_RETURN_TYPE_T wakeupThread(TaskFuncCallback p_func);//用户调用此接口唤醒线程执行任务,参数为传入的任务执行函数地址API_RETURN_TYPE_T AutoComputeOptimumThreadNum(int wait_que_num,int &_u4sequence);//一种自动计算需要增加多少线程到线程池,当任务繁多时会调到。API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadJoin();//所有线程阻塞API_RETURN_TYPE_T ReleaseSubThreadPool();//释放备用线程池API_RETURN_TYPE_T DestroyThreadPool();//释放线程池
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
下面是cpp的实现:
//线程池初始化的实现
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::ThreadPoolInit(int num_thr)
{printf("num = %d.\n",num_thr); if(num_thr == 0){return API_SUCCESS;}//设置创建线程的属性为DETACHED,线程被释放后,资源会被回收。pthread_attr_t attr;pthread_attr_init (&attr);pthread_attr_setdetachstate (&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);int i = 0;if(F_improve_ThrdPoll == 1)//备用线程池创建的标志位,初始化线程不会走这边{_thread_bak = new pthread_t[num_thr];for(;i < num_thr;i++){if(RET_OK != pthread_create(&(_thread_bak[i]), &attr, &thread_func, this)){return API_FAIL;}}return API_SUCCESS;}//create thread pool.for(;i < num_thr;i++){if(RET_OK != pthread_create(&(_thread[i]), &attr, &thread_func, this)){return API_FAIL;}}pthread_attr_destroy (&attr);return API_SUCCESS;
}
//创建的所有线程都会跑到这个线程函数,最终指向run
void *thread_func(void *arg)
{ThreadPool *thread = (ThreadPool*)arg;thread->run();
}
//线程池核心内容
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::run()
{//printf("this is run thread.\n");void *arg;while(1)//线程池内部一直在循环{printf ("thread 0x%x begin\n", pthread_self ()); this->mutex->lock();//上锁if((CANCEL_SIGNAL == 0) && (task_doing_queue.length() < _num_threads || F_improve_ThrdPoll == 1) )//以上条件第一个是备用线程释放标志,第二个是任务执行队列数量为0,第三个是备用线程创建标志(或的关系,为了满足新增线程进入wait状态),第一次这些条件都会满足{printf ("thread 0x%x is waiting\n", pthread_self ()); this->task_cond->wait(mutex);//每次创建的新线程都会阻塞到这里,执行完任务的线程也会阻塞在这里,等待唤醒的signal,虽然是阻塞在这里,但是互斥锁已经是unlock状态了,这是linux的机制。}usleep(200000);this->mutex->unlock();//解锁pthread_testcancel();//设置取消线程点pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE,NULL);//(1)头尾保护下面这段code,保证在执行任务的时候屏蔽外部的线程取消信号if(callback != NULL){callback(arg); //执行回调函数,此时的回调函数应该指向当前任务执行函数的地址callback = NULL;}task_doing_queue.popFront();//执行完任务,任务执行队列出队列元素一个pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE,NULL);//同(1)printf("wait len =%d.\n",task_wait_queue.length());printf("thread 0x%x done.length() = %d.\n",pthread_self (),task_doing_queue.length());}return API_SUCCESS;}//管理线程的初始化
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::ManagerThreadInit()
{//create manager threadpool thread.if(RET_OK != pthread_create(&taskqueue_thread, NULL, &thread_task_queue, this)){ return API_FAIL;}return API_SUCCESS;
}
//管理线程的执行函数
void *thread_task_queue(void *arg)
{ ThreadPool *thread = (ThreadPool*)arg;thread->managerThread();}
//管理线程的核心内容
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::managerThread()
{while(1){usleep(400000);printf("managerThread!.\n");this->mutex->lock();//上锁TASK_QUEUE_T task1; //初始化两个队列元素对象TASK_QUEUE_T task2;task1.sTask = TASK_DOING;if(task_wait_queue.length() != 0){//printf("len =%d.\n",task_doing_queue.length());if(task_doing_queue.length() < _num_threads)//只要任务执行队列的数目小于线程池中线程的总数,就会执行{task2 = task_wait_queue.popFront();//pop任务等待队列的元素,并得到这个元素的对象callback = task2.cTaskFunc;//获得任务的执行函数地址task_doing_queue.pushBack(task1);//将任务push到任务执行队列task_cond->signal();//发送信号,唤醒一个空闲线程printf("signal cond.\n");}}//当人任务队列的等待任务数量大于线程池线程总数时会执行if(task_wait_queue.length() >= _num_threads && F_improve_ThrdPoll == 0){//通过简单的机制计算当前是否需要另外新增线程到线程池AutoComputeOptimumThreadNum(task_wait_queue.length(),u4sequence);F_improve_ThrdPoll = 1;ThreadPoolInit(u4sequence);//如果需要新增线程,u4sequence不为0. sleep(2);//缓冲线程创建}if(F_improve_ThrdPoll == 1 ){//检测到备用线程池的创建while(task_wait_queue.length() == 0 && task_doing_queue.length() == 0){//也就是当前任务等待队列和任务执行队列都没有任务时printf("no task!.\n");usleep(500000);wait_time++;//计时等待一段时间if(wait_time == NO_TASK_TIMEOUT){this->mutex->unlock();ReleaseSubThreadPool();//释放备用线程池printf("release!.\n");F_improve_ThrdPoll = 2;wait_time = 0;break;}}wait_time = 0;}if(F_improve_ThrdPoll != 2)this->mutex->unlock();}return API_SUCCESS;}//自动计算是否需要创建新的线程池的简单机制,后续会结合读取当前CPU的使用率进一步优化此机制
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::AutoComputeOptimumThreadNum(int wait_que_num,int &_u4sequence)
{if(wait_que_num >= 4*_num_threads){_u4sequence = _num_threads;}else if(wait_que_num >= 2*_num_threads){_u4sequence = _num_threads/2;}else{_u4sequence = 0;}return API_SUCCESS;
}//释放备用线程池,待优化API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::ReleaseSubThreadPool()
{this->mutex->lock();CANCEL_SIGNAL = 1;this->mutex->unlock();task_cond->broadcast();for(int i = 0;i < _num_threads;i++){if(RET_OK != pthread_cancel(_thread_bak[i])){return API_FAIL;}}this->mutex->lock();printf("4444.\n");CANCEL_SIGNAL = 0;this->mutex->unlock();return API_SUCCESS;
}
//摧毁线程池,待优化
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::DestroyThreadPool()
{//first ,destroy manager thread.if(RET_OK != pthread_cancel(taskqueue_thread)){return API_FAIL;}return API_SUCCESS;
}API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::ThreadJoin()
{for(int i = 0;i < _num_threads;i++){pthread_join(_thread[i],NULL);}pthread_join(taskqueue_thread,NULL);return API_SUCCESS;}
//用户调用此函数接口唤醒
API_RETURN_TYPE_T ThreadPool::wakeupThread(TaskFuncCallback p_func)
{printf("wakeupThread in .\n");this->mutex->lock();TASK_QUEUE_T task;task.cTaskFunc = p_func;//将函数执行地址赋值到队列元素中task.sTask = TASK_WAIT;if(task_wait_queue.length() < MAX_TASK_NUM ){ this->task_wait_queue.pushBack(task); //push任务到等待任务队列中}else{//线程池数量过多,此机制后续会优化printf("Current Thread Buffer is full!Please wait a moment!\n");this->mutex->unlock();return API_FAIL;}this->mutex->unlock();return API_SUCCESS;}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
下面新加的关于LVQueue的实现:
#ifndef QUEUE_H_INCLUDED
#define QUEUE_H_INCLUDEDtemplate < typename T >
class LVQueue {friend struct Iterator;struct Item {T value;Item * next;Item * prev;Item(T & v) : value(v), next(NULL), prev(NULL) {}};Item * head;Item * tail;int count;Item * remove(Item * p) {if (!p)return NULL;if (!p->prev)head = p->next;elsep->prev->next = p->next;if (!p->next)tail = p->prev;elsep->next->prev = p->prev;p->next = NULL;p->prev = NULL;count--;if (count == 0) {head = tail = NULL;}return p;}void moveToHead(Item * item) {Item * p = remove(item);if (head) {head->prev = p;p->next = head;head = p;} else {head = tail = p;}count++;}
public:struct Iterator {private:LVQueue * queue;Item * currentItem;public:Iterator(const Iterator & v) {queue = v.queue;currentItem = v.currentItem;}Iterator(LVQueue * _queue) : queue(_queue), currentItem(NULL) {}T get() { return currentItem ? currentItem->value : T(); }void set(T value) { if (currentItem) currentItem->value = value; }bool next() {if (!currentItem) {// first timecurrentItem = queue->head;} else {// continuecurrentItem = currentItem->next;}return currentItem != NULL;}T remove() {if (!currentItem)return T();Item * next = currentItem->next;Item * p = queue->remove(currentItem);currentItem = next;T res = p->value;delete p;return res;}void moveToHead() {if (currentItem)queue->moveToHead(currentItem);}};public:Iterator iterator() { return Iterator(this); }LVQueue() : head(NULL), tail(NULL), count(0) {}~LVQueue() { clear(); }
// T & operator [] (int index) {
// Item * p = head;
// for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
// if (!p)
// return
// }
// }int length() { return count; }void pushBack(T item) {Item * p = new Item(item);if (tail) {tail->next = p;p->prev = tail;tail = p;} else {head = tail = p;}count++;}void pushFront(T item) {Item * p = new Item(item);if (head) {head->prev = p;p->next = head;head = p;} else {head = tail = p;}count++;}T popFront() {if (!head)return T();Item * p = remove(head);T res = p->value;delete p;return res;}T popBack() {if (!tail)return T();Item * p = remove(tail);T res = p->value;delete p;return res;}void clear() {while (head) {Item * p = head;head = p->next;delete p;}head = NULL;tail = NULL;count = 0;}
};#endif // LVQUEUE_H_INCLUDED- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
以下是简单的test程序:
ThreadPool *thread3 = ThreadPool::createThreadPool(8);//得到线程池对象printf("task coming.\n");//test threadpoolfor(int i = 0;i < 15;i++){thread3->wakeupThread(thread11_func);//每隔一秒唤醒线程,thread11_func一个函数的地址sleep(1);thread3->wakeupThread(thread3_func);}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
下面是test程序运行的结果,线程唤醒无一秒间隔
num = 8.
task coming.
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
wakeupThread in .
thread 0xd528c700 begin
thread 0xd528c700 is waiting
thread 0xd4a8b700 begin
thread 0xd4a8b700 is waiting
thread 0xd428a700 begin
thread 0xd428a700 is waiting
thread 0xd5a8d700 begin
thread 0xd5a8d700 is waiting
thread 0xd628e700 begin
thread 0xd628e700 is waiting
thread 0xd6a8f700 begin
thread 0xd6a8f700 is waiting
thread 0xd7290700 begin
thread 0xd7290700 is waiting
thread 0xd7a91700 begin
thread 0xd7a91700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
num = 4.
thread 0xd2286700 begin
thread 0xd2a87700 begin
thread 0xd3288700 begin
thread 0xd3a89700 begin
thread 0xd2286700 is waiting
thread 0xd2a87700 is waiting
thread 0xd3288700 is waiting
thread 0xd3a89700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
signal cond.
managerThread!.
managerThread!.
managerThread!.
managerThread!.
managerThread!.
rate = 4.82897
this is 0 task thread.
wait len =22.
thread 0xd528c700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd528c700 begin
thread 0xd528c700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
rate = 4.64646
this is 1 task thread.
wait len =21.
thread 0xd4a8b700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd4a8b700 begin
thread 0xd4a8b700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
rate = 4.64646
this is 2 task thread.
wait len =20.
thread 0xd428a700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd428a700 begin
thread 0xd428a700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
rate = 4.25101
this is 3 task thread.
wait len =19.
thread 0xd5a8d700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd5a8d700 begin
thread 0xd5a8d700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
rate = 4.23387
this is 4 task thread.
wait len =18.
thread 0xd628e700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd628e700 begin
thread 0xd628e700 is waiting
managerThread!.
signal cond.
rate = 4.04858
this is 5 task thread.
wait len =17.
thread 0xd6a8f700 done.length() = 7.
thread 0xd6a8f700 begin
thread 0xd6a8f700 is waiting- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
可以看到一次性唤醒了30个线程,创建了8个线程的线程池,后来通过优化计算又新增了4个线程到当前线程池中,每唤醒一个线程执行任务,大概是6s的时间,执行完后,又进入等待唤醒信号的状态。管理线程检测到当前所有线程都在执行,便会阻塞当前signal行为,直到有空余线程,马上signal。
这些源代码还有一些数据类型的封装还没公布出来,因为还在优化中,所以准备等到优化完毕,将会把完整的源代码交到GitHub上托管,小弟资历尚浅,如有出错的地方,烦请不吝赐教。
函数)
)
)







)








)