问题
如何使用 ASP.NET Core 服务容器进行依赖注入?
答案
创建一个服务
public interface IGreetingService {
string Greet(string to); }
public class GreetingService : IGreetingService {
public string Greet(string to){ return $"Hello {to}";} }
然后可以在需要的时候注入,下面将此服务注入一个中间件(Middleware):
public class HelloWorldMiddleware {
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public HelloWorldMiddleware(RequestDelegate next){_next = next;}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context, IGreetingService greetingService){
var message = greetingService.Greet("World (via DI)"); await context.Response.WriteAsync(message);} }
使用此中间件的扩展方法(IApplicationBuilder):
public static class UseMiddlewareExtensions {
public static IApplicationBuilder UseHelloWorld(this IApplicationBuilder app){ return app.UseMiddleware<HelloWorldMiddleware>();} }
下面需要将此服务添加到ASP.NET Core的服务容器中,位于Startup.cs文件的ConfigureServices()方法:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {services.AddScoped<IGreetingService, GreetingService>(); }
然后在请求管道中(request pipeline)使用此中间件,位于Startup.cs文件的Configure()方法:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) {app.UseHelloWorld(); }
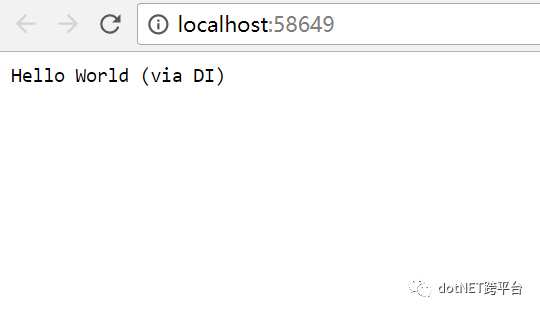
运行,此时页面输出:
创建一个带输入参数的服务
如果你的服务需要更复杂的初始化参数,下面我们创建一个FlexibleGreetingService:
public class FlexibleGreetingService : IGreetingService {
private readonly string _sayWhat;
public FlexibleGreetingService(string sayWhat){_sayWhat = sayWhat;}
public string Greet(string to){
return $"{_sayWhat} {to}";} }
我们可以使用AddScoped的一个重载工厂方法来添加此服务到容器中:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {services.AddScoped<IGreetingService, FlexibleGreetingService>(factory =>{
return new FlexibleGreetingService("Hi");}); }
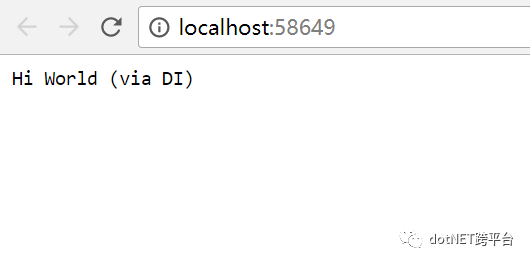
运行,此时页面输出:
如果是单件生命周期,还有一个接受服务实例的重载方法:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {services.AddSingleton<IGreetingService>(new FlexibleGreetingService("Hi ")); }
讨论
ASP.NET Core内置了一个轻量级的服务容器。我们可以在Startup.cs类的ConfigureServices()方法中配置需要的服务。这个方法在Configure()方法之前执行,所以我们可以在任意中间件使用之前配置的服务(包含MVC服务)。
依赖注入默认是通过公开构造函数来完成的,大多数情况下这是最佳实践。
服务的生命周期
服务容器管理着添加到服务器列表的生命周期。下面列出了添加服务的三种方法:
-
AddScoped():服务会在一个请求内部只创建一次。
-
AddTransient():服务会在每次需要时创建一次。
-
AddSingleton():服务会在第一次需要时创建一次,并在随后保持不变。
注:EF的生命周期应该是Scoped,我们可以通过IServiceCollection.AddDbContext来创建EF服务(内部也是作为Scoped实现)。
工厂方法
上面的方法都有一个重载方法来使用工厂方法来添加服务。对于需要复杂配置的服务这是很有用的。
这些方法的签名看起来如下所示:
AddScoped(Func<IServiceProvider, TService>)
框架提供的服务
ConfigureServices()接受的IServiceCollection参数拥有很多内置的服务(由框架提供),可以参考ASP.NET Core文档。
IServiceCollection有很多有用的扩展方法来添加常用服务,比如AddDbContext,AddIdentity,AddOptions和AddMvc。
销毁服务
服务容器会自动调用所有实现了IDisposable接口的服务类型,除了那些作为实例(而不是类型)添加的服务。
获取服务(Request Services)
尽管通过构造函数来注入服务被认为是最佳实践,我们依然可以通过IServiceProvider的GetService方法来获取服务。在中间件中IServiceProvider对象可以通过HttpContext来获取:
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) {
var greetingService = context.RequestServices.GetService<IGreetingService>(); var message = greetingService.Greet("World (via GetService)");
await context.Response.WriteAsync(message); }
注:需要添加Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection引用才能上述使用GetService的泛型重载方法。
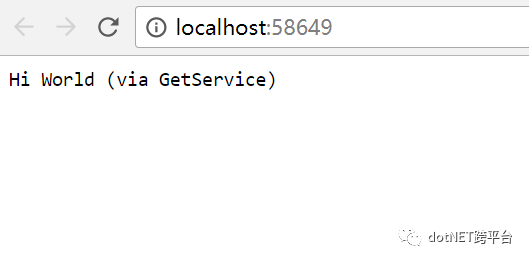
运行,此时页面输出:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sanshi/p/7705617.html
.NET社区新闻,深度好文,微信中搜索dotNET跨平台或扫描二维码关注




:使用基于JWT标准的Token访问WebApi)


)





上下位机通讯原理)





:.扩展国际化语言资源)
