2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
在Activity的onCreate方法中,可以通过setContentView()方法来设置此Activity要显示的界面。在xml中的布局文件需要先解析成View树才能加载显示,通过View的onMeasure,onLayout,onDraw方法完成View的测量大小,布局以及View自身的绘制。在此想说一下Activity生命周期的onCreate,onStart,onResume方法和View自身的测量,布局等方法的调用顺序问题。
先重写Activity的这几个方法并打印log
public class FlowActivity extends Activity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);Log.e("onCreate", "onCreate");setContentView(R.layout.flow);}@Overrideprotected void onResume() {Log.e("onResume", "onResume");super.onResume();}@Overrideprotected void onStart() {Log.e("onStart", "onStart");super.onStart();}
}在重写ViewGroup方法FlowLayout
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {public FlowLayout(Context context) {super(context);}public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {super(context, attrs, defStyle);// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub}public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub}@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {Log.e("onMeasure", "onMeasure");setMeasuredDimension(totalWidth, resolveSize(totalHeight, heightMeasureSpec));}@Overrideprotected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {Log.e("onSizeChanged", "onSizeChanged");super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);}@Overrideprotected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {Log.e("onLayout", "onLayout");}@Overrideprotected void onFinishInflate() {Log.e("onFinishInflate", "onFinishInflate");super.onFinishInflate();}
}打印Log可以看出Activity生命周期的函数和View的测量,布局等函数的调用顺序。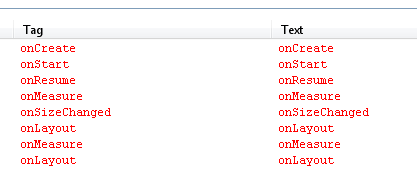
因此,我们通常在onCreate方法里面是获取不到某个View测量的宽高值,获取的值为0.
只有当Activity的onResume方法调用完毕之后,当前的窗口将要显示可见,才会去测量,绘制View树。setContentView方法只是把xml文件解析为View树的过程,并没有发起绘制View树。当解析完毕之后会调用OnFinishInflate方法,完成解析。
当View的“大小”发生改变的时候会调用onSizeChanged方法,这个大小,个人理解为布局大小,并非测量大小。是在onMeasure之后,onLayout之前调用的方法。
理解了这些调用顺序,我们可以知道在何时去获取或设置一些值。


函数来设置socket状态以及getsockopt函数只用总结)

)











![allegro下快捷键设置[转贴]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/allegro下快捷键设置[转贴])


