1、为甚需要进程池,线程池

介绍官网:https://docs.python.org/dev/library/concurrent.futures.html concurrent.futures模块提供了高度封装的异步调用接口 ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池,提供异步调用 ProcessPoolExecutor: 进程池,提供异步调用 Both implement the same interface, which is defined by the abstract Executor class.

2、基本方法
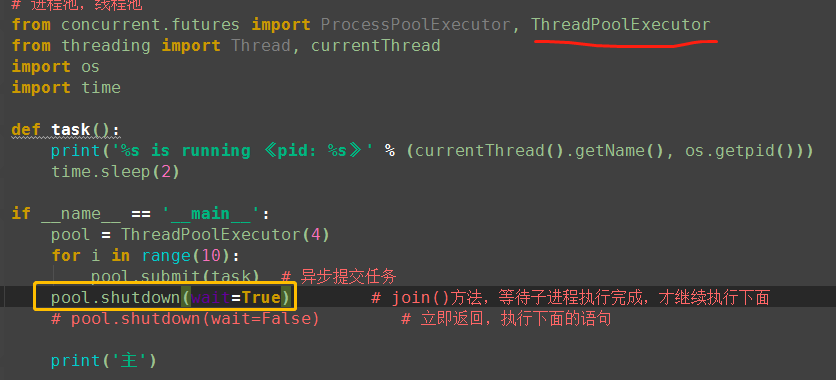
1、submit(fn, *args, **kwargs) 异步提交任务2、map(func, *iterables, timeout=None, chunksize=1) 取代for循环submit的操作3、shutdown(wait=True)
相当于进程池的pool.close()+pool.join()操作
wait=True,等待池内所有任务执行完毕回收完资源后才继续
wait=False,立即返回,并不会等待池内的任务执行完毕
但不管wait参数为何值,整个程序都会等到所有任务执行完毕
submit和map必须在shutdown之前4、result(timeout=None) 取得结果5、add_done_callback(fn) 回调函数
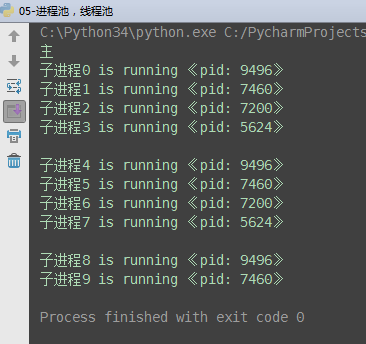
3、进程池
The ProcessPoolExecutor class is an Executor subclass that uses a pool of processes to execute calls asynchronously.
ProcessPoolExecutor uses the multiprocessing module, which allows it to side-step the Global Interpreter Lock but also means that only picklable objects can be executed and returned.class concurrent.futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=None, mp_context=None) An Executor subclass that executes calls asynchronously using a pool of at most max_workers processes. If max_workers is None or not given, it will default to the number of processors on the machine.If max_workers is lower or equal to 0, then a ValueError will be raised.
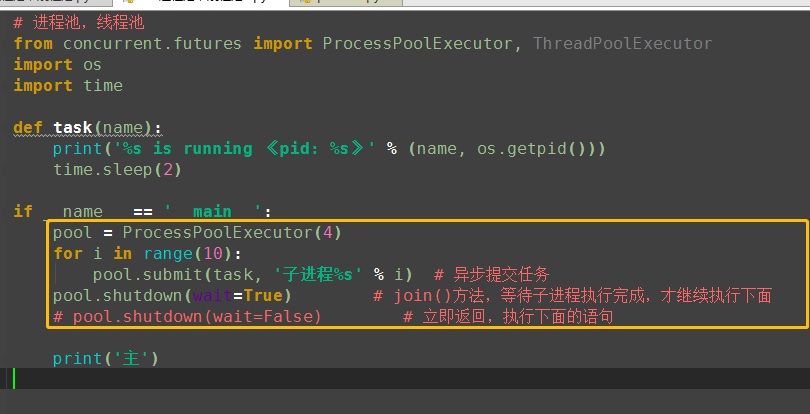
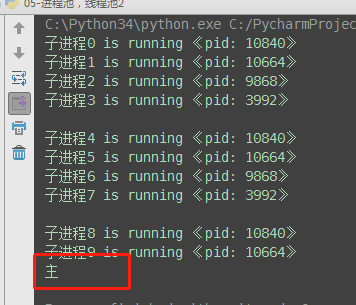
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor, ThreadPoolExecutor import os import timedef task(name):print('%s is running 《pid: %s》' % (name, os.getpid()))time.sleep(2)if __name__ == '__main__':# p = Process(target=task, args=('子',))# p.start pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(4) # 进程池max_workers:4个for i in range(10): # 总共执行10次,每次4个进程的执行pool.submit(task, '子进程%s' % i)print('主')
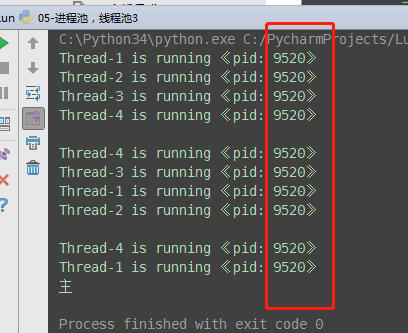
4、线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor is an Executor subclass that uses a pool of threads to execute calls asynchronously. class concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=None, thread_name_prefix='') An Executor subclass that uses a pool of at most max_workers threads to execute calls asynchronously.Changed in version 3.5: If max_workers is None or not given, it will default to the number of processors on the machine, multiplied by 5, assuming that ThreadPoolExecutor is often used to overlap I/O instead of CPU work and the number of workers should be higher than the number of workers for ProcessPoolExecutor.New in version 3.6: The thread_name_prefix argument was added to allow users to control the threading. Thread names for worker threads created by the pool for easier debugging.
5、map函数:取代了for+submit
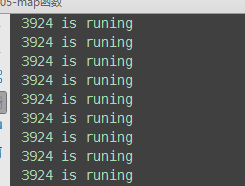
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutorimport os,time,random def task(n):print('%s is runing' %os.getpid())time.sleep(random.randint(1,3))return n**2if __name__ == '__main__':executor=ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3)# for i in range(11):# future=executor.submit(task,i) executor.map(task,range(1,12)) #map取代了for+submit
6、异步调用与回调机制
(1)提交任务的两种方式
# 提交任务的两种方式
# 1、同步调用 提交完任务后,拿到结果,再执行下一行代码,导致程序是串行执行
# 2、异步调用 提交完任务后,不用等待任务执行完毕
(2)同步调用
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import time import random# 吃饭 def eat(name):print('%s is eat' % name)time.sleep(random.randint(1,5))ret = random.randint(7, 13) * '#'return {'name': name, 'ret': ret}# 称重 def weight(body):name = body['name']size = len(body['ret'])print('%s 现在的体重是%s' %(name, size))if __name__ == '__main__':pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(15)rice1 = pool.submit(eat, 'alex').result() # 取得结果 # 执行函数eatweight(rice1) # 执行函数weight rice2 = pool.submit(eat, 'jack').result() weight(rice2)rice3 = pool.submit(eat, 'tom').result() weight(rice3)
(2)同步调用2
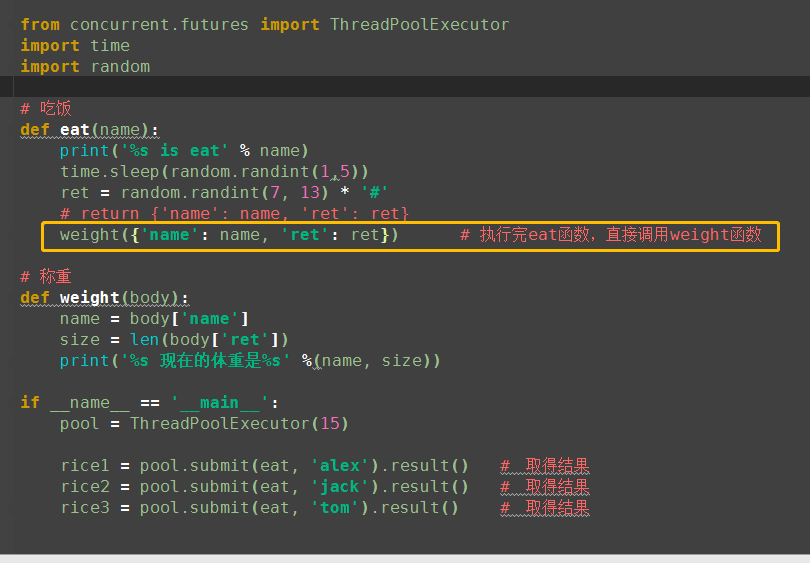
(3)回调函数

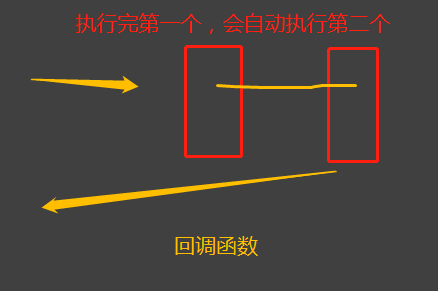
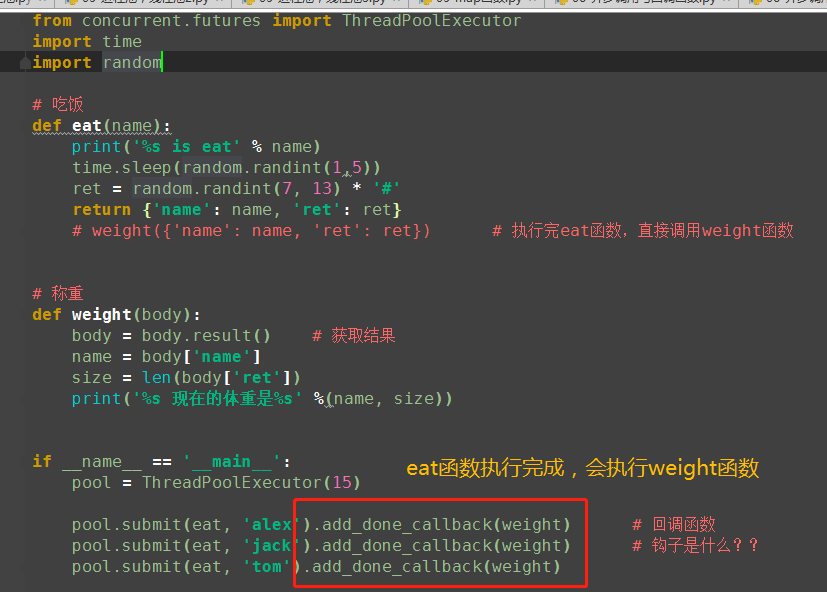
(4)是钩子函数?
钩子函数是Windows消息处理机制的一部分,通过设置“钩子”,应用程序可以在系统级对所有消息、事件进行过滤,访问在正常情况下无法访问的消息。钩子的本质是一段用以处理系统消息的程序,通过系统调用,把它挂入系统 --- 百度百科的定义
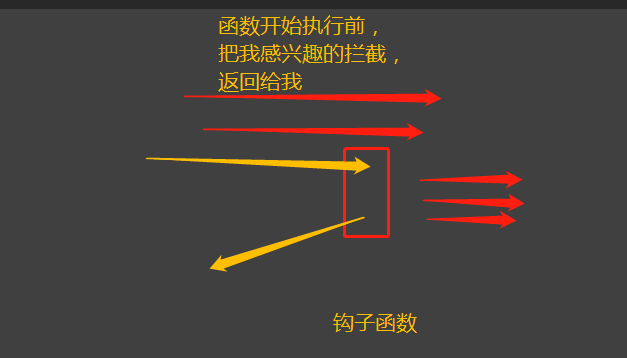
对于前端来说,钩子函数就是指再所有函数执行前,我先执行了的函数,即 钩住 我感兴趣的函数,只要它执行,我就先执行。此概念(或者说现象)跟AOP(面向切面编程)很像
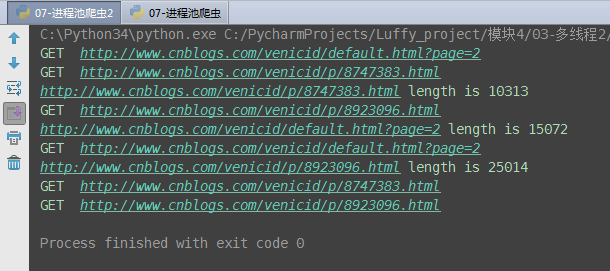
7.线程池爬虫应用
(1)requests模块
import requests# 输入网址,得到网址的源代码 response = requests.get('http://www.cnblogs.com/venicid/p/8923096.html') print(response) # 输出<Response [200]> print(response.text) # 以文本格式输出
(2)线程池爬虫
import requests import time from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor# 输入网址,得到网址的源代码 def get_code(url):print('GET ', url)response = requests.get(url)time.sleep(3)code = response.textreturn {'url': url, 'code': code}# 打印源代码的长度 def print_len(ret):ret = ret.result()url = ret['url']code_len = len(ret['code'])print('%s length is %s' % (url, code_len))if __name__ == '__main__':url_list = ['http://www.cnblogs.com/venicid/default.html?page=2','http://www.cnblogs.com/venicid/p/8747383.html','http://www.cnblogs.com/venicid/p/8923096.html',]pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(2)for i in url_list:pool.submit(get_code, i).add_done_callback(print_len)pool.map(get_code, url_list)