dom4j 是一种解析 XML 文档的开放源代码 XML 框架。dom4j下载地址
本文主要记载了一些简单的使用方法。
一、xml文件的解析
dom4j既可以解析普通的xml文件,也可以解析一个InputStream,先看看xml文件长什么样子:
<books><book><id>1</id><name>Java编程思想</name><price>80</price><author>张三</author></book><book><id>2</id><name>三国演义</name><price>30</price><author>罗贯中</author></book><book><id>3</id><name>红楼梦</name><price>35</price><author>曹雪芹</author></book><book><id>4</id><name>西游记</name><price>25</price><author>吴承恩</author></book><book><id>5</id><name>水浒传</name><price>30</price><author>施耐庵</author></book>
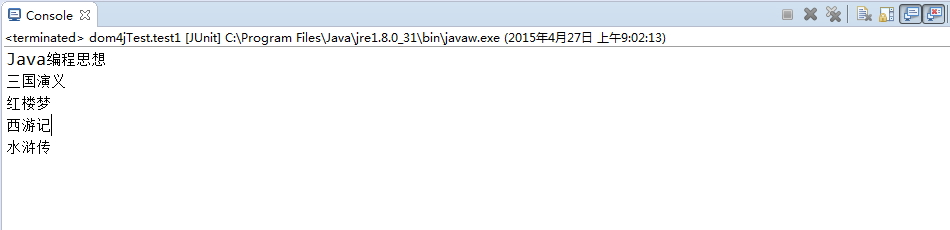
</books>通过读取这一段xml文件并解析,将xml文件中的内容存储到javabean中。
private List<Book> bs;private Book b;//读取xml文件获得Document对象@Testpublic void test1(){try {//1.读取xml文件,获取document对象SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));//2.获取根节点<books>Element root = document.getRootElement();bs = new ArrayList<Book>();//3.迭代,获取根节点的所有子节点<book>for (Iterator<Element> es = root.elementIterator(); es.hasNext();) {Element e = es.next();b = new Book();//4.再次迭代,获取子节点的子节点<id><name><price><author>for (Iterator<Element> e_son = e.elementIterator();e_son.hasNext();) {Element ee = e_son.next();if(ee.getName().equals("id")){b.setId(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText().toString()));}else if(ee.getName().equals("name")){b.setName(ee.getText());}else if(ee.getName().equals("price")){b.setPrice(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText()));}else if(ee.getName().equals("auhtor")){b.setAuthor(ee.getText());}}bs.add(b);}} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (Book bk : bs) {System.out.println(bk.getName());}}Book.java
public class Book {private int id;private String name;private int price;private String author;private Detail detail;private Attribute attribute;public Attribute getAttribute() {return attribute;}public void setAttribute(Attribute attribute) {this.attribute = attribute;}public Detail getDetail() {return detail;}public void setDetail(Detail detail) {this.detail = detail;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(int price) {this.price = price;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}
}Attribute.java
public class Attribute {private String category;private String edition;public String getCategory() {return category;}public void setCategory(String category) {this.category = category;}public String getEdition() {return edition;}public void setEdition(String edition) {this.edition = edition;}}Detail.java
public class Detail {private String pressTime;private String storyTime;public String getPressTime() {return pressTime;}public void setPressTime(String pressTime) {this.pressTime = pressTime;}public String getStoryTime() {return storyTime;}public void setStoryTime(String storyTime) {this.storyTime = storyTime;}
}好,我们稍微修改一下xml文件,再看看个该如何解析:
<books><book><id>1</id><name>Java编程思想</name><price>80</price><author>张三</author><detail><pressTime>天朝</pressTime><storyTime>21世纪</storyTime></detail></book><book><id>2</id><name>三国演义</name><price>30</price><author>罗贯中</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>汉末</storyTime></detail></book><book><id>3</id><name>红楼梦</name><price>35</price><author>曹雪芹</author><detail><pressTime>清朝</pressTime><storyTime>不详</storyTime></detail></book><book><id>4</id><name>西游记</name><price>25</price><author>吴承恩</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大唐</storyTime></detail></book><book><id>5</id><name>水浒传</name><price>30</price><author>施耐庵</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大宋</storyTime></detail></book>
</books>又多了一层嵌套,看解析方式:
private List<Book> bs;private Book b;private Detail detail;// 读取xml文件获得Document对象@Testpublic void test1() {try {// 1.读取xml文件,获取document对象SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));// 2.获取根节点<books>Element root = document.getRootElement();bs = new ArrayList<Book>();// 3.迭代,获取根节点的所有子节点<book>for (Iterator<Element> es = root.elementIterator(); es.hasNext();) {Element e = es.next();b = new Book();// 4.再次迭代,获取子节点的子节点<id><name><price><author>for (Iterator<Element> e_son = e.elementIterator(); e_son.hasNext();) {Element ee = e_son.next();if (ee.getName().equals("id")) {b.setId(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText().toString()));} else if (ee.getName().equals("name")) {b.setName(ee.getText());} else if (ee.getName().equals("price")) {b.setPrice(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText()));} else if (ee.getName().equals("auhtor")) {b.setAuthor(ee.getText());} else if (ee.getName().equals("detail")) {detail = new Detail();for (Iterator<Element> ds = ee.elementIterator(); ds.hasNext();) {Element d = ds.next();if (d.getName().equals("pressTime")) {detail.setPressTime(d.getText());} else if (d.getName().equals("storyTime")) {detail.setStoryTime(d.getText());}}b.setDetail(detail);}}bs.add(b);}} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (Book bk : bs) {System.out.println(bk.getName()+","+bk.getDetail().getPressTime());}}继续修改xml文件,为之添加属性:
<books><book category="编程技术" edition="8"><id>1</id><name>Java编程思想</name><price>80</price><author>张三</author><detail><pressTime>天朝</pressTime><storyTime>21世纪</storyTime></detail></book><book category="历史小说" edition="1"><id>2</id><name>三国演义</name><price>30</price><author>罗贯中</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>汉末</storyTime></detail></book><book category="小说" edition="2"><id>3</id><name>红楼梦</name><price>35</price><author>曹雪芹</author><detail><pressTime>清朝</pressTime><storyTime>不详</storyTime></detail></book><book category="神话小说" edition="4"><id>4</id><name>西游记</name><price>25</price><author>吴承恩</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大唐</storyTime></detail></book><book category="小说" edition="5"><id>5</id><name>水浒传</name><price>30</price><author>施耐庵</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大宋</storyTime></detail></book>
</books>给每一个book都添加了属性,又该怎么遍历呢?attribute的遍历和element的遍历非常类似,看代码:
// 读取xml文件获得Document对象@Testpublic void test1() {try {// 1.读取xml文件,获取document对象SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));// 2.获取根节点<books>Element root = document.getRootElement();bs = new ArrayList<Book>();// 3.迭代,获取根节点的所有子节点<book>for (Iterator<Element> es = root.elementIterator(); es.hasNext();) {Element e = es.next();b = new Book();book_attr = new lenve.test.Attribute();for (Iterator<Attribute> as = e.attributeIterator();as.hasNext();) {Attribute attr = as.next();if(attr.getName().equals("category")){book_attr.setCategory(attr.getText());}else if(attr.getName().equals("edition")){book_attr.setEdition(attr.getText());}}b.setAttribute(book_attr);// 4.再次迭代,获取子节点的子节点<id><name><price><author>for (Iterator<Element> e_son = e.elementIterator(); e_son.hasNext();) {Element ee = e_son.next();if (ee.getName().equals("id")) {b.setId(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText().toString()));} else if (ee.getName().equals("name")) {b.setName(ee.getText());} else if (ee.getName().equals("price")) {b.setPrice(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText()));} else if (ee.getName().equals("auhtor")) {b.setAuthor(ee.getText());} else if (ee.getName().equals("detail")) {detail = new Detail();for (Iterator<Element> ds = ee.elementIterator(); ds.hasNext();) {Element d = ds.next();if (d.getName().equals("pressTime")) {detail.setPressTime(d.getText());} else if (d.getName().equals("storyTime")) {detail.setStoryTime(d.getText());}}b.setDetail(detail);}}bs.add(b);}} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (Book bk : bs) {System.out.println(bk.getName()+","+bk.getDetail().getPressTime()+","+bk.getAttribute().getCategory());}}如果我们只想遍历某一个节点呢?比如我们只想遍历名称为id的节点,该怎么办?
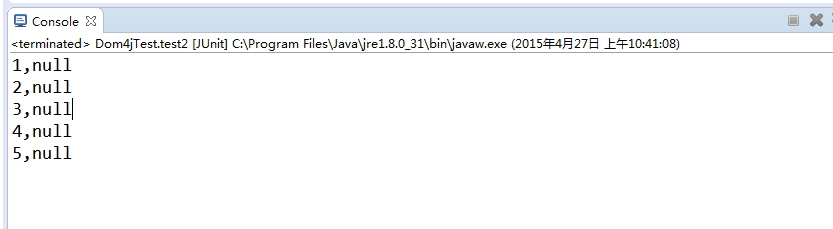
private List<Book> bs;private Book b;@Testpublic void test2() {try {// 1.读取xml文件,获取document对象SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));// 2.获取根节点<books>Element root = document.getRootElement();bs = new ArrayList<Book>();// 3.迭代,获取根节点的所有子节点<book>for (Iterator<Element> es = root.elementIterator(); es.hasNext();) {Element e = es.next();b = new Book();// 4.再次迭代,获取子节点的子节点<id><name><price><author>for (Iterator<Element> e_son = e.elementIterator("id"); e_son.hasNext();) {Element ee = e_son.next();b.setId(Integer.parseInt(ee.getText().toString()));}bs.add(b);}} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (Book bk : bs) {System.out.println(bk.getId()+","+bk.getAuthor());}}输出:
最后一个问题,怎样以字符串的形式拿到一个xml文件:
@Testpublic void test3(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));String text = document.asXML();System.out.println(text);} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}二、使用程序写一个xml文件
1.怎样把一个字符串文件写成xml文件:
@Testpublic void test4() {try {String text = "<fruits><fruit><name>苹果</name><color>red</color><price>3元</price></fruit></fruits>";Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(text);//两种方式皆可
// FileWriter out = new FileWriter(new File("F:\\test\\str2xml.xml"));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\s2x.xml"));document.write(out);out.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}这样输出的xml文件没有格式,可读性较差,换个方式再看看:
@Testpublic void test5() {try {String text = "<fruits><fruit><name>苹果</name><color>red</color><price>3元</price></fruit></fruits>";Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(text);PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\s2x1.xml"));XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(out, new OutputFormat().createPrettyPrint());writer.write(document);writer.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}输出结果:
这样的输出格式也是极好的。
2.通过程序一个元素一个元素的写入:
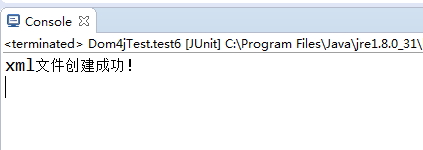
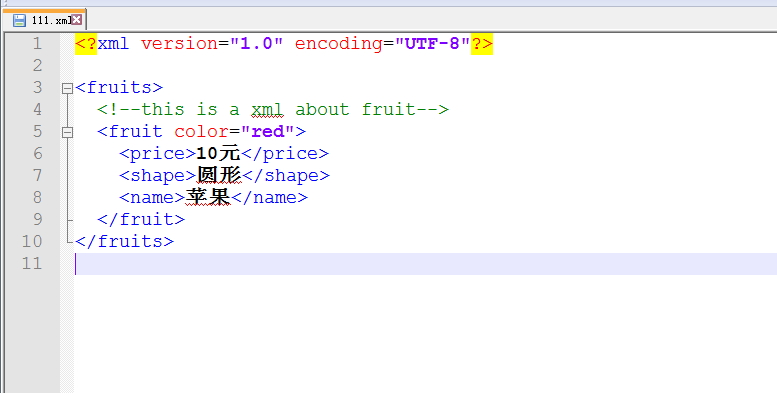
@Testpublic void test6(){int res = createXMLFile();if(res==1){System.out.println("xml文件创建成功!");}else{System.out.println("xml文件创建失败!");}}public int createXMLFile(){//返回0表示创建成功,返回1表示创建失败int result = 0;Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument();//建立根节点Element root = document.addElement("fruits");//加入注释root.addComment("this is a xml about fruit");Element f1 = root.addElement("fruit");f1.addAttribute("color", "red");Element f11 = f1.addElement("price");f11.setText("10元");Element f12 = f1.addElement("shape");f12.setText("圆形");Element f13 = f1.addElement("name");f13.setText("苹果");//将xml写入文件中try {PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\111.xml"));XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(out, new OutputFormat().createPrettyPrint());writer.write(document);writer.close();result = 1;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return result;}再看看新创建的xml文件长什么样:
这里使用最多的就是三个方法,一个是addElement(),一个是addAttribute(),还有一个是setText(),对每一个节点都可以执行这三个操作,你想创建的任何形状的xml都可以通过层层的嵌套实现。
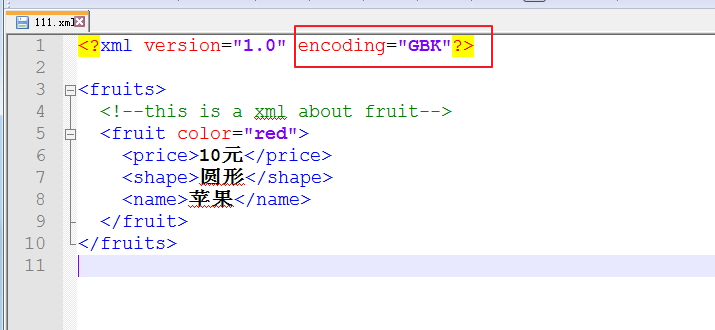
如果想手动指定输出编码格式:
@Testpublic void test6(){int res = createXMLFile();if(res==1){System.out.println("xml文件创建成功!");}else{System.out.println("xml文件创建失败!");}}public int createXMLFile(){//返回0表示创建成功,返回1表示创建失败int result = 0;Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument();//建立根节点Element root = document.addElement("fruits");//加入注释root.addComment("this is a xml about fruit");Element f1 = root.addElement("fruit");f1.addAttribute("color", "red");Element f11 = f1.addElement("price");f11.setText("10元");Element f12 = f1.addElement("shape");f12.setText("圆形");Element f13 = f1.addElement("name");f13.setText("苹果");//将xml写入文件中try {PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\111.xml"));OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();//缩进显示//默认输出编码是UTF-8,可以手动设置为GBKformat.setEncoding("GBK");XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(out, format);writer.write(document);writer.close();result = 1;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return result;}输出的xml文件为(注意看编码):
三、修改xml文件
我们要修改一下xml文件:
<books><book category="编程技术" edition="8"><id>1</id><name>Java编程思想</name><price>80</price><author>张三</author><detail><pressTime>天朝</pressTime><storyTime>21世纪</storyTime></detail></book><book category="历史小说" edition="1"><id>2</id><name>三国演义</name><price>30</price><author>罗贯中</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>汉末</storyTime></detail></book><book category="小说" edition="2"><id>3</id><name>红楼梦</name><price>35</price><author>曹雪芹</author><detail><pressTime>清朝</pressTime><storyTime>不详</storyTime></detail></book><book category="神话小说" edition="4"><id>4</id><name>西游记</name><price>25</price><author>吴承恩</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大唐</storyTime></detail></book><book category="小说" edition="5"><id>5</id><name>水浒传</name><price>30</price><author>施耐庵</author><detail><pressTime>明朝</pressTime><storyTime>大宋</storyTime></detail></book>
</books>1.把所有的edition属性的值为8的修改为100
使用xpath查找对象时,依赖于jaxen.jar包,所以要先下载这个包。查找对象时,如果查找的是节点,直接写名称,如:/books/book/name,如果查找的是属性,要在属性前加上@,如:/books/book/@edition
@Testpublic void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));//先利用xpath查找对象List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book/@edition");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Attribute attr = (Attribute) iter.next();if(Integer.parseInt(attr.getValue())==8){attr.setValue("100");}}//输出修改后的文件PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m1.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out,OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} }2.把“Java编程思想”修改为“Java语言程序设计”并在该name属性所在的book节点中添加buyTime节点,节点值为2015-04-27:
@Testpublic void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));//先利用xpath查找对象List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book/name");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Element e = (Element) iter.next();if(e.getText().equals("Java编程思想")){e.setText("Java语言程序设计");Element pe = e.getParent();Element new_e = pe.addElement("buyTime");new_e.setText("2015-04-27");}}//输出修改后的文件PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m2.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out,OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} }3.若edition属性值为8,则删除该属性
@Testpublic void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book/@edition");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Attribute attr = (Attribute) iter.next();if(Integer.parseInt(attr.getValue())==8){attr.getParent().remove(attr);}}try {PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m3.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out,OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}4.把id为3的书的name节点删除:
@Test
public void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book/id");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Element e = (Element) iter.next();if(e.getText().equals("3")){e.getParent().remove(e.getParent().element("name"));}}PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m4.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out, OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
5.移除所有文件的id属性:
方式一:
直接查找id节点,再删除
@Testpublic void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book/id");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Element e = (Element) iter.next();e.getParent().remove(e);}PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m5.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out,OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}方法二:
查找book节点,再删除book节点的id节点:
@Testpublic void modifyXmlFile(){try {SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document document = reader.read(new File("F:\\test\\books.xml"));List<Node> ns = document.selectNodes("/books/book");Iterator<Node> iter = ns.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){Element e = (Element) iter.next();e.remove(e.element("id"));}PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("F:\\test\\m6.xml"));XMLWriter w = new XMLWriter(out,OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());w.write(document);w.close();} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}好了,先写这么多,这些东东基本上够项目使用了。

的实际应用)







)





)




