初学者,推荐大家使用----emp(雇员信息表)和dept(部门表),这两张表的字段及数据内容都设计的比较经典。来吧!先跟着我的操作,导入我提供的数据库脚本。
导入两张表sql脚本到数据库create database testdb;
use testdb;
drop table if exists `emp`;
create table `emp` (
`empno` int(4) default null comment '雇员编号',
`ename` varchar(10) default null comment '雇员名称',
`job` varchar(9) default null comment '雇员工作',
`mgr` int(4) default null comment '上级领导编号',
`hiredate` date default null comment '雇佣日期',
`sal` decimal(7,2) default null comment '雇员工资',
`comm` decimal(7,2) default null comment '雇员奖金',
`deptno` int(2) default null comment '部门编号'
) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into `emp`(`empno`,`ename`,`job`,`mgr`,`hiredate`,`sal`,`comm`,`deptno`) values (7369,'smith','clerk',7902,null,'800.00',null,20),(7499,'allen','salesman',7698,null,'1600.00','300.00',30),(7521,'ward','salesman',7698,null,'1250.00','500.00',30),(7566,'jones','manager',7839,null,'2975.00',null,20),(7654,'martin','salesman',7698,null,'1250.00','1400.00',30),(7698,'blake','manager',7839,null,'2850.00',null,30),(7782,'clark','manager',7839,null,'2450.00',null,10),(7788,'scott','analyst',7566,null,'3000.00',null,20),(7839,'king','president',null,null,'5000.00',null,10),(7844,'turner','salesman',7698,null,'1500.00','0.00',30),(7876,'adams','clerk',7788,null,'1100.00',null,20),(7900,'james','clerk',7698,null,'950.00',null,30),(7902,'ford','analyst',7566,null,'3000.00',null,20),(7934,'miller','clerk',7782,null,'1300.00',null,10);
drop table if exists `dept`;
create table `dept` (
`deptno` int(2) not null comment '部门编号',
`dname` varchar(14) default null comment '部门名称',
`loc` varchar(13) default null comment '部门地址'
) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into `dept`(`deptno`,`dname`,`loc`) values (10,'accounting','new york'),
(20,'research','dallas'),(30,'sales','chicago'),(40,'operations','boston');
-- 投影操作
指定查询结果中能显示哪些列
-- 选择操作
指定哪些行出现在结果中
-- 排序操作
指定查询的结果以什么样的顺序显示
--查询语句 select
*是统配符,代表所有的字段。
--查询所有雇员信息
select * from emp;
--查询所有雇员的工资、名字、以及工作,
select sal,ename,job from emp;
--表前缀
select emp.ename from emp;
--列别名 -- 别名不影响表的结构
select ename as 雇员姓名 from emp;
--表别名
select e.ename from emp as e;
--计算列
select sal+100 from emp;
--排除重复数据 distinct -- 重要
--查询雇员信息表,工种有多少种。
select distinct job from emp;
--返回限定行数 limit --分页
select * from 表名 limit 开始序号,返回的行数;
select * from emp limit 0,5;
从emp表中查询第3页的数据,每页显示10条。
第几页 每页显示多少条
页数: pageSize = 2
条数: indexSize = 5
第一个参数:
int firstParam = (pageSize-1)*indexSize;
select * from emp limit firstParam,indexSize;
--选择条件 where
--查询雇员姓名为smith的员工信息
select * from emp where ename = 'smith';
--查询雇员工作为salesman的员工的姓名和工资
select ename,sal from emp where job = 'salesman';
--查询雇员工资大于1600的雇员姓名
select ename from emp where sal > 1600;
注意:写sql语句,先找输出什么字段内容,再找条件是什么。
条件运算符
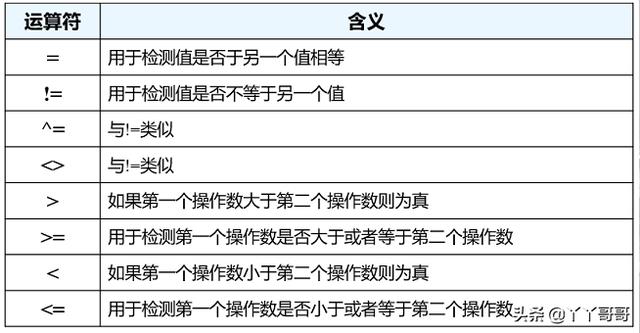
--查询奖金大于100的雇员工资
select sal from emp where comm > 100;
--多条件的操作
and 与 并且
or 或
--查询工作为salesman并且工资大于1600的雇员信息
条件:job = 'salesman' and sal > 1600
输出信息:雇员信息
select * from emp where job = 'salesman' and sal > 1600;
--执行范围 between and []
--查询工资大于等于1600小于等于3000的雇员信息
select * from emp where sal >= 1600 and sal <= 3000;
select * from emp where sal between 1600 and 3000; -- 效率高
--定义集合关系(IN或NOT IN)
in
not in
--查询雇员编号为7369、7698、7788的雇员信息
select * from emp where empno = 7369 or empno = 7698 or empno = 7788;
select * from emp where empno in(7369,7698,7788);
--查询雇员编号除了7369、7698、7788以外的雇员信息
select * from emp where empno not in(7369,7698,7788);
--模糊查询 like
通配符
“_”通配符 ? 表示任何单个字符
“%”通配符 ? 表示包含零个或多个任意字符
--查询雇员姓名是以s开头的雇员信息
select * from emp where ename like 's%';
--查询雇员姓名中含s字母的雇员信息
select * from emp where ename like '%s%';
--查询雇员姓名是以s结尾的雇员信息
select * from emp where ename like '%s';
--查询雇员姓名是以s开头第三字母为o的雇员信息
select * from emp where ename like 's_o%';
--查询雇员姓名是以%开头的雇员信息
--当模糊查询中出现通配符_和%时,需用反斜杠\\转义
select * from emp where ename like '\\%%';
--处理空值数据 is null 、 is not null
--查询没有奖金的雇员信息
select * from emp where comm != null; --错误的
select * from emp where comm is null; --正确的
--查询有奖金的雇员信息
select * from emp where comm is not null and comm !=0;
--排序操作 order by
--查询雇员信息,工资从小到大排序。 asc 升序
select * from emp order by sal asc; --默认可以不写asc
--查询雇员信息,工资从大到小排序 desc 降序
select * from emp order by sal desc;
--查询雇员信息,工资从小到大排序,奖金从大到小。 ---顺序确定优先级
select * from emp order by sal asc,comm desc;
SQL操作顺序
第一步:执行FROM
第二步:WHERE条件过滤
第三步:执行SELECT投影列
第四步:执行ORDER BY 排序
--查询雇员工作为‘salesman’的雇员信息,并且按照工资多少降序排序。
select * from emp where job = 'salesman' order by sal desc;
聚合函数的分类
在查询分析的SQL中我们经常会对一些数据进行统计查询。
比如统计某个班有多少个学生、全班总分多少、平均分多少、最高分是多少、最低分是多少。要实现这些数据的统计就需要要用到SQL提供的聚合函数。
COUNT:统计行数量
SUM:获取单个列的合计值
AVG:计算某个列的平均值
MAX:计算列的最大值
MIN:计算列的最小值
--count:统计行数量
--统计emp表中有多少个员工
select count(*) from emp; -- * 所有行,包括null都行
select count(empno) from emp; -- 推荐 ,所有行,只是null排除。
--共计emp表中工作为salesman的人数
select count(empno) from emp where job = 'salesman';
--统计有奖金的人数
select count(comm) from emp;
select count(all empno) from emp; -- all排除了null,加不加都没关系
--统计emp表中有多少种工作
select count(distinct job) from emp; --去掉重复,再统计。 -- 重点
--SUM:获取单个列的合计值
--统计所有员工的工资总和
select sum(sal) from emp;
--AVG:计算某个列的平均值
--统计所有员工平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp;
--MAX:计算列的最大值
--查询工资最高的雇员信息
select ename,max(sal) from emp;
--分组操作 group by
--查询emp中有多少个工作岗位
select * from emp group by job;
--查询每个岗位中工资大于1500的员工人数
select job,count(empno) from emp where sal > 1500 group by job;


java: 程序包 不存在,解决办法)
![再学 GDI+[91]: TGPImage(11) - 转灰度图像](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/再学 GDI+[91]: TGPImage(11) - 转灰度图像)

)








![[MySQL FAQ]系列 -- 快速还原MyISAM表索引](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[MySQL FAQ]系列 -- 快速还原MyISAM表索引)





