文章目录
- Sigmoid(x)
- 双曲正切
- 线性整流函数 rectified linear unit (ReLu)
- PReLU(Parametric Rectified Linear Unit) Leaky ReLu
- 指数线性单元 Exponential Linear Units (ELU)
- 感知机激活
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = "png"
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 5)
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Simhei'] #替代字体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #解决坐标轴负数的铅显示问题
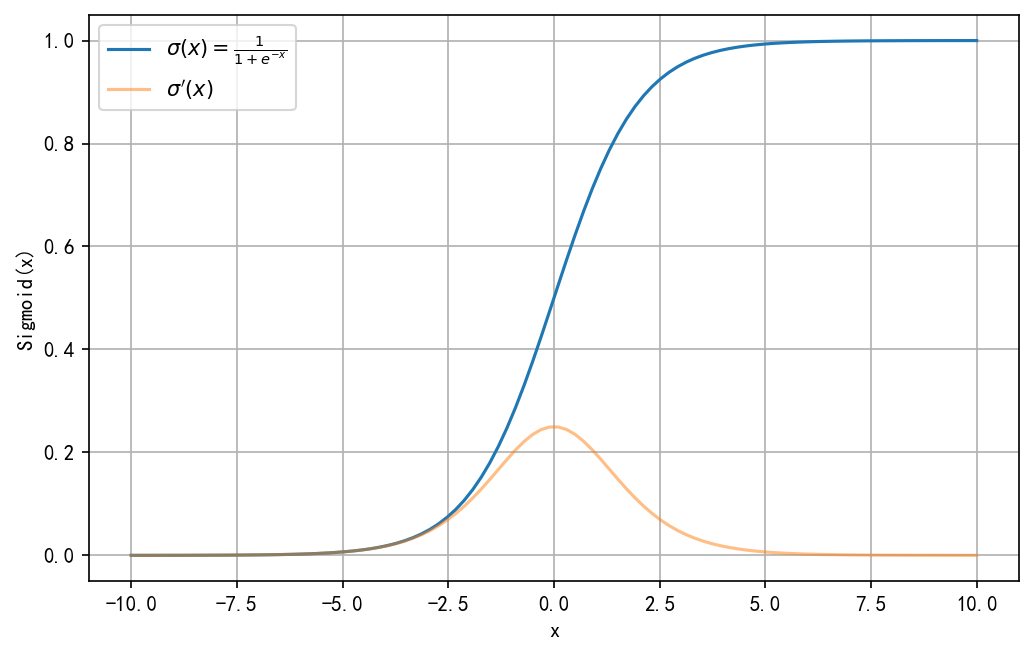
Sigmoid(x)
sigmoid(x)=σ(x)=11+e−x\text{sigmoid}(x)= \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}sigmoid(x)=σ(x)=1+e−x1
σ′(x)=[(1+e−x)−1]′=(−1)(1+e−x)−2(−1)e−x=(1+e−x)−2e−x=e−x(1+e−x)2=1+e−x−1(1+e−x)2=1+e−x(1+e−x)2−1(1+e−x)2=1(1+e−x)(1−1(1+e−x))=σ(x)(1−σ(x))\begin{aligned} \sigma'(x) =&[(1+e^{-x})^{-1}]' \\ =&(-1)(1+e^{-x})^{-2}(-1)e^{-x}\\ =&(1+e^{-x})^{-2}e^{-x}\\ =&\frac{e^{-x}}{(1+e^{-x})^2} \\ =&\frac{1+e^{-x}-1}{(1+e^{-x})^2} \\ =&\frac{1+e^{-x}}{(1+e^{-x})^2} - \frac{1}{(1+e^{-x})^2} \\ =&\frac{1}{(1+e^{-x})}(1-\frac{1}{(1+e^{-x})}) \\ =&\sigma(x)(1-{\sigma(x)}) \end{aligned}σ′(x)========[(1+e−x)−1]′(−1)(1+e−x)−2(−1)e−x(1+e−x)−2e−x(1+e−x)2e−x(1+e−x)21+e−x−1(1+e−x)21+e−x−(1+e−x)21(1+e−x)1(1−(1+e−x)1)σ(x)(1−σ(x))
def sigmoid(x):return np.divide(1, 1 + np.e**(-x))def d_sigmoid(x):return sigmoid(x) * (1 - sigmoid(x))x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
f_x = sigmoid(x)# df_x is derivative
df_x = d_sigmoid(x)plt.plot(x, f_x, label=r"$\sigma(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} $")
plt.plot(x, df_x, label=r"$\sigma'(x)$", alpha=0.5)plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Sigmoid(x)')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
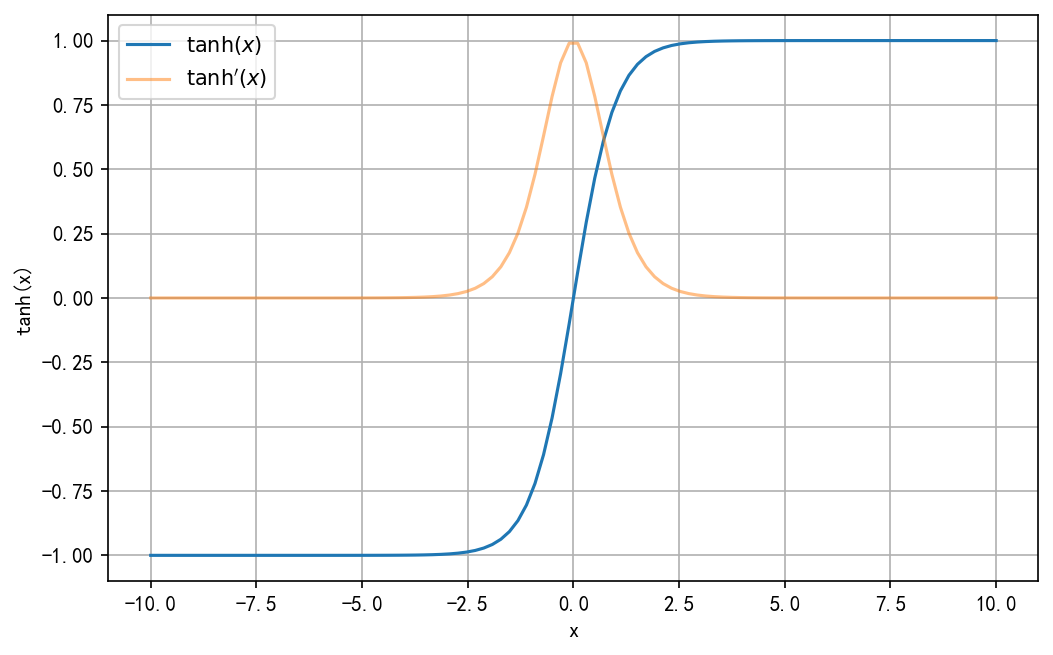
双曲正切
tanh(x)=sinh(x)cosh(x)=ex−e−xex+e−x\tanh(x) = \frac{\sinh(x)}{\cosh(x)} = \frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}}tanh(x)=cosh(x)sinh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x
tanh′(x)=(ex−e−xex+e−x)′=[(ex−e−x)(ex+e−x)−1]′=(ex+e−x)(ex+e−x)−1+(ex−e−x)(−1)(ex+e−x)−2(ex−e−x)=1−(ex−e−x)2(ex+e−x)−2=1−(ex−e−x)2(ex+e−x)2=1−tanh2(x)\begin{aligned} \tanh'(x) =& \big(\frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}}\big)' \\ =& \big[(e^x - e^{-x})(e^x + e^{-x})^{-1}\big]' \\ =& (e^x + e^{-x})(e^x + e^{-x})^{-1} + (e^x - e^{-x})(-1)(e^x + e^{-x})^{-2} (e^x - e^{-x}) \\ =& 1-(e^x - e^{-x})^2(e^x + e^{-x})^{-2} \\ =& 1 - \frac{(e^x - e^{-x})^2}{(e^x + e^{-x})^2} \\ =& 1- \tanh^2(x) \\ \end{aligned}tanh′(x)======(ex+e−xex−e−x)′[(ex−e−x)(ex+e−x)−1]′(ex+e−x)(ex+e−x)−1+(ex−e−x)(−1)(ex+e−x)−2(ex−e−x)1−(ex−e−x)2(ex+e−x)−21−(ex+e−x)2(ex−e−x)21−tanh2(x)
def tanh(x):return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))def d_tanh(x):return 1 - tanh(x)**2x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)f_x = tanh(x)# df_x is derivative
df_x = d_tanh(x)plt.plot(x, f_x, label=r"$\tanh(x)}$")
plt.plot(x, df_x, label=r"$\tanh'(x)$", alpha=0.5)plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('tanh(x)')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
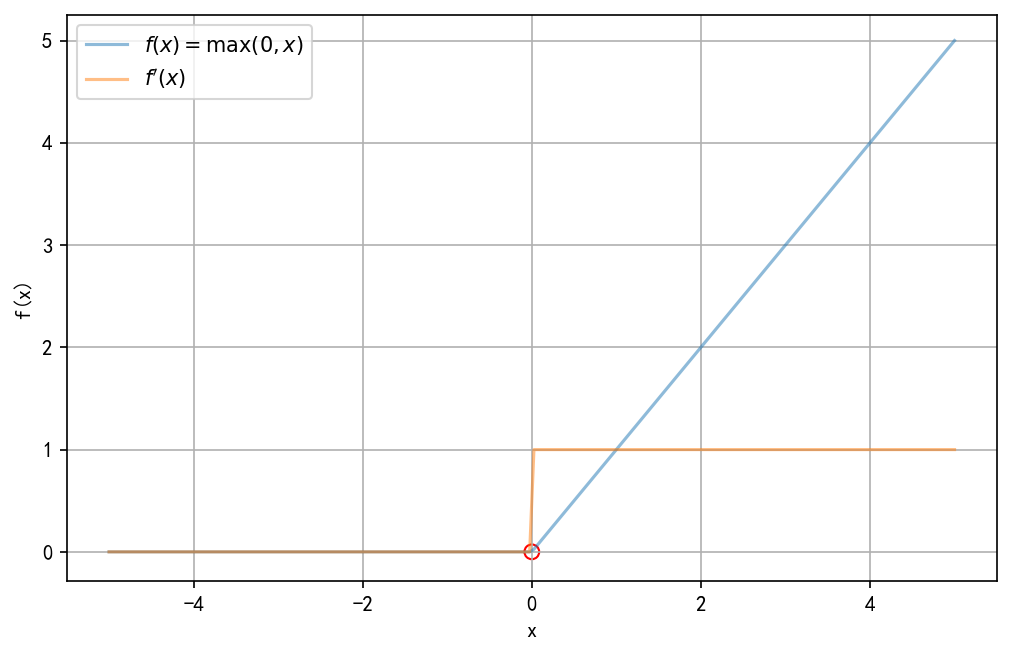
线性整流函数 rectified linear unit (ReLu)
f(x)=relu(x)=max(0,x)={x,x>00,x≤0f(x) = \text{relu}(x) = \max(0, x) = \begin{cases} x, &x>0 \\ 0, &x\leq 0 \end{cases}f(x)=relu(x)=max(0,x)={x,0,x>0x≤0
f(x)是连续的f(x)是连续的f(x)是连续的
f′(x)=limh→0f(0)=f(0+h)−f(0)h=max(0,h)−0hf'(x)=\lim_{h\to 0}f(0) = \frac{f(0 + h)-f(0)}{h}=\frac{\max(0, h) - 0}{h}f′(x)=limh→0f(0)=hf(0+h)−f(0)=hmax(0,h)−0
limh→0−=0h=0\lim_{h\to0^-}=\frac{0}{h} = 0limh→0−=h0=0
limh→0+=hh=1\lim_{h\to0^+}=\frac{h}{h} = 1limh→0+=hh=1
所以f′(0)f'(0)f′(0)处不可导
所以f′(x)={1,x>00,x<0f'(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x < 0 \end{cases}f′(x)={1,0,x>0x<0
f2=f(f(x))=max(0,f1(x)){f1(x),f1(x)>00,f1(x)≤0f_2=f(f(x))=max(0,f_1(x))\begin{cases} f_1(x), & f_1(x)>0 \\ 0, & f_1(x)\leq 0 \end{cases}f2=f(f(x))=max(0,f1(x)){f1(x),0,f1(x)>0f1(x)≤0
df2dx={1,f1(x)>00,f1(x)≤0\dfrac{df_2}{dx}=\begin{cases} 1, & f_1(x)>0 \\ 0, &f_1(x)\leq 0 \end{cases}dxdf2={1,0,f1(x)>0f1(x)≤0
def relu(x):return np.where(x < 0, 0, x)def d_relu(x):return np.where(x < 0, 0, 1)x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 200)f_x = relu(x)# df_x is derivative
df_x = d_relu(x)plt.plot(x, f_x, label=r"$ f(x) = \max(0, x)} $", alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(x, df_x, label=r"$f'(x)$", alpha=0.5)
# There is no derivative at (0)
plt.scatter(0, 0, color='', marker='o', edgecolors='r', s=50)plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
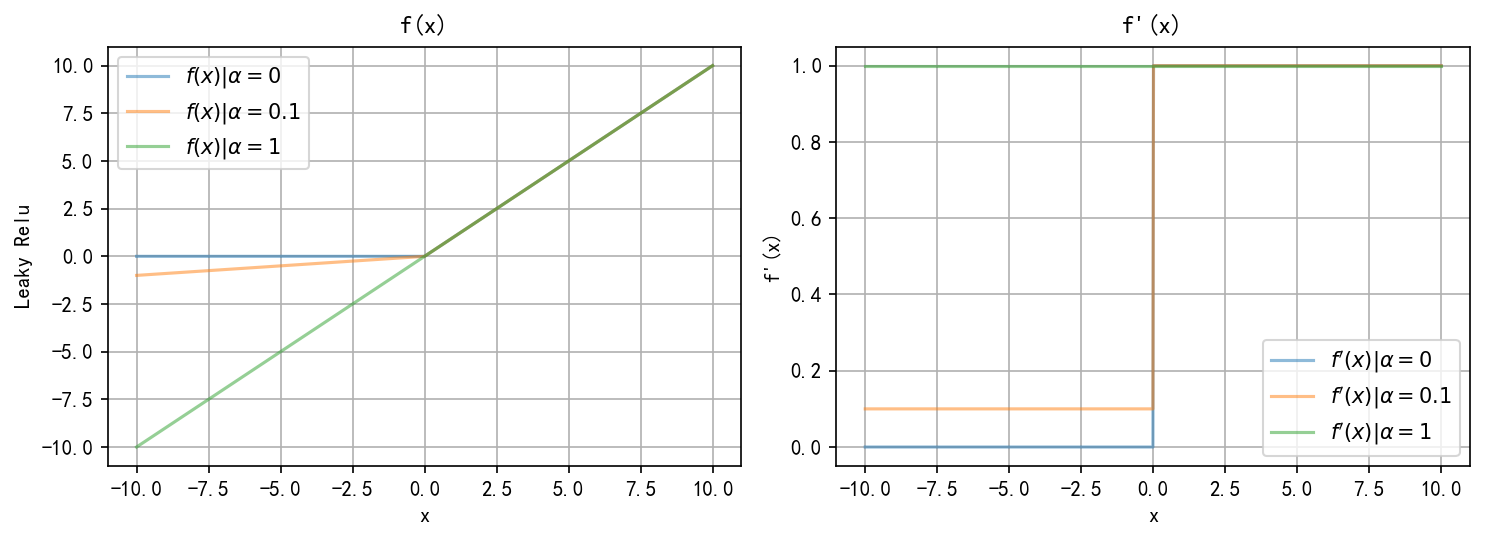
PReLU(Parametric Rectified Linear Unit) Leaky ReLu
f(x)=max(αx,x)={x,x>0αx,x≤0,当α<1,α≠0f(x) = \max(\alpha x, x) = \begin{cases} x, & x > 0 \\ \alpha x, & x\leq 0 \end{cases}, \quad 当 \alpha<1, \alpha\neq0f(x)=max(αx,x)={x,αx,x>0x≤0,当α<1,α=0,
f(x)=max(αx,x)={αx,x>0x,x≤0,当α≥1f(x) = \max(\alpha x, x) = \begin{cases} \alpha x, &x>0 \\ x, &x \leq 0 \end{cases} , \quad 当\alpha\geq1f(x)=max(αx,x)={αx,x,x>0x≤0,当α≥1
f(x)=max(αx,x)={x,x>00,x≤0,当α=0,就是ReLuf(x) = \max(\alpha x, x) = \begin{cases} x, & x>0 \\ 0, & x \leq 0 \end{cases}, \quad 当\alpha=0,就是ReLuf(x)=max(αx,x)={x,0,x>0x≤0,当α=0,就是ReLu
当α≥1时,f1(x)={αx,x>0x,x≤0当\alpha \geq 1时, \quad f_1(x) = \begin{cases} \alpha x, & x>0 \\ x, & x\leq 0 \end{cases}当α≥1时,f1(x)={αx,x,x>0x≤0
df1dx={α,x>01,x≤0\dfrac{df_1}{dx} = \begin{cases} \alpha, & x > 0 \\ 1, & x \leq 0 \end{cases}dxdf1={α,1,x>0x≤0
当α<1,f1(x)={x,x>0αx,x≤0当\alpha < 1, \quad f_1(x) = \begin{cases} x, &x > 0 \\ \alpha x, & x \leq 0 \end{cases}当α<1,f1(x)={x,αx,x>0x≤0
df1dx={1,x>0α,x≤0\dfrac{df_1}{dx} = \begin{cases} 1, & x > 0 \\ \alpha, &x \leq 0 \end{cases}dxdf1={1,α,x>0x≤0
把leaky relu的α\alphaα设置成可以训练的参数,就是PReLU(Parametric Rectified Linear Unit)
def leaky_relu(x, alpha: float = 1):return np.where(x <= 0, alpha * x, x)def d_leaky_relu(x, alpha: float = 1):return np.where(x < 0, alpha, 1)x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)alpha = [0, 0.1, 1]fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 3.7))for alpha_i in alpha:f1 = leaky_relu(x, alpha=alpha_i)ax[0].plot(x, f1, label=r"$ f(x)|\alpha={0} $".format(alpha_i), alpha=0.5)ax[0].set_xlabel('x')ax[0].set_ylabel('Leaky Relu')ax[0].grid(True)ax[0].legend()ax[0].set_title('f(x)')df1 = d_leaky_relu(x, alpha_i)ax[1].plot(x, df1, label=r"$f'(x)|\alpha={0}$".format(alpha_i), alpha=0.5)ax[1].set_xlabel('x')ax[1].set_ylabel("f'(x)")ax[1].grid(True)ax[1].legend()ax[1].set_title("f'(x)")plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
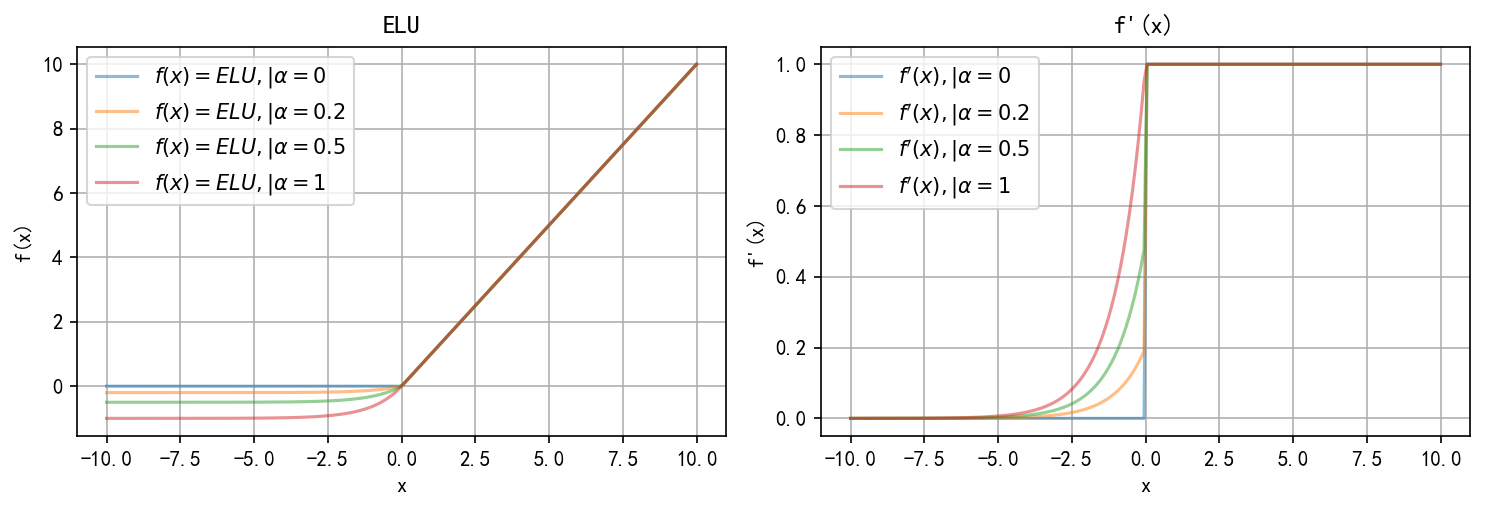
指数线性单元 Exponential Linear Units (ELU)
f(x)=elu(x)={x,x>0α(ex−1),x≤0f(x) = \text{elu}(x) = \begin{cases} x, & x>0 \\ \alpha(e^x - 1), & x \leq 0 \end{cases}f(x)=elu(x)={x,α(ex−1),x>0x≤0
f′(x)=limh→0f(0)=f(0+h)−f(0)hf'(x) = \lim_{h\to 0}f(0) = \frac{f(0+h)-f(0)}{h}f′(x)=limh→0f(0)=hf(0+h)−f(0)
limh→0−=α(eh−1)−0h=0\lim_{h\to0^-} = \frac{\alpha (e^h - 1) - 0}{h} = 0limh→0−=hα(eh−1)−0=0
limh→0+=hh=1\lim_{h\to0^+} = \frac{h}{h} = 1limh→0+=hh=1
所以f′(0)f'(0)f′(0)处不可导
所以f′(x)={1,x>0αex,x≤0f'(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x>0 \\ \alpha e^x, &x\leq0 \end{cases}f′(x)={1,αex,x>0x≤0
def elu(x, alpha: float = 1):return np.where(x <= 0, alpha * (np.exp(x) - 1), x)def d_elu(x, alpha: float = 1):return np.where(x <= 0, alpha * np.exp(x), 1)x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 200)alpha = [0, 0.2, 0.5, 1]fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 3.5))
for alpha_i in alpha:f1 = elu(x, alpha=alpha_i)df1 = d_elu(x, alpha_i)ax[0].plot(x,f1,label=r"$f(x)=ELU,|\alpha = {0}$".format(alpha_i),alpha=0.5)ax[0].set_xlabel('x')ax[0].set_ylabel('f(x)')ax[0].grid(True)ax[0].legend()ax[0].set_title('ELU')ax[1].plot(x,df1,label=r"$f'(x),|\alpha = {0}$".format(alpha_i),alpha=0.5)ax[1].set_xlabel('x')ax[1].set_ylabel("f'(x)")ax[1].grid(True)ax[1].legend()ax[1].set_title("f'(x)")plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
感知机激活
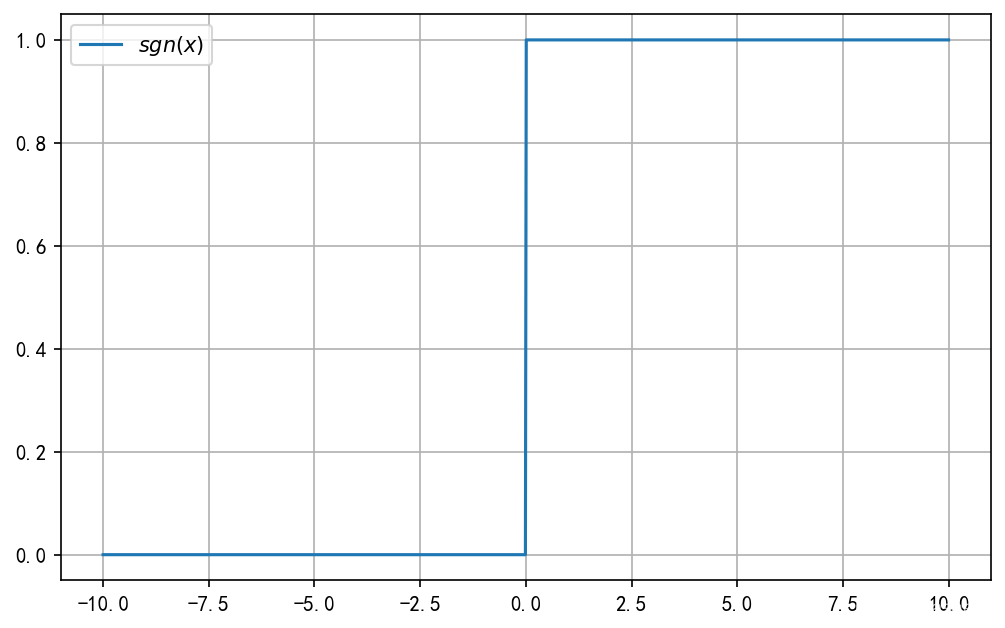
sgn(x)={1,x≥0−1,x<0\text{sgn}(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x \geq 0 \\ -1, & x < 0 \end{cases}sgn(x)={1,−1,x≥0x<0
- 这里的值也可以是1,0
def sgn(x):return np.where(x <= 0, 0, 1)x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)f_x = sgn(x)plt.plot(x, f_x, label=r"$sgn(x)$", alpha=1)
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.show()




)





)





-------第一次使用动态数组vector)

源码解析)
