1.背景
生产环境,某云的某个业务Redis实例,触发内存使用率,连续 3 次 平均值 >= 85 %告警。
运维同学告知,看看需要怎么优化或者升级配置?分享了其实例RDB的内存剖析链接。
通过内存剖析详情发现,存在某类未设置过期时间且无用的keys,其内存占用约3.8GB,内存占比25%。
内存占比挺大,有确定的成本经济收益。
做事有动力啦!
Redis实例信息
某云Redis实例的基本信息
- 实例规格:16G主从版
- 版本:Redis 2.8(兼容3.0特性)

某云的Redis RDB内存剖析
- 基本信息
- 分析方法:使用已有备份集 (选择的备份文件:完成于)
- 详情
- Key内存占有情况
- Key数量分布情况
- Elements内存占用情况
- Elements数量分布情况
- Key过期时间分布 (内存)
- Key过期时间分布 (数量)

2.目标
- 在线异步地删除缓存数据
- 不影响线上业务,不确定的风险可控(风险紧急预案)
3.结论先行
- 在线清理了
5GB+内存 - 已使用内存总量,15.5GB -> 10.2GB
4.技术方案
变更三板斧:可灰度、可观测/可监控、可回滚
使用spring-data-redis提供的RedisCacheWriter#clean开源解决方案,在其基础上加入异步和并发控制。
- 【批量策略】在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除,每批10/20个key
- 先SCAN匹配,再批量DEL
- SCAN(keyPattern) + DEL(allMatchKeys)
- 【执行策略】预发环境,业务低峰时期执行
- 【可观测】Redis实例性能监控,业务监控
- 【风险紧急预案-兜底方案】删除容器实例,kill杀掉异步守护线程,停止执行(可回滚)
spring-boot版本
- spring-data-redis-2.7.16
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis-2.7.16
可观测-Redis实例性能监控
- key模式: “message:queue:*_lock”
- 清理时间: [2023-12-04 21:15:39.405, 2023-12-05 00:28:24.21]
清理途中,觉得每批10个key有些慢,调整到每批20个key。
【注意】应用重启后,会重新从头开始扫描,存在一段时间未删除keys,需要等一会才能看到删除效果。
不建议中途调整每批key数量!
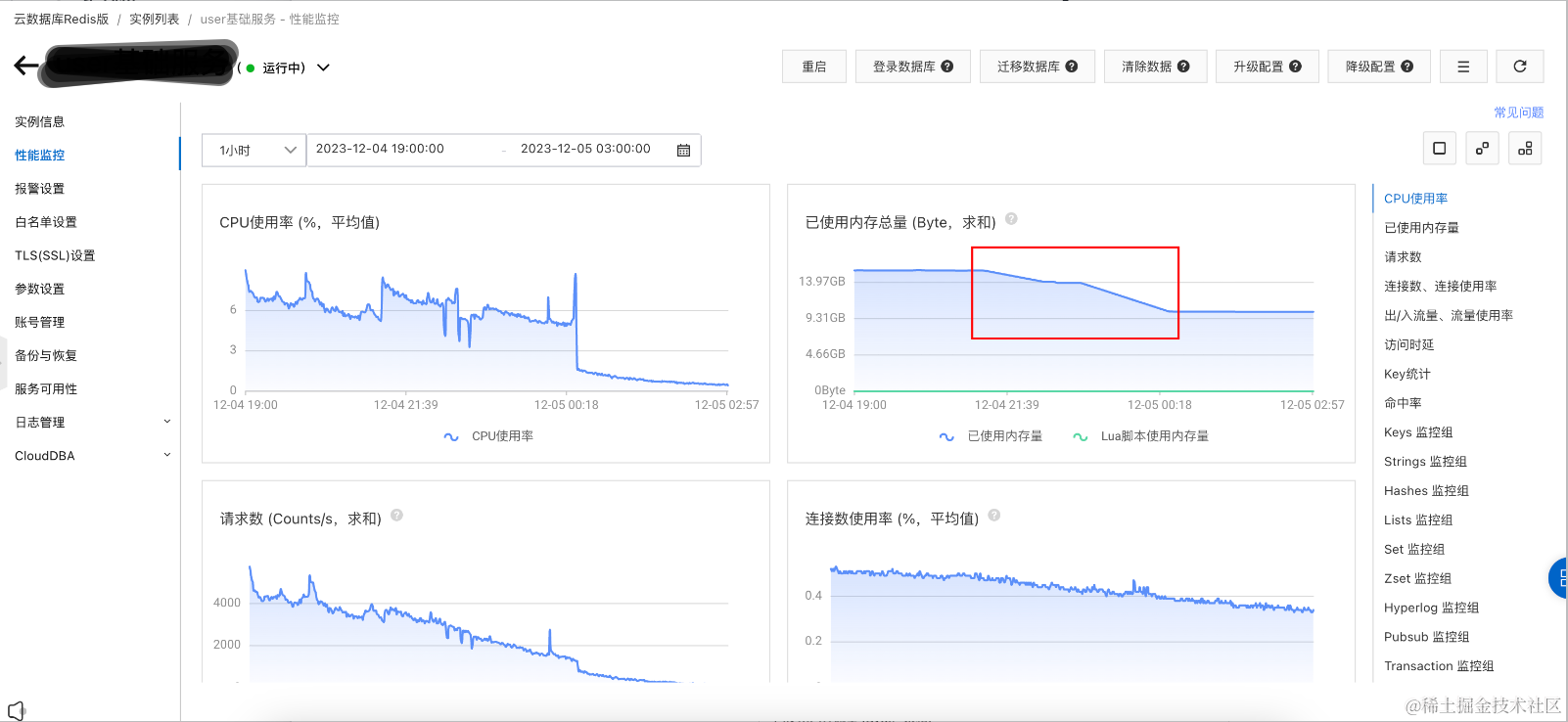
CPU使用率 (%,平均值)
CPU使用率,增长
1~3%
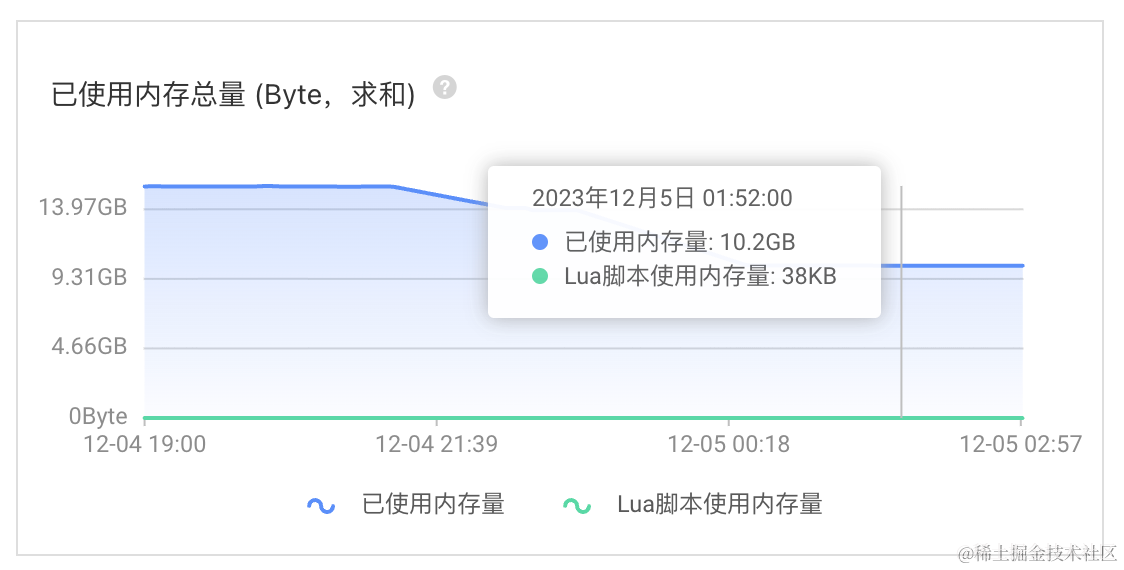
已使用内存总量 (Byte,求和)
已使用内存总量,15.5GB -> 10.22GB

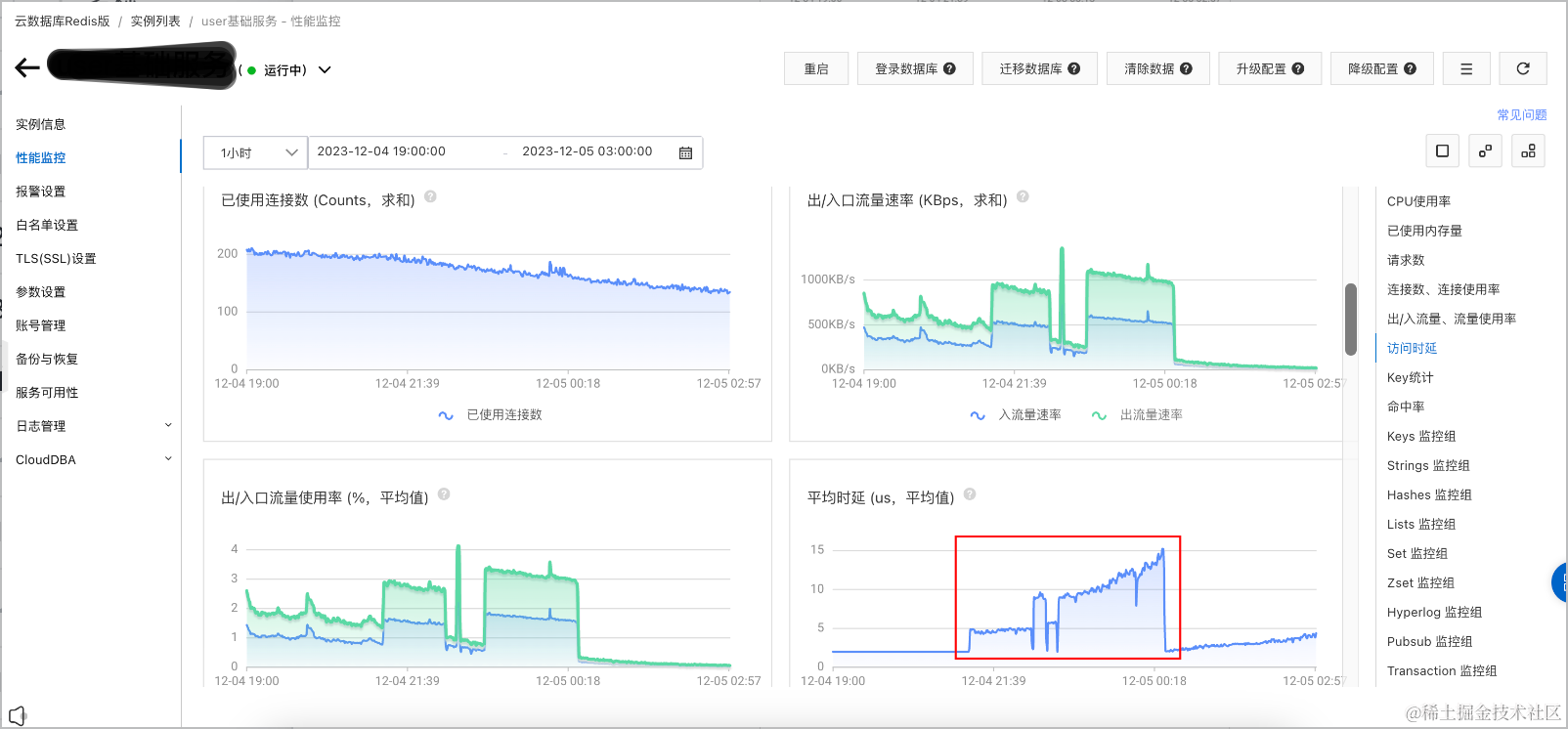
平均时延 (us,平均值)
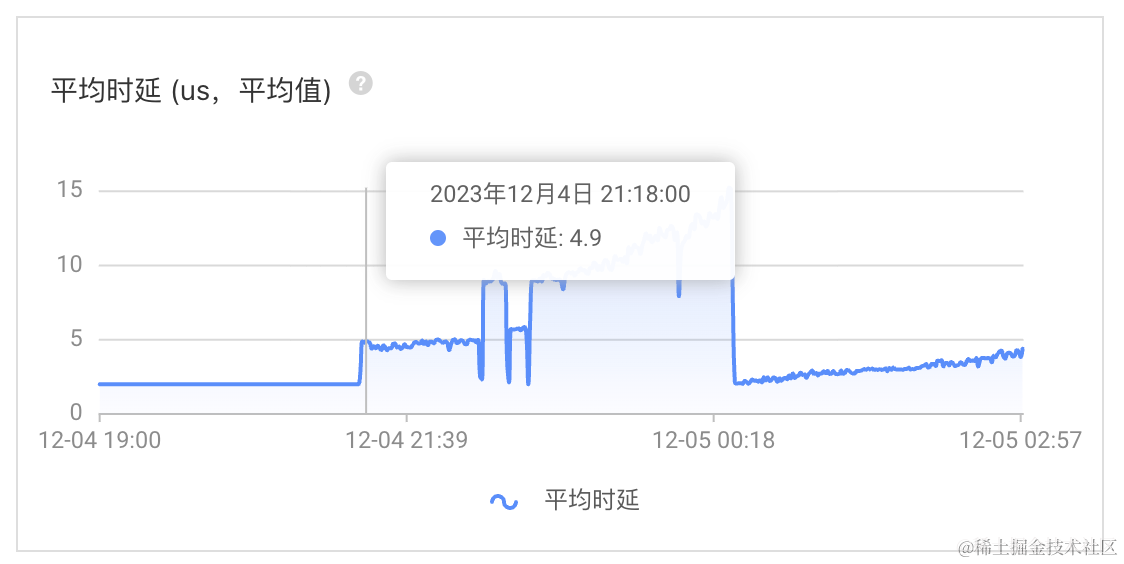
每批10个key,时延增长
2~3微秒每批20个key,时延增长
7~13微秒
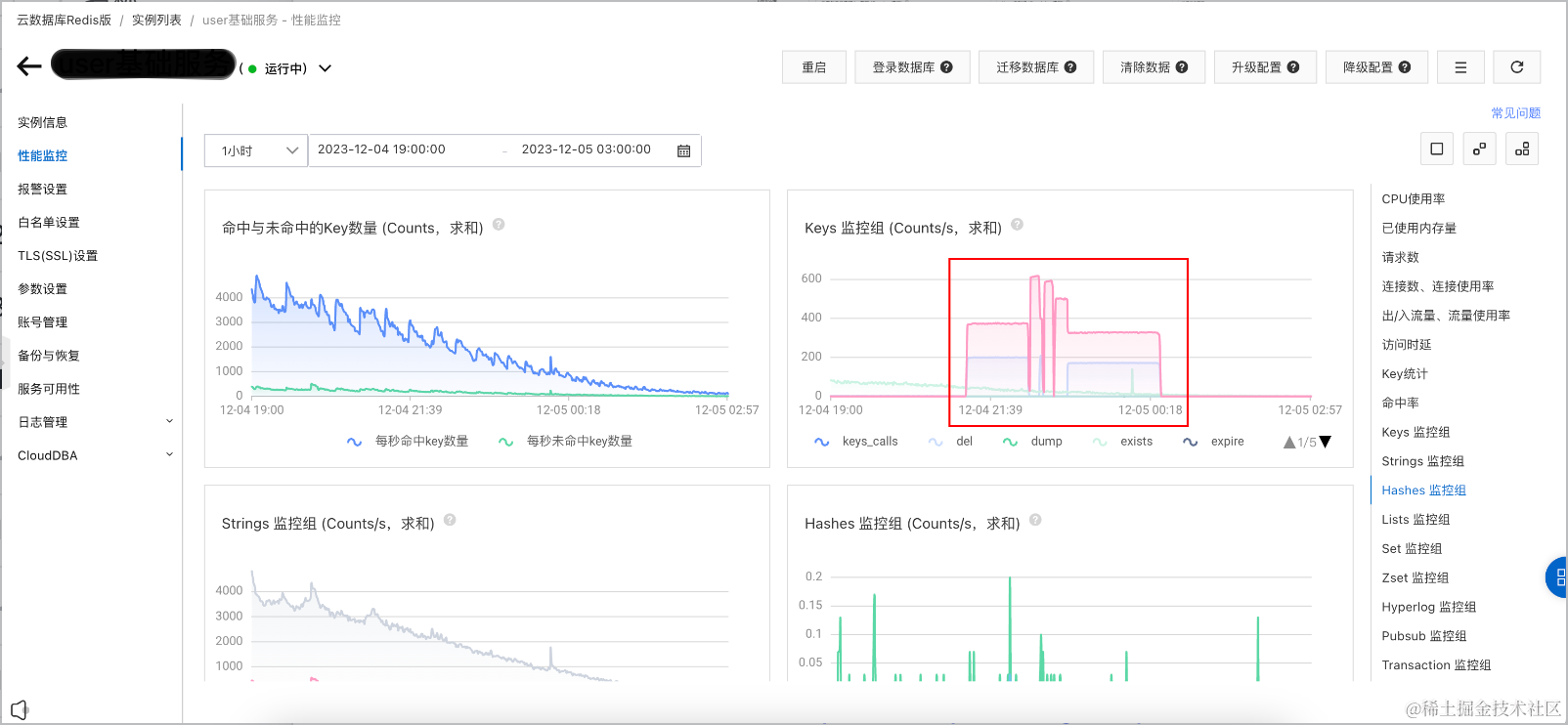
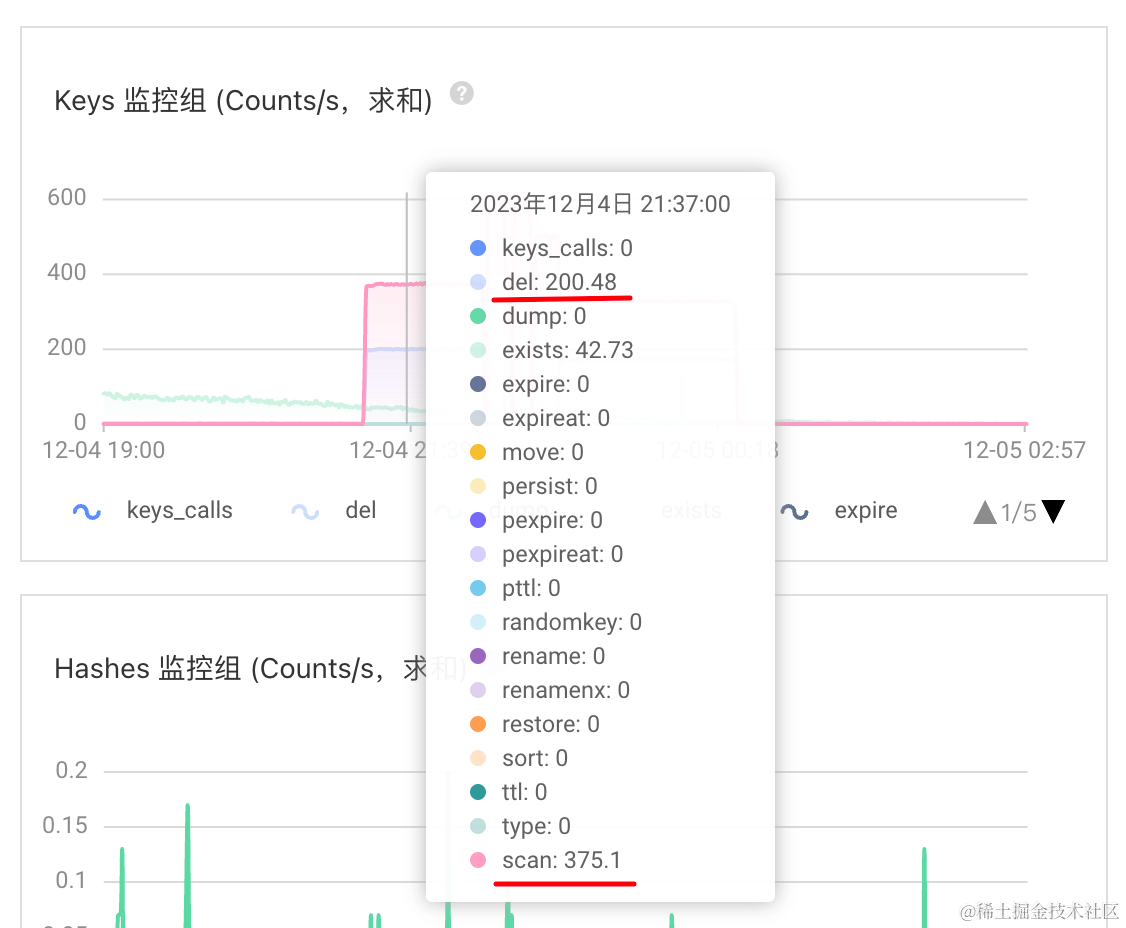
Keys 监控组 (Counts/s,求和)
del: 200
scan: 375
具体实现
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadFactoryBuilder;
import com.spring.boot.redis.example.model.CacheKey;
import com.spring.boot.redis.example.service.CacheService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategies;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;/*** 缓存服务实现** @author guang.yi* @since 2023/7/30*/
@Slf4j
@Service("cacheService")
public class CacheServiceImpl implements CacheService {/*** 并发开关*/private final ConcurrentMap<String, Boolean> concurrentSwitch = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);private final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 5L, TimeUnit.MINUTES,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNamePrefix("cache-clean-").setDaemon(true).build());private final RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;public CacheServiceImpl(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {this.redisConnectionFactory = redisConnectionFactory;log.info("create CacheServiceImpl");}@Overridepublic boolean cleanCache(CacheKey cacheKey) {String keyPattern = cacheKey.getKeyPattern();// 避免多次重复地操作if (concurrentSwitch.putIfAbsent(keyPattern, Boolean.TRUE) == null) {// 异步地执行executorService.execute(() -> this.clean(cacheKey));return true;}return false;}private void clean(CacheKey cacheKey) {log.info("cleanCache start, cacheKey={}", cacheKey);StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch("cleanCache");stopWatch.start();this.clean(cacheKey.getCacheName(), cacheKey.getKeyPattern());stopWatch.stop();log.info("cleanCache end, cacheKey={}, stopWatch={}", cacheKey, stopWatch);}/*** 缓存Redis的历史数据清理* <pre>* 【批量策略】在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除,每批10个key* 先SCAN,再批量DEL* 【执行策略】预发环境,业务低峰时期* </pre>** @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean* @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean*/private void clean(String cacheName, String keyPattern) {// 【批量策略】SCAN,每批10个keyRedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory, BatchStrategies.scan(10));// 先SCAN,再批量DELredisCacheWriter.clean(cacheName, keyPattern.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}}
# .A.1. Core Properties
spring:# RedisPropertiesredis:database: 0host: "localhost"port: 6379timeout: 1sconnect-timeout: 300ms
# client-name: "user-cache"
# client-type: lettuce
# sentinel:
# master: ""
# nodes: "host:port"
# cluster:
# nodes: "host:port"
# max-redirects: 3
# jedis:
# pool:
# enabled: true
# max-idle: 8
# min-idle: 0
# max-active: 8
# max-wait: 300ms
# time-between-eviction-runs: 5mlettuce:shutdown-timeout: 100mspool:enabled: truemax-idle: 8min-idle: 0max-active: 8max-wait: -1time-between-eviction-runs: 5m开源解决方案有哪些坑?
深入源代码,深究实现细节,趴开裤子看看底细。
源代码做了简化
开源解决方案结论
深入源代码看,scan批量策略的实现方案靠谱。keys批量策略存在大坑,不靠谱。
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
RedisCacheWriter#clean
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean
BatchStrategy批量策略,有keys和scan两种,分别对应Redis的KEYS和SCAN命令。
批量策略默认使用keys,对于真实业务使用场景,一点都不实用。
因为KEYS命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量DEL删除命令。
对于大量的keys需要删除时,其操作可能夯住线上Redis实例,存在严重影响Redis实例干活的风险。
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.time.Duration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** {@link RedisCacheWriter} provides low level access to Redis commands ({@code SET, SETNX, GET, EXPIRE,...}) used for* caching. <br />* The {@link RedisCacheWriter} may be shared by multiple cache implementations and is responsible for writing / reading* binary data to / from Redis. The implementation honors potential cache lock flags that might be set.* <p>* The default {@link RedisCacheWriter} implementation can be customized with {@link BatchStrategy} to tune performance* behavior.** @author Christoph Strobl* @author Mark Paluch* @since 2.0*/
public interface RedisCacheWriter extends CacheStatisticsProvider {/*** Create new {@link RedisCacheWriter} without locking behavior.** @param connectionFactory must not be {@literal null}.* @return new instance of {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter}.*/static RedisCacheWriter nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {return nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory, BatchStrategies.keys());}/*** Create new {@link RedisCacheWriter} without locking behavior.** @param connectionFactory must not be {@literal null}.* @param batchStrategy must not be {@literal null}.* @return new instance of {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter}.* @since 2.6*/static RedisCacheWriter nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,BatchStrategy batchStrategy) {Assert.notNull(connectionFactory, "ConnectionFactory must not be null!");Assert.notNull(batchStrategy, "BatchStrategy must not be null!");return new DefaultRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory, batchStrategy);}/*** Remove all keys following the given pattern.* 按照给定模式删除所有键。** @param name The cache name must not be {@literal null}.* @param pattern The pattern for the keys to remove. Must not be {@literal null}.*/void clean(String name, byte[] pattern);}DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean
源代码做了简化
RedisCacheWriter#clean默认实现是org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean
通过批量策略清理缓存数据batchStrategy.cleanCache(connection, name, pattern)
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;import org.springframework.dao.PessimisticLockingFailureException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStringCommands.SetOption;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.types.Expiration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** {@link RedisCacheWriter} implementation capable of reading/writing binary data from/to Redis in {@literal standalone}* and {@literal cluster} environments. Works upon a given {@link RedisConnectionFactory} to obtain the actual* {@link RedisConnection}. <br />* {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter} can be used in* {@link RedisCacheWriter#lockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory) locking} or* {@link RedisCacheWriter#nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory) non-locking} mode. While* {@literal non-locking} aims for maximum performance it may result in overlapping, non atomic, command execution for* operations spanning multiple Redis interactions like {@code putIfAbsent}. The {@literal locking} counterpart prevents* command overlap by setting an explicit lock key and checking against presence of this key which leads to additional* requests and potential command wait times.** @author Christoph Strobl* @author Mark Paluch* @author André Prata* @since 2.0*/
class DefaultRedisCacheWriter implements RedisCacheWriter {private final RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory;private final Duration sleepTime;private final CacheStatisticsCollector statistics;private final BatchStrategy batchStrategy;/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean(java.lang.String, byte[])*/@Overridepublic void clean(String name, byte[] pattern) {Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null!");Assert.notNull(pattern, "Pattern must not be null!");execute(name, connection -> {boolean wasLocked = false;try {if (isLockingCacheWriter()) {doLock(name, connection);wasLocked = true;}// 通过批量策略清理缓存数据long deleteCount = batchStrategy.cleanCache(connection, name, pattern);while (deleteCount > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {statistics.incDeletesBy(name, Integer.MAX_VALUE);deleteCount -= Integer.MAX_VALUE;}statistics.incDeletesBy(name, (int) deleteCount);} finally {if (wasLocked && isLockingCacheWriter()) {doUnlock(name, connection);}}return "OK";});}}BatchStrategy批量策略
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategy
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} to be used with {@link RedisCacheWriter}.* <p>* Mainly used to clear the cache.* <p>* Predefined strategies using the {@link BatchStrategies#keys() KEYS} or {@link BatchStrategies#scan(int) SCAN}* commands can be found in {@link BatchStrategies}.** @author Mark Paluch* @author Christoph Strobl* @since 2.6*/
public interface BatchStrategy {/*** Remove all keys following the given pattern.** @param connection the connection to use. Must not be {@literal null}.* @param name The cache name. Must not be {@literal null}.* @param pattern The pattern for the keys to remove. Must not be {@literal null}.* @return number of removed keys.*/long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern);}BatchStrategies批量策略实现
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategies
BatchStrategy批量策略,有keys和scan两种,分别对应Redis的KEYS和SCAN命令。
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
keys批量策略,对于真实业务使用场景,一点都不实用。
因为KEYS命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量DEL删除命令。
对于大量的keys需要删除时,其操作可能夯住线上Redis实例,存在严重影响Redis实例干活的风险。
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Optional;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.Cursor;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ScanOptions;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** A collection of predefined {@link BatchStrategy} implementations using {@code KEYS} or {@code SCAN} command.** @author Mark Paluch* @author Christoph Strobl* @since 2.6*/
public abstract class BatchStrategies {private BatchStrategies() {// can't touch this - oh-oh oh oh oh-oh-oh}/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} using a single {@code KEYS} and {@code DEL} command to remove all matching keys.* {@code KEYS} scans the entire keyspace of the Redis database and can block the Redis worker thread for a long time* on large keyspaces.* <p>* {@code KEYS} is supported for standalone and clustered (sharded) Redis operation modes.** @return batching strategy using {@code KEYS}.*/public static BatchStrategy keys() {return Keys.INSTANCE;}/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} using a {@code SCAN} cursors and potentially multiple {@code DEL} commands to remove all* matching keys. This strategy allows a configurable batch size to optimize for scan batching.* <p>* Note that using the {@code SCAN} strategy might be not supported on all drivers and Redis operation modes.** @return batching strategy using {@code SCAN}.*/public static BatchStrategy scan(int batchSize) {Assert.isTrue(batchSize > 0, "Batch size must be greater than zero!");return new Scan(batchSize);}/*** {@link BatchStrategy} using {@code KEYS}.*/static class Keys implements BatchStrategy {static Keys INSTANCE = new Keys();@Overridepublic long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern) {// `KEYS`命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量`DEL`删除命令byte[][] keys = Optional.ofNullable(connection.keys(pattern)).orElse(Collections.emptySet()).toArray(new byte[0][]);if (keys.length > 0) {connection.del(keys);}return keys.length;}}/*** {@link BatchStrategy} using {@code SCAN}.*/static class Scan implements BatchStrategy {private final int batchSize;Scan(int batchSize) {this.batchSize = batchSize;}@Overridepublic long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern) {// 批量扫描匹配删除,每批10/20个key// 先SCAN匹配,再批量DEL// SCAN(keyPattern, match, batchSize) + DEL(allMatchKeys, batchSize)Cursor<byte[]> cursor = connection.scan(ScanOptions.scanOptions().count(batchSize).match(pattern).build());long count = 0;PartitionIterator<byte[]> partitions = new PartitionIterator<>(cursor, batchSize);while (partitions.hasNext()) {List<byte[]> keys = partitions.next();count += keys.size();if (keys.size() > 0) {connection.del(keys.toArray(new byte[0][]));}}return count;}}/*** Utility to split and buffer outcome from a {@link Iterator} into {@link List lists} of {@code T} with a maximum* chunks {@code size}.** @param <T>*/static class PartitionIterator<T> implements Iterator<List<T>> {private final Iterator<T> iterator;private final int size;PartitionIterator(Iterator<T> iterator, int size) {this.iterator = iterator;this.size = size;}@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return iterator.hasNext();}@Overridepublic List<T> next() {if (!hasNext()) {throw new NoSuchElementException();}List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(size);while (list.size() < size && iterator.hasNext()) {list.add(iterator.next());}return list;}}
}5.参考引用
- Spring Data Redis / Redis / Redis Cache
- redis-spring-boot-starter-example
献给杭州2023年的第一场雪❄️
2023.12.18


)
)

)


)
)



))



![php伪协议 [NISACTF 2022]easyssrf](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/php伪协议 [NISACTF 2022]easyssrf)
覆盖优化 - 附代码)