微服务化的负载均衡组件源码剖析与实战开发全流程
- 什么是负载均衡
- 负载均衡的种类
- 服务器端负载均衡(S-LB)
- 客户端负载均衡(C-LB)
- 注解@LoadBalanced
- LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类
- LoadBalancerClient类
- 源码分析
- ServiceInstanceChooser类
- 内置负载均衡策略的介绍
- IRule
- `IRule`的源码
- `IRule`接口定义了3个方法
- 主要方法是
- IRule的实现类
- 八种常见的负载均衡策略
- 负载均衡的自定义
- 通过代码实现 - 配置类
- 同时使用2种以上的不同策略算法
- 移除@Configuration 注解
- 操作处理方式
- 通过配置配置文件实现不同的算法
- 如何对负载均衡策略进行扩展
- 继承 AbstractLoadBalancerRule 类
- 通过配置文件
- 总结分析
什么是负载均衡
负载均衡是通过将请求流量分发到多个服务器来实现资源分配的一种策略。它可以确保各个服务器在处理请求方面的负载均衡,并能够更高效地利用系统资源。负载均衡的主要目标是避免服务器过载,并通过在不同的服务器之间分发负载,提高系统的可伸缩性和可用性。
负载均衡的种类
通过负载均衡,我们可以在服务器集群中有效地分配请求,从而实现更快的响应时间和更好的用户体验。目前负载均衡的方式分类主要有两种:服务器端负载均衡(nginx)和客户端负载均衡(Ribbon)

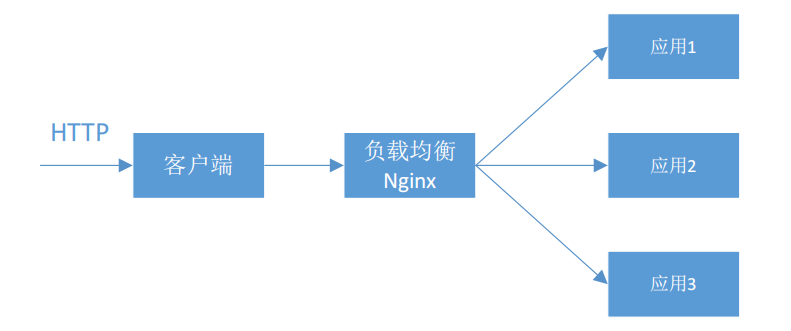
服务器端负载均衡(S-LB)
服务器端负载均衡(如Nginx)是一种将请求流量分发到多个服务器的方法,以提高系统的性能和可靠性。通过将请求分发到不同的服务器,负载均衡可以避免单个服务器的过载,并能够更均衡地分配请求负载,从而提高整体的响应能力。
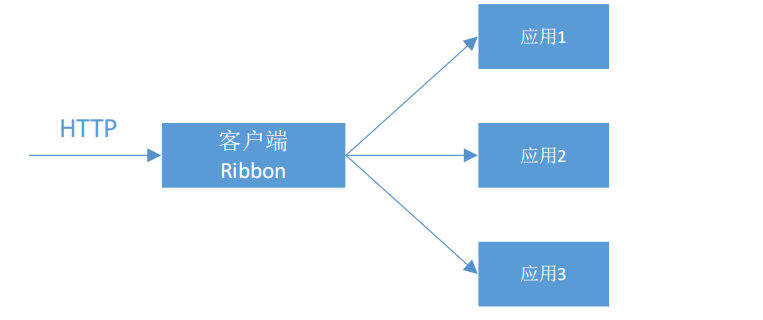
客户端负载均衡(C-LB)
客户端负载均衡(如Ribbon)是在客户端层面上进行的负载均衡。当客户端发起请求时,通过负载均衡算法,Ribbon可以选择最合适的服务器来处理请求。这种方式使得客户端可以根据实际情况选择最佳的服务器,提高了系统的可扩展性和容错性。
注解@LoadBalanced
作用:识别应用名称,并进行负载均衡。
在Spring Cloud应用中,使用RestTemplate进行服务间的通讯时,我们可以添加@LoadBalanced注解来开启负载均衡。
在一个微服务架构中,通常一个服务会有多个实例,并且这些实例部署在不同的服务器上。为了保证服务的高可用性,我们需要在这些实例之间进行负载均衡。Spring Cloud提供了@LoadBalanced注解,它可以在RestTemplate中实现负载均衡:
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfiguration {@LoadBalanced // 使用 @LoadBalanced 注解实现负载均衡@Beanpublic RestTemplate restTemplate() {return new RestTemplate();}}
在RestTemplate添加了@LoadBalanced注解之后,我们就可以直接使用服务名来调用其他服务,而不再需要关心具体的IP和端口号。
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;public String runTaskExecute() {return restTemplate.getForObject("http://serviceName/execute", String.class);
}
当发起请求时,Ribbon会自动从服务注册中心获取serviceName的所有实例,然后根据负载均衡策略选择一个实例进行调用,这样就实现了负载均衡。默认负载均衡策略是基于轮询算法,平均分配请求给每个服务实例。
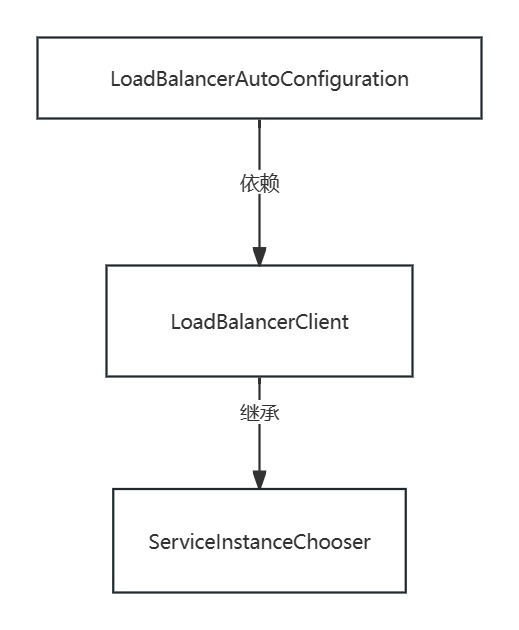
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类
Ribbon的负载均衡自动配置需满足两个条件:
- RestTemplate类必须在当前项目的环境中可用,
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class) - Spring的Bean工厂中必须存在LoadBalancerClient的实现类的Bean实例。
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
下面是LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration的源码:
/*** Auto configuration for Ribbon (client side load balancing).* @author Spencer Gibb* @author Dave Syer* @author Will Tran*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {@LoadBalanced@Autowired(required = false)private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList();@Beanpublic SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializer(final List<RestTemplateCustomizer> customizers) {return new SmartInitializingSingleton() {@Overridepublic void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) {for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) {customizer.customize(restTemplate);}}}};}
}
LoadBalancerClient类
LoadBalancerClient的接口的定义,该接口在Spring Cloud中被用来实现客户端的负载均衡。它是一个Spring Cloud特有的接口,扩展自ServiceInstanceChooser接口。这个接口定义了如何从服务注册中心获取服务实例并对其进行负载均衡。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;/*** Represents a client side load balancer.* * @author Spencer Gibb*/
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser {/*** Execute request using a serviceInstance from the LoadBalancer for the specified service.** @param serviceId the service id to look up the LoadBalancer* @param request allows implementations to execute pre and post actions such as incrementing metrics* @return the result of the LoadBalancerRequest callback on the selected ServiceInstance */<T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;/*** Execute request using a ServiceInstance from the LoadBalancer for the specified service.** @param serviceId the service id to look up the LoadBalancer* @param serviceInstance the service to execute the request to* @param request allows implementations to execute pre and post actions such as incrementing metrics* @return the result of the LoadBalancerRequest callback on the selected serviceInstance */<T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;/*** Create a proper URI with a real host and port for systems to utilize.* Some systems use a URI with the logical service name as the host, such as http://myservice/path/to/service.* This will replace the service name with the host:port from the serviceInstance.** @param instance* @param original a URI with the host as a logical service name* @return a reconstructed URI*/URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original);
}源码分析
这些方法主要在客户端向服务端发起请求时使用,以实现负载均衡的效果:
-
execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException:负载均衡器选择的服务实例执行请求。serviceId是要查找负载均衡器的服务的id,request参数让实现类在服务调用前后执行一些操作,如度量增量等。 -
execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException:增加了serviceInstance参数,该参数表示要执行请求的服务,是在已经选择了服务实例后执行请求。 -
reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original):一些系统使用的是逻辑服务名作为主机的URI,如http://myservice/path/to/service,这种URI中的主机名不是真实的网络地址,而是服务名。
在基于服务名进行路由的微服务系统,为了获取实际的网络地址(host:port),就需要这个转换方法,把逻辑服务名替换为从服务实例获取的真实主机名和端口。
ServiceInstanceChooser类
接口ServiceInstanceChooser,该接口在Ribbon中被用作负载均衡策略的接口,应用可以实现这个接口来自定义自己的负载均衡策略。在这个接口中定义了一个choose方法,该方法用于从负载均衡器中为特定服务选择一个服务实例。
/*** Implemented by classes which use a load balancer to choose a server to* send a request to.** @author Ryan Baxter*/
public interface ServiceInstanceChooser {/*** Choose a ServiceInstance from the LoadBalancer for the specified service.** @param serviceId the service id to look up the LoadBalancer* @return a ServiceInstance that matches the serviceId*/ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId);
}
负载均衡器具备以下几个主要职能:

-
能够根据特定的服务ID从负载均衡器中选取一个合适的服务实例。
-
能够利用选取的服务实例执行特定的任务或请求。
-
能够为系统生成一个有效的“主机名:端口号”格式的URI,以便于系统的其他部分使用。
内置负载均衡策略的介绍
IRule
IRule是Ribbon客户端内置负载均衡策略的接口定义,所有Ribbon内建策略或者自定义策略都需要实现这个接口。它主要的决定了服务选择的策略,即根据什么样的规则从一组服务中选取一个有效的服务实例。
IRule的源码
package com.netflix.loadbalancer;/** The class that will be used by clients of Ribbon API to pick a server from* the already filtered list of servers. The responsibility of implementations* will be to spread the load of request traffic among the list of servers.*/
public interface IRule {/** set load balancer** @param lb*/public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);/** get load balancer** @return*/public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();/** Choose a server from load balancer.** @param key An object that the load balancer may use to determine* which server to return. key is defined by client, and* can be anything. load balancer implementations may* choose to return a server based on key or not.** @return server chosen*/public Server choose(Object key);
}
IRule接口定义了3个方法
setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb): 用来设置负载均衡器。getLoadBalancer(): 用来获取负载均衡器。choose(Object key): 用来从已经过滤过的服务列表中选择合适的服务。key参数是由客户端定义的,可以是任何对象。实现此接口的类可以选择根据key选择服务,也可以忽略key。
主要方法是
public abstract Server choose(Object key);
- 出参:
Server:这是Ribbon定义的一个类,代表了一个可以达到的、执行某个服务的物理或者虚拟的实例。 - 入参:
choose(Object key):此方法根据传入的key(key的具体含义根据实现类的解读可能有所不同),选择并返回一个Server。
IRule的实现类
当你实现IRule接口时,你可以自己定义服务选择的规则,比如你可以根据服务的实际情况(如服务器负载、网络延迟等信息)来选择最符合你需求的服务,创建出定制化的负载均衡策略。
八种常见的负载均衡策略
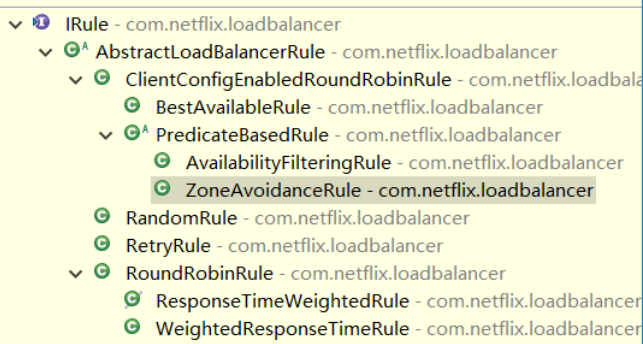
八种常见的负载均衡策略(BestAvailableRule、AvailabilityFilteringRule等)都是IRule的实现类,每种策略都有自己独特的服务选择规则。
| 策略名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BestAvailableRule | 该策略选择并发请求最少的server。若某个Server处于熔断状态,将忽略该Server。 |
| AvailabilityFilteringRule | 过滤掉连续连接失败被标记为熔断的Server,以及并发连接高的Server。 |
| ZoneAvoidanceRule | 复合判断Server所在区域的性能和Server的可用性来选择Server,剔除不可用的区域的所有Server和连接数过多的Server。 |
| RandomRule | 随机策略,会在所有可用的Server中进行随机选择。 |
| RetryRule | 为选定的负载均衡策略添加重试机制。在配置的时间段内若无法成功选择Server,将会持续重试。 |
| RoundRobinRule | 轮询策略,每次请求会轮询选择一个Server。此为默认策略。 |
| WeightedResponseTimeRule | 根据响应时间分配权重,响应时间较长的Server权重越小,被选中的可能性越低。 |
| ResponseTimeWeightedRule | 与WeightedResponseTimeRule一致,是其旧版本名称。 |
负载均衡的自定义
通过代码实现 - 配置类
仅需两个简洁的配置,即可确定轮询的策略。
@Configuration
public class RandomRuleConfig {@Beanpublic IRule randomRule() {return new RandomRule();}
}@Configuration
@RibbonClient(name = "client-balance-provider", configuration = RandomRuleConfig.class)
public class ProviderConfiguration {
}
注意,如果在
RandomRuleConfig类中添加了@Configuration注解,所有的负载均衡策略将被覆盖。这是因为如果RandomRuleConfig类被SpringContext扫描到,这会导致所有的策略被@RibbonClients共享,从而实现覆盖。
同时使用2种以上的不同策略算法
移除@Configuration 注解
以下是整理和优化后的代码:
// Define the round robin rule configuration.
public class RoundRobinRuleConfig {@Beanpublic IRule roundRobinRule() {return new RoundRobinRule();}
}
RoundRobinRuleConfig类定义了roundRobinRule方法,该方法生成了RoundRobinRule的实例,表示采用轮询负载均衡策略。
// The configuration class for the Ribbon client.
@Configuration
@RibbonClient(name = "spring-cloud-provider2", configuration = RoundRobinRuleConfig.class)
public class Provider2Configuration {}
Provider2Configuration类则是spring-cloud-provider2服务的Ribbon配置类,该类指定在调用spring-cloud-provider2服务时,使用RoundRobinRuleConfig类中定义的轮询策略。
操作处理方式
需要新增RoundRobinRuleConfig类,并移除其中的@Configuration注解。同时,也要移除RandomRuleConfig类中的@Configuration注解。
-
可以通过指定
@ComponentScan的扫描路径实现(默认情况下,扫描路径为主类所在的所有文件夹)。 -
将
RoundRobinRuleConfig类移至主类之外,防止主程序进行扫描,一定要确保SpringContext无法扫描到这些类。
通过配置配置文件实现不同的算法
通过配置文件,可以让应用来灵活的选择不同的负载均衡策略。设置格式为:<application-name>.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=<fully-qualified-class-name>。
这样就可以根据应用的实际需要,选择最适合的负载均衡策略。
#设置策略
spring-cloud-provider.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
#spring-cloud-provider2.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
如何对负载均衡策略进行扩展
当内置的负载均衡策略不满足业务需求的时候,我们就需要自定义 Ribbon 的负载策略。
继承 AbstractLoadBalancerRule 类
扩展了AbstractLoadBalancerRule`抽象类,用于定义自定义的负载均衡规则。这个规则是,从所有可用的服务实例(upList)中,选择端口为7779的服务实例为提供服务的实例。如果没有找到,或者选中的实例已经不可用,则重新选择。如果因为线程中断导致获取服务实例错误,直接返回null。
/*** Custom Ribbon load balancing strategy.*/
public class RoncooCustomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {private Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {if (lb == null) {return null;}Server server = null;while (server == null) {if (Thread.interrupted()) {return null;}// Available service instancesList<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();// Only fetch service instance with port: 7779for (Server s : upList) {if (s.getPort() == 7779) {server = s;break;}}if (server == null) {Thread.yield();continue;}if (server.isAlive()) {return server;}server = null;Thread.yield();}return server;}@Overridepublic Server choose(Object key) {return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);}@Overridepublic void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) {// No-Operation}
}
通过配置文件
spring-cloud-provider.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.roncoo.education.configuration.RoncooCustomRule
总结分析
Ribbon是Netflix开发的一款基于HTTP和TCP的客户端负载均衡器。它在Spring Cloud环境中广泛使用于执行HTTP请求的负载均衡,其主要知识点和技术特性包括:
-
客户端负载均衡:Ribbon是一个客户端的负载均衡器,这意味着它会在客户端运行,并在发起请求时对一组服务实例进行选择。
-
灵活的负载均衡策略:Ribbon内置了多种负载均衡策略,如轮询、随机、响应时间加权等。用户也可以自定义策略以满足特殊要求。
-
故障转移:在访问某个服务实例失败时,Ribbon可以自动选择另一个实例进行访问,以提高系统的可用性。
-
扩展性良好:Ribbon的结构让它可以方便地扩展和定制,以支持各种各样的需求。






)
)









具体图片等下载资源)


