目录
1 安装face_recognition
2 涉及的函数
3 人脸识别方案
4 实践
使用face_recognition进行人脸识别。
1 安装face_recognition
pip install face_recognition或者
pip --default-timeout=100 install face_recognition -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com第二种方式安装得更快。
2 涉及的函数
- face_recognition.api.load_image_file()函数
face_recognition.api.load_image_file(file, mode='RGB')函数功能:下载图片文件(.jpg .png等)转成numpy array。
输入:
①file:要加载的图像文件名或文件对象
②mode:将图像转换成的格式。支持“RGB”(8位,3通道)和“L”(黑白)
返回:
①Numpy array 的图像内容。
- face_recognition.api.face_locations()函数
face_recognition.api.face_locations(img,number_of_times_to_upsample=1, model='hog')函数功能:返回图片中所有人脸的Bbox(array)
输入:
①img:输入的图片(numpy array)
②number_of_times_to_upsample:上采样的次数,次数越多越能找到更小的人脸。
③model:“hog”为默认;“hog”在上不精准,但是快。“cnn”是更精准的深度学习模型,需要GPU/CUDA加速。
返回:
①人脸定位元组(top, right, bottom, left)的List。
- face_recognition.api.face_encodings()函数
face_recognition.api.face_encodings(face_image, known_face_locations=None, num_jitters=1)函数功能:图像中的每张人脸返回128维的人脸编码。
输入:
①face_image:包含一张或者更多张人脸的图片
②known_face_locations:-可选-每个人脸的Bbox(已知)
③num_jitters:编码时重采样的次数。越高越准确,但是速度会慢些。
返回:
①128维的人来你编码List(图像中的每张脸都有)。
- face_recognition.api.face_distance()函数
face_recognition.api.face_distance(face_encodings, face_to_compare)输入:
①face_encodings:人脸编码List。
②face_to_compare:用来比较的一个人脸编码。
返回:
①与人脸编码List顺序相同的距离array。
3 人脸识别方案
①制作人脸库。
knownImg文件夹下有如下几张图片。依次读取文件夹中的图片,定位人脸,将人脸区域编码并存于face_encoding_list中。图片的名字依次存于label_list中。也就是说face_encoding_list中的人脸编码结果与label_list中的名字是一一对应的。

本文中,get_Known_faces_info()函数实现这一功能。
def get_Known_faces_info(dir_path): face_encoding_list = [] label_list = [] for imgs_name in os.listdir(dir_path): img = face_recognition.load_image_file(dir_path + imgs_name) print(dir_path + imgs_name) face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(img) face_encodings = [] face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(img, face_locations) if len(face_encodings) != 0: face_encodings = face_encodings[0] face_encoding_list.append(face_encodings) label_list.append(imgs_name[:-4]) return face_encoding_list, label_list ②人脸识别
首先,读取输入的图像test.png,将图像中的所有人脸检测出来并将人脸区域编码。将每一个待识别的编码结果与人脸库的face_encoding_list对比并得出与人脸编码List顺序相同的距离结果。min_index为距离最小值对应的索引。选取数值最小的距离与阈值进行比较。如果小于阈值,则该人脸的标签为label_list[min_index]。如果大于阈值,则这一人脸编码对应的标签为Unknown,即人脸库中没有这一人脸数据,因此无法识别。
然后,将识别结果展示出来。
本文中,dealImageResult()函数实现这一功能。
def dealImageResult(unknown_face_path, face_encoding_list, label_list, face_threshold): im = cv2.imread(unknown_face_path) unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file(unknown_face_path) face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(unknown_image) face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(unknown_image, face_locations) face_names = [] for i, face_encoding in enumerate(face_encodings): name = "Unknown" face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(face_encoding_list, face_encoding) min_index = np.argmin(face_distances) if face_distances[min_index] < face_threshold: name = label_list[min_index] face_names.append(name) # Display the results for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names): # Draw a box around the face cv2.rectangle(unknown_image, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.rectangle(unknown_image, (left, bottom), (right, bottom + 30), (0, 255, 255), cv2.FILLED) font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX cv2.putText(unknown_image, name, (left + 6, bottom + 25), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1) im = dealImg(im) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) titles = ["img", "result"] images = [im, unknown_image] for i in range(2): plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1), plt.imshow(images[i], "gray") plt.title("{}".format(titles[i]), fontsize=20, ha='center') plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # plt.subplots_adjust(left=None, bottom=None, right=None, top=None, wspace=0.3, hspace=0) # plt.tight_layout() plt.show() fig.savefig('test_results.jpg', bbox_inches='tight') 4 实践
- 代码
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import face_recognition
import os
def dealImg(img):b, g, r = cv2.split(img)img_rgb = cv2.merge([r, g, b])return img_rgb
def get_Known_faces_info(dir_path):face_encoding_list = []label_list = []for imgs_name in os.listdir(dir_path):img = face_recognition.load_image_file(dir_path + imgs_name)print(dir_path + imgs_name)face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(img)face_encodings = []face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(img, face_locations)if len(face_encodings) != 0:face_encodings = face_encodings[0]face_encoding_list.append(face_encodings)label_list.append(imgs_name[:-4])return face_encoding_list, label_list
def dealImageResult(unknown_face_path, face_encoding_list, label_list, face_threshold):im = cv2.imread(unknown_face_path)unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file(unknown_face_path)face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(unknown_image)face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(unknown_image, face_locations)face_names = []for i, face_encoding in enumerate(face_encodings):name = "Unknown"face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(face_encoding_list, face_encoding)min_index = np.argmin(face_distances)if face_distances[min_index] < face_threshold:name = label_list[min_index]face_names.append(name)# Display the resultsfor (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):# Draw a box around the facecv2.rectangle(unknown_image, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)cv2.rectangle(unknown_image, (left, bottom), (right, bottom + 30), (0, 255, 255), cv2.FILLED)font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEXcv2.putText(unknown_image, name, (left + 6, bottom + 25), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1)im = dealImg(im)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))titles = ["img", "result"]images = [im, unknown_image]for i in range(2):plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1), plt.imshow(images[i], "gray")plt.title("{}".format(titles[i]), fontsize=20, ha='center')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])# plt.subplots_adjust(left=None, bottom=None, right=None, top=None, wspace=0.3, hspace=0)# plt.tight_layout()plt.show()fig.savefig('test_results.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
if __name__ == '__main__':face_encoding_list, label_list = get_Known_faces_info("knownImg/")dealImageResult("test.png", face_encoding_list, label_list, 0.4)pass- 效果图
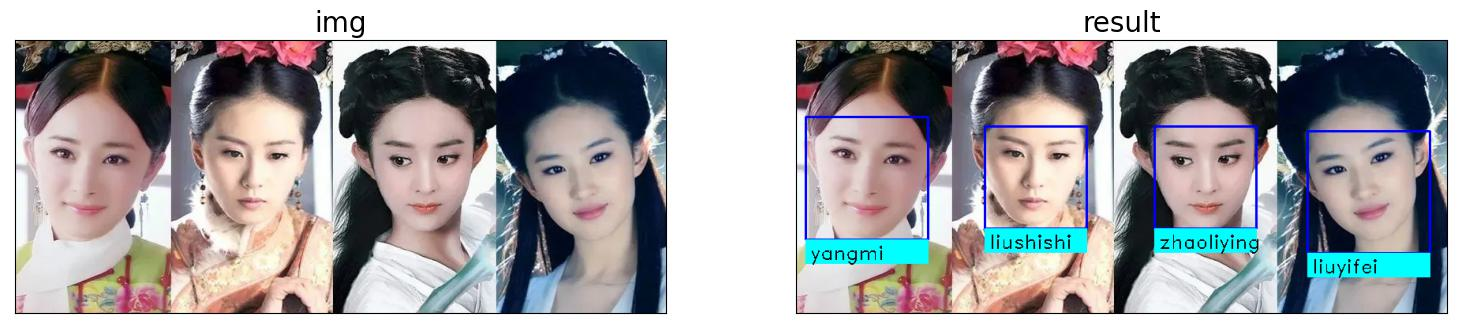
注:本文中的图片来自于网络,如有侵权,请联系作者删除。
前文回顾
入门篇目录
数字图像处理(入门篇)一 图像的数字化与表示
数字图像处理(入门篇)二 颜色空间
数字图像处理(入门篇)三 灰度化
数字图像处理(入门篇)四 像素关系
数字图像处理(入门篇)五 图像数据预处理之颜色空间转换
数字图像处理(入门篇)六 图像数据预处理之坐标变化
数字图像处理(入门篇)七 图像数据预处理之灰度变化
数字图像处理(入门篇)八 图像数据预处理之直方图
数字图像处理(入门篇)九 图像数据预处理之滤波
数字图像处理(入门篇)十 边缘检测
数字图像处理(入门篇)十一 形态学处理
数字图像处理(入门篇)十二 自适应阈值分割
数字图像处理(入门篇)十三 仿射变换
数字图像处理(入门篇)十四 透视变换
实践篇目录
数字图像处理(实践篇)一 将图像中的指定目标用bBox框起来吧!
数字图像处理(实践篇)二 画出图像中目标的轮廓
数字图像处理(实践篇)三 将两张图像按照指定比例融合
数字图像处理(实践篇)四 图像拼接-基于SIFT特征点和RANSAC方法
数字图像处理(实践篇)五 使用Grabcut算法进行物体分割
数字图像处理(实践篇)六 利用hough变换进行直线检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)七 利用霍夫变换进行圆环检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)八 Harris角点检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)九 基于边缘的模板匹配
数字图像处理(实践篇)十 图像质量检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)十一 图像中的条形码解析
数字图像处理(实践篇)十二 基于小波变换的图像降噪
数字图像处理(实践篇)十三 数据增强之给图像添加噪声!
数字图像处理(实践篇)十四 图像金字塔
数字图像处理(实践篇)十五 基于傅里叶变换的高通滤波和低通滤波
数字图像处理(实践篇)十六 基于分水岭算法的图像分割
数字图像处理(实践篇)十七 Shi-Tomasi 角点检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)十八 人脸检测
数字图像处理(实践篇)十九 漫水填充
数字图像处理(实践篇)二十 人脸特征提取

)

)

)

![[陇剑杯 2021]日志分析](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[陇剑杯 2021]日志分析)

 基于SSM 的商城购物系统(完整源代码以及开发文档))
)

:27、移除元素)






