说明:本文介绍设计模式中结构型设计模式中的,适配器模式;
插头转换器
适配器模式属于结构型设计模式,设计思想体现在结构上的。以插头转换器为例,当你需要给手机充电,但是眼前只有一个三孔插座,二脚充电器无法使用三孔插座。
这时如果有一个插头转换器,可以将二孔插头转为三脚插头,就可以解决眼前问题。这个转换器扮演的就是适配器的角色。如下:
(TwoPin,二脚插座接口,只提供二脚插头充电)
/*** 二脚插座*/
public interface TwoPin {/*** 二脚充电*/public void charge(int l, int r);
}
(ThreePin,三脚插座接口,只提供三脚插头充电)
/*** 三脚插座*/
public interface ThreePin {/*** 三脚充电*/public void charge(int l, int r, int g);
}
(Phone,手机,充电器属于二脚插头)
/*** 手机*/
public class Phone implements TwoPin{@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r) {System.out.println("手机充电中..." + l + "====" + r);}
}
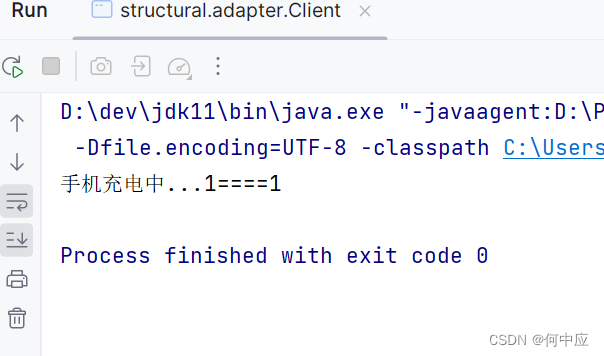
(客户端类,演示手机充电过程,二孔插头无法插入三孔插座,类型错误)

为了解决上面问题,我们可以创建一个适配器类,用来适配手机类使用三孔插座,如下:
/*** 适配器*/
public class Adapter implements ThreePin{/*** 适配器持有手机对象*/private Phone phone;/*** 适配手机使用三脚插座* @param l* @param r* @param g*/@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r, int g) {phone.charge(l, r);}
}
(Client,客户端,演示手机使用三脚插座)
/*** 客户端*/
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {// 借助适配器,手机使用三脚插座充电Phone phone = new Phone();new Adapter(phone).charge(1, 1, 0);}
}
借助适配器,手机就可以使用三脚插座了;
专属适配器
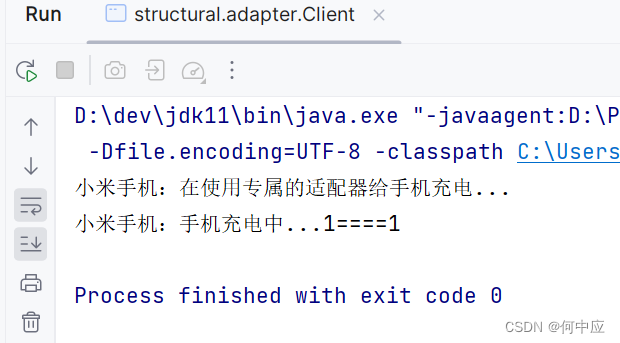
当我们想让该适配器专属于手机,而不给其他类使用时,我们可以通过继承的方式来实现。
如下:
(Phone,手机类,给手机一个name属性,表示手机的名称)
/*** 手机*/
public class Phone implements TwoPin{/*** 手机名称*/protected String name;public Phone(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r) {System.out.println(name + ":手机充电中..." + l + "====" + r);}
}
(PhoneAdapter,手机专属适配器,继承于手机,实现三脚插座接口)
/*** 手机专属适配器*/
public class PhoneAdapter extends Phone implements ThreePin{/*** 适配器持有手机对象*/private Phone phone;public PhoneAdapter(Phone phone) {super(phone.name);this.phone = phone;}@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r, int g) {System.out.println(name + ":在使用专属的适配器给手机充电...");super.charge(l, r);}(Client,客户端,演示小米手机使用手机专属的适配器,用三孔插座充电)
/*** 客户端*/
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {// 小米手机使用手机专属的适配器,用三孔插座充电Phone phone = new Phone("小米手机");new PhoneAdapter(phone).charge(1, 1, 0);}
}
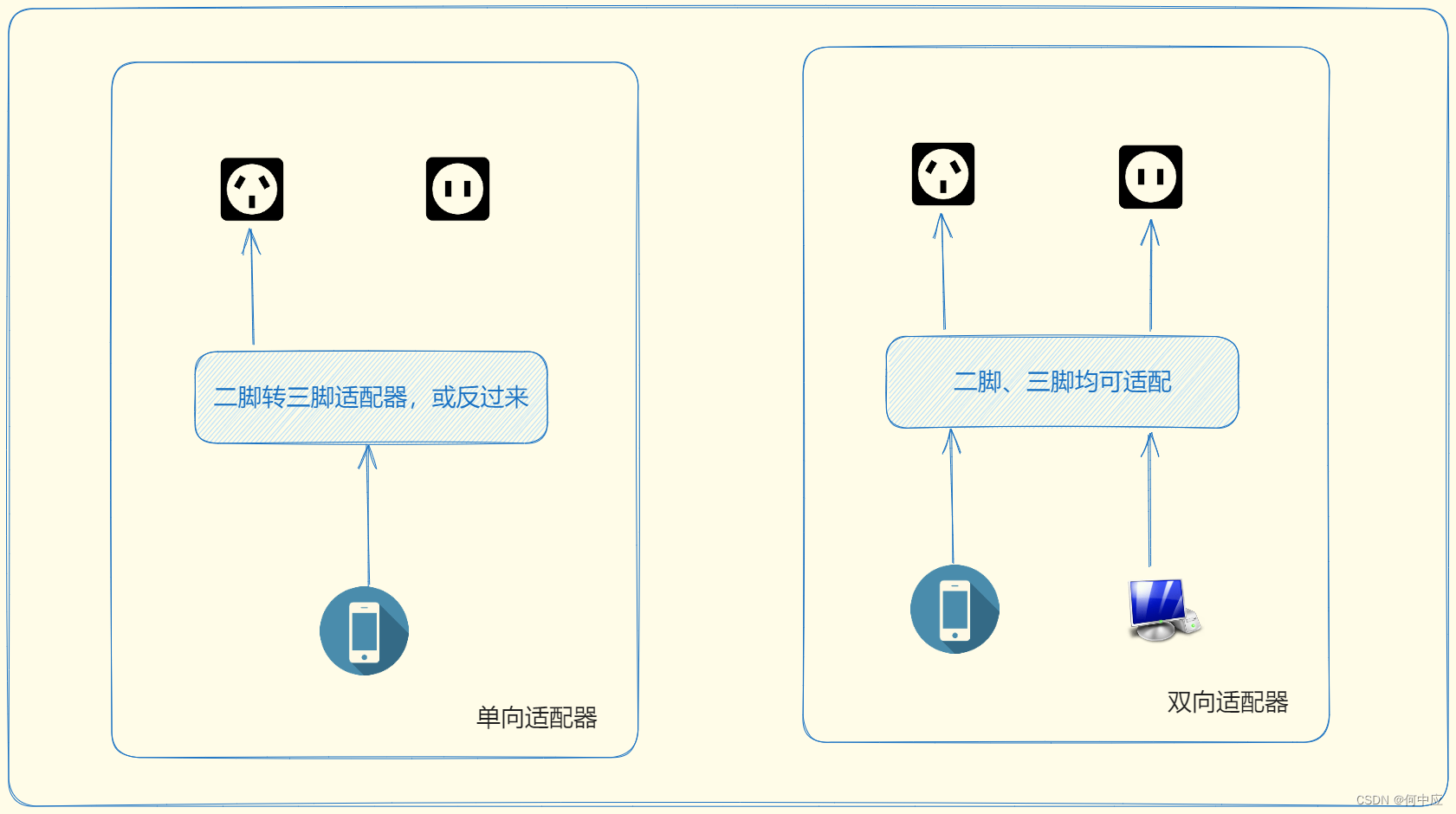
双向适配器
双向适配器,就是该适配器对二孔插头、三孔插头的充电器都可以适配,如下:
代码实现如下:
(MultipleAdapter,多重适配器,实现两个接口,注入两个对象,创建对应的两个构造方法)
/*** 多重适配器*/
public class MultipleAdapter implements ThreePin, TwoPin{/*** 三孔插座*/private ThreePin threePin;/*** 二孔插座*/private TwoPin twoPin;public MultipleAdapter(ThreePin threePin) {this.threePin = threePin;}public MultipleAdapter(TwoPin twoPin) {this.twoPin = twoPin;}/*** 三孔插座充电* @param l* @param r* @param g*/@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r, int g) {this.twoPin.charge(l, r);}/*** 二孔插座充电* @param l* @param r*/@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r) {this.threePin.charge(l, r, 0);}
}
(Computer,创建一个电脑类,使用三孔插座的)
/*** 电脑*/
public class Computer implements ThreePin{/*** 电脑名称*/protected String name;public Computer(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void charge(int l, int r, int g) {System.out.println(name + ":充电中..." + l + "====" + r + "====" + g);}
}
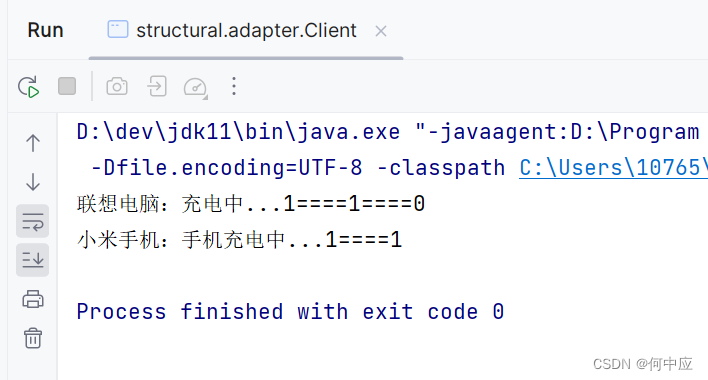
(Client,客户端,演示手机、电脑使用多重适配器给手机充电)
/*** 客户端*/
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {// 电脑使用多重适配器,用二孔插座充电Computer computer = new Computer("联想电脑");new MultipleAdapter(computer).charge(1,1);// 手机使用多重适配器,用三孔插座充电Phone phone = new Phone("小米手机");new MultipleAdapter(phone).charge(1,1,0);}
}
(不论是二孔插头还是三孔插头,都行)
以上就是适配器模式的内容,适配的思想还是非常常见的,在Java中,方法重载不正是适配器模式在方法上的一种体现吗?而适配器模式,是在类的层面上,对多种类、对象之间的一种适配。
总结
本文参考《设计模式的艺术》、《秒懂设计模式》两书

)




)




)





![[JVM 基础 - Java 类加载机制]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[JVM 基础 - Java 类加载机制])

——循环语句)