配置文件的作用
整个项目中所有重要的数据都是在配置文件中配置,如数据库的连接信息,项目的启动端口,用于发现和定位问题的普通日志和异常日志等等。配置文件可以分为两类
- 系统使用的配置文件(系统配置文件),如端口号的设置,连接数据库的配置
- 用户自定义的配置文件
配置文件的格式
Spring Boot的配置文件可以分为 .properties和 .yml两种格式。.properties属于早期时代的格式,也是Spring Boot项目的默认配置文件。当一个项目中存在两种格式的配置文件,并且两个配置文件都设置了相同的配置项,但值不同,那么properties的优先级更高。通常在一个项目中只会存在一种格式的配置文件。
properties的用法
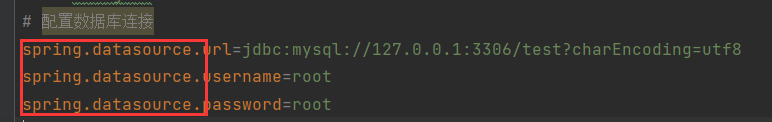
- properties是以键值的形式配置的,key和value之间用“=”连接,中间没有空格。
# 系统配置端口号
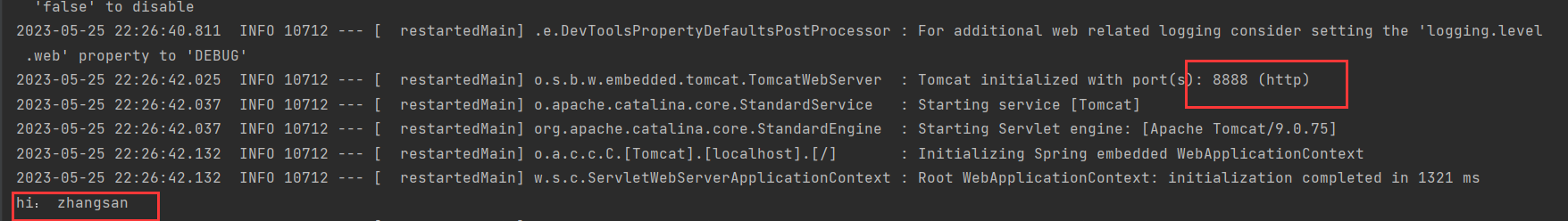
server.port=8888
# 自定义配置
name=zhangsan
- 使用@Value注解使用${}的格式读取配置文件
@RestControllerpublic class Controller {@Value("${name}")//要和配置文件中的key值相同private String name;@PostConstructpublic void sayHi() {System.out.println("hi: " + name);}}
:::info
- propertices的缺点
:::
我们发现properties有很多冗余信息,而使用yml就可以很好的解决
yml配置文件
yml的优点
- yml写法简单,可读性高
- yml支持更多数据类型,如数组,对象
- yml支持多语言
稍微规模大点的公司都开始使用微服务,像字节内部有java,go,python,php语言,只关心业务是否能够实现,使用什么语言并不关心。如果使用properties配置文件就要写多份,而yml就很好的解决了这个问题。
key: value
注意:key和value之间使用冒号和空格组成
yml版本的连接数据库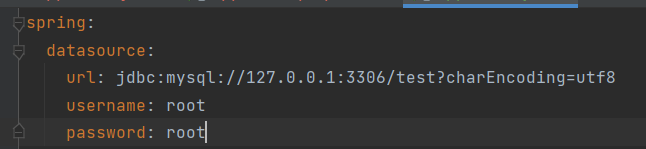
yml进阶
配置不同数据类型
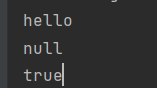
#字符串
string.value: hello
#布尔值
boolean.value: true
boolean.value2: false
#整数
int.value: 10
#浮点数
float.value: 3.14
#空值,~表示Null
null.value: ~
读取配置文件中的基础类型使用@Value(“${}”)注解
@RestControllerpublic class Controller {//要和key值对应@Value("${string.value}")private String hello;@PostConstructpublic void postConstruct() {System.out.println(hello);}@Value("${boolean.value}")private boolean bool;@PostConstructpublic void postConstruct2() {System.out.println(bool);}@Value("${null.value}")private Integer integer;@PostConstructpublic void postConstruct3() {System.out.println(integer);}}
:::success
注意:value值加单/双引号
:::
string:str1: hello \n Spring Bootstr2: 'hello \n Spring Boot'str3: "hello \n Spring Boot"
@RestController
public class Controller {@Value("${string.str1}")private String str1;@PostConstructpublic void construct1() {System.out.println("str1: " + str1);}@Value("${string.str2}")private String str2;@PostConstructpublic void construct2() {System.out.println("str2: " + str2);}@Value("${string.str3}")private String str3;@PostConstructpublic void construct3() {System.out.println("str3: " + str3);}
}
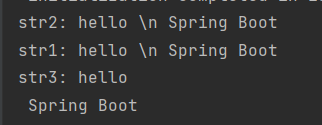
由上可知
- 字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号
- 单引号会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
- 双引号不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符,特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
配置对象
#自定义一个对象,两种写法
#student:
# id: 1
# name: zhangsan
# age: 18
student: {id: 1, name: zhangsan, age: 18}
读取配置文件中的对象使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
@Component
//三种写法
//@ConfigurationProperties(value = "student")
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@ConfigurationProperties("student")
@Data //需要提供get,set方法才能够把配置文件的信息读取出来
public class Student {//类型和名字要一一对应private int id;private String name;private int age;
}
配置集合
#自定义集合
#list:
# array:
# - 1
# - 2
# - 3
list: {array: [1,2,3]}
读取配置文件中的集合使用@ConfigurationProperties
@Component@ConfigurationProperties("list")@Datapublic class MyList {private List<Integer> array;}
properties和yml的区别
- properties是以key=value的形式进行配置,而yml是使用类json格式。
- properties为早期且默认的配置文件格式,其配置存在一定的冗余数据,使用yml可以很好的解决数据冗余的问题
- yml通用性更好,支持多种语言,例如开发一个云服务器,可以使用同一份配置文件作为java和go的共同配置文件
- yml支持更多的数据类型
设置不同环境的配置文件
在一个项目中有多种环境,如开发环境,测试环境,生产环境。每个环境的配置项都有所不同,如何让一个配置文件适应不同的环境呢?
把配置文件设为生产环境
spring:profiles:active: prod
server:port: 9999
server:port: 7777

此时使用的就是生产环境配置的端口号





)


)










