目录
一.C/C++内存分布
二. C语言中动态内存管理方式:malloc/calloc/realloc/free
三. C++内存管理方式
1.new/delete操作内置类型
2.new和delete操作自定义类型
四.C语言中的动态开辟内存空间和C++中的区别
1.对于开辟内置类型
2.对于开辟自定义类型
一.C/C++内存分布
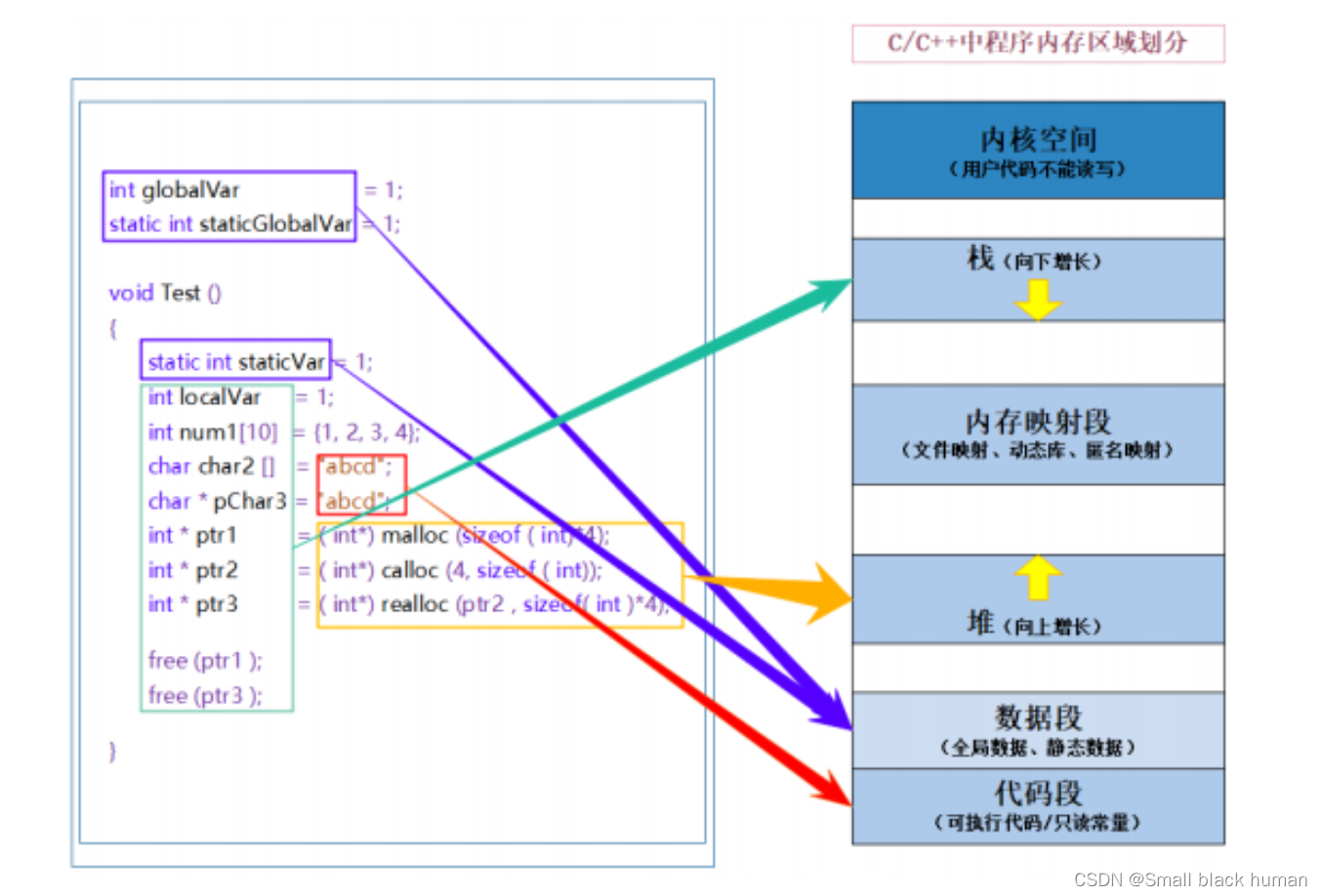
int globalVar = 1;
static int staticGlobalVar = 1;
void Test()
{static int staticVar = 1;int localVar = 1;int num1[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };char char2[] = "abcd";const char* pChar3 = "abcd";int* ptr1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 4);int* ptr2 = (int*)calloc(4, sizeof(int));int* ptr3 = (int*)realloc(ptr2, sizeof(int) * 4);free(ptr1);free(ptr3);
}
1. 选择题:选项: A.栈 B.堆 C.数据段(静态区) D.代码段(常量区)globalVar在哪里?____ staticGlobalVar在哪里?____staticVar在哪里?____ localVar在哪里?____num1 在哪里?____char2在哪里?____ *char2在哪里?___pChar3在哪里?____ *pChar3在哪里?____ptr1在哪里?____ *ptr1在哪里?____
2. 填空题:sizeof(num1) = ____; sizeof(char2) = ____; strlen(char2) = ____;sizeof(pChar3) = ____; strlen(pChar3) = ____;sizeof(ptr1) = ____;
3. sizeof 和 strlen 区别? 【说明】
1. 栈又叫堆栈--非静态局部变量/函数参数/返回值等等,栈是向下增长的。
2. 内存映射段是高效的I/O映射方式,用于装载一个共享的动态内存库。用户可使用系统接口创建共享共享内存,做进程间通信。
3. 堆用于程序运行时动态内存分配,堆是可以上增长的。
4. 数据段--存储全局数据和静态数据。
5. 代码段--可执行的代码/只读常量。
二. C语言中动态内存管理方式:malloc/calloc/realloc/free
void Test ()
{
int* p1 = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
free(p1);
// 1.malloc/calloc/realloc的区别是什么?
int* p2 = (int*)calloc(4, sizeof (int));
int* p3 = (int*)realloc(p2, sizeof(int)*10);
// 这里需要free(p2)吗?
free(p3 );
}三. C++内存管理方式
C语言内存管理方式在C++中可以继续使用,但有些地方就无能为力,而且使用起来比较麻烦,因 此C++又提出了自己的内存管理方式:通过new和delete操作符进行动态内存管理。
1.new/delete操作内置类型
void Test()
{// 动态申请一个int类型的空间int* ptr4 = new int;// 动态申请一个int类型的空间并初始化为10int* ptr5 = new int(10);// 动态申请10个int类型的空间int* ptr6 = new int[3];delete ptr4;delete ptr5;delete[] ptr6;
}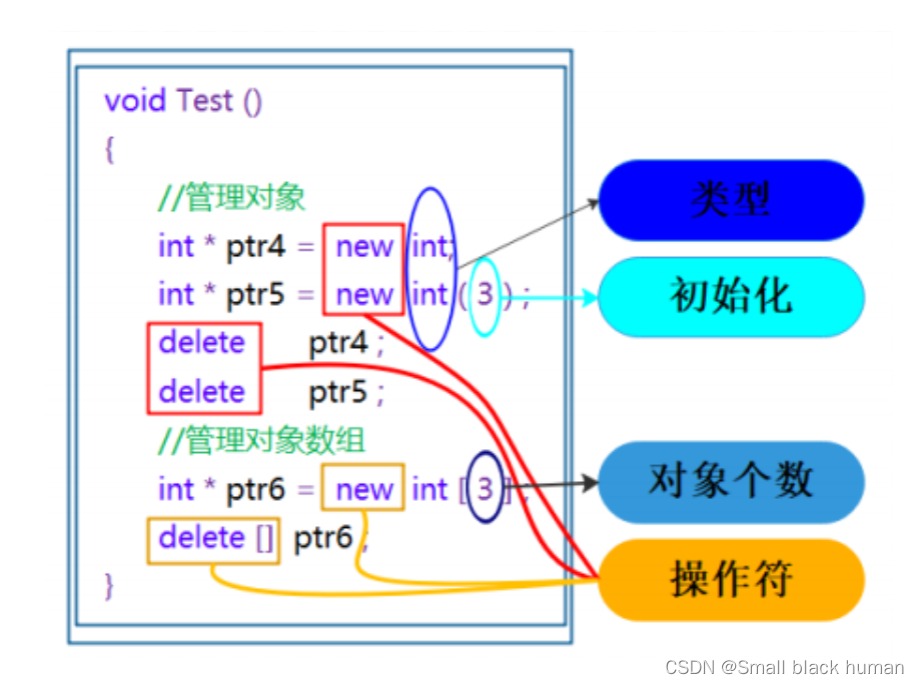
注意:申请和释放单个元素的空间,使用new和delete操作符,申请和释放连续的空间,使用 new[]和delete[],注意:匹配起来使用。
2.new和delete操作自定义类型
class A
{
public:A(int a = 0): _a(a){cout << "A():" << this << endl;
}~A(){cout << "~A():" << this << endl;}
private:int _a;
};
int main()
{// new/delete 和 malloc/free最大区别是 new/delete对于【自定义类型】除了开空间
还会调用构造函数和析构函数A* p1 = (A*)malloc(sizeof(A));A* p2 = new A(1);free(p1);delete p2;// 内置类型是几乎是一样的int* p3 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)); // Cint* p4 = new int;
free(p3);
delete p4;A* p5 = (A*)malloc(sizeof(A)*10);A* p6 = new A[10];free(p5);delete[] p6;return 0;
} 注意:在申请自定义类型的空间时,new会调用构造函数,delete会调用析构函数,而malloc与 free不会。
四.C语言中的动态开辟内存空间和C++中的区别
1.对于开辟内置类型
此时两个没有什么明显的区别。
2.对于开辟自定义类型
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Date
{friend ostream& operator<< (ostream& cout, const Date& d);public:Date(int year = 2023,int month = 12, int day = 31){_year = year ;_month = month;_day = day ;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main(void)
{Date* p1 = (Date*)malloc(sizeof(Date));Date* p2 = new Date; //此时如果没有默认构造函数会报错free(p1);delete p2;return 0;
}ostream& operator<< (ostream& cout, const Date& d)
{cout << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day << endl;return cout;
}对于new为自定义类型申请空间,首先回去调用operator new(其实在operator new中封装了malloc),然后在去调用该类构造函数对申请到的空间进行初始化。
对于delete去释放申请到的类的空间,首先去调用该类的析构函数,然后在去调用opertaor delete(其实在operator delete 中封装了free) 去销毁空间。
operator new 和operator delete就是两个全局函数。
A* p1 = (A*)malloc(sizeof);
p1是内置类型不会去主动调用类的构造函数和析构函数。
显示调用构造函数
new(p1)A;
p->~A();

)





)











