MVI架构的原理和流程
MVI架构是一种基于响应式编程的架构模式,它将应用程序分为四个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)、意图(Intent)和状态(State)。 原理:
- 模型(Model):负责处理数据的状态和逻辑。
- 视图(View):负责展示数据和用户界面。
- 意图(Intent):代表用户的操作,如按钮点击、输入等。
- 状态(State):反映应用程序的当前状态。
流程:
- 用户通过视图(View)发起意图(Intent)。
- 意图(Intent)被传递给模型(Model)。
- 模型(Model)根据意图(Intent)进行状态(State)的更新。
- 状态(State)的变化被传递给视图(View),视图(View)进行相应的界面更新。
优点:
- 单向数据流:通过单向的数据流动,可确保状态的一致性和可预测性。
- 响应式特性:MVI利用响应式编程的思想,实现了对状态变化的高效处理。
- 易于测试:由于数据流的清晰性,测试模型的行为变得更加容易。
缺点:
- 学习曲线较陡:相对于传统的MVC或MVP,MVI架构需要开发者熟悉响应式编程的概念和工具。
- 增加了一些复杂性:引入状态管理和数据流管理,可能会增加一定的复杂性。
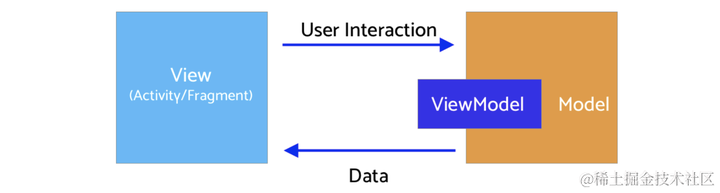
单向数据流
用户操作以Intent的形式通知Model => Model基于Intent更新State => View接收到State变化刷新UI。数据永远在一个环形结构中单向流动,不能反向流动:
一个Sample快速搭建一个MVI架构的项目
代码示例
代码结构如下:

Sample中的依赖库
// Added Dependencies
implementation "androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.1.0"
implementation 'android.arch.lifecycle:extensions:1.1.1'
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.2.0'
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.2.0'
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.11.0'//retrofit
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.8.1'
implementation "com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-moshi:2.6.2"//Coroutine
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.3.6"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.3.6"
代码中使用以下API进行请求
https://reqres.in/api/users
将得到结果:

1. 数据层
1.1 User
定义User的data class
package com.my.mvi.data.modeldata class User(@Json(name = "id")val id: Int = 0,@Json(name = "first_name")val name: String = "",@Json(name = "email")val email: String = "",@Json(name = "avator")val avator: String = ""
)
1.2 ApiService
定义ApiService,getUsers方法进行数据请求
package com.my.mvi.data.apiinterface ApiService {@GET("users")suspend fun getUsers(): List<User>
}
1.3 Retrofit
创建Retrofit实例
object RetrofitBuilder {private const val BASE_URL = "https://reqres.in/api/user/1"private fun getRetrofit() = Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(BASE_URL).addConverterFactory(MoshiConverterFactory.create()).build()val apiService: ApiService = getRetrofit().create(ApiService::class.java)}
1.4 Repository
定义Repository,封装API请求的具体实现
package com.my.mvi.data.repositoryclass MainRepository(private val apiService: ApiService) {suspend fun getUsers() = apiService.getUsers()}
2. UI层
Model定义完毕后,开始定义UI层,包括View、ViewModel以及Intent的定义
2.1 RecyclerView.Adapter
首先,需要一个RecyclerView来呈现列表结果,定义MainAdapter如下:
package com.my.mvi.ui.main.adapterclass MainAdapter(private val users: ArrayList<User>
) : RecyclerView.Adapter<MainAdapter.DataViewHolder>() {class DataViewHolder(itemView: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {fun bind(user: User) {itemView.textViewUserName.text = user.nameitemView.textViewUserEmail.text = user.emailGlide.with(itemView.imageViewAvatar.context).load(user.avatar).into(itemView.imageViewAvatar)}}override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int) =DataViewHolder(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.item_layout, parent,false))override fun getItemCount(): Int = users.sizeoverride fun onBindViewHolder(holder: DataViewHolder, position: Int) =holder.bind(users[position])fun addData(list: List<User>) {users.addAll(list)}}
item_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/container"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="60dp"><ImageViewandroid:id="@+id/imageViewAvatar"android:layout_width="60dp"android:layout_height="0dp"android:padding="4dp"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /><androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatTextViewandroid:id="@+id/textViewUserName"style="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Large"android:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_marginStart="8dp"android:layout_marginTop="4dp"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/imageViewAvatar"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/><androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatTextViewandroid:id="@+id/textViewUserEmail"android:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@+id/textViewUserName"app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textViewUserName" /></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.2 Intent
定义Intent用来包装用户Action
package com.my.mvi.ui.main.intentsealed class MainIntent {object FetchUser : MainIntent()}
2.3 State
定义UI层的State结构体
sealed class MainState {object Idle : MainState()object Loading : MainState()data class Users(val user: List<User>) : MainState()data class Error(val error: String?) : MainState()}
2.4 ViewModel
ViewModel是MVI的核心,存放和管理State,同时接受Intent并进行数据请求
package com.my.mvi.ui.main.viewmodelclass MainViewModel(private val repository: MainRepository
) : ViewModel() {val userIntent = Channel<MainIntent>(Channel.UNLIMITED)private val _state = MutableStateFlow<MainState>(MainState.Idle)val state: StateFlow<MainState>get() = _stateinit {handleIntent()}private fun handleIntent() {viewModelScope.launch {userIntent.consumeAsFlow().collect {when (it) {is MainIntent.FetchUser -> fetchUser()}}}}private fun fetchUser() {viewModelScope.launch {_state.value = MainState.Loading_state.value = try {MainState.Users(repository.getUsers())} catch (e: Exception) {MainState.Error(e.localizedMessage)}}}
}
我们在handleIntent中订阅userIntent并根据Action类型执行相应操作。本case中当出现FetchUser的Action时,调用fetchUser方法请求用户数据。用户数据返回后,会更新State,MainActivity订阅此State并刷新界面。
2.5 ViewModelFactory
构造ViewModel需要Repository,所以通过ViewModelFactory注入必要的依赖
class ViewModelFactory(private val apiService: ApiService) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {override fun <T : ViewModel?> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T {if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(MainViewModel::class.java)) {return MainViewModel(MainRepository(apiService)) as T}throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown class name")}}
2.6 定义MainActivity
package com.my.mvi.ui.main.viewclass MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {private lateinit var mainViewModel: MainViewModelprivate var adapter = MainAdapter(arrayListOf())override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)setupUI()setupViewModel()observeViewModel()setupClicks()}private fun setupClicks() {buttonFetchUser.setOnClickListener {lifecycleScope.launch {mainViewModel.userIntent.send(MainIntent.FetchUser)}}}private fun setupUI() {recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)recyclerView.run {addItemDecoration(DividerItemDecoration(recyclerView.context,(recyclerView.layoutManager as LinearLayoutManager).orientation))}recyclerView.adapter = adapter}private fun setupViewModel() {mainViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this,ViewModelFactory(ApiHelperImpl(RetrofitBuilder.apiService))).get(MainViewModel::class.java)}private fun observeViewModel() {lifecycleScope.launch {mainViewModel.state.collect {when (it) {is MainState.Idle -> {}is MainState.Loading -> {buttonFetchUser.visibility = View.GONEprogressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE}is MainState.Users -> {progressBar.visibility = View.GONEbuttonFetchUser.visibility = View.GONErenderList(it.user)}is MainState.Error -> {progressBar.visibility = View.GONEbuttonFetchUser.visibility = View.VISIBLEToast.makeText(this@MainActivity, it.error, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()}}}}}private fun renderList(users: List<User>) {recyclerView.visibility = View.VISIBLEusers.let { listOfUsers -> listOfUsers.let { adapter.addData(it) } }adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()}
}
MainActivity中订阅mainViewModel.state,根据State处理各种UI显示和刷新。
activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context=".ui.main.view.MainActivity"><androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerViewandroid:id="@+id/recyclerView"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:visibility="gone" /><ProgressBarandroid:id="@+id/progressBar"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"android:visibility="gone"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/buttonFetchUser"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="@string/fetch_user"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /></androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
如上,一个完整的MVI项目完成了。
实战讲解和代码示例
为了更好地理解MVI架构,让我们通过一个例子进行实战演示。我们将创建一个天气预报应用,展示当前天气和未来几天的天气预报信息。 在代码示例中,我们会用到以下库:
- RxJava:用于处理响应式数据流。
- LiveData:用于将数据流连接到视图。
首先,我们定义模型(Model)的状态(State)类,包含天气预报的相关信息,例如温度、湿度和天气状况等。
data class WeatherState(val temperature: Float,val humidity: Float,val condition: String
)
接下来,我们创建视图(View)界面,展示天气信息,并提供一个按钮用于刷新数据。
class WeatherActivity : AppCompatActivity() {// 初始化ViewModelprivate val viewModel: WeatherViewModel by viewModels()override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)setContentView(R.layout.activity_weather)// 监听状态变化,更新UIviewModel.weatherState.observe(this, Observer { state ->// 更新温度、湿度和天气状况的显示temperatureTextView.text = state.temperature.toString()humidityTextView.text = state.humidity.toString()conditionTextView.text = state.condition})// 刷新按钮点击事件refreshButton.setOnClickListener {// 发送刷新数据的意图viewModel.processIntent(RefreshIntent)}}
}
然后,我们创建意图(Intent)类,代表用户操作的动作。在这个例子中,我们只有一个刷新数据的意图。
object RefreshIntent : WeatherIntent
接下来,我们实现模型(Model)部分,包括状态管理和数据流的处理。
class WeatherViewModel : ViewModel() {// 状态管理private val _weatherState = MutableLiveData<WeatherState>()val weatherState: LiveData<WeatherState> = _weatherState// 处理意图fun processIntent(intent: WeatherIntent) {when (intent) {RefreshIntent -> fetchWeatherData()}}// 获取天气数据private fun fetchWeatherData() {// 发起网络请求或其他数据获取逻辑// 更新状态val weatherData = // 获取的天气数据val newState = WeatherState(temperature = weatherData.temperature,humidity = weatherData.humidity,condition = weatherData.condition)_weatherState.value = newState}
}
全文对Android中MVI的架构讲解,其中包括原理、项目演示以及实战演练。有关更多的Android架构学习进阶可以参考《Android核心技术手册》文档,点击可以查看详细的内容板块。
总结
MVI架构通过响应式数据流和单向数据流的特性,提供了一种可维护、可测试且具备响应式特性的架构模式。尽管学习曲线较陡,但在大型复杂应用开发中,MVI架构能够更好地管理状态和响应用户操作。通过合理设计状态模型和注意副作用管理,我们可以充分发挥MVI架构的优势,提升应用的可维护性和用户体验。



)













)

