这个系统是帮我一同学的哥哥的做的座位编排系统,他是某个学校的教育从事者
基本需求:就是能够根据他提供的各个分科班级同学的成绩单来选择相同分科的考场编排(按成绩高低),同时输入相应的考场数,和每个考场的人数。如果某个分科的人数超过了规定的考场数与规定的考场人数的乘积,那么就会将人数均匀的分配到前几个考场;此外还有一种情况,如果分科后的人数对每个考场的人数取余后,不为0,那么就是要将余出来的人进行均匀分配,同样往前面几个考场依次插入。
效果展示:
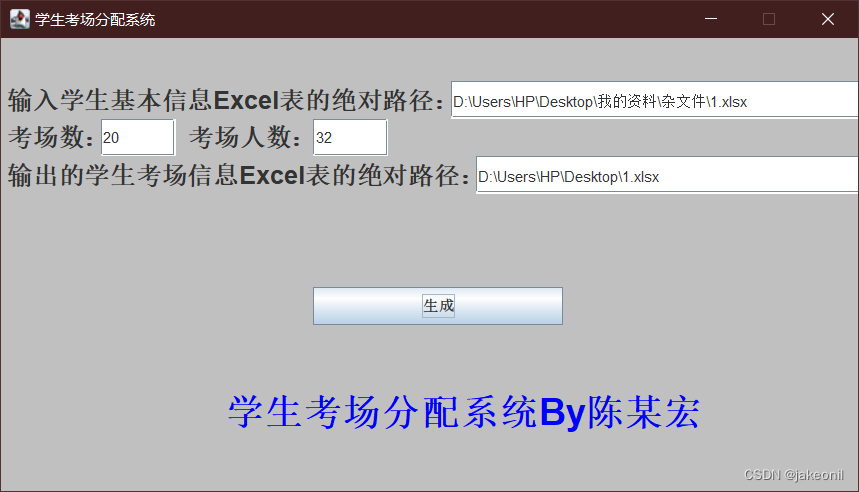
提供的excel:

输出的excel:

这里用到了aly的easyexcel
直接上代码了:
package com.csh.student_places.gui;import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.csh.student_places.entity.PlaceStudent;
import com.csh.student_places.entity.StudentInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class MainView extends JFrame {public void mainview(){//主界面的进入JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("学生考场分配系统");//创建对象jFrame.setVisible(true);//窗口的可视化jFrame.setBounds(650, 150, 700, 400);//窗口的初始化jFrame.setResizable(false);Container container = jFrame.getContentPane();container.setBackground(Color.lightGray);jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭事件container.setLayout(null);//初始化按钮信息JLabel jLabelr = new JLabel("学生考场分配系统By陈某宏");jLabelr.setFont(new Font("行书", Font.BOLD, 30));jLabelr.setForeground(Color.BLUE);jLabelr.setBounds(180, 250, 400, 100);container.add(jLabelr);JLabel label1 = new JLabel("输入学生基本信息Excel表的绝对路径:");JTextField inexcel = new JTextField();label1.setBounds(5,0,400,100);label1.setFont(new Font("行书", Font.BOLD, 20));inexcel.setBounds(360,35,500,30);JLabel inexcellable = new JLabel("考场数:");inexcellable.setBounds(5,30,100,100);inexcellable.setFont(new Font("行书", Font.BOLD, 20));JTextField numberplace = new JTextField();numberplace.setBounds(80,65,60,30);JLabel inexcellable1 = new JLabel("考场人数:");inexcellable1.setBounds(150,30,200,100);inexcellable1.setFont(new Font("行书", Font.BOLD, 20));JTextField numberperson = new JTextField();numberperson.setBounds(250,65,60,30);JLabel label2 = new JLabel("输出的学生考场信息Excel表的绝对路径:");JTextField outexcel = new JTextField();label2.setBounds(5,60,400,100);label2.setFont(new Font("行书", Font.BOLD, 20));outexcel.setBounds(380,95,500,30);JButton jButton = new JButton("生成");jButton.setBounds(250,200,200,30);container.add(jButton);container.add(label2);container.add(outexcel);container.add(inexcellable1);container.add(numberperson);container.add(numberplace);container.add(inexcellable);container.add(label1);container.add(inexcel);jFrame.update(jFrame.getGraphics());jButton.addActionListener(new AbstractAction() {@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {//点击这个按钮之后开始读取String inexcelname = inexcel.getText();//取到输入表的路径String outexcelname = outexcel.getText();//输出表的路径String numberplace1 = numberplace.getText();//考场数String numberperson1 = numberperson.getText();//考场人数int n= Integer.parseInt(numberplace1);//考场数int m= Integer.parseInt(numberperson1);//考场人数String substring = inexcelname.substring(1);String substring1 = outexcelname.substring(1);ArrayList<StudentInfo> studentInfos = new ArrayList<>();EasyExcel.read(substring, StudentInfo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<StudentInfo>() {// 每解析一行数据,该方法会被调用一次@Overridepublic void invoke(StudentInfo studentInfo, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {studentInfos.add(studentInfo);}// 全部解析完成被调用@Overridepublic void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {System.out.println("解析完成...");// 可以将解析的数据保存到数据库}}).sheet().doRead();
// System.out.println(studentInfos.toString());//拿到了学生的所有数据//进行分组int size = studentInfos.size();//拿到了所有的人数Map<String, List<StudentInfo>> studentMap1 = studentInfos.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(StudentInfo::getGroup));
// System.out.println(studentMap.toString());List<Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo>>> list = new LinkedList<>(studentMap1.entrySet());Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo>>>() {public int compare(Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo>> o1, Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo>> o2) {return o2.getKey().length() - o1.getKey().length();}});Map<String, List<StudentInfo>> studentMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();for (Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo>> entry : list) {studentMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());}ArrayList<PlaceStudent> placeStudents = new ArrayList<>();//总的排考表int testplace=1;int lastplace=1;ArrayList<ArrayList<PlaceStudent>> all = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<PlaceStudent> placeStudents1 = new ArrayList<>();//全到这个map里面了,每一个组合在一个map中,遍历整个map,取出每一个mapfor (Map.Entry<String, List<StudentInfo >> entry : studentMap.entrySet()) { //key是分组条件name//通过key取value,value是Person对象,可能有多个,用list取List<StudentInfo> list11 = (List<StudentInfo>) studentMap.get(entry.getKey());
// System.out.println(list11.toString());
// System.out.println("**********************************");int size1 = list11.size();//取到每个组合的人数System.out.println(size1);//随机打乱顺序
// Random random = new SecureRandom();
// Collections.shuffle(list11, random);// System.out.println(list11.toString());
// System.out.println("__________________________________________________________________________________");for(StudentInfo s: list11){if(s.getGrade()==null||!Character.isDigit(s.getGrade().charAt(0))){s.setGrade("0");}}list11.sort(new AgeComparator());//判断余数int lastperson = size1 % m;//剩的人int i1 = size1 / m;//看这个组合需要多少考场,向下取整这里//先排一下if(lastperson>0){i1++;}ArrayList<ArrayList<PlaceStudent>> arrayLists = newArrayList<>(i1);//这个组合的考场集合for (int i = 0; i < i1; i++) {arrayLists.add(new ArrayList<PlaceStudent>(2000)); // 向 arrayLists 中添加 i1 个空的 ArrayList<StudentInfo> 元素}int flag=0;for (int i=0;i<i1;i++){
// ArrayList<StudentInfo> studentInfos1 = new ArrayList<>();//类比于当中的一个考场for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(flag==size1){//此时已全部取完break;}PlaceStudent placeStudent = new PlaceStudent();BeanUtils.copyProperties(list11.get(flag),placeStudent);placeStudent.setPlace(testplace);//设置考场数placeStudent.setSeatnumber(j+1);if(testplace<10){if(j<9){placeStudent.setTestid(list11.get(flag).getClass1()+"0"+testplace+"0"+(j+1));}else{placeStudent.setTestid(list11.get(flag).getClass1()+"0"+testplace+(j+1));}}else{if(j<9){placeStudent.setTestid(list11.get(flag).getClass1()+testplace+"0"+(j+1));}else{placeStudent.setTestid(list11.get(flag).getClass1()+testplace+(j+1));}}arrayLists.get(i).add(placeStudent);flag++;//向下取}testplace++;}if(lastperson<=25&&lastperson!=0){//此时将人往前面考场排,向下取整的考场数int flag1=0;ArrayList<PlaceStudent> laststudentInfos = arrayLists.get(i1 - 1);//n拿到的是最后一个教室要往前排的人i1--;//减少一个考场while(lastperson>0)//还有要排的人{for(int i=0;i<i1;i++)//往前加人,除去最后一个教室{if(lastperson>0){PlaceStudent placeStudent = laststudentInfos.get(flag1);placeStudent.setPlace(lastplace+i);placeStudent.setSeatnumber(arrayLists.get(i).size()+1);//学生考号if(lastplace+i<10){placeStudent.setTestid(placeStudent.getClass1()+"0"+(lastplace+i)+placeStudent.getSeatnumber());}else{placeStudent.setTestid(placeStudent.getClass1()+(lastplace+i)+placeStudent.getSeatnumber());}arrayLists.get(i).add(placeStudent);flag1++;lastperson--;}else{testplace--;break;}}}}else{//此时不需要往前塞人了//这个考场已经排满}//再合并起来ArrayList<PlaceStudent> studentInfos1 = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<i1;i++){studentInfos1.addAll(arrayLists.get(i));}
// System.out.println(studentInfos1.toString());lastplace=testplace;all.add(studentInfos1);placeStudents1.addAll(studentInfos1);}System.out.println(placeStudents1.toString());System.out.println(all.toString());System.out.println(substring1);EasyExcel.write(substring1, PlaceStudent.class).sheet("2").doWrite(placeStudents1);}});}}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<StudentInfo> {public int compare(StudentInfo p1, StudentInfo p2) {return p2.getGrade().compareTo(p1.getGrade());}
}



![[nlp] 多语言大模型不同语种/语系数据的数据配比调节](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[nlp] 多语言大模型不同语种/语系数据的数据配比调节)




 独立模式单通道中断采集)
覆盖优化 - 附代码)




)
)


