1、C++绘制爱心图像
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>using namespace std;int main() {// 心形曲线公式 (x^2 + y^2 - a)^3 - x^2*y^3 = 0double a = 1;double bound = 1.5 * sqrt(a);double step = 0.05;for (double y = bound; y >= -bound; y -= step) {for (double x = -bound; x <= bound; x += 0.5*step) {double result = pow((pow(x,2) + pow(y, 2) - a), 3) - pow(x,2) * pow(y, 3);if(result <= 0) {cout << "*";} else {cout << " ";}}cout << "\n";}return 0;
}
2、旋转矩阵90°
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>using namespace std;int main() {// 矩阵旋转const int n = 4;int image[n][n] = {{5, 1, 8, 11},{2, 4, 8, 10},{13, 3, 6, 7},{15, 14, 12, 16}};// 矩阵转置for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {swap(image[i][j], image[j][i]);}}// 行内翻转for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n/2; j++) {swap(image[i][j], image[i][n-j-1]);}}// 输出for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cout << image[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}3、std::initializer_list<int>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class P {
public:P(int, int) {std::cout << "(int, int)" << std::endl;}P(std::initializer_list<int>) {std::cout << "(std::initializer_list<int>)" << std::endl;}
};int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {P p1(77, 5);P p2{77, 5};P r{77, 5, 42};P s = {77, 5};return 0;
}输出
(int, int)
(std::initializer_list<int>)
(std::initializer_list<int>)
(std::initializer_list<int>)#include <iostream>using namespace std;class P {
public:P(int, int) {std::cout << "(int, int)" << std::endl;}// P(std::initializer_list<int>) {// std::cout << "(std::initializer_list<int>)" << std::endl;// }
};int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {P p1(77, 5);P p2{77, 5};// P r{77, 5, 42};P s = {77, 5};return 0;
}
输出:
(int, int)
(int, int)
(int, int)
4、template
#include <iostream>using namespace std;void print() {}template<typename T, typename... Type>
void print(const T& firstArgs, const Type&... args) {std::cout << firstArgs << std::endl;print(args...);
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {print("aaaa", 1, "fefefe", 1.3, 'a');return 0;
}输出:
aaaa
1
fefefe
1.3
a下面的代码也可以:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;template <typename T>
void print(const T& arg) {std::cout << arg << std::endl;
}template<typename T, typename... Type>
void print(const T& firstArgs, const Type&... args) {std::cout << firstArgs << std::endl;print(args...);
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {print("aaaa", 1, "fefefe", 1.3, 'a');return 0;
}5、lambda表达式
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {int x = 0, y = 32;auto qqq = [x, &y]() {std::cout << "x: " << x << std::endl;std::cout << "y: " << y << std::endl;++y;};x = y = 77; //这一步y会跟新到lambda中y,但是x不会qqq();qqq();std::cout << "final y: " << y << std::endl; return 0;
}
输出:
x: 0
y: 77
x: 0
y: 78
final y: 79#include <iostream>
#include <functional>using namespace std;std::function<int(int,int)> returnLambda() {return [](int x, int y) {return x*y;};
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {auto f = returnLambda();std::cout << f(6, 7) << std::endl;return 0;
}
输出:42
6、算法
You are given numbers, an array of non-negative integers. Your task is to perform the following algorithm on this array:
step 1. Find the index i of the leftmost non-zero element numbers[i] = x != 0, if there is no such element, finish the algorithm.
step 2. Starting at index i and going to eht right, attemp to subtract x from each element.
if the element is strictly less than x, move on to step 3;
Otherwise, subtract x from the element and move on to the next element;
if you reach the end of the array, move on to the step 3;
step 3. Add x to the final result.
step 4. Go back to step 1.
import randomdef algo(num_list, x):if x <= 0:return 0final_result = 0flag_find_leftmost_x = False# 记录那些将来会被找到的num_list[i] = x的下标record_list = []# 向下传递的减法操作的次数op_times = 0for i, n in enumerate(num_list):# 找到leftmost 等于xif num_list[i] == x and not flag_find_leftmost_x:flag_find_leftmost_x = Truerecord_list.append([i, 0])op_times = 1continue# 表示减法在这里传递失败,更新可以向下传递的次数if flag_find_leftmost_x and n - op_times * x <= 0:op_times = n // x# 如果上次记录的x的后面还没有出现一个小于x的,则标记为出现,在这个题里面record_list中的元素的第二个数字并没有实际用到,# 但是如果题目稍作更改,则第二维度的数字就可以排上用场了if record_list[-1][1] == 0:record_list[-1][1] = 1# 减完之后还能够等于x,则这个位置就是下一轮能够找到的num_list[i] = x的位置elif flag_find_leftmost_x and n - op_times * x == x:op_times += 1record_list.append([i, 0])# 没有找到x,则返回0if not flag_find_leftmost_x:return final_result# print(record_list)total_len = len(record_list)final_result = total_len * xreturn final_result# 最原始的方法
def algo_complexity(num_list, x):if x <= 0:return 0total_len = len(num_list)i = 0final_result = 0# print(num_list)while i < total_len:if num_list[i] == x:flag = Falsefor j in range(i, total_len):if num_list[j] >= x:num_list[j] -= xelse:final_result += xi = -1flag = Truebreakif not flag:final_result += x# print(num_list)i += 1return final_result# num_list = [1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 2, 4, 6]
# num_list = [1, 2, 1, 1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 6]
# num_list = [1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 6]# num_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 6]
# num_list = [1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 6] # 2
# num_list = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 6] # 2 + 2
# num_list = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 4] # 2 + 2 + 2
# num_list = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 3, 4, 0, 1, 0, 2] # 2 + 2 + 2 + 2
# num_list = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 3, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0] # 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2# print(algo(num_list, 20))
# print(algo_complexity(num_list.copy(), 20))# 进行10000次测试
for i in range(10000):# 随机生成测试列表的长度list_len = random.randint(6, 500)# 随机生成列表num_list = [random.randint(1, 100) for j in range(list_len)]x = random.randint(1,100)# print("output1: ", algo(num_list, x))# print("output2: ", algo_complexity(num_list, x))a1 = algo(num_list, x)a2 = algo_complexity(num_list.copy(), x)if a1 != a2:print(a1, ",", a2)print(num_list)print(x)print("finished")7、C++解析CSV文件到vector中
CSV文件格式:a,b,c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>vector<double> getFileData(char* fileName) {vector<double> res;ifstream is(fileName);if (!is) {return res;}string temp;const char* split = ",";while(getline(is, temp)) {char* line = (char*)temp.c_str();char* data = strtok(line, split);whlie(data!=NULL) {res.push_back(atof(data));data = strtok(NULL, split);}}is.close();return res;
}8、C++异常体系

异常类定义于许多头文件中,为了能够处理标准库可能抛出的所有异常,必须包含:
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <system_error>
#include <new>
#include <ios>
#include <future>
#include <typeinfo>9、bind(), async()的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <future>
using namespace std;void func(int x, int y) {std::cout << "func" << std::endl;
}auto l = [](int x, int y) {std::cout << "lambda l" << std::endl;
};class C {
public:void operator() (int x, int y) const {std::cout << "class C operator" << std::endl;}void memfunc(int x, int y) const {std::cout << "memfunc" << std::endl;}
};int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {C c;std::shared_ptr<C> sp(new C);// bind()std::bind(func, 22, 22)(); // calls func(22, 22)std::bind(l, 22, 33)(); // calls l(22, 33)std::bind(C(), 33, 333)(); // calls C::operator()(33, 333)std::bind(&C::memfunc, c, 22, 33)(); // calls c.memfunc(22, 33)std::bind(&C::memfunc, sp, 33, 33)(); // calls sp->memfunc(33, 33)// async()std::async(func, 23, 43); // calls func(22, 43)std::async(l, 112, 32); // calls l(112, 32)std::async(c, 23, 32); // calls c.operator()(23, 32)std::async(&C::memfunc, &c, 23, 23); // calls c.memfunc(23, 23)std::async(&C::memfunc, sp, 23, 23); // calls sp->memfunc(42, 77)return 0;
}typedef std::pair<int, float> IntFloatPair;
IntFloatPair p(42, 3.14);
std::get<0>(p);
std::get<1>(p);
std::tuple_size<IntFloatPair>::value;
std::tuple_element<0, IntFloatPair>::type 10、C++用迭代器删除map元素
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {vector<int> nums{1, 2, 3};for (auto it = nums.begin(); it != nums.end(); ) {if (*it == 2) {it = nums.erase(it);} else {it++;}}for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {cout << nums[i] << " ";}map<int, int> mp{{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end();) {if(it->first == 3) {it = mp.erase(it);} else {it++;}}for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;}return 0;
}
11、map和unordered_map底层实现
unordered_map和map的区别,从算法,底层实现原理区别,效率,桶树等结构等等多个层面解析(c++角度)_unordermap和map性能比较-CSDN博客
12、从非常大的数据里面找出出现次数最多的数
经典面试问题: Top K 之 ---- 海量数据找出现次数最多或,不重复的。 - 指尖下的幽灵 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
13、connect函数HOOK
14、unique_ptr如何实现独享
C++ 智能指针unique_ptr原理与自定义实现_unique_ptr move_newchenxf的博客-CSDN博客
15、share_ptr是否线程安全?
c++11总结15——shared_ptr在多线程下的安全性问题_shared_ptr多线程-CSDN博客
所以当我们多个线程访问同一个shared_ptr时,应该要进行加锁操作。
16、线程有哪些数据是独享的
线程的共享资源与独立资源_线程独有的资源-CSDN博客
17、tuple的输出
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;// tuple的输入输出
// helper: print element with index IDX of tuple with MAX elements
template<int IDX, int MAX, typename ...Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE {static void print(std::ostream& strm, const std::tuple<Args...>& t) {strm << std::get<IDX>(t) << (IDX+1 == MAX? "": ",");PRINT_TUPLE<IDX+1, MAX, Args...>::print(strm, t);}
};
// partial specialization to end the recursion
template<int MAX, typename... Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE<MAX, MAX, Args...>{static void print(std::ostream& strm, const std::tuple<Args...>& t) {}
};// ou
template <typename... Args>
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& strm, const std::tuple<Args...> &t) {strm << "[";PRINT_TUPLE<0, sizeof...(Args), Args...>::print(strm, t);strm << "]";
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {std::tuple<int, float, string> t(44, 2.2, "more light");std::cout << "io: " << t << endl;return 0;
}18、智能指针删除器
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;// 自定义智能指针的删除器int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {// 使用lambda函数std::shared_ptr<int> p(new int[10], [](int* p) {delete []p;});std::shared_ptr<int> p1(new int[10],std::default_delete<int[]>());std::unique_ptr<int[]> p2(new int[10]); //okstd::shared_ptr<int[]> p3(new int[10]); // error// unique_ptr必须明确第二个模板参数,指出自己的deleterstd::unique_ptr<int, void(*)(int*)> p4(new int[10], [](int* p) {delete[] p;});return 0;
}指向某个文件的最后一个引用销毁时,该文件被移除:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <tuple>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;// 自定义智能指针的删除器class FileDeleter {
private:std::string filename;
public:FileDeleter(const std::string& file):filename(file){}void operator() (std::ofstream* fp) {fp->close();std::remove(filename.c_str());}
};int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {std::shared_ptr<std::ofstream> fp(new std::ofstream("tmpfile.txt"), FileDeleter("tmpfile.txt"));*fp << "ddd";return 0;
}
使用shared_ptr处理共享内存
linux 共享内存 shm_open ,mmap的正确使用-CSDN博客
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
#include <tuple>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;// 自定义智能指针的删除器
// 使用shared_ptr处理共享内存
class SharedMemoryDetacher {
public:void operator()(int* p) {std::cout << "unlink /tmp1234" << std::endl;if (shm_unlink("/tmp1234") != 0) {std::cerr << "OOPS: shm_unlink() failed" << std::endl;}}
};std::shared_ptr<int> getSharedIntMemory(int num) {void* mem;int shmfd = shm_open("/tmp1234", O_CREAT | O_RDWR, S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG);if (shmfd < 0) {throw std::string(strerror(errno));}if (ftruncate(shmfd, num*sizeof(int)) == -1) {throw std::string(strerror(errno));}mem = mmap(nullptr, num*sizeof(int), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shmfd, 0);if (mem == MAP_FAILED) {throw std::string(strerror(errno));}return std::shared_ptr<int>(static_cast<int*>(mem), SharedMemoryDetacher());
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {std::shared_ptr<int> smp(getSharedIntMemory(100));for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {smp.get()[i] = i*42;}// deal with shared memory somewhere elsestd::cout << "<return>" << std::endl;std::cin.get();smp.reset();return 0;
}19、weak_ptr的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>using namespace std;//weak_ptr
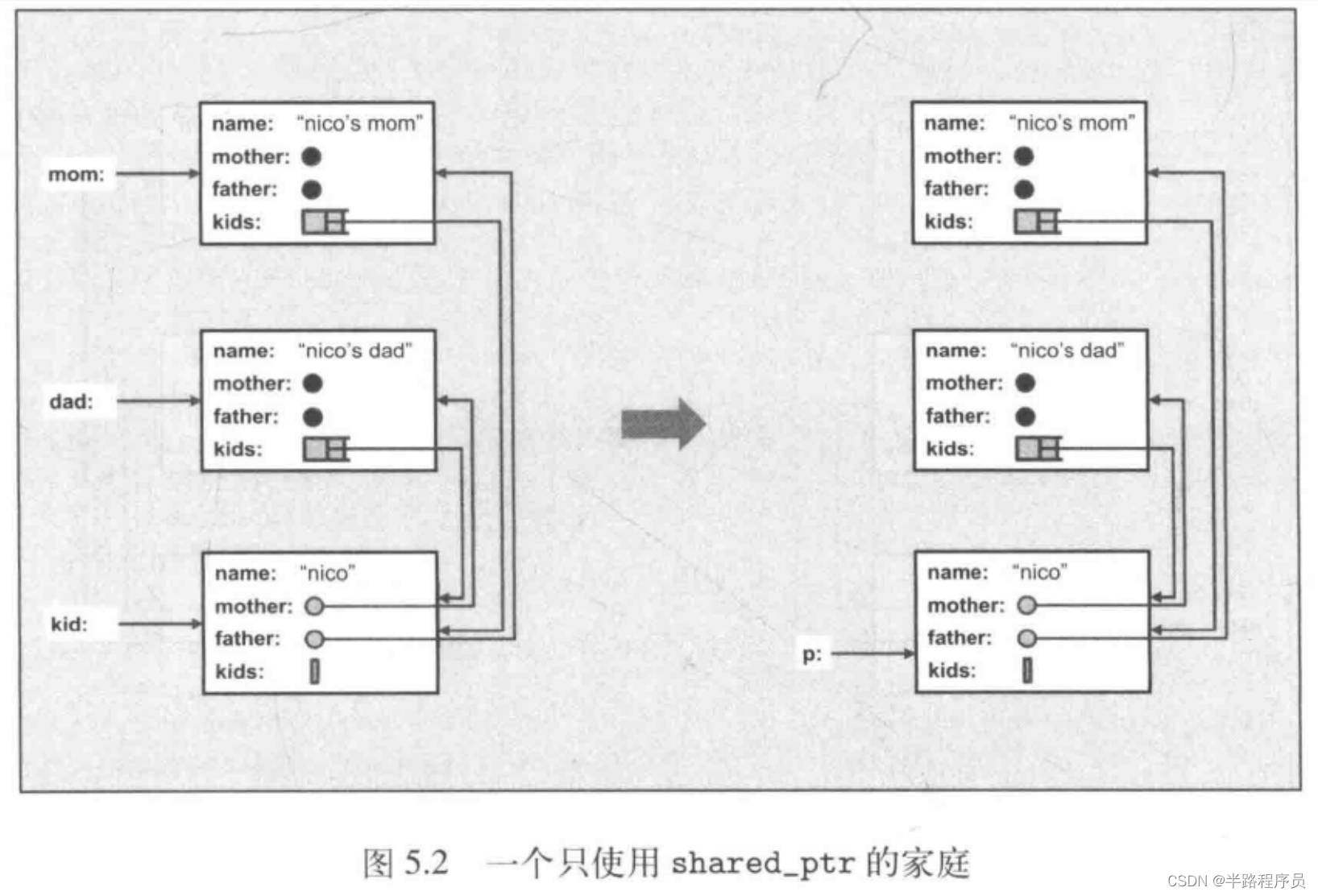
class Person {
public:string name;shared_ptr<Person> mother;shared_ptr<Person> father;vector<shared_ptr<Person>> kids;Person(const string& n, shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) :name(n), mother(m), father(f) {}~Person() {cout << "delete " << name << endl;}
};shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name) {shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom"));shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad"));shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad));mom->kids.push_back(kid);dad->kids.push_back(kid);return kid;
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico");cout << "nico's family exists" << endl;cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl;cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: "<< p->mother->kids[0]->name << endl;// 重新修改p的指向,会发现没有delete函数被调用p = initFamily("jim");cout << "jim's family exists" << endl;return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>using namespace std;//weak_ptr
class Person {
public:string name;shared_ptr<Person> mother;shared_ptr<Person> father;vector<weak_ptr<Person>> kids; //使用weak_ptrPerson(const string& n, shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) :name(n), mother(m), father(f) {}~Person() {cout << "delete " << name << endl;}
};shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name) {shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom"));shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad"));shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad));mom->kids.push_back(kid);dad->kids.push_back(kid);return kid;
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico");cout << "nico's family exists" << endl;cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl;cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: "<< p->mother->kids[0].lock()->name << endl; //使用weak_ptr时,这里需要修改,因为weak_ptr没有* ->操作符// 重新修改p的指向,会发现没有delete函数被调用p = initFamily("jim");cout << "jim's family exists" << endl;return 0;
}输出:
nico's family exists
- nico is shared 1 times
- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: nico
delete nico
delete nico's dad
delete nico's mom
jim's family exists
delete jim
delete jim's dad
delete jim's mom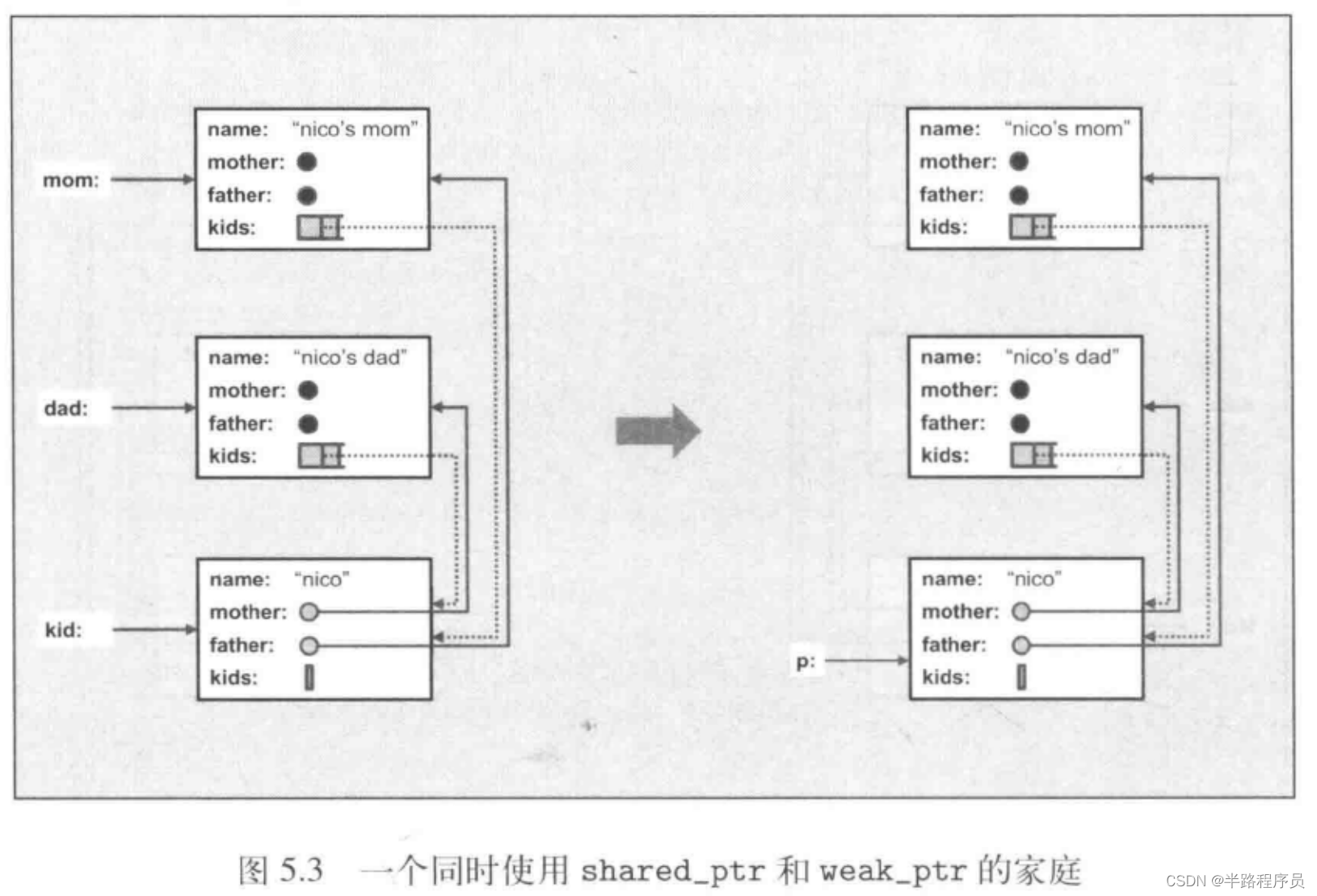
如果不确定weak_ptr背后的对象是否存活,可以使用如下三个方法检查weak_ptr
(1)调用expired(),它会在weak_ptr不再共享对象时,返回true,等同于检查use_count()是否为0.
(2)使用响应的shared_ptr构造函数明确的将weak_ptr转换为一个shared_ptr,如果对象不存在,构造函数会抛出异常bad_weak_ptr异常,其what()会产生bad_weak_ptr。
(3)调用use_count(),询问相应对象拥有者的数量,返回0表示不存在任何有效对象。
try {shared_ptr<string> sp(new string("hi"));weak_ptr<string> wp = sp;sp.reset();cout << wp.use_count() << endl; // 0cout << boolalpha << wp.expired() << endl; // trueshared_ptr<string> p(wp); // bad_weak_ptr} catch (const std::exception& e) {cerr << "exception: " << e.what() << endl;
}






)




-settings)






