1.简述
函数语法
x = lsqnonlin(fun,x0)
函数用于:
解决非线性最小二乘(非线性数据拟合)问题
解决非线性最小二乘曲线拟合问题的形式
变量x的约束上下限为ub和lb,
x = lsqnonlin(fun,x0)从x0点开始,找到fun中描述的函数的最小平方和。函数fun应该返回一个向量(或数组),而不是值的平方和。(该算法隐式地计算了fun(x)元素的平方和。)
2.代码
主程序:
%% 用lsqnonlin求解最小二乘问题
clear all
x0 = [0.3 0.4]; % 初值点
[x,resnorm] = lsqnonlin(@f1211,x0) % 调用最优化函数求 x 和 平方和残差
子程序:
function [xCurrent,Resnorm,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOB] = lsqnonlin(FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options,varargin)
%LSQNONLIN solves non-linear least squares problems.
% LSQNONLIN attempts to solve problems of the form:
% min sum {FUN(X).^2} where X and the values returned by FUN can be
% X vectors or matrices.
%
% LSQNONLIN implements two different algorithms: trust region reflective
% and Levenberg-Marquardt. Choose one via the option Algorithm: for
% instance, to choose Levenberg-Marquardt, set
% OPTIONS = optimoptions('lsqnonlin', 'Algorithm','levenberg-marquardt'),
% and then pass OPTIONS to LSQNONLIN.
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0) starts at the matrix X0 and finds a minimum X to
% the sum of squares of the functions in FUN. FUN accepts input X
% and returns a vector (or matrix) of function values F evaluated
% at X. NOTE: FUN should return FUN(X) and not the sum-of-squares
% sum(FUN(X).^2)). (FUN(X) is summed and squared implicitly in the
% algorithm.)
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,LB,UB) defines a set of lower and upper bounds on
% the design variables, X, so that the solution is in the range LB <= X
% <= UB. Use empty matrices for LB and UB if no bounds exist. Set LB(i)
% = -Inf if X(i) is unbounded below; set UB(i) = Inf if X(i) is
% unbounded above.
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,LB,UB,OPTIONS) minimizes with the default
% optimization parameters replaced by values in OPTIONS, an argument
% created with the OPTIMOPTIONS function. See OPTIMOPTIONS for details.
% Use the SpecifyObjectiveGradient option to specify that FUN also
% returns a second output argument J that is the Jacobian matrix at the
% point X. If FUN returns a vector F of m components when X has length n,
% then J is an m-by-n matrix where J(i,j) is the partial derivative of
% F(i) with respect to x(j). (Note that the Jacobian J is the transpose
% of the gradient of F.)
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(PROBLEM) solves the non-linear least squares problem
% defined in PROBLEM. PROBLEM is a structure with the function FUN in
% PROBLEM.objective, the start point in PROBLEM.x0, the lower bounds in
% PROBLEM.lb, the upper bounds in PROBLEM.ub, the options structure in
% PROBLEM.options, and solver name 'lsqnonlin' in PROBLEM.solver. Use
% this syntax to solve at the command line a problem exported from
% OPTIMTOOL.
%
% [X,RESNORM] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns
% the value of the squared 2-norm of the residual at X: sum(FUN(X).^2).
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns the value of the
% residual at the solution X: RESIDUAL = FUN(X).
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns an
% EXITFLAG that describes the exit condition. Possible values of EXITFLAG
% and the corresponding exit conditions are listed below. See the
% documentation for a complete description.
%
% 1 LSQNONLIN converged to a solution.
% 2 Change in X too small.
% 3 Change in RESNORM too small.
% 4 Computed search direction too small.
% 0 Too many function evaluations or iterations.
% -1 Stopped by output/plot function.
% -2 Bounds are inconsistent.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns a
% structure OUTPUT with the number of iterations taken in
% OUTPUT.iterations, the number of function evaluations in
% OUTPUT.funcCount, the algorithm used in OUTPUT.algorithm, the number
% of CG iterations (if used) in OUTPUT.cgiterations, the first-order
% optimality (if used) in OUTPUT.firstorderopt, and the exit message in
% OUTPUT.message.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...)
% returns the set of Lagrangian multipliers, LAMBDA, at the solution:
% LAMBDA.lower for LB and LAMBDA.upper for UB.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOBIAN] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,
% X0,...) returns the Jacobian of FUN at X.
%
% Examples
% FUN can be specified using @:
% x = lsqnonlin(@myfun,[2 3 4])
%
% where myfun is a MATLAB function such as:
%
% function F = myfun(x)
% F = sin(x);
%
% FUN can also be an anonymous function:
%
% x = lsqnonlin(@(x) sin(3*x),[1 4])
%
% If FUN is parameterized, you can use anonymous functions to capture the
% problem-dependent parameters. Suppose you want to solve the non-linear
% least squares problem given in the function myfun, which is
% parameterized by its second argument c. Here myfun is a MATLAB file
% function such as
%
% function F = myfun(x,c)
% F = [ 2*x(1) - exp(c*x(1))
% -x(1) - exp(c*x(2))
% x(1) - x(2) ];
%
% To solve the least squares problem for a specific value of c, first
% assign the value to c. Then create a one-argument anonymous function
% that captures that value of c and calls myfun with two arguments.
% Finally, pass this anonymous function to LSQNONLIN:
%
% c = -1; % define parameter first
% x = lsqnonlin(@(x) myfun(x,c),[1;1])
%
% See also OPTIMOPTIONS, LSQCURVEFIT, FSOLVE, @, INLINE.
% Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
% ------------Initialization----------------
defaultopt = struct(...
'Algorithm','trust-region-reflective',...
'DerivativeCheck','off',...
'Diagnostics','off',...
'DiffMaxChange',Inf,...
'DiffMinChange',0,...
'Display','final',...
'FinDiffRelStep', [], ...
'FinDiffType','forward',...
'FunValCheck','off',...
'InitDamping', 0.01, ...
'Jacobian','off',...
'JacobMult',[],...
'JacobPattern','sparse(ones(Jrows,Jcols))',...
'MaxFunEvals',[],...
'MaxIter',400,...
'MaxPCGIter','max(1,floor(numberOfVariables/2))',...
'OutputFcn',[],...
'PlotFcns',[],...
'PrecondBandWidth',Inf,...
'ScaleProblem','none',...
'TolFun', 1e-6,...
'TolFunValue', 1e-6, ...
'TolPCG',0.1,...
'TolX',1e-6,...
'TypicalX','ones(numberOfVariables,1)',...
'UseParallel',false );
% If just 'defaults' passed in, return the default options in X
if nargin==1 && nargout <= 1 && strcmpi(FUN,'defaults')
xCurrent = defaultopt;
return
end
if nargin < 5
options = [];
if nargin < 4
UB = [];
if nargin < 3
LB = [];
end
end
end
problemInput = false;
if nargin == 1
if isa(FUN,'struct')
problemInput = true;
[FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options] = separateOptimStruct(FUN);
else % Single input and non-structure.
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InputArg'));
end
end
% No options passed. Set options directly to defaultopt after
allDefaultOpts = isempty(options);
% Prepare the options for the solver
options = prepareOptionsForSolver(options, 'lsqnonlin');
% Set options to default if no options were passed.
if allDefaultOpts
% Options are all default
options = defaultopt;
end
if nargin < 2 && ~problemInput
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:NotEnoughInputs'))
end
% Check for non-double inputs
msg = isoptimargdbl('LSQNONLIN', {'X0','LB','UB'}, ...
xCurrent,LB, UB);
if ~isempty(msg)
error('optim:lsqnonlin:NonDoubleInput',msg);
end
caller = 'lsqnonlin';
[funfcn,mtxmpy,flags,sizes,~,xstart,lb,ub,EXITFLAG,Resnorm,FVAL,LAMBDA, ...
JACOB,OUTPUT,earlyTermination] = lsqnsetup(FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options,defaultopt, ...
allDefaultOpts,caller,nargout,length(varargin));
if earlyTermination
return % premature return because of problem detected in lsqnsetup()
end
xCurrent(:) = xstart; % reshape back to user shape before evaluation
% Catch any error in user objective during initial evaluation only
switch funfcn{1}
case 'fun'
try
initVals.F = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
initVals.J = [];
case 'fungrad'
try
[initVals.F,initVals.J] = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
case 'fun_then_grad'
try
initVals.F = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
try
initVals.J = feval(funfcn{4},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidJacobFun')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
otherwise
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:UndefCallType'))
end
% Check for non-double data typed values returned by user functions
if ~isempty( isoptimargdbl('LSQNONLIN', {'F','J'}, initVals.F, initVals.J) )
error('optim:lsqnonlin:NonDoubleFunVal',getString(message('optimlib:commonMsgs:NonDoubleFunVal','LSQNONLIN')));
end
% Flag to determine whether to look up the exit msg.
flags.makeExitMsg = logical(flags.verbosity) || nargout > 4;
[xCurrent,Resnorm,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOB] = ...
lsqncommon(funfcn,xCurrent,lb,ub,options,defaultopt,allDefaultOpts,caller,...
initVals,sizes,flags,mtxmpy,varargin{:});
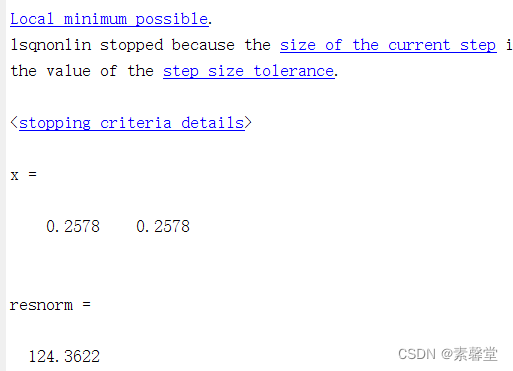
3.运行结果






![flag{网鼎杯之java代码审计入门} - file-in-java[ctf]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/flag{网鼎杯之java代码审计入门} - file-in-java[ctf])
对音频数据(城市声音)进行分类(Matlab代码实现))









)

(中---实验介绍))