文章目录
- 图像轮廓
- 查找轮廓
- 绘制轮廓
- 轮廓的面积与周长
- 多边形逼近与凸包
- 外接矩形
- 项目总览【车辆统计】
- 视频加载【车辆统计】
- 去背景【车辆统计】
- 形态学处理【车辆统计】
- 逻辑处理【车辆统计】
- 显示信息【车辆统计】
图像轮廓

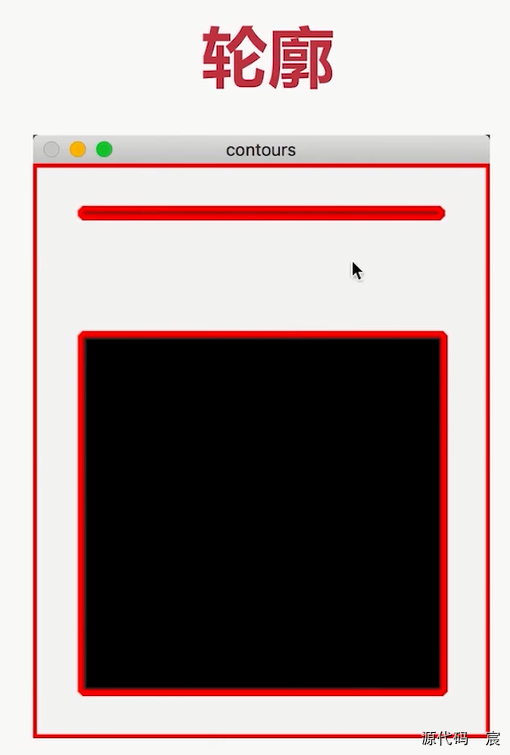








查找轮廓
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('./contours1.jpeg')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
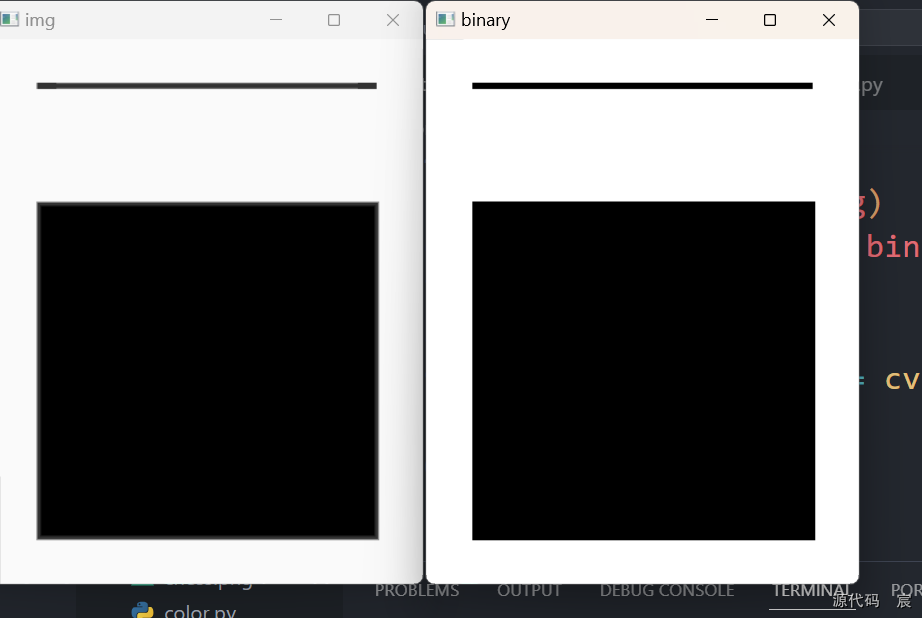
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)cv2.imshow('img', img)
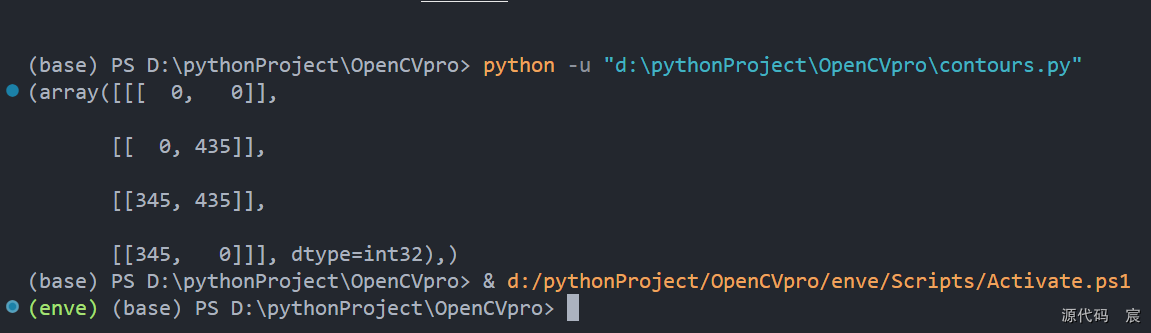
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)# 轮廓查找
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)print(contours)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
绘制轮廓

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('./contours1.jpeg')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
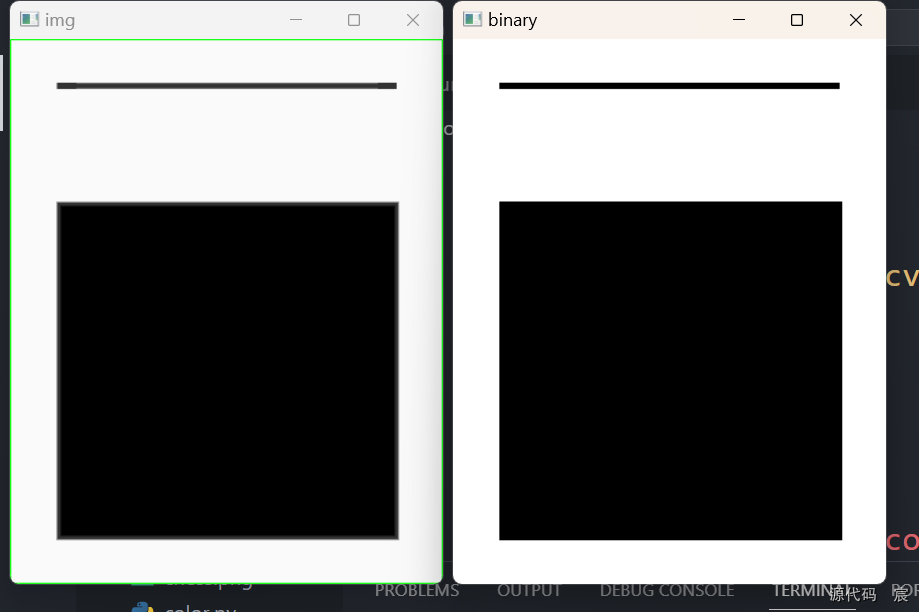
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)print(contours)# 绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
详细可参考官方资料
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('./contours1.jpeg')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
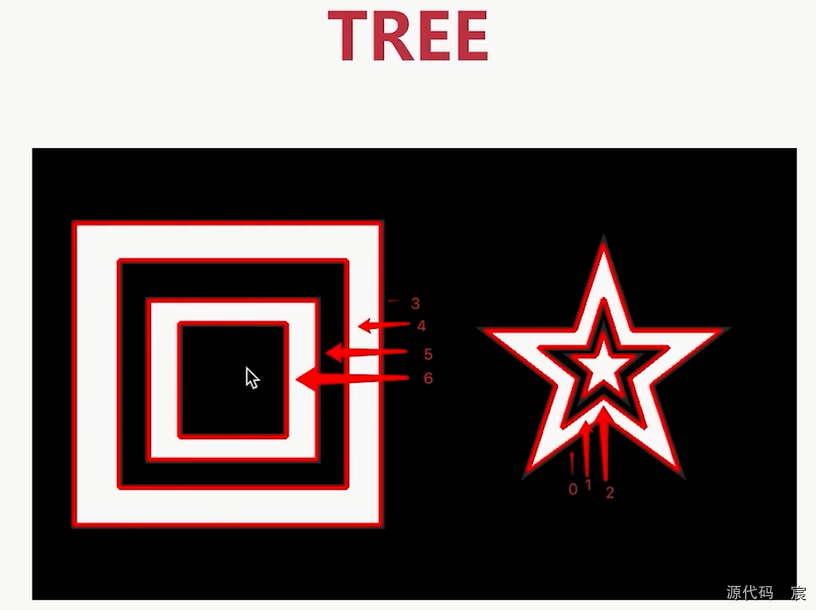
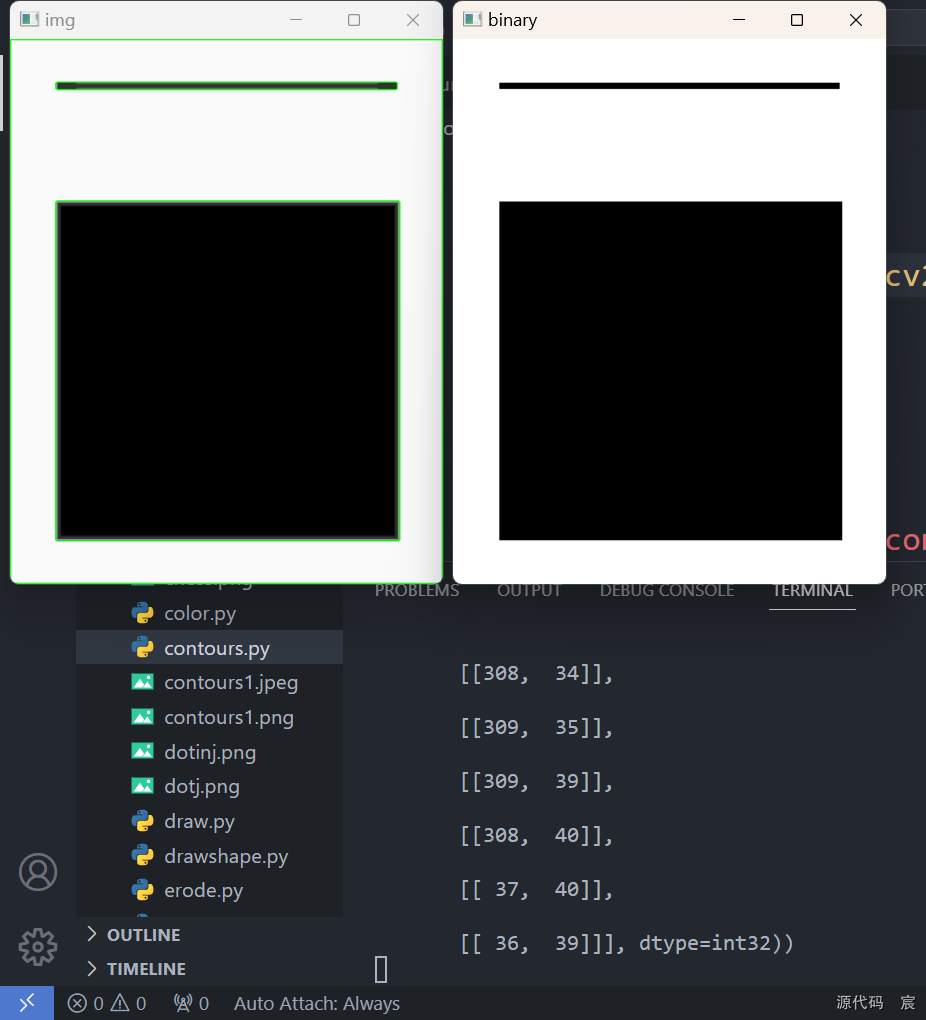
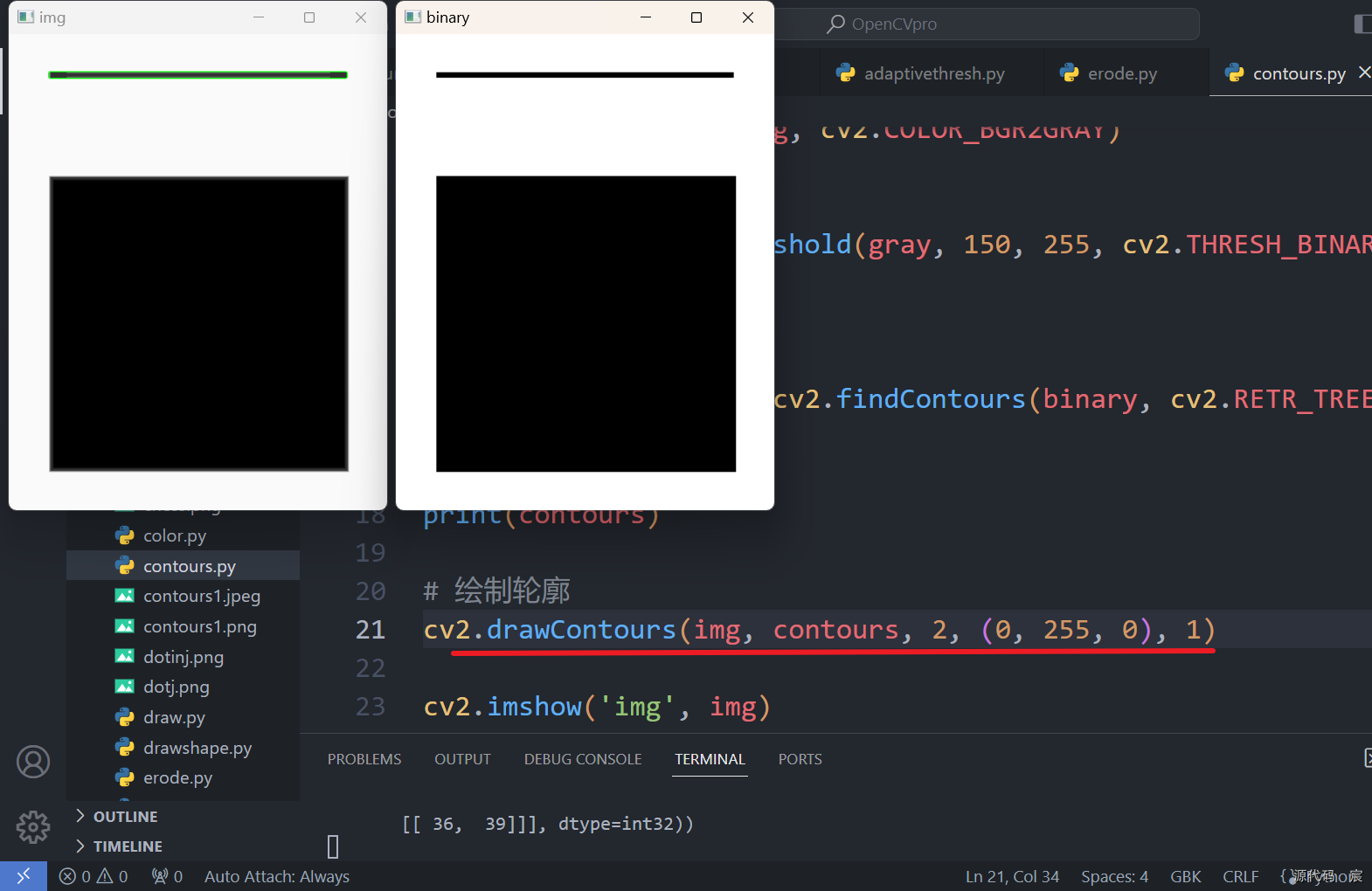
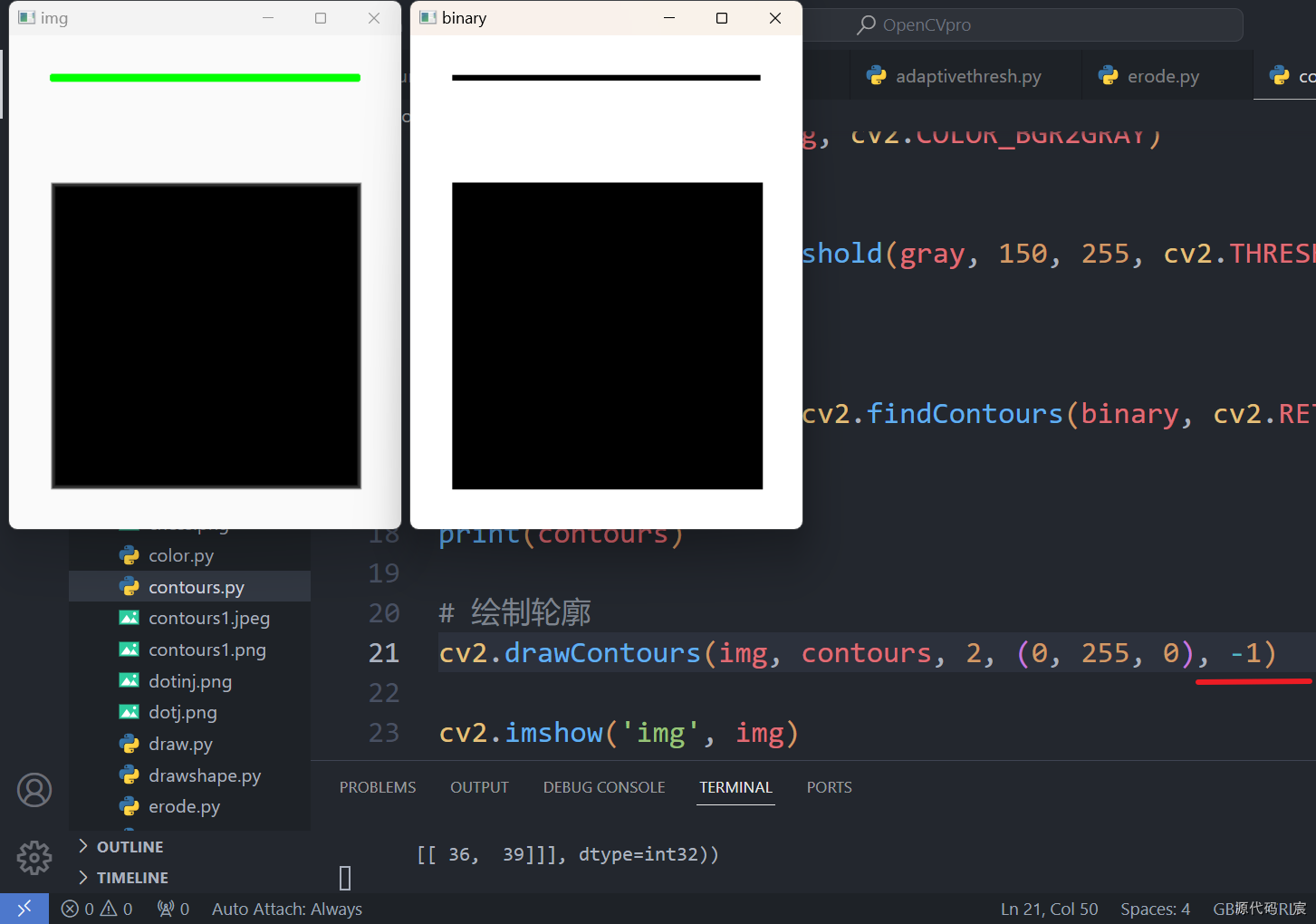
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)print(contours)# 绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
轮廓的面积与周长


# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('./contours1.jpeg')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)print(contours)# 绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, 0, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 计算面积
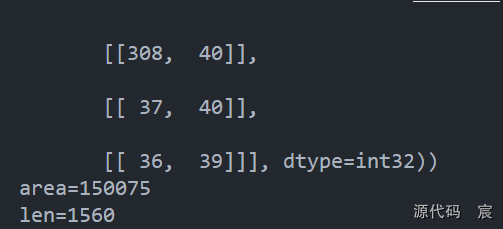
area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
print("area=%d"%(area))# 计算周长
len = cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True)
print("len=%d"%(len))# cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('binary', binary)# key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
# if key == ord('q'):
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
多边形逼近与凸包



# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('./hand.png')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
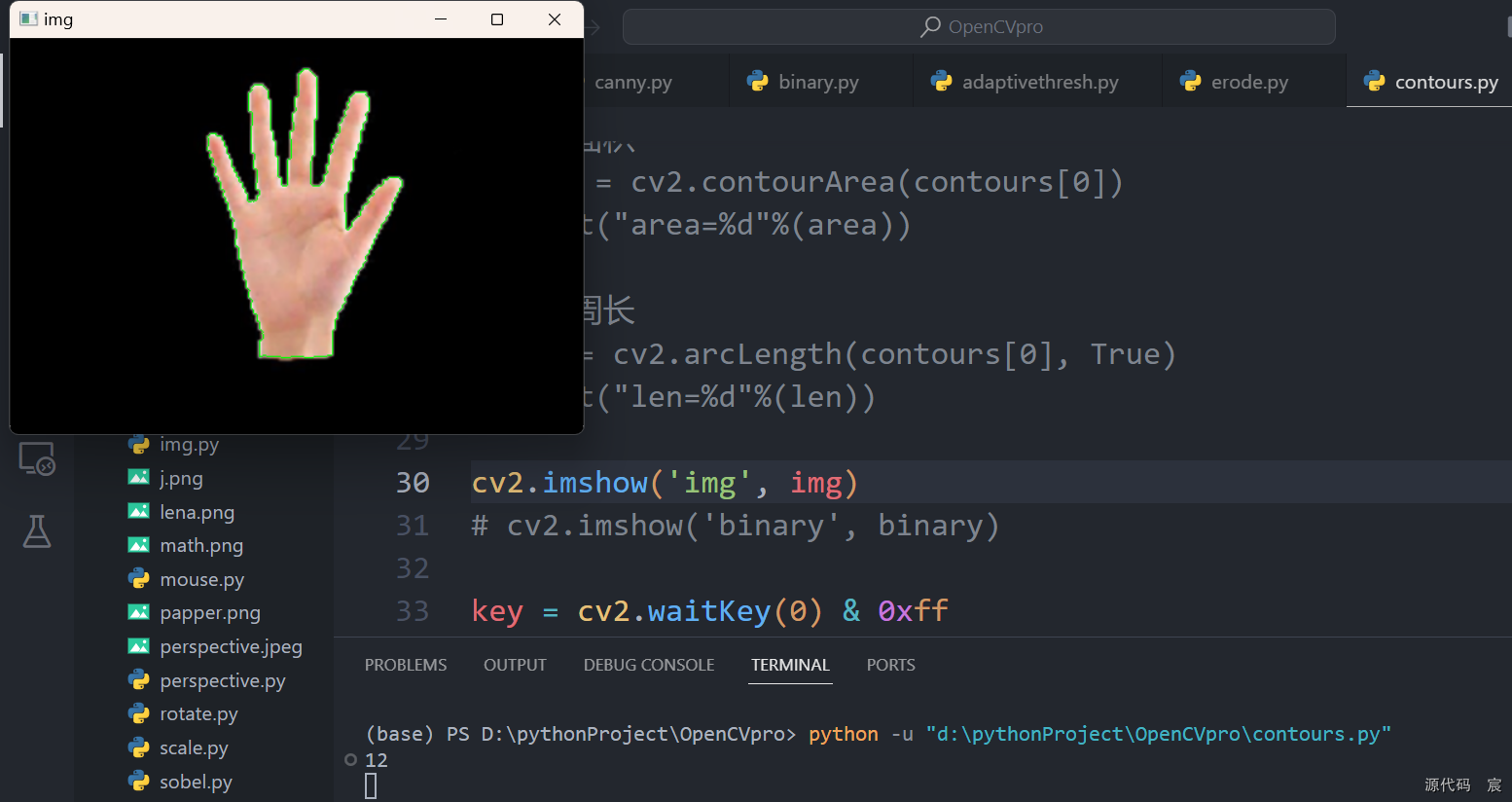
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)print(len(contours))# 绘制轮廓
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, 0, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 计算面积
# area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
# print("area=%d"%(area))# 计算周长
# len = cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True)
# print("len=%d"%(len))cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('binary', binary)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npdef drawShape(src, points):i = 0while i < len(points):if(i == len(points) - 1):x, y = points[i][0]x1, y1 = points[0][0]cv2.line(src, (x, y), (x1, y1), (0, 255, 0), 2)else:x, y = points[i][0]x1, y1 = points[i + 1][0]cv2.line(src, (x, y), (x1, y1), (0, 255, 0), 2)i = i + 1img = cv2.imread('./hand.png')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# print(len(contours))# 绘制轮廓
# cv2.drawContours(img, contours, 0, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 计算面积
# area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
# print("area=%d"%(area))# 计算周长
# len = cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True)
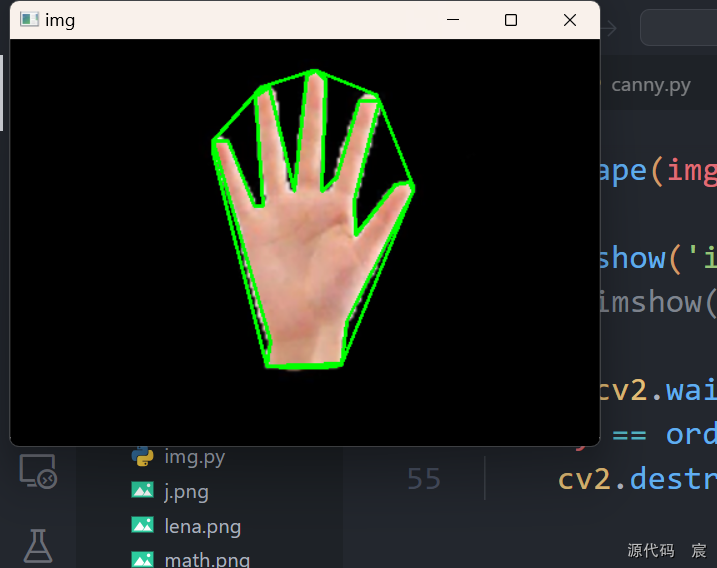
# print("len=%d"%(len))e = 5
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0], e, True)
drawShape(img, approx)hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
drawShape(img, hull)cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('binary', binary)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
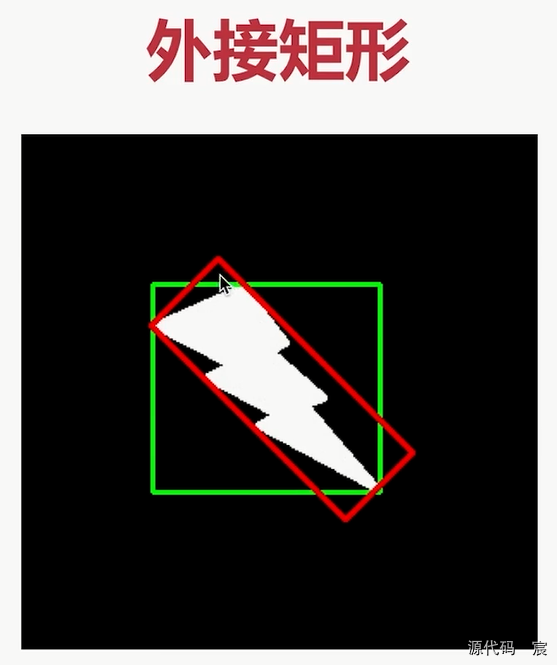
外接矩形

红框就是最小外接矩形,绿框就是最大外接矩形。
最小外接矩形可以看图形有没有旋转



详情见参考文档
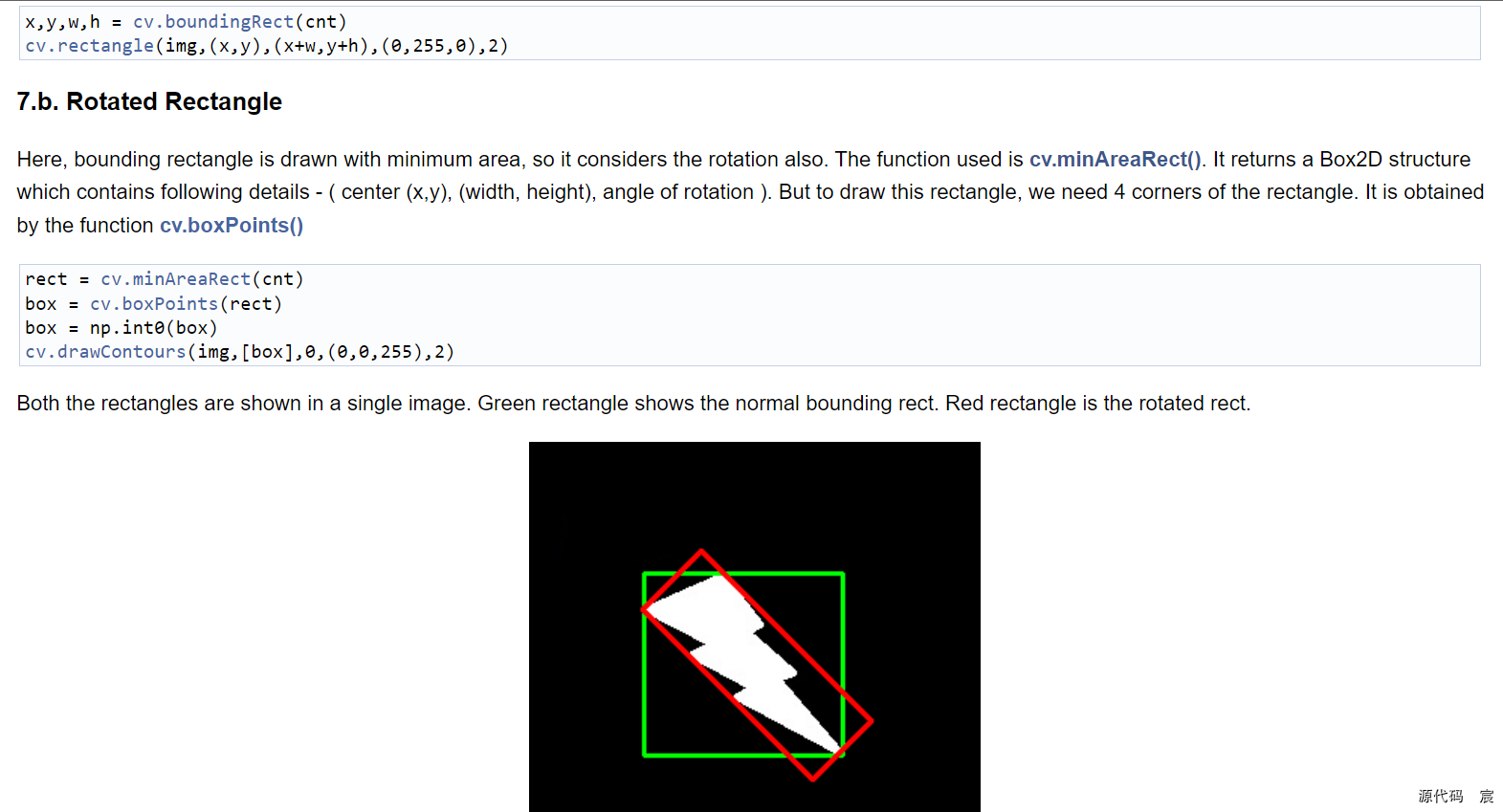
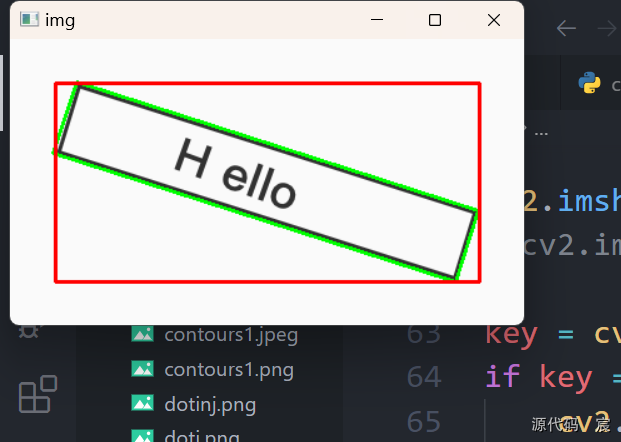
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npdef drawShape(src, points):i = 0while i < len(points):if(i == len(points) - 1):x, y = points[i][0]x1, y1 = points[0][0]cv2.line(src, (x, y), (x1, y1), (0, 255, 0), 2)else:x, y = points[i][0]x1, y1 = points[i + 1][0]cv2.line(src, (x, y), (x1, y1), (0, 255, 0), 2)i = i + 1img = cv2.imread('./hello.jpeg')
# print(img.shape)# 转变为单通道
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# print(gray.shape)# 轮廓查找
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# print(len(contours))# 绘制轮廓
# cv2.drawContours(img, contours, 1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 计算面积
# area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
# print("area=%d"%(area))# 计算周长
# len = cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True)
# print("len=%d"%(len))# e = 5
# 多边形逼近
# approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0], e, True)
# drawShape(img, approx)# 凸包
# hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
# drawShape(img, hull)r = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[1])
box = cv2.boxPoints(r)
box = np.int0(box)
cv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[1])
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255), 2)cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('binary', binary)key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff
if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()
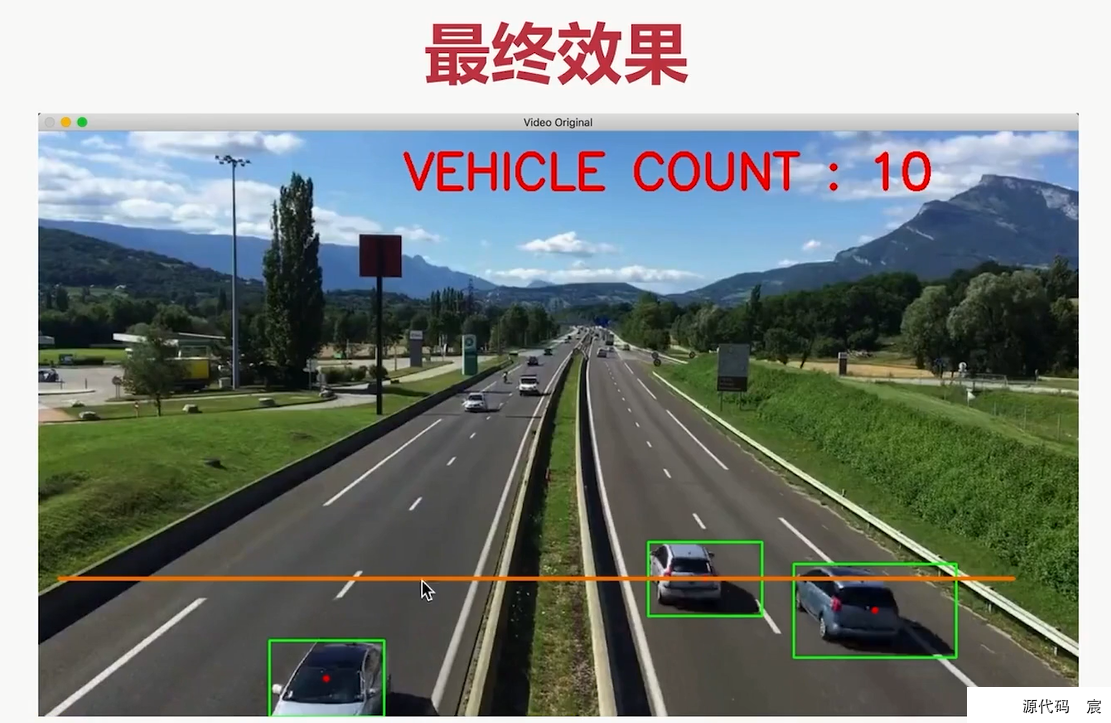
项目总览【车辆统计】


视频加载【车辆统计】
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npcap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):cv2.imshow('video', frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
去背景【车辆统计】
如果视频是25fps,即每秒25帧,即1000ms过25帧,那么200ms就走5帧(25/1000*200=5)


运动的物体为前景,静止的物体就是背景
详细可以参考官方文档
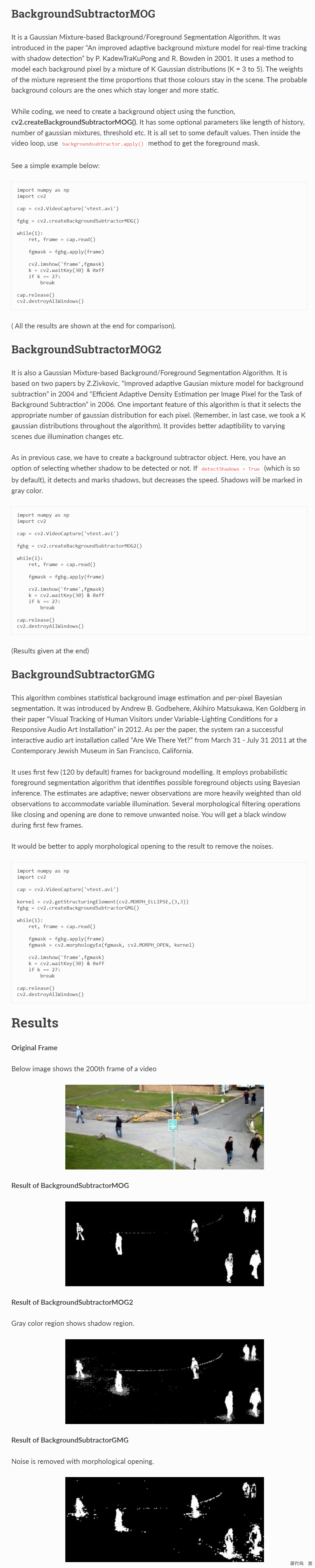
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npcap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')bgsubmog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):mask = bgsubmog.apply(frame)cv2.imshow('video', mask)key = cv2.waitKey(1)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
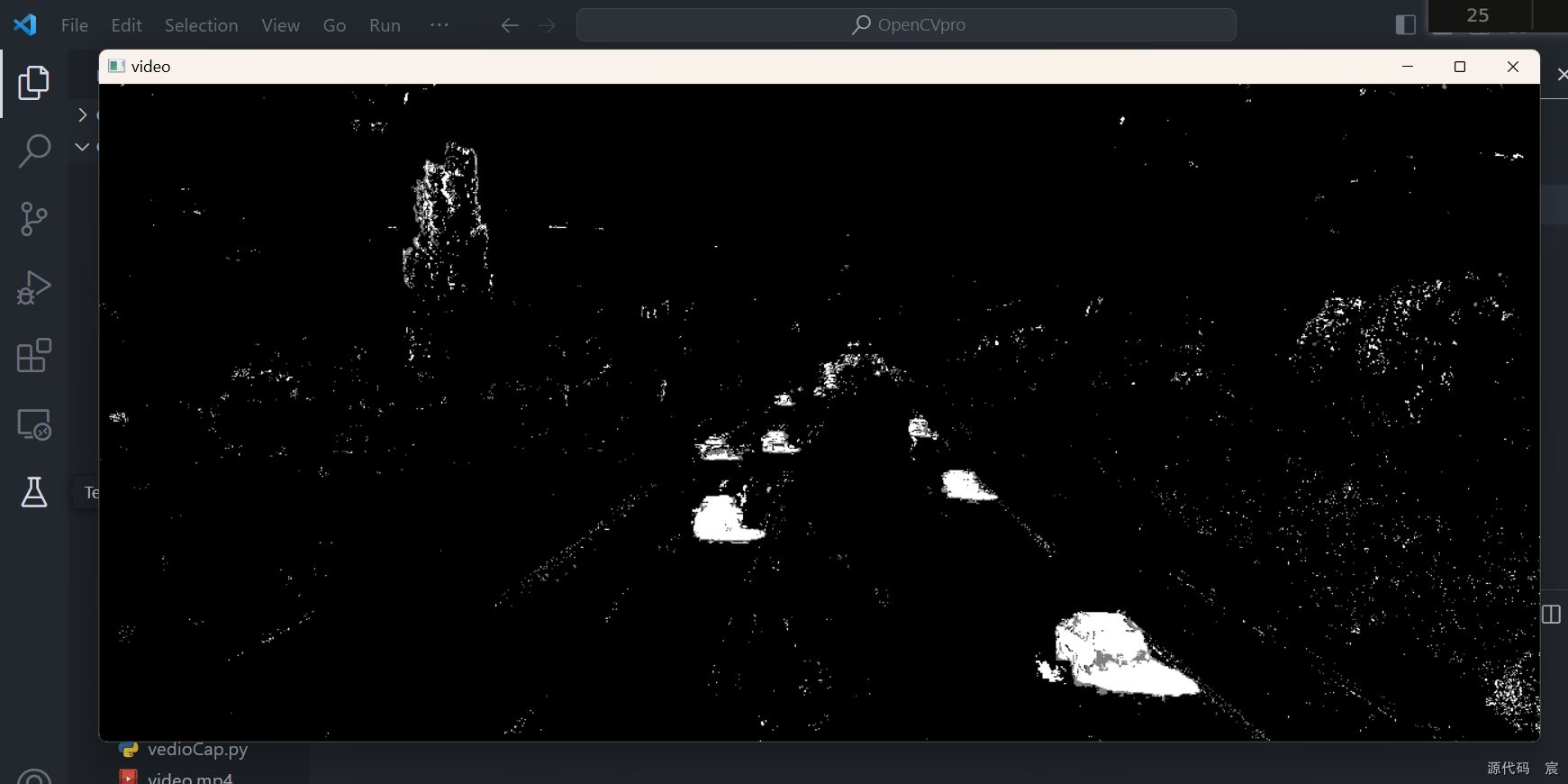
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npcap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')bgsubmog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
tst = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):# 灰度图cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 去噪(高斯)blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (3, 3), 5)# 去背景mask = bgsubmog.apply(blur)t = tst.apply(frame)cv2.imshow('video', mask)cv2.imshow('t', t)key = cv2.waitKey(40)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
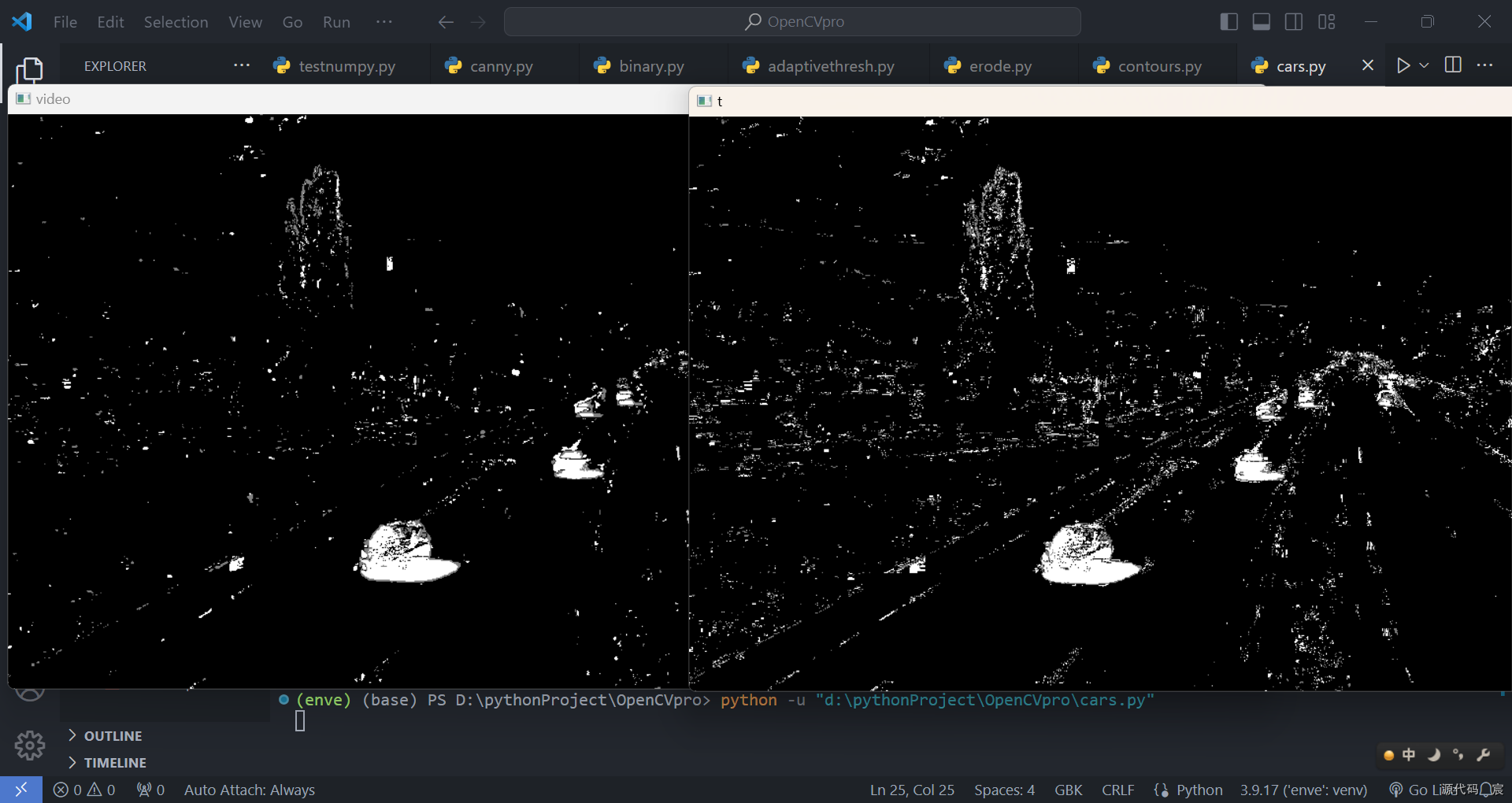
形态学处理【车辆统计】
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npcap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')bgsubmog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
# tst = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()# 形态学kernel
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
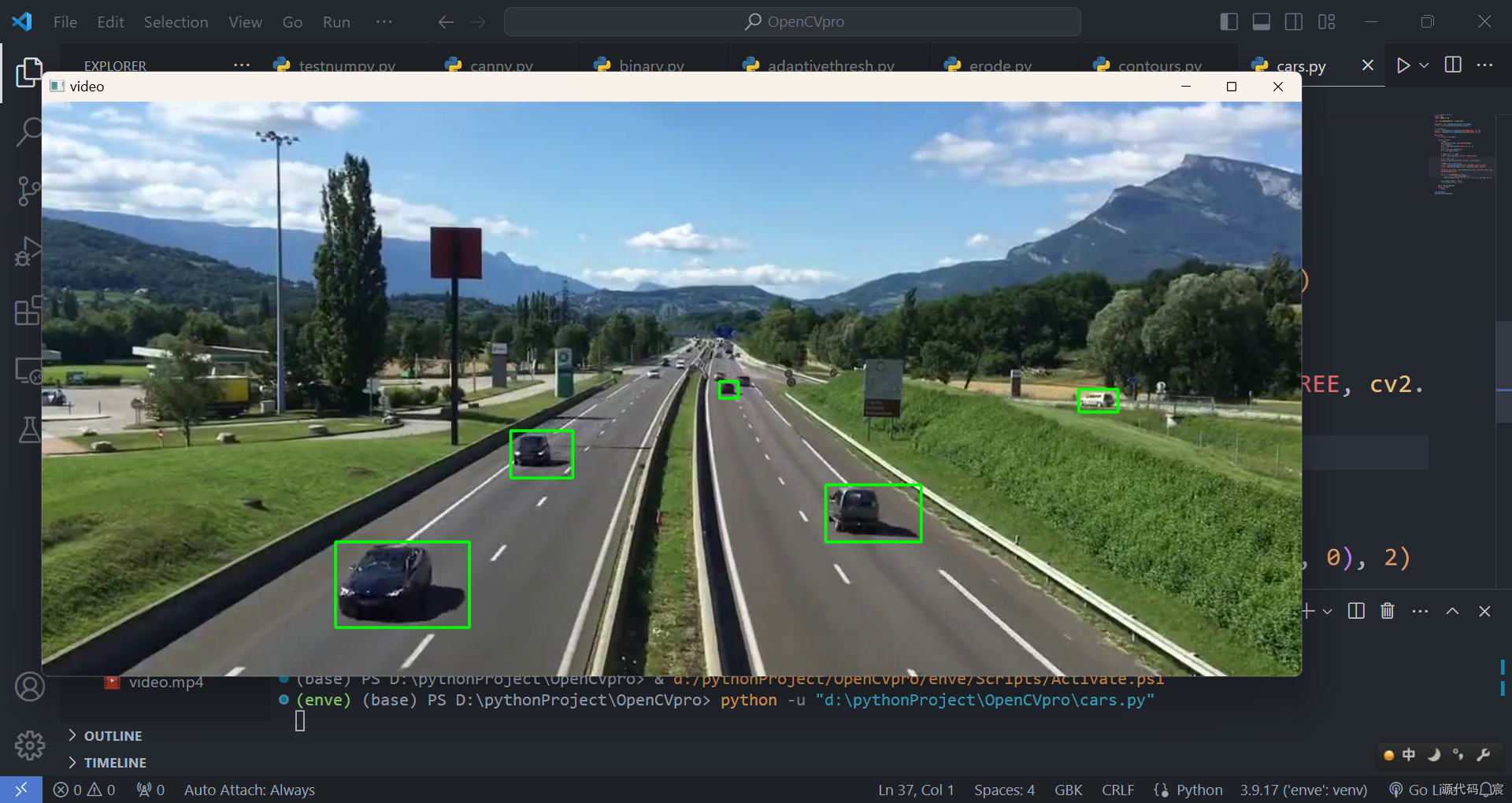
kernel2 = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):# 灰度图cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 去噪(高斯)blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (3, 3), 1)# 去背景mask = bgsubmog.apply(blur)# t = tst.apply(frame)# 腐蚀,去掉图中小斑块erode = cv2.erode(mask, kernel, iterations=1)# 膨胀,还原放大dilate = cv2.dilate(erode, kernel2, iterations=5)# 闭操作,去掉物体内部噪声close = cv2.morphologyEx(dilate, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)close = cv2.morphologyEx(close, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)for i, c in enumerate(contours):x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.imshow('video', frame)# cv2.imshow('erode', close)key = cv2.waitKey(40)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
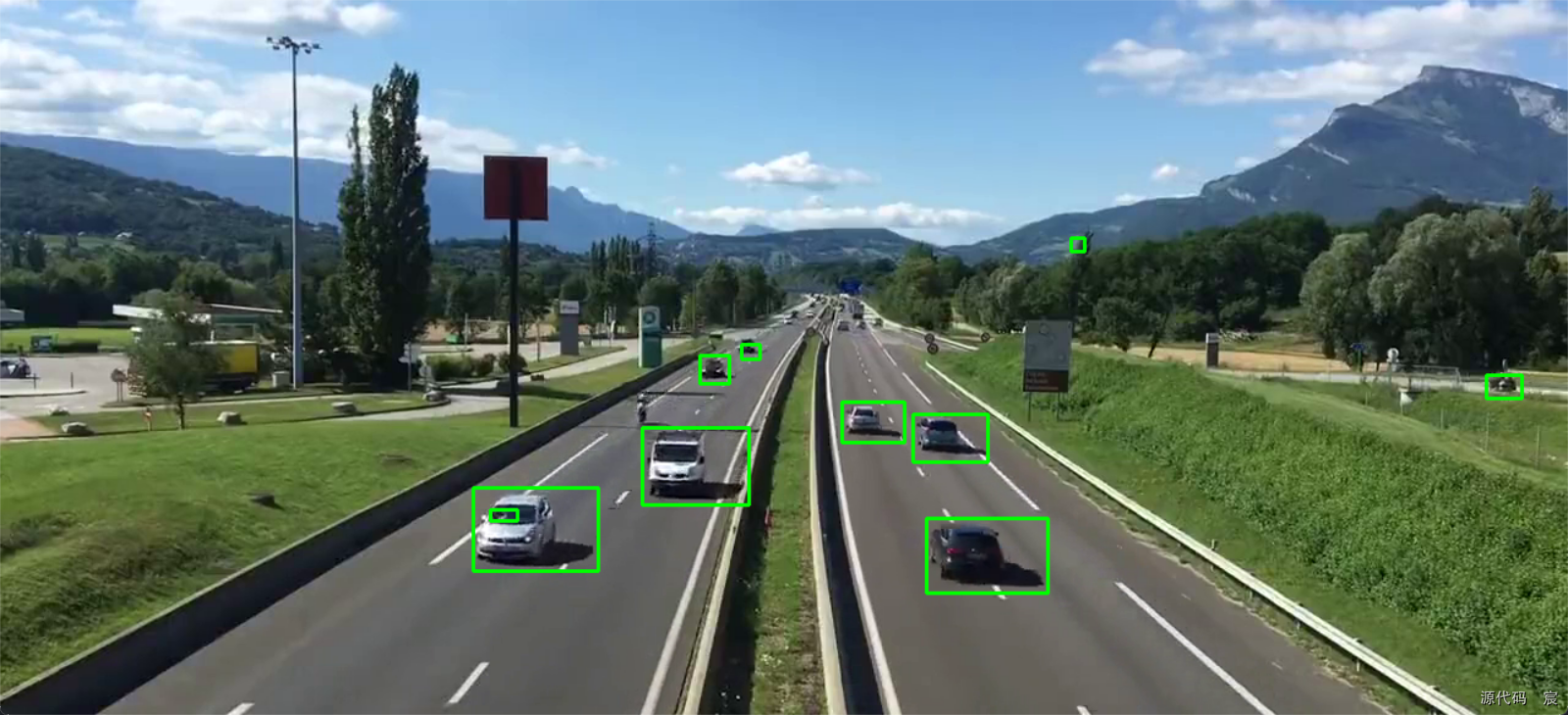
逻辑处理【车辆统计】
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npmin_w = 50
min_h = 50
max_w = 800
max_h = 800# 检测线的高度
line_high = 480# 存放有效车辆数组
cars = []# 统计车的数量
carnums = 0# 线的偏移
offset = 10# 求中心点
def center(x, y, w, h):x1 = int(w / 2)y1 = int(h / 2)cx = x + x1cy = y + y1return cx, cycap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')bgsubmog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
# tst = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()# 形态学kernel
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
kernel2 = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):# print(frame.shape)# (584, 1280, 3)# 灰度图cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 去噪(高斯)blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (3, 3), 1)# 去背景mask = bgsubmog.apply(blur)# t = tst.apply(frame)# 腐蚀,去掉图中小斑块erode = cv2.erode(mask, kernel, iterations=1)# 膨胀,还原放大dilate = cv2.dilate(erode, kernel2, iterations=3)# 闭操作,去掉物体内部噪声close = cv2.morphologyEx(dilate, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)close = cv2.morphologyEx(close, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)cv2.line(frame, (100, line_high), (1100, line_high), (255, 255, 0), 2)for i, c in enumerate(contours):x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)# 对车辆的宽高进行判断,以验证是否是有效车辆isValid = (x >= min_w) and (h >= min_h) and (x <= max_w) and (h <= max_h)if(not isValid):continue# 有效的车cpoint = center(x, y, w, h)cars.append(cpoint)cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)for xc, yc in cars:if(yc > line_high - offset and yc < line_high + offset):carnums += 1cars.remove((xc, yc))print(carnums)cv2.imshow('video', frame)# cv2.imshow('erode', close)key = cv2.waitKey(40)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
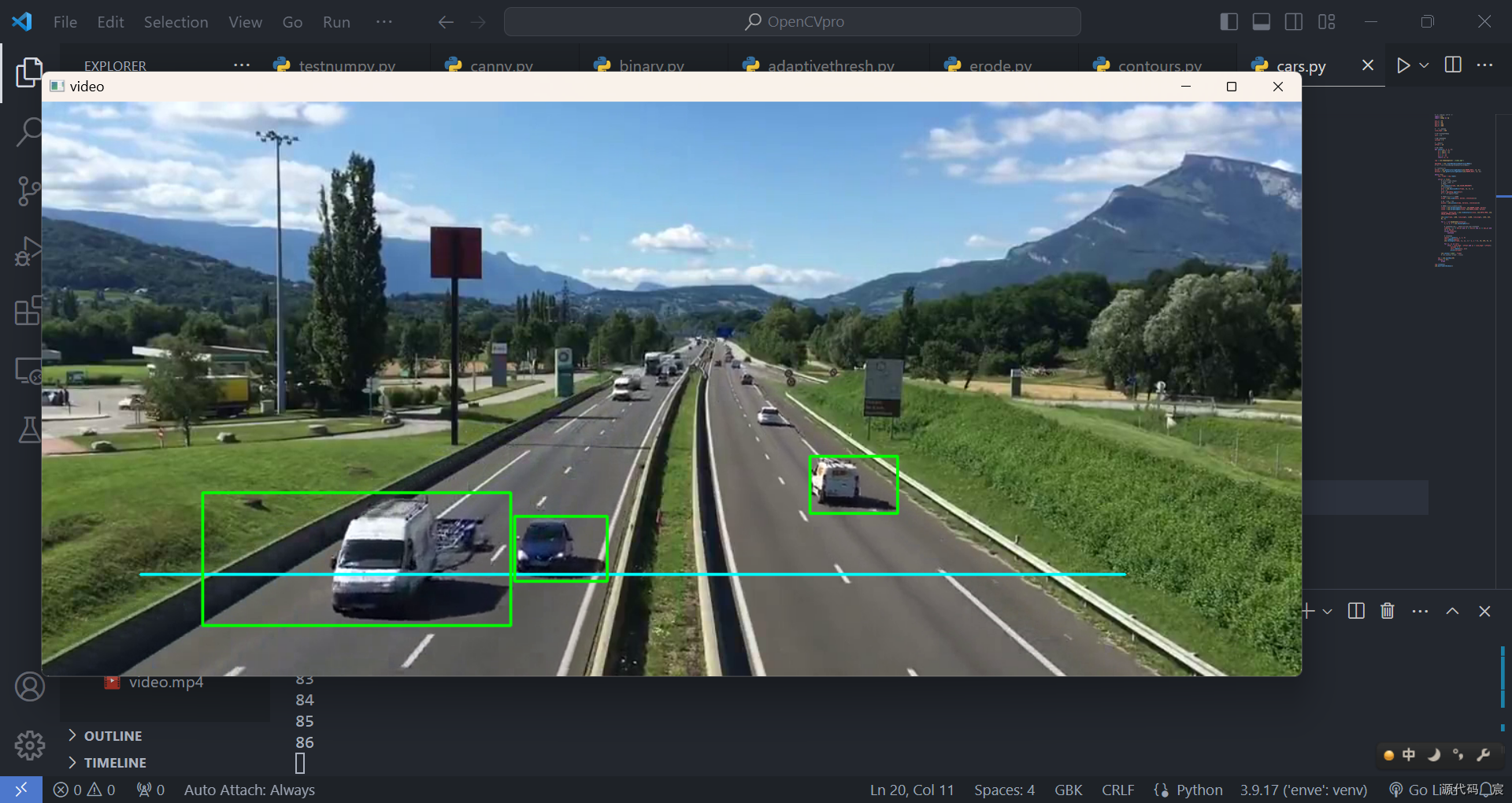
显示信息【车辆统计】
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as npmin_w = 50
min_h = 50
max_w = 800
max_h = 800# 检测线的高度
line_high = 480# 存放有效车辆数组
cars = []# 统计车的数量
carnums = 0# 线的偏移
offset = 10# 求中心点
def center(x, y, w, h):x1 = int(w / 2)y1 = int(h / 2)cx = x + x1cy = y + y1return cx, cycap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video.mp4')bgsubmog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
# tst = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()# 形态学kernel
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
kernel2 = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if(ret == True):# print(frame.shape)# (584, 1280, 3)# 灰度图cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 去噪(高斯)blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (3, 3), 1)# 去背景mask = bgsubmog.apply(blur)# t = tst.apply(frame)# 腐蚀,去掉图中小斑块erode = cv2.erode(mask, kernel, iterations=1)# 膨胀,还原放大dilate = cv2.dilate(erode, kernel2, iterations=3)# 闭操作,去掉物体内部噪声close = cv2.morphologyEx(dilate, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)close = cv2.morphologyEx(close, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# 画一条检测线cv2.line(frame, (100, line_high), (1100, line_high), (255, 255, 0), 2)for i, c in enumerate(contours):x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)# 对车辆的宽高进行判断,以验证是否是有效车辆isValid = (x >= min_w) and (h >= min_h) and (x <= max_w) and (h <= max_h)if(not isValid):continue# 有效的车cpoint = center(x, y, w, h)cars.append(cpoint)cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.circle(frame, (cpoint), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)for xc, yc in cars:if(yc > line_high - offset and yc < line_high + offset):carnums += 1cars.remove((xc, yc))print(carnums)cv2.putText(frame, "Cars Count:" + str(carnums), (500, 60), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (0, 255, 0), 3)cv2.imshow('video', frame)# cv2.imshow('erode', close)key = cv2.waitKey(40)if(key == 27):breakcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

通过实践可以发现传统的目标检测缺点很多,比方说可能重复计数…所以之后我们需要结合深度学习来提高目标检测的精度
之后我会持续更新,如果喜欢我的文章,请记得一键三连哦,点赞关注收藏,你的每一个赞每一份关注每一次收藏都将是我前进路上的无限动力 !!!↖(▔▽▔)↗感谢支持!


)





)





)

)


