文章目录
- 1 车辆统计项目
- 1.1 背景减除
- 1.2 车辆统计
- 2 特征点检测和匹配
- 2.1 harris角点检测
- 2.2 shi-tomasi角点检测
- 2.3 SIFT关键点检测
- 2.4 SURF特征检测
- 2.5 ORB特征检测
- 3 特征匹配
- 3.1 暴力特征匹配
- 3.2 FLANN特征匹配
- 3.3 图像查找
- 3.3.1 单应性矩阵
- 4 模版匹配
- 4.1 模版匹配
- 4.2 匹配多个对象
- 4.3 处理模版图片
- 4.4 数字模版处理和信用卡图片形态学操作
- 5 图像分割
- 5.1 分水岭法
- 5.2 GrabCut
- 5.3 MeanShift
- 6 图像修复
- 7 人脸检测
1 车辆统计项目

import cv2
import numpy as np# 读取视频
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video/car.mp4')# 循环读取视频每一帧
while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if ret:cv2.imshow('video',frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1)# 用户按esc推出if key == 27:break# 最后释放资源
cap.release()
# 关闭窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
1.1 背景减除

import cv2
import numpy as npcap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
bgs = cv2.bgsegm.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG()
while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if ret:fgmask = bgs.apply(frame)cv2.imshow('video', fgmask)key = cv2.waitKey(1)# ESC键if key == 27:break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
1.2 车辆统计
import cv2
import numpy as np# 读取视频
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('./video/car.mp4')
# 创建mog对象
mog = cv2.bgsegm.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG()
# 获取腐蚀卷积核
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))# 最大外接矩形的宽
min_w = 40
# 最大外接矩形的高
min_h = 30
# 线高
line_high = 630
# 车辆集合
cars = []
# 阈值
offset = 6
# 计数
car_num = 0# 计算外接矩形的中心点
def center(x, y, w, h):x1 = int(w / 2)y1 = int(h / 2)cx = int(x) + x1cy = int(y) + y1return cx, cy# 循环读取视频每一帧
while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if ret:# 把原始帧进行灰度化,然后去噪# # 灰度gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)# # 去噪blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (3, 3), 5)# 去背景mask = mog.apply(blur)# 腐蚀erode = cv2.erode(mask, kernel, iterations=2)# 膨胀2次dialte = cv2.dilate(erode, kernel, iterations=2)# 消除内部的小块# 闭运算close = cv2.morphologyEx(dialte, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)# cv2.imshow('video',dialte)# cv2.imshow('close',close)# 划线cv2.line(frame, [10, line_high], [1270, line_high], [255, 0, 0], 2)# 查找轮廓contours, h = cv2.findContours(close, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# 画出所有检测出来的轮廓for contour in contours:# 最大外接矩形(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(contour)is_valid = (w >= min_w) and (h >= min_h)if not is_valid:continue# 要求坐标点都是整数cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(x), int(y)), (int(x + w), int(y + h)), (0, 0, 255), 2)# 如何计数# 把车抽象为一点,即外接矩形的中心点# 通过外接矩形,计算车的中心点cpoint = center(x, y, w, h)# 将符合条件的车存入列表cars.append(cpoint)cv2.circle(frame, (cpoint), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)# 判断汽车是否过检测线for (x, y) in cars:if (line_high - offset) < y < (line_high + offset):# 落入了有效区间# 计数加一car_num += 1# 然后remove掉cars.remove((x, y))print(car_num)# 添加字符串cv2.putText(frame, 'Vechicle Count:' + str(car_num), [500, 60], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], 5)cv2.imshow('frame', frame)key = cv2.waitKey(3)# 用户按esc推出if key == 27:break# 最后释放资源
cap.release()
# 关闭窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2 特征点检测和匹配
2.1 harris角点检测


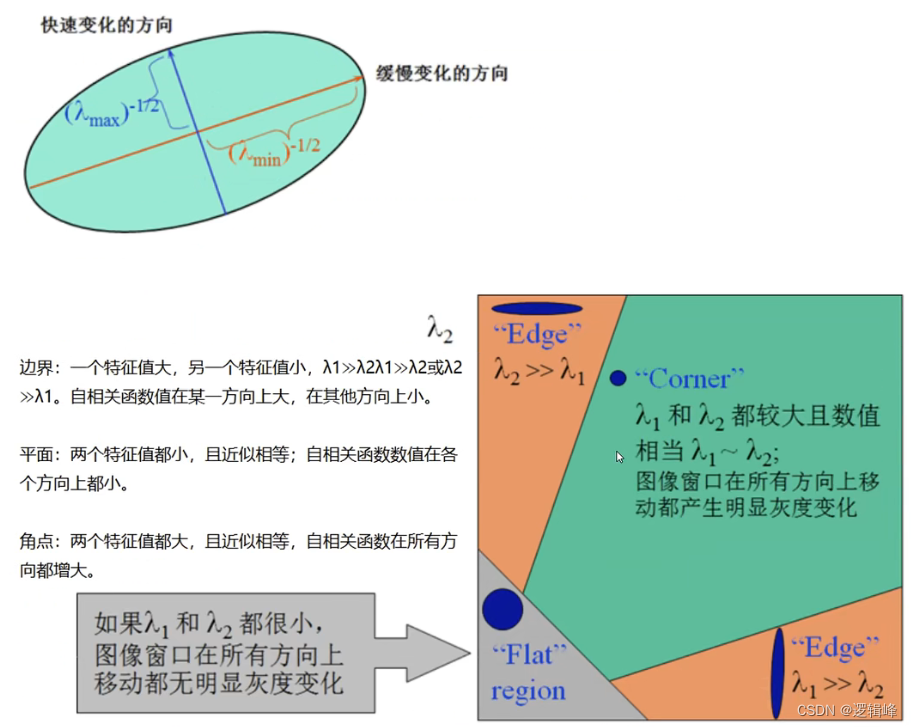

import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('./image/dog.png')# 变成灰度图片
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# harris角点检测
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, blockSize=2, ksize=3, k=0.04)
#返回的东西叫做角点响应.每一个像素点都能计算出一个角点响应来#
print(dst)
print(dst.shape)#显示角点
#我们认为角点响应大于0.01倍的dst.max()就可以认为是角点了.
img[dst > 0.01* dst.max()]= [0,0,255]
cv2.imshow('img',img)cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.2 shi-tomasi角点检测

import cv2
import numpy as np
#harris
# bLockSize = 2
# ksize = 3
# k = e.e4
# Shi-Tomasi
maxCorners = 1000
ql = 0.01
minDistance = 10img = cv2.imread('./image/dog.png')#灰度化
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
corners = cv2.goodFeaturesToTrack(gray,maxCorners,ql, minDistance)
corners = np.int16(corners)
#Shi-Tomasi绘制角点
for i in corners:x,y = i.ravel()cv2.circle(img,(x,y), 3,(255,0,0)

)
![BUUCTF [BJDCTF2020]一叶障目 1](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BUUCTF [BJDCTF2020]一叶障目 1)

)


Java EE 简述(Java EE 发展历程、什么是Web开发? Web网站的工作流程、什么是框架?Java EE 框架学习概览))




![BUUCTF [BJDCTF2020]鸡你太美 1](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BUUCTF [BJDCTF2020]鸡你太美 1)
---Web新手区题目WP)




