1. 什么是MyBatis?
简单说,MyBatis就是一个完成程序与数据库交互的工具,也就是更简单的操作和读取数据库的工具。
2. 怎么学习Mybatis
Mybatis学习只分为两部分:
- 配置MyBatis开发环境
- 使用MyBatis模式和语法操作数据库
3. 第一个MyBatis查询
开始搭建MyBatis之前,我们先来看一下MyBatis在整个框架的定位,框架交互流程图:
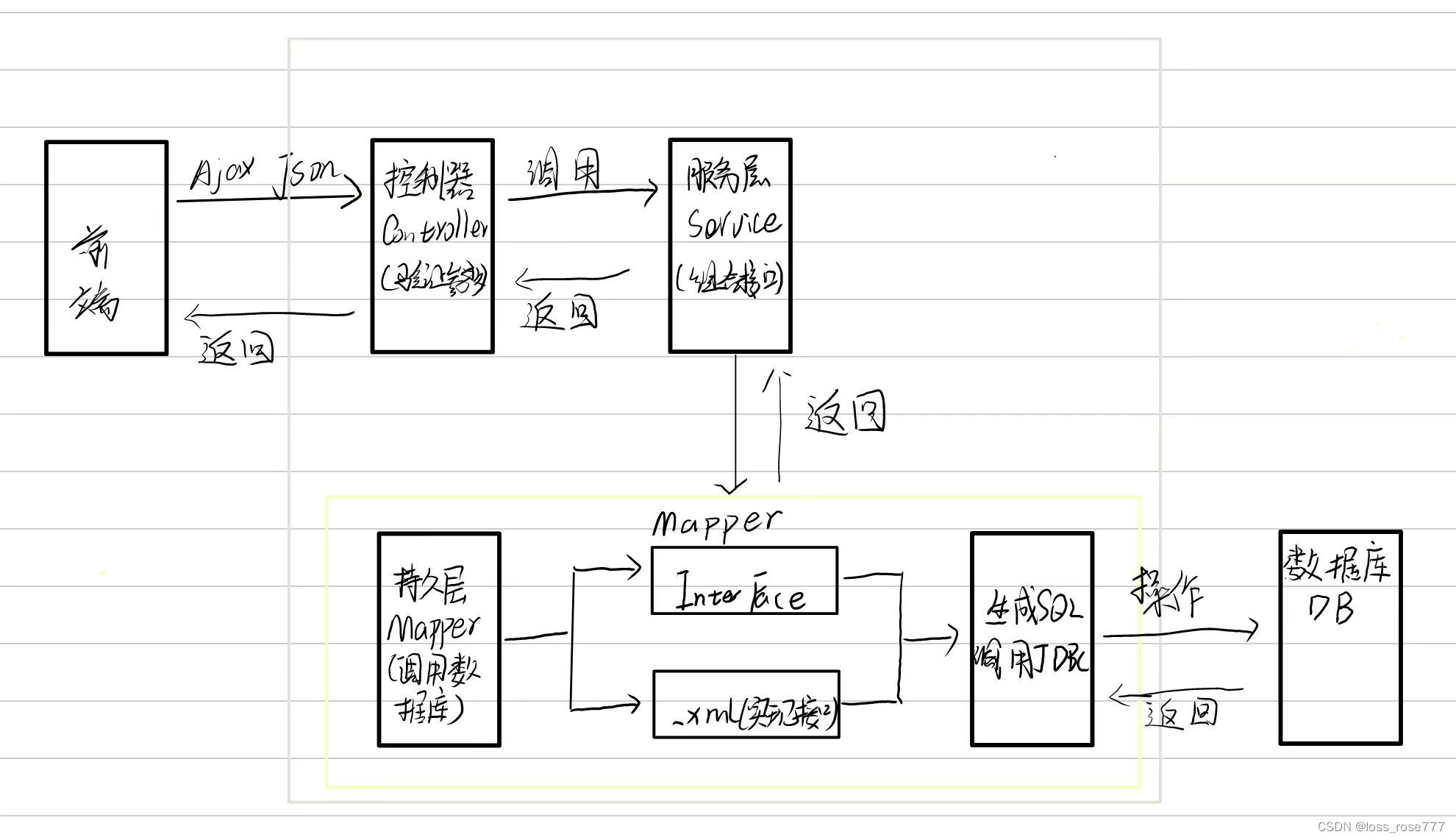
MyBatis也是一个ORM框架,ORM(Object Relational Mappping),即对象关系映射。在面向对象编程语言中,将关系型数据库与对象建立起映射关系,进而自动完成数据与对象的相互转换:
- 将输入数据+SQL映射成原生的SQL
- 将结构及映射为返回对象,即输出对象
3.1 创建数据库和表
-- 创建数据库
drop database if exists mycnblog;
create database mycnblog DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;-- 使用数据数据
use mycnblog;-- 创建表[用户表]
drop table if exists userinfo;
create table userinfo(id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(100) not null,password varchar(32) not null,photo varchar(500) default '',createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,`state` int default 1
) default charset 'utf8mb4';-- 创建文章表
drop table if exists articleinfo;
create table articleinfo(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(100) not null,content text not null,createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,uid int not null,rcount int not null default 1,`state` int default 1
)default charset 'utf8mb4';-- 创建视频表
drop table if exists videoinfo;
create table videoinfo(vid int primary key,`title` varchar(250),`url` varchar(1000),createtime timestamp default current_timestamp,updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp,uid int
)default charset 'utf8mb4';-- 添加一个用户信息
INSERT INTO `mycnblog`.`userinfo` (`id`, `username`, `password`, `photo`, `createtime`, `updatetime`, `state`) VALUES
(1, 'admin', 'admin', '', '2021-12-06 17:10:48', '2021-12-06 17:10:48', 1);-- 文章添加测试数据
insert into articleinfo(title,content,uid)values('Java','Java正文',1);-- 添加视频
insert into videoinfo(vid,title,url,uid) values(1,'java title','http://www.baidu.com',1);3.2 创建MyBatis项目
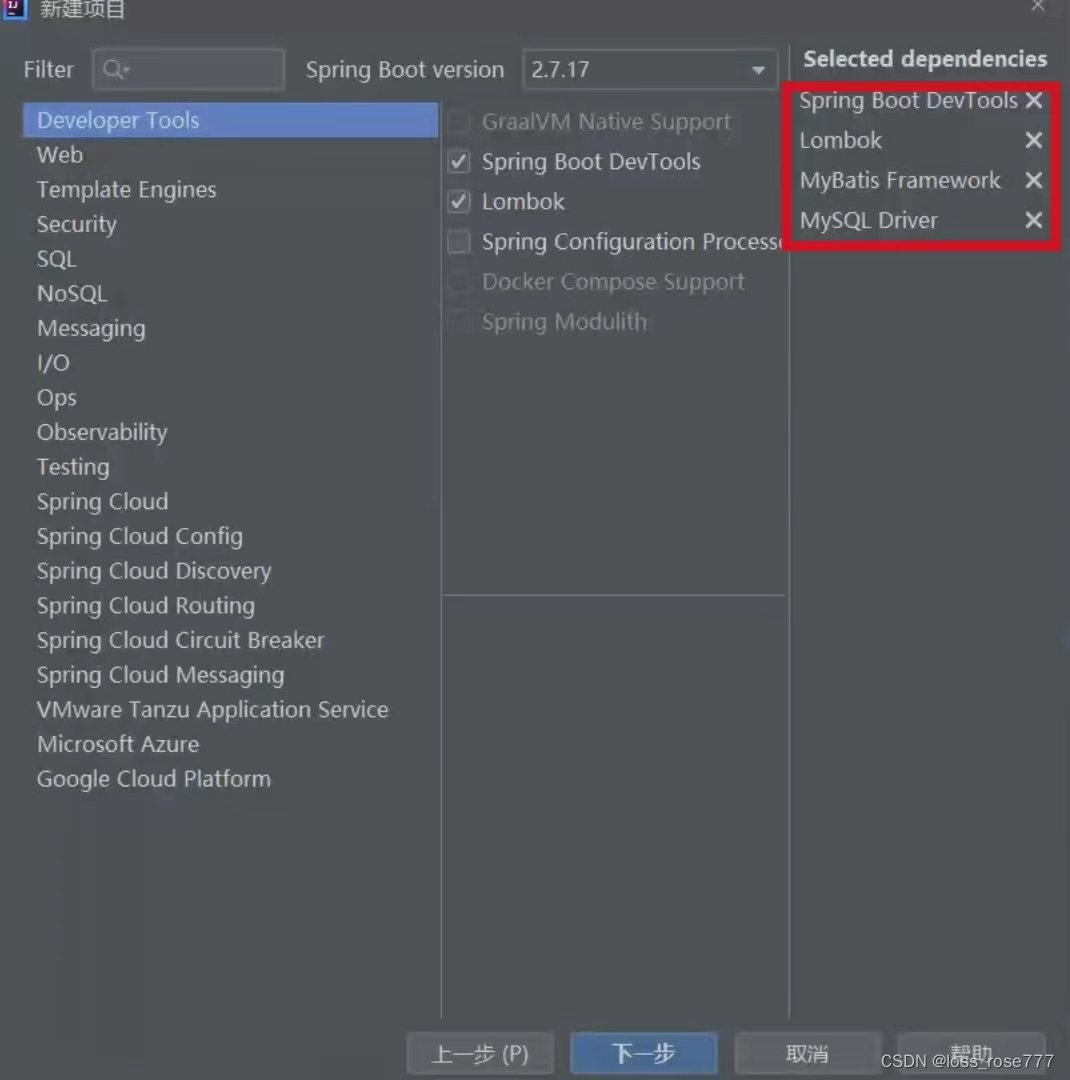
3.3 配置连接字符串和MyBatis
3.3.1 设置MyBatis配置
如果是application.properties添加如下内容:
#配置数据库的连接字符串
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/myblog
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=1111
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 设置 Mybatis 的 xml 保存路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/*Mapper.xml
# 将数据库中的下换线转换成驼峰,比如 user_name -> userName
mybatis-plus,configuration,map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
# 配置打印 MyBatis 执行的 SQL
mybatis.configuration,log-impl=org.apache,ibatis,logging.stdout,StdoutImpl
# 配置打印 MyBatis 执行的 SQL
Logging.level.com.example.demo=debug3.4 添加业务代码
下面按照后端开发的工程思路。也就是下面的流程来实现MyBatis查询所有用户的功能:
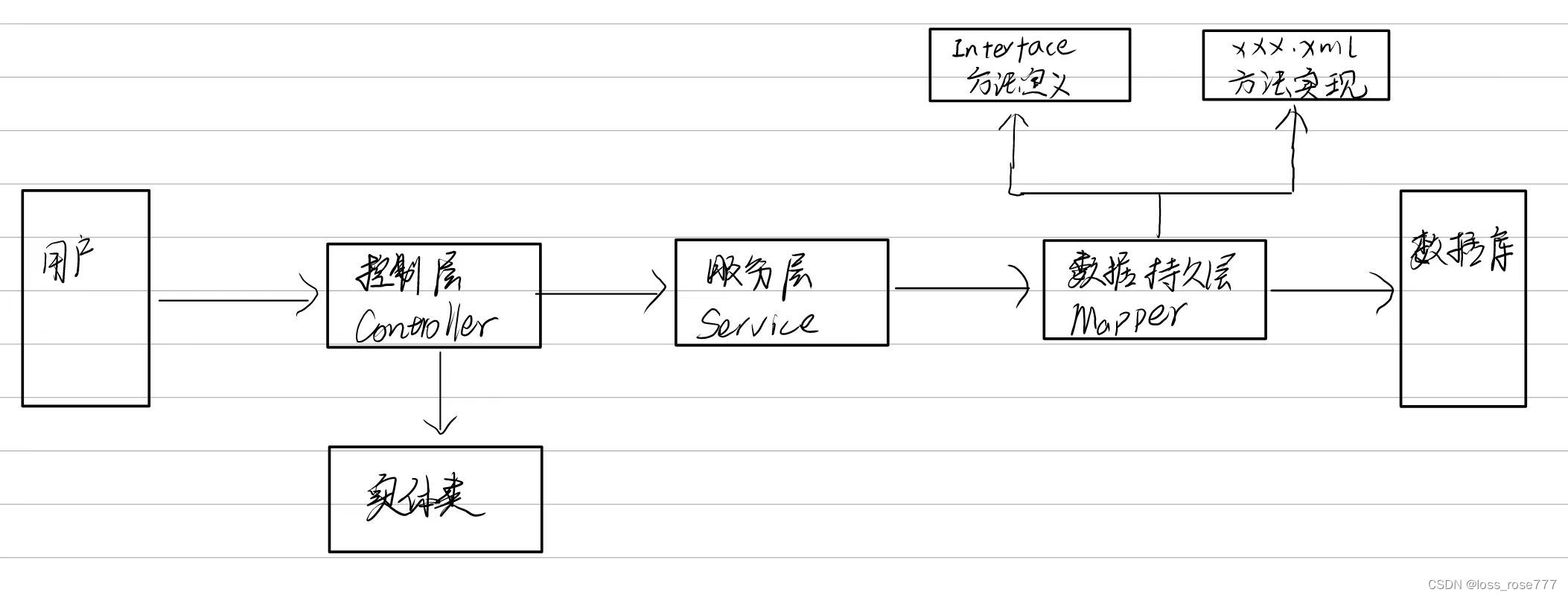
3.4.1 添加实体类
先添加用户的实体类:
@Data
public class User { private int id;private String username;private String password;private String photo;private Date createTime;private Date updateTime;
}3.4.2 添加mapper接口
数据持久层接口定义:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {public List<User> getAll();
}
3.4.3 添加UserMapper.xml
数据持久层的实现,mybatis的固定xml格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybati
s.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper"></mapper>UserMapper.xml查询所有用户具体实现SQL:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybati
s.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper"><select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo </select>
</mapper>以下是堆标签的说明:
- <mapper>标签:需要指定namespace属性,表示命名空间,值为mapper接口的全限定名,包括全包名.类名
- <select>查询标签:是用来执行数据库的查询操作的:
id:是和interface(接口)中定义的方法名称一样的,表hi堆积恶口的具体实现方法
resultType:时返回的数据类型,也就是开头我们定义的实体类
3.4.4 添加Service
服务层实现代码如下:
@Service
public class UserService {@Autowiredprivate UserMapper userMapper;public List<User> getAll(){return userMapper.getAll();}
}
3.3.5 添加Controller
控制器层的实现代码如下;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@RequestMapping("/getall")public List<User> getAll(){return userService.getAll();}}上述代码写完,则很难哥哥MyBatis的查询功能就实现完了,接下来使用postman来测试一下
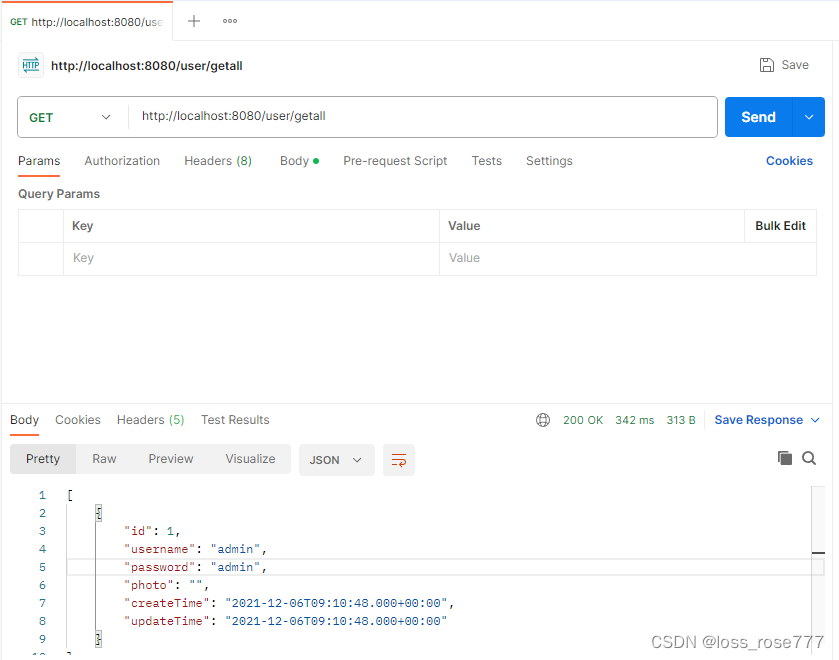
3.3.6 使用 postman 测试
4. 增删改操作
接下来,我们实现一个用户的增加、删除、修改操作,对应的MyBatis的标签如下:
- <insert>标签:插入语句
- <update>标签:修改语句
- <delete>标签:删除语句
4.1 增加用户操作
controller实现代码:
@RequestMapping("/add")public int add(@RequestBody User user){return userService.getadd(user);}mapper接口代码
public int add(User user);mapper.xml
<insert id="add">insert into userinfo(username,password,photo,state)values(#{username},#{password},#{photo},1)
</insert>postman访问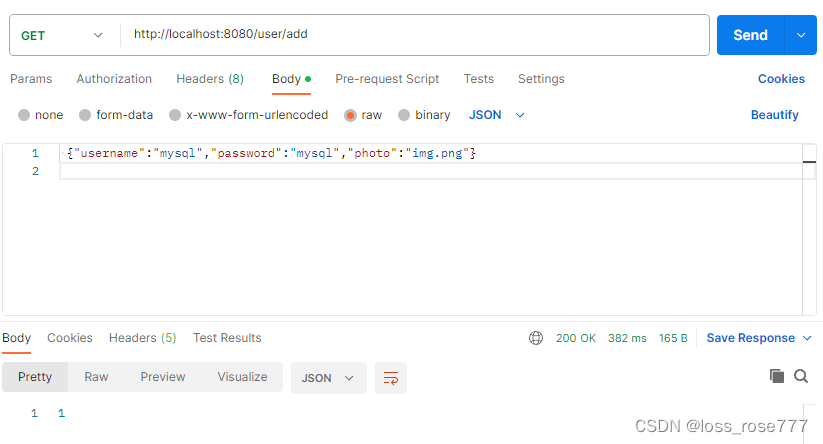
默认情况会返回受影响的行数
4.2 修改用户操作
controller代码:
@RequestMapping("/update")
public int getupdate(Integer id,String name){return userService.update(id,name);
}mapper.xml实现代码:
<update id="update">update userinfo set username=#{name} where id=#{id}
</update>切记修改操作只能用post方法接收参数
4.3 删除用户操作
<delete id="delById">delete from userinfo where id=#{id}</delete>5. 查询操作
5.1 单表查询
controller:
@RequestMapping("/getuser")
public User getUserById(Integer id) {return userService.getUserById(id);
}Mapper.xml
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>这里上面添加业务代码中 我们都已经提及了,所以不做具体的解释了,我们直接切入重点,参数占位符#{}和${}
5.1.1 参数占位符#{}和${}
- #{}:预编译处理
- ${}:字符直接替换
预编译处理是指:MyBatis 在处理#{}时,会将 SQL 中的 #{} 替换为?号,使⽤ PreparedStatement 的 set ⽅法来赋值。直接替换:是MyBatis 在处理 ${} 时,就是把 ${} 替换成变量的值。
我们在执行#{}的查询操作的时候,控制栏会显示

当我们使用${}的时候:
 这个就是区别所在
这个就是区别所在
5.1.2 ${}优点
在我们使用淘宝一系列的软件的时候,会有按照价格从高到底排序和从低到高排序,此时我们使用的sql是
<select id="getAllBySort" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.
example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo order by id ${sort}
</select>从小到大查询:
SELECT * FROM your_table ORDER BY id ASC;
从大到小查询:
SELECT * FROM your_table ORDER BY id DESC;
只有末尾差一个desc,如果我们使用#{sort}就不可以查询,因为使用#{sort}查询的时候,如果传递的值是String则会加上单引号,导致sql错误
5.1.3 SQL注入问题
SQL注入是一种常见的安全漏洞,它允许攻击者通过在应用程序的用户界面中插入恶意的SQL代码来执行未经授权的数据库查询。以下是一个简单的SQL注入示例:
假设有一个简单的登录页面,用户通过提供用户名和密码登录。系统使用以下查询来验证用户是否存在:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '输入的用户名' AND password = '输入的密码';
正常情况下,如果用户输入了有效的用户名和密码,他们将被成功验证,否则登录将失败。
然而,如果应用程序没有正确处理用户输入,攻击者可以尝试输入恶意的输入,例如:
' OR '1'='1'; --
如果这个输入被简单地拼接到原始的SQL查询中,那么查询就变成了:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '' OR '1'='1'; --' AND password = '输入的密码';
这个查询中的' OR '1'='1'; --部分使得条件永远为真('1'='1'永远成立),并且--后面的内容是SQL注释,它会使查询的其余部分被忽略。
因此,无论用户输入了什么密码,这个查询都会返回第一个用户,因为条件始终为真。攻击者可能会成功绕过身份验证,进而登录到系统中,即使他们没有提供有效的用户名和密码。
为了防止SQL注入,应用程序应该使用参数化查询或预编译语句,而不是简单地拼接用户输入到SQL查询中。这样可以确保用户输入不会被解释为SQL代码。所以我们应该尽量使用#{}预编译
6. 动态SQL
在 MyBatis 中,动态 SQL 是一种用于根据条件生成不同 SQL 片段的机制。<if>、<where> 和 <set> 是 MyBatis 动态 SQL 中常用的元素之一。
下面简要介绍一下 <if>、<where> 和 <set> 的用法:
6.1 if标签
<if> 元素:<if> 元素允许你在 SQL 中包含条件判断,以便根据条件动态生成 SQL 片段。例如:
<select id="getUserByCondition">SELECT * FROM usersWHERE<if test="username != null and username != ''">username = #{username}</if><if test="email != null and email != ''">AND email = #{email}</if>
</select>
但是我们可以发现如果我们 第一个条件不满足的话,第二个条件满足sql语句就会出现问题变成
SELECT * FROM users WHERE AND email = #{email} 所以我们就要提到where标签
6.2 where标签
<where> 元素:<where> 元素用于将所有条件组装在一个 WHERE 子句中,并自动处理条件之间的 AND 连接。示例:
<select id="getUserByCondition" parameterType="map" resultType="User">SELECT * FROM users<where><if test="username != null and username != ''">AND username = #{username}</if><if test="email != null and email != ''">AND email = #{email}</if></where>
</select>
<where> 元素会自动去除不必要的 AND。
6.3 set标签
<set> 元素:<set> 元素用于动态生成 UPDATE 语句中的 SET 子句,根据传入的参数动态设置更新的字段。示例:
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">UPDATE users<set><if test="username != null">username = #{username},</if><if test="password != null">password = #{password},</if><if test="email != null">email = #{email},</if></set>WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
但是如果set中的条件只满足一个的话就会出现一个问题 在末尾会多出一个,来,这个时候我们就需要trim标签了
6.4 trim标签
<trim> 元素是用于处理动态 SQL 时非常有用的元素之一。它允许你定义一种修剪(trim)行为,用于删除生成 SQL 语句中多余的字符,例如多余的逗号、AND 或 OR 等。
<!-- 在 set 子句中使用 trim 元素 -->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">UPDATE users<set><trim suffixOverrides=","><if test="username != null">username = #{username},</if><if test="password != null">password = #{password},</if><if test="email != null">email = #{email},</if></trim></set>WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
trim标签中具有很多的参数我们一一介绍一下:
prefix(可选): 在整个 <trim> 元素内容的最前面插入指定的前缀。示例:
<trim prefix="AND (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="AND"><!-- content -->
</trim>
suffix(可选): 在整个 <trim> 元素内容的最后面插入指定的后缀。示例
<trim prefix="AND (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="AND"><!-- content -->
</trim>
prefixOverrides(可选): 从整个 <trim> 元素内容的最前面开始检查,去除第一个匹配的指定前缀。示例:
<trim prefix="AND (" suffix=")" prefixOverrides="AND"><!-- content -->
</trim>
suffixOverrides(可选): 从整个 <trim> 元素内容的最后面开始检查,去除第一个匹配的指定后缀。示例:
<trim prefix="AND (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="AND"><!-- content -->
</trim>



电力机器人应用与创新发展论坛-核心PPT资料下载)


)



)








