哈希的使用和开闭散列的模拟实现
- 1. 使用
- 1.1 unordered_map的接口
- 1.2 unordered_set的接口
- 2. 哈希底层
- 2.1 概念
- 2.2 解决哈希冲突
- 3. 实现
- 3.1 开放寻址法
- 3.2 拉链法
1. 使用
1.1 unordered_map的接口
- 构造

void test1()
{// 空的unordered_map对象unordered_map<int, int> m1(10);cout << "桶的实际个数->" << m1.bucket_count() << endl;// 用列表初始化来进行初始化unordered_map<int, int> m2{ {1,1}, {2,2}, {3,3} };cout << "列表初始化-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : m2){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;// 迭代器区间初始化unordered_map<int, int> m3(m2.begin(), m2.end());cout << "迭代器区间初始化-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : m2){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test1();return 0;
}
运行结果 :
桶的实际个数->16
列表初始化->
1 1
2 2
3 3迭代器区间初始化->
1 1
2 2
3 3
- 容量

- 元素访问

void test2()
{unordered_map<string, int> mat{ {"小呆呆", 1}, {"波比", 2} };cout << "初始化-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;mat["猪猪侠"];cout << "插入功能-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;mat["波比"] = 5;cout << "修改功能-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;mat["超人强"] = 6;cout << "插入 + 修改功能-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test2();return 0;
}
运行结果 :
初始化->
小呆呆 1
波比 2插入功能->
小呆呆 1
猪猪侠 0
波比 2修改功能->
小呆呆 1
猪猪侠 0
波比 5插入 + 修改功能->
小呆呆 1
猪猪侠 0
波比 5
超人强 6
- 查询

void test3()
{unordered_map<string, int> mat{ {"小呆呆", 1}, {"波比", 2} };mat["猪猪侠"] = 5;mat["猪猪侠"] = 7;size_t cnt = mat.count("猪猪侠");cout << cnt << endl;auto it = mat.find("小呆呆");if (it != mat.end()){cout << it->first << " is " << it->second << endl;}else{cout << "查无元素! " << endl;}cout << endl;auto git = mat.find("超人强");if (git != mat.end()){cout << git->first << " is " << git->second << endl;}else{cout << "查无元素! " << endl;}}int main()
{test3();return 0;
}
运行结果 :
1
小呆呆 is 1查无元素!
- 修改

void test4()
{unordered_map<string, int> mat1{ {"小呆呆", 1}, {"波比", 2} };// 插入mat1.insert({ "小呆呆", 5 });mat1.insert({ "超人强", 6 });for (const auto& e : mat1){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;// 删除mat1.erase("波比");mat1.erase("猪猪侠");for (const auto& e : mat1){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;// 交换unordered_map<string, int> mat2{ {"迪迦",1}, {"戴拿",2}};mat1.swap(mat2);cout << "交换后的mat1-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat1){cout << e.first << " is " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;cout << "交换后的mat2-> " << endl;for (const auto& e : mat2){cout << e.first << " is " << e.second << endl;}
}int main()
{test4();return 0;
}
运行结果 :
小呆呆 1
波比 2
超人强 6小呆呆 1
超人强 6交换后的mat1->
迪迦 is 1
戴拿 is 2交换后的mat2->
小呆呆 is 1
超人强 is 6
- 桶操作

void test5()
{unordered_map<string, int> mat1{ {"小呆呆", 1}, {"波比", 2}, {"迪迦", 3} };// 桶的个数cout << mat1.bucket_count() << endl << endl;// 每个桶的有效个数for (int i = 0; i < mat1.bucket_count(); i++){printf("[%d] -> %d\n", i, mat1.bucket_size(i));}cout << endl;// 各个key所在的桶for (const auto& e : mat1){cout << mat1.bucket(e.first) << endl;}
}int main()
{test5();return 0;
}
运行结果 :
8[0] -> 1
[1] -> 0
[2] -> 1
[3] -> 0
[4] -> 0
[5] -> 0
[6] -> 1
[7] -> 02
6
0
1.2 unordered_set的接口
unordered_set 和 unordered_map的接口大致一样, 但是没有 operator [ ]
2. 哈希底层
2.1 概念
unordered_set 和 unordered_map的效率高的原因 ⇒ 底层是哈希结构
- 理想中的搜索方法 :
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较。顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即O( l o g 2 N log_2 N log2N),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素的比较次数。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。
如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素.
使元素的存储位置和关键码建立一 一映射的关系, 这个方法称为 哈希(散列)方法,
通过一个函数使得存储位置和关键码建立一 一映射的关系, 这个函数称为 哈希函数,
最终形成的结构, 称为 哈希(散列)表, HashTable
不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为 哈希冲突或哈希碰撞
-
先浅浅地看一下哈希结构, 来理解一下概念

-
常见的哈希函数
哈希冲突的一个重要原因就是 哈希函数设置的不好
那么, 我们来了解一下最常见的两个哈希函数-
直接寻址法 :
一个key对应一个位置
前提 : 知道数据集合的大小 和 分布情况
适合场景: 数据量小且均匀

-
除留余数法 :
准备一个基准值去估计数据量的多少, 设为m, 采用 hash(key) = key % m的方法去建立元素和下标的一 一 映射关系
-
-
采用直接寻址法 — —
数据量小 且 集中
字符串中第一个唯一字符
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {// <s中的每个字符, 个数>int hash[26] = {0};// 映射for(auto e : s){hash[e-'a']++;}// 查找for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){if(hash[s[i] - 'a'] == 1){return i;}}return -1;}
};
-
采用除留余数法 — —
任何场景下都可
下面的 哈希冲突解决 和 实现 都是采用的除留余数法 -
哈希函数设置的越巧妙, 哈希冲突就越低, 但是
哈希冲突无法避免
2.2 解决哈希冲突
解决哈希冲突主要有两种方法 : 闭散列 和 开散列
- 闭散列
闭散列, 也叫开放寻址法,
思路是 :当冲突发生时, 必然有空位置, 那么把冲突的元素放到 "下一个空位置" 即可!
-
插入逻辑

-
查找逻辑

- 这从另一方面也体现了
哈希表的有效数据不应该占比太大 ⇒ 否则就是遍历这个哈希结构, O(N)
但是也不能占比太少 ⇒ 浪费空间
⇒一般, 控制 有效个数 / 哈希结构的大小 在 [0.7, 0.8]的范围内是比较合理的
- 这从另一方面也体现了
-
删除逻辑
首先, 能确定的是不能直接把这个位置去掉

那么该位置要进行保留, 那么值该怎么处理呢 ?
改为 0, -1 … … 等无意义的数值?
其实这些都是不行的,你怎么知道你修改后的数据是无意义的呢⇒ 能确定的是该位置的值也要进行保留
⇒该位置要进行保留, 值也要进行保留 && 不能影响后面的查找逻辑那么该怎么把它删掉呢? ⇒引入每个下标的状态 : 删除状态, 空白状态, 存在状态 -
由于删除逻辑而导致新的插入逻辑

-
由于删除逻辑而导致新的查找逻辑

- 开散列
开散列, 又叫作拉链法
上面的开放地址法解决哈希冲突的办法是将经过哈希函数处理过的 相同的key, "延后落座"
拉链法的解决思路是将经过哈希函数处理的 相同的key 放到一个单链表中, 然后将每一个单链表的头结点放到一个数组里面. 本质是一个指针数组

- 这里的插入删除, 查找逻辑就是在
key那个桶进行单链表操作
🗨️ 有同学就会说, 这不是单链表操作吗, 不过如此!
- 我们可以控制
有效数据个数 / 桶的大小 = 1 ⇒ 平均下来就是一个桶一个数据
3. 实现
这里都先实现 数据位pair<K, V>类型的
3.1 开放寻址法

- STATE类型
enum STATE
{EXIT,DELETE,EMPTY
};
- HashData类
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{public:HashData(){}HashData(const pair<K, V>& kv):_data(kv){}public:pair<K, V> _data;STATE _st = EMPTY;
};
- Hash类
template<class K, class V, class Com = DEFAULT<K>>
class hash
{public:hash(){// 1. 先给4个空间// 2. size 和 capacity一样大_table.resize(4);}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){// 扩容逻辑if ((double)_sz / _table.size() >= 0.7){size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;hash<K, V> new_ht;new_ht._table.resize(newsize);// 挪动数据for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){// 不用挪动删除状态的值if (_table[i]._st == EXIT){new_ht.insert(_table[i]._data);}}std::swap(*this, new_ht);}// 线性探测for (const auto& e : _table){if (kv.first == e._data.first){return false;}}size_t hashi = com(kv.first) % _table.size();while (_table[hashi]._st == EXIT){++hashi;hashi %= _table.size();}_sz++;_table[hashi] = kv;_table[hashi]._st = EXIT;return true;}// 返回有key,// 不允许用户在外面更改key,// 所以返回<const K, V>*HashData<const K, V>* find(const K& key){size_t hashi = com(key) % _table.size();while (_table[hashi]._st != EMPTY){if (_table[hashi]._st == EXIT && _table[hashi]._data.first == key){return (HashData<const K, V>*)&_table[hashi];}hashi++;hashi %= _table.size();}return nullptr;}bool erase(const K& key){// 复用findHashData<const K, V>* res = find(key);if (res){res->_st = DELETE;_sz--;return true;}else{return false;}//for (auto e : _table)//{// if (e._data.first == key)// {// e._st = DELETE;// _sz--;// return true;// }//}//return false;}private:vector<HashData<K, V>> _table;size_t _sz = 0;Com com;
};
- DEFAULT —
通过仿函数来解决 字符串 不能进行 % 的问题
// 通过仿函数来解决 字符串 不能进行 %
template<class K>
struct DEFAULT
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};// 模版的特化 -- 全特化
// 解决 字符串问题
template<>
struct DEFAULT<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){int res = 0;for (auto e : key){res += e * 131;}return res;}
};
3.2 拉链法
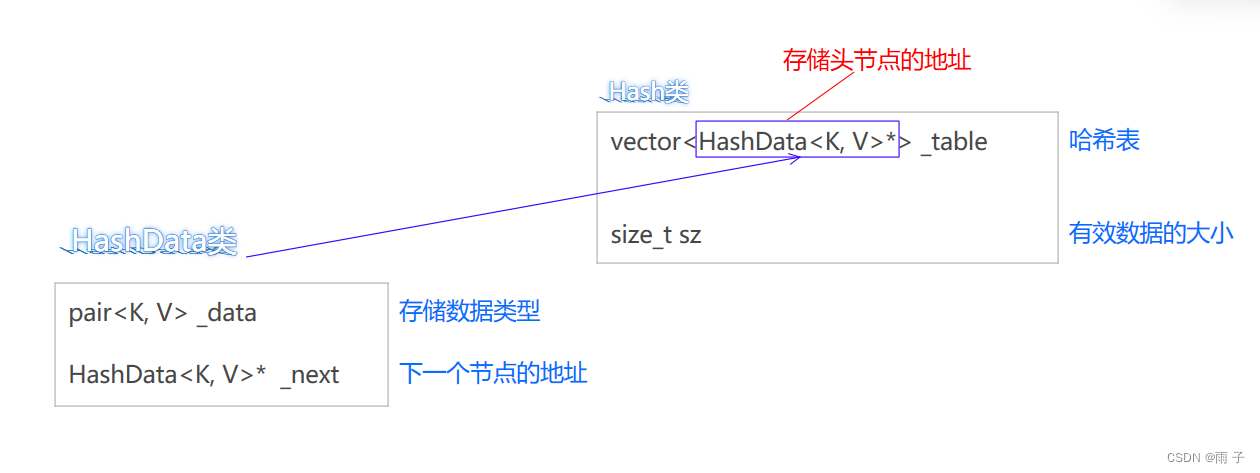
- HashData类
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
public:
HashData(const pair<K, V>& kv):_data(kv)
{}public:
pair<K, V> _data;
HashData<K, V>* _next;
};
- Hash类
template<class K, class V, class Com = DEFAULT<K>>
class hash
{typedef HashData<const K, V> Node;
public:hash(){_table.resize(4, nullptr);}Node* find(const K& key){size_t hashi = com(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (com(cur->_data.first) == com(key)){return cur;}cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){Node* res = find(kv.first);if (res){return false;}// 扩容逻辑if (_sz == _table.size()){vector<Node*> new_table;new_table.resize(_table.size() * 2, nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];// 顺手牵走这个桶的内容while (cur){// 提前保存 next, 后面会改变的Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = com(cur->_data.first) % new_table.size();// 先让cur链接上新表中该桶的内容cur->_next = new_table[hashi];// 再让cur成为新表中该桶的头节点new_table[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}}_table.swap(new_table);}// 插入逻辑size_t hashi = com(kv.first) % _table.size();Node* newnode = new Node(kv);newnode->_next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = newnode;++_sz;return true;}bool erase(const K& key){Node* res = find(key);if (res == nullptr){return false;}else{size_t hashi = com(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_data.first == key){if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = cur->_next;}else{prev->_next = cur->_next;}}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}--_sz;delete cur;}return true;}void print(){for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];printf("[%d]->", i);while (cur){printf("%d", cur->_data.first);cur = cur->_next;}cout << "NULL" << endl;}cout << endl;}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _sz = 0;Com com;
};
- DEFAUL —
通过仿函数来解决 字符串 不能 % 的问题
// 通过仿函数来解决 字符串 不能进行 %
template<class K>
struct DEFAULT
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};// 模版的特化 -- 全特化
// 解决 字符串问题
template<>
struct DEFAULT<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){int res = 0;for (auto e : key){res += e * 131;}return res;}
};
无心买酒谒青春,对镜空嗟白发新。
花下少年应笑我,垂垂羸马访高人。
— — 岳飞 <过张溪赠张完>












--安装)






