目录
一 概念
二 运算符重载的实现
三 关于时间的所有运算符重载
四 默认赋值运算符
五 const取地址操作符重载
一 概念
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
注意:
不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型 + ,不能改变其含义
作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐藏的this
总之如何去比较自定义类型, 并且要有可读性, 那就需要运算符重载
二 运算符重载的实现
// 全局的operator==
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
// 这里会发现运算符重载成全局的就需要成员变量是公有的,那么问题来了,封装性如何保证?
// 这里其实可以用我们后面学习的友元解决,或者干脆重载成成员函数。
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1._year == d2._year//如果成员变量不是共有的那就访问不到了&& d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day == d2._day;
}
void Test1()
{Date d1(2018, 9, 26);Date d2(2018, 9, 27);/*cout << operator>(d1, d2) << endl;cout << operator==(d1, d2) << endl;*/cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;
}int main()
{Test1();return 0;
}
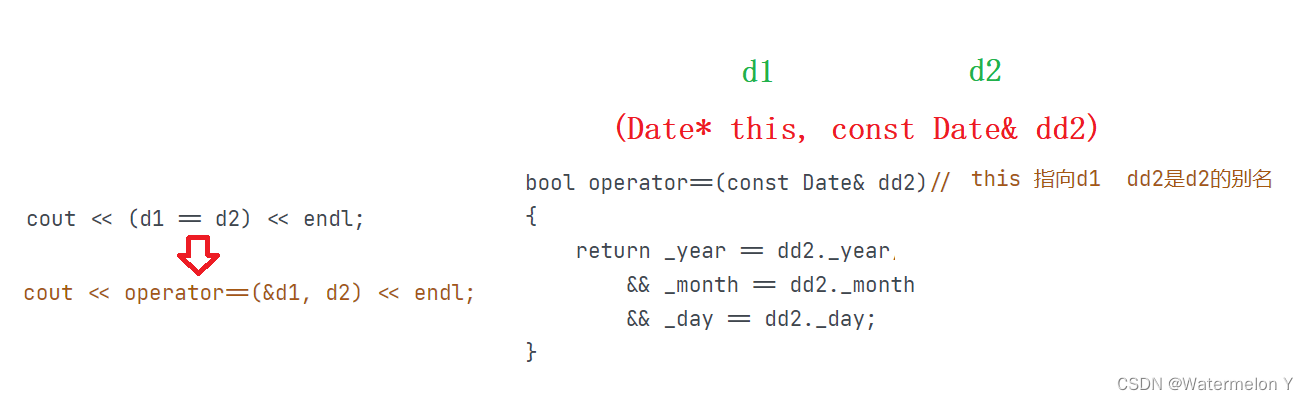
现在我们把==运算符重载到成员函数中
// 全局的operator==
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}bool operator==(const Date& dd2){return _year == dd2._year&& _month == dd2._month&& _day == dd2._day; }private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};void Test2()
{Date d1(2018, 9, 26);Date d2(2018, 9, 27);/*cout << operator>(&d1, d2) << endl;cout << operator==(&d1, d2) << endl;*/cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;
}int main()
{Test2();return 0;
}
总结:
运算符重载 函数重载 他们之间没有关联
运算符重载:自定义类型可以直接使用运算符
函数重载:可以允许参数不同的同名函数,
内置类型对象可以直接用各种运算符,内置类型都是简单类型
语言自己定义,编译直接转换成指令
自定义类型呢?不支持 所以运算符重载诞生
不能被重载的运算符只有5个, 点号.三目运算 ? : 作用域访问符::运算符sizeof 以及.*(*是可以重载的 只是点星是不能的)
三 关于时间的所有运算符重载
1 Date.h
#pragma once#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public://全缺省参数只需要在声明中Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);Date& operator=(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& y);bool operator!=(const Date& y);bool operator>(const Date& y);bool operator<(const Date& y);bool operator>=(const Date& y);bool operator<=(const Date& y);int operator-(const Date& d);Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day);Date& operator++();Date operator++(int);Date& operator--();Date operator--(int);//友元函数friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
2 Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Date.h"int Date:: GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{int days[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };int day = days[month];if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) && (year % 100 == 0)){day += 1;}return day;
}//构造函数
Date:: Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}//赋值运算符
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{if (*this != d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;
}
//赋值运算符如果不显式实现,编译器会生成一个默认的。此时用户再在类外自己实现一个全局的赋值运算符重载,
//就和编译器在类中生成的默认赋值运算符重载冲突了,故赋值运算符重载只能是类的成员函数bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return (_day == d._day && _month == d._month && _year == d._year);
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}else{return false;}}bool Date:: operator>=(const Date& d)
{return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}bool Date:: operator<=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}//在类里面是不用区分函数顺序的
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this -= (-day);}_day = _day + day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}Date& Date:: operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day < 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}//++d1
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}//d1++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}//--d1
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}//d1--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}//d1 -100
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{//假设左大右小int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){flag = -1;min = *this;max = d;}int n = 0;while (min != max){min++;n++;}return n * flag;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}
3 Test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date.h"void TestDate1()
{Date d1(2023, 10, 24);d1.Print();Date ret1 = d1 - 100;ret1.Print();Date ret2 = d1 - 10000;ret2.Print();Date ret3 = d1 + 100;ret3.Print();Date ret4 = d1 + 10000;ret4.Print();
}void TestDate2()
{Date d1(2023, 10, 24);d1.Print();// 语法设计,无法逻辑闭环,那么这时就只能特殊处理// 特殊处理++d1;d1.operator++();d1.Print();d1++;d1.operator++(10);d1.operator++(1);d1.Print();
}void TestDate3()
{Date d1(2023, 10, 24);d1.Print();Date d2(2024, 5, 5);d2.Print();Date d3(2024, 8, 1);d3.Print();cout << d2 - d1 << endl;cout << d1 - d3 << endl;}void TestDate4()
{Date d1(2023, 10, 24);d1 += -100;d1.Print();
}void Test5()
{Date d1(2023, 10, 21);Date d2(2023, 12, 31);d1.Print();cout << d1;cin >> d2;cout << d2 << d1 << endl;
}int main()
{TestDate1();TestDate2();TestDate3();TestDate4();Test5();return 0;
}
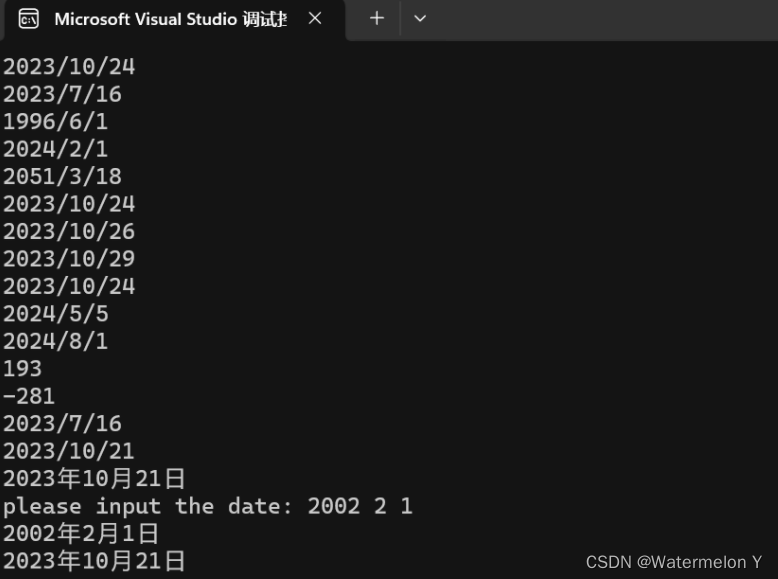
解释一下<< >>运算符重载

四 默认赋值运算符
用户没有显式实现时,编译器会生成一个默认赋值运算符重载,以值的方式逐字节拷贝。注 意:内置类型成员变量是直接赋值的,而自定义类型成员变量需要调用对应类的赋值运算符 重载完成赋值。
Date MyStack这些就不用自己构造赋值运算符重载, 但是栈这些就必须要自己构造, 因为涉及到了资源的拷贝
注意:如果类中未涉及到资源管理,赋值运算符是否实现都可以;一旦涉及到资源管理则必 须要实现。
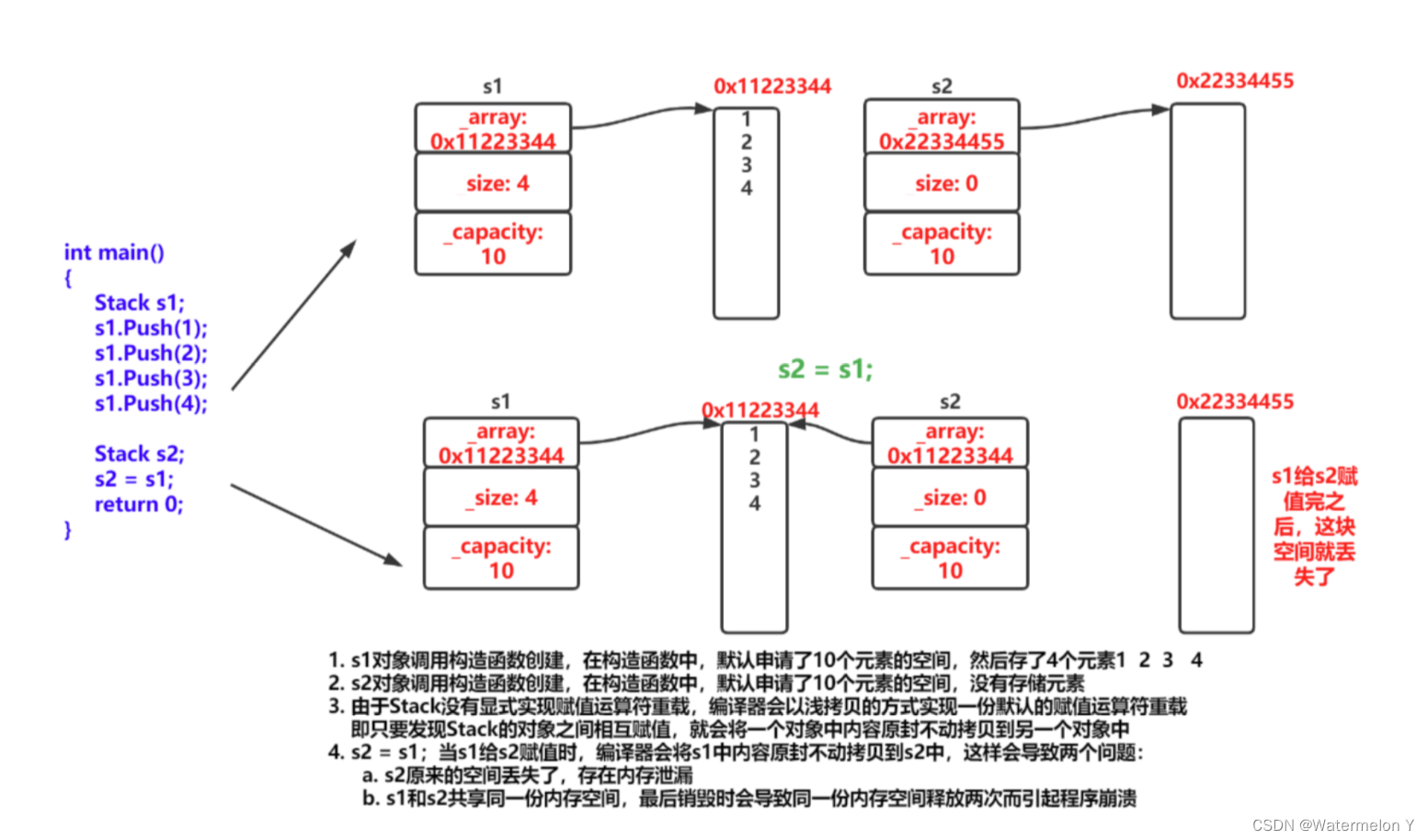
// 这里会发现下面的程序会崩溃 这里就需要我们以后讲的深拷贝去解决。
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(size_t capacity = 10){_array = (DataType*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(DataType));if (nullptr == _array){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_size = 0;_capacity = capacity;}void Push(const DataType& data){// CheckCapacity();_array[_size] = data;_size++;}~Stack(){if (_array){free(_array);_array = nullptr;_capacity = 0;_size = 0;}}
private:DataType* _array;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{Stack s1;s1.Push(1);s1.Push(2);s1.Push(3);s1.Push(4);Stack s2;s2 = s1;return 0;
}
改正如下
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(size_t capacity = 10){_array = (DataType*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(DataType));if (nullptr == _array){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_size = 0;_capacity = capacity;}void Push(const DataType& data){// CheckCapacity();_array[_size] = data;_size++;}void Pop(){_size--;}DataType Top(){return _array[_size - 1];}bool Empty(){return _size == 0;}Stack& operator=(Stack& st){_array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * st._capacity);if (_array == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_array, st._array, sizeof(int) * st._size);_size = st._size;_capacity = st._capacity;}~Stack(){if (_array){free(_array);_array = nullptr;_capacity = 0;_size = 0;}}
private:DataType* _array;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{Stack s1;s1.Push(1);s1.Push(2);s1.Push(3);s1.Push(4);while (!s1.Empty()){printf("%d ", s1.Top());s1.Pop();}printf("\n");Stack s2;s2 = s1;s2.Push(5);s2.Push(6);s2.Push(7);s2.Push(8);while (!s2.Empty()){printf("%d ", s2.Top());s2.Pop();}return 0;
}
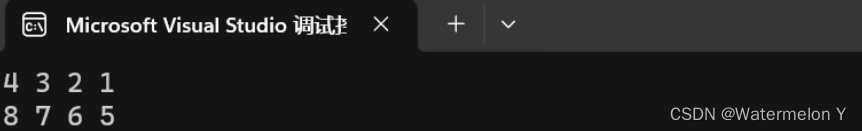
讲一下为什么
五 const取地址操作符重载
这两个默认成员函数一般不用重新定义 ,编译器默认会生成。
Date* operator&() //返回类型为 Date*{cout << "Date* operator&()" << endl;return this;}const Date* operator&()const//返回类型为 const Date*{cout << "const Date* operator&()const" << endl;return this;}
当然不是const的地址也可以调用const类型, 只不过两个都存在的时候, 会优先调用最匹配的一个
这两个运算符一般不需要重载,使用编译器生成的默认取地址的重载即可,只有特殊情况,才需 要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容!
本节感觉理解起来还是比较抽象, 有时候记住咋用就行了, 祖师爷就是这样规定的, 但是底层的东西我们还是得好好琢磨一下.对于类和对象基础要求挺高. 大家可以看看我之前的博客.
继续加油!




-使用设计模式实现简易版springIoc)


添加导入导出功能)








)


