目录
概述
七、OrderBy
八、OrderByDescending
九、Skip
十、Take
十一、Any
十二、All
C# Linq 详解一
1.Where
2.Select
3.GroupBy
4.First / FirstOrDefault
5.Last / LastOrDefault
C# Linq 详解二
1.OrderBy
2.OrderByDescending
3.Skip
4.Take
5.Any
6.All
C# Linq 详解三
1.Sum / Min / Max / Average
2.Distinct
3.Concat
4.Join
5.ToList
6.ToArray
7.ToDictionary
C# Linq 详解四
1.SelectMany
2.Aggregate
3.DistinctBy
4.Reverse
5.SequenceEqual
6.Zip
7.SkipWhile
8.TakeWhile
C# Linq 详解一_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# Linq 详解三_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# Linq 详解四_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
概述
语言集成查询 (LINQ) 是一系列直接将查询功能集成到 C# 语言的技术统称。 数据查询历来都表示为简单的字符串,没有编译时类型检查或 IntelliSense 支持。 此外,需要针对每种类型的数据源了解不同的查询语言:SQL 数据库、XML 文档、各种 Web 服务等。 借助 LINQ,查询成为了最高级的语言构造,就像类、方法和事件一样。
对于编写查询的开发者来说,LINQ 最明显的“语言集成”部分就是查询表达式。 查询表达式采用声明性查询语法编写而成。 使用查询语法,可以用最少的代码对数据源执行筛选、排序和分组操作。 可使用相同的基本查询表达式模式来查询和转换 SQL 数据库、ADO .NET 数据集、XML 文档和流以及 .NET 集合中的数据。
七、OrderBy
OrderBy 方法用于对集合中的元素进行升序排序。它返回一个新的排序后的集合,而不会修改原始集合。
这里是根据用户的年龄做了一个排序,在 OrderBy 方法的参数就是要排序的内容。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<People> peopleList = new List<People>(){new People(){Name="张三", Age=12, Career="学生" },new People(){Name="柱子", Age=25, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="铁蛋", Age=23, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="狗剩", Age=34, Career="职员" },new People(){Name="二狗", Age=28, Career="职员" },};var collect = peopleList.OrderBy(x => x.Age);foreach (var people in collect){Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}", people.Name, people.Age);}Console.ReadKey();}}class People{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Career { get; set; }}
}运行:

另一种就是纯数字了,这种排序的用法和上面一样
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int[] numbers = { 5, 2, 8, 4, 1 };var sortedNumbers = numbers.OrderBy(n => n);foreach (var number in sortedNumbers){Console.WriteLine(number);}Console.ReadKey();}}
}运行:

八、OrderByDescending
OrderByDescending 方法用于对集合中的元素进行降序排序。它返回一个新的排序后的集合,而不会修改原始集合。
OrderByDescending 是 OrderBy 的降序排序,用法和 OrderBy 也差不多,只是返回的值顺序不一样
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<People> peopleList = new List<People>(){new People(){Name="张三", Age=12, Career="学生" },new People(){Name="柱子", Age=25, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="铁蛋", Age=23, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="狗剩", Age=34, Career="职员" },new People(){Name="二狗", Age=28, Career="职员" },};var collect = peopleList.OrderByDescending(x => x.Age);foreach (var people in collect){Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}", people.Name, people.Age);}Console.ReadKey();}}class People{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Career { get; set; }}
}运行:

九、Skip
Skip方法用于跳过序列中指定数量的元素,并返回剩下的元素。
案例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<People> peopleList = new List<People>(){new People(){Name="张三", Age=12, Career="学生" },new People(){Name="柱子", Age=25, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="铁蛋", Age=23, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="狗剩", Age=34, Career="职员" },new People(){Name="二狗", Age=28, Career="职员" },};var collect = peopleList.Skip(1);foreach (People people in collect){Console.WriteLine(people.Name);}Console.ReadKey();}}class People{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Career { get; set; }}
}
运行:

注意这里,skip 传入的是1,它表示从数组中的1这里开始,包含1的下标在里面,一起返回回来
这么写可能不明显,用数字来写会更明显一点,看下面的案例,传入的索引是3,那么就是数组中的下标3这里开始,包含3在里面,一直到结束,下标3这里是数字是24,那么就是24-15
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<int> numList = new List<int> { 1, 4, 5, 24, 43, 67, 12, 90, 15 };var collect = numList.Skip(3);foreach (int num in collect){Console.WriteLine(num);}Console.ReadKey();}}
}运行:

十、Take
Take 方法用于从集合中选择指定数量的元素。它返回一个新的集合,其中包含原始集合中的前几个元素。
Skip 获取的是后半部分,那么 Take 则是获取前半部分,用法差异不大。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<int> numList = new List<int> { 1, 4, 5, 24, 43, 67, 12, 90, 15 };var collect = numList.Take(4);foreach (int num in collect){Console.WriteLine(num);}Console.ReadKey();}}
}运行:

十一、Any
Any 方法用于检查集合中是否存在满足指定条件的元素。它返回一个布尔值,表示集合中是否存在符合条件的元素。
any 方法只要数组中条件满足一个,就会返回 true,比如数组中是否有一个年龄大于 23的人,它会从数组的第一个元素开始遍历,假设第一个元素满足条件,那么就立马返回 true。
案例1,查找是否存在年龄大于23的元素
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<People> peopleList = new List<People>(){new People(){Name="张三", Age=12, Career="学生" },new People(){Name="柱子", Age=25, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="铁蛋", Age=23, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="狗剩", Age=34, Career="职员" },new People(){Name="二狗", Age=28, Career="职员" },};bool result = peopleList.Any(x => x.Age > 23);Console.WriteLine("寻找结果:{0}", result);Console.ReadKey();}}class People{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Career { get; set; }}
}运行:

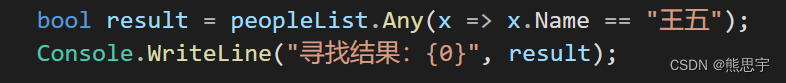
案例2,查找是否存在名字叫二狗的人
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<People> peopleList = new List<People>(){new People(){Name="张三", Age=12, Career="学生" },new People(){Name="柱子", Age=25, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="铁蛋", Age=23, Career="农民" },new People(){Name="狗剩", Age=34, Career="职员" },new People(){Name="二狗", Age=28, Career="职员" },};bool result = peopleList.Any(x => x.Name == "二狗");Console.WriteLine("寻找结果:{0}", result);Console.ReadKey();}}class People{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Career { get; set; }}
}运行:
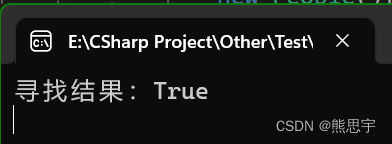
如果将名字改为王五,那么就找不到了
运行:

十二、All
All 方法用于检查集合中的所有元素是否都满足指定的条件。它返回一个布尔值,表示集合中的所有元素是否都满足条件。
和 any 不一样的是,all 会判断所有的元素是否满足条件,只要有一个不满足条件,就返回 false
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<int> numList = new List<int> { 1, 4, 5, 24, 43, 67, 12, 90, 15 };bool result = numList.All(x => x > 0);Console.WriteLine("结果:{0}", result);Console.ReadKey();}}
}运行:

当前数组中的所有值都大于0,所以返回是 true,下面换一种写法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;namespace LinqTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<int> numList = new List<int> { 1, 4, 5, 24, 43, 67, 12, 90, 15 };bool result = numList.All(x => x > 23);Console.WriteLine("结果:{0}", result);Console.ReadKey();}}
}运行:

end









下安装mariadb10详解)









