文章目录
- 为什么要有AVL树
- 什么是AVL树
- AVL树的实现
- 元素的插入
- 平衡因子的更新
- AVL树的旋转
- AVL树的检查
- 完整实现
本篇总结的是AVL树中的全部内容,配有详细的图解过程
为什么要有AVL树
前面对map/multimap/set/multiset进行了简单的介绍,在其文档介绍中发现,这几个容器有个共同点是:其底层都是按照二叉搜索树来实现的,但是二叉搜索树有其自身的缺陷,假如往树中插入的元素有序或者接近有序,二叉搜索树就会退化成单支树,时间复杂度会退化成O(N),因此map、set等关联式容器的底层结构是对二叉树进行了平衡处理,即采用平衡树来实现
什么是AVL树
当一个二叉搜索树形如下面的场景时,进行查找的时候效率会相当低下

甚至当接近为单支树的时候,查找效率会相当于在顺序表中的查找效率,因此俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii和E.M.Landis发明了一个解决方案:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度,这也就是AVL树的由来
一棵AVL树或者是空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉搜索树:
- 它的左右子树都是
AVL树 - 左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过
1
左右子树的高度差也叫做平衡因子,在这样的树中进行搜索,时间复杂度是O(logN)
AVL树的实现
元素的插入
首先定义出节点,由于AVL树对于向上寻找信息有需求,因此在定义节点信息的时候要有该节点指向父亲的指针
// 定义AVL树的节点
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(val), bf(0){}// 左子树指针 右子树指针 父亲节点指针 节点值 平衡因子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;pair<K, V> _kv;int bf;
};
下面定义AVL树的插入,AVL树的插入主要是先插入到一个二叉搜索树中,再对于二叉搜索树进行平衡,因此要先插入到二叉搜索树
bool Insert(const pair<K, V> kv)
{Node* newnode = new Node(kv);if (_root == nullptr){_root = newnode;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (newnode->_kv.first > cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (newnode->_kv.first < cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}if (newnode->_kv.first > parent->_kv.first){parent->_right = newnode;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = newnode;cur->_parent = parent;}
}
上面就是二叉搜索树的基本部分,下面开始的是AVL树平衡问题
平衡因子的更新
新节点插入后,AVL树的平衡性可能会遭到破坏,引入平衡因子的意义也就在于此,因此插入后的第一步是要更新平衡因子,看有没有遭到破坏,对于平衡因子的调整有下面的几种情况
- 如果插入到节点的左侧,平衡因子-1即可
- 如果插入到节点的右侧,平衡因子+1即可
节点插入后会有新的问题,看下面的场景
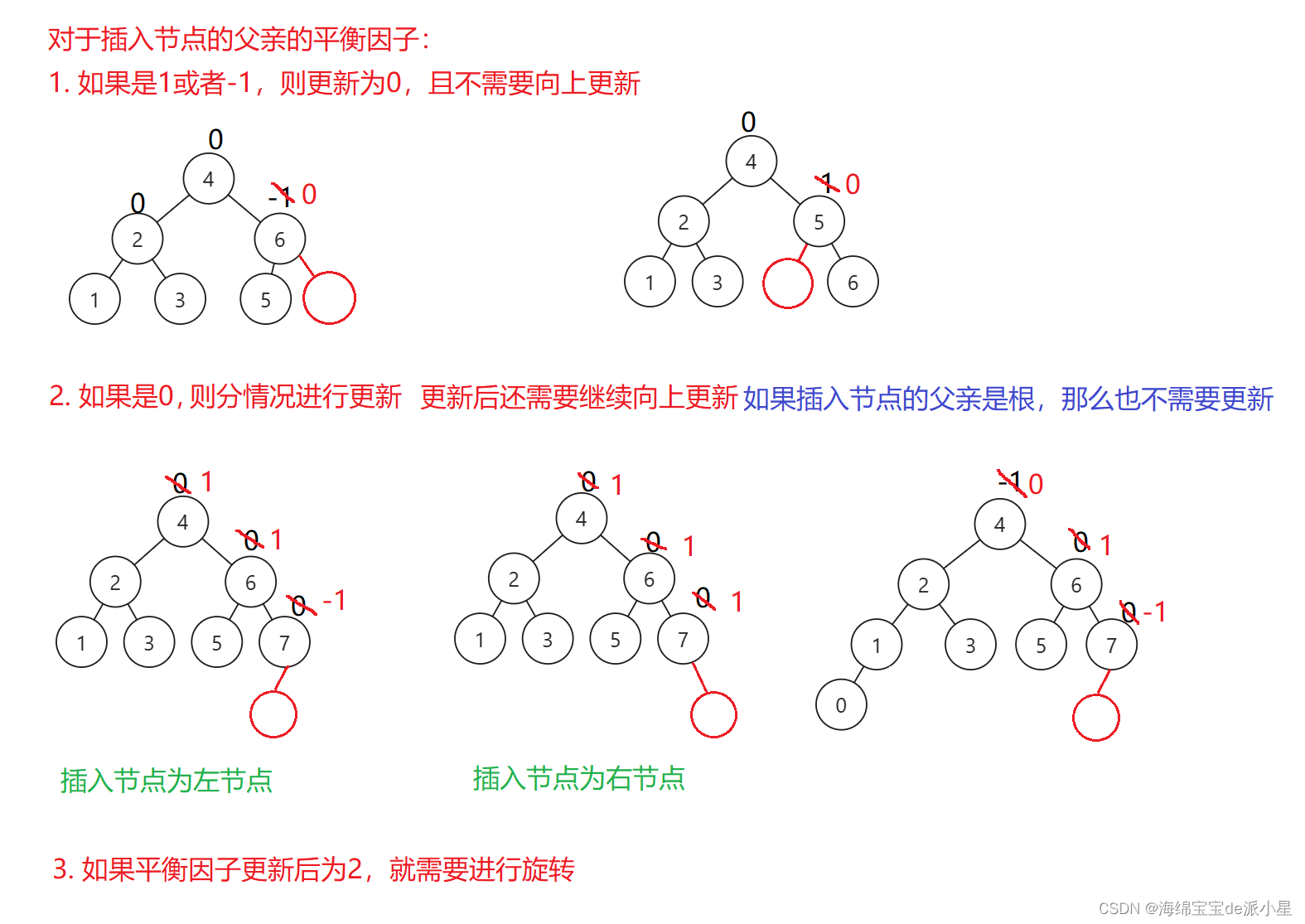
依据这个原理,可以写出代码来更新平衡因子
// 节点的插入// 节点插入的逻辑和搜索树基本一致,只是如果不符合要求需要进行旋转bool Insert(const pair<K, V> kv){Node* newnode = new Node(kv);if (_root == nullptr){_root = newnode;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (newnode->_kv.first > cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (newnode->_kv.first < cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}if (newnode->_kv.first > parent->_kv.first){parent->_right = newnode;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = newnode;cur->_parent = parent;}// 上面就是二叉搜索树的基本部分,下面更新平衡因子while (parent){// 如果cur是parent的左节点,平衡因子-1,如果是右节点,平衡因子+1if (cur == parent->_left){parent->_bf--;}else{parent->_bf++;}// 判断父节点平衡因子绝对值的情况:// 1. 如果为0,则证明不需要向上更新// 2. 如果为1,则需要向上更新// 3. 如果为2,则需要进行旋转if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){// 开始进行旋转}else{// 如果绝对值比2大,说明平衡因子出错了,强制结束assert(false);}}}
AVL树的旋转
那当上面的情况已经发生,AVL树应该如何进行平衡?这就引入了旋转的概念
在AVL树中,当破坏了AVL树的平衡后,总共有四种会引发的旋转
1. 新节点插入较高左子树的左侧,引发右单旋
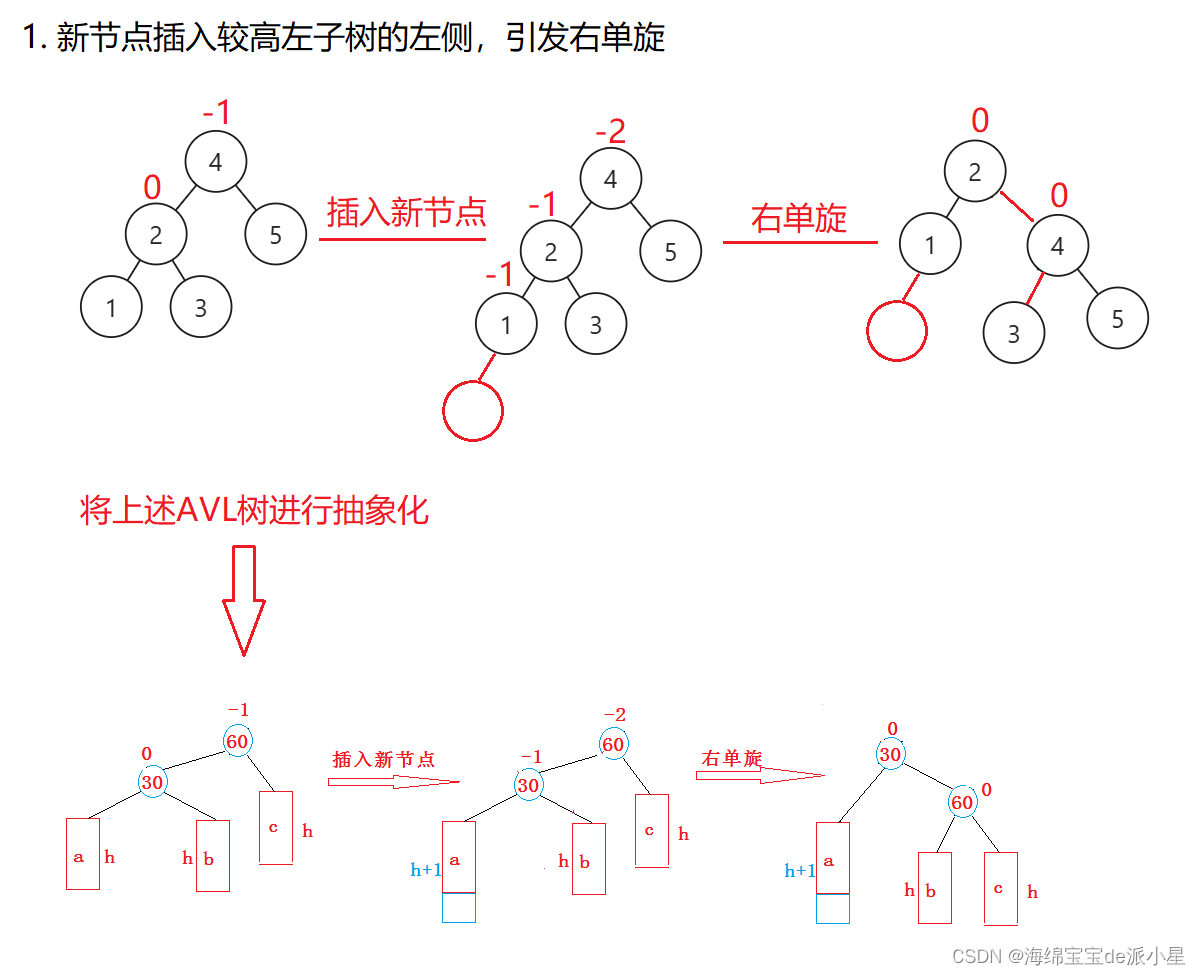
因此下面实现右单旋的代码实现:
// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}2. 新节点插入在较高右子树的右侧,引发左单旋
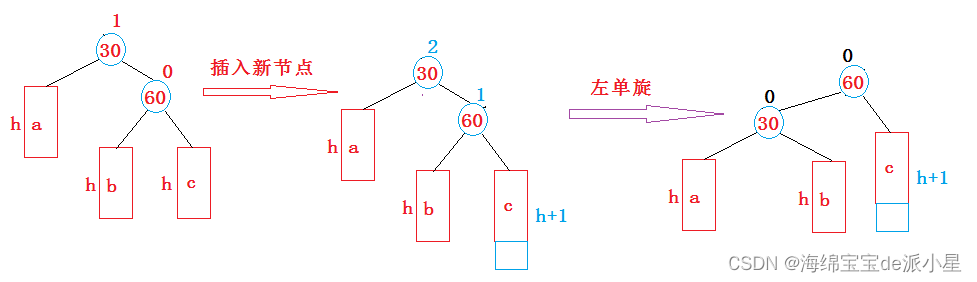
// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;// 更新节点parent->_right = subRL;parent->_parent = subR;subR->_left = parent;subR->_parent = parentParent;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;// 更新parentParentif (_root == parent){_root = subR;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}}parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}3. 新节点插入较高右子树的左侧,引发先右单旋再左单旋
对于这种情况来说,总共有下面的两种情况
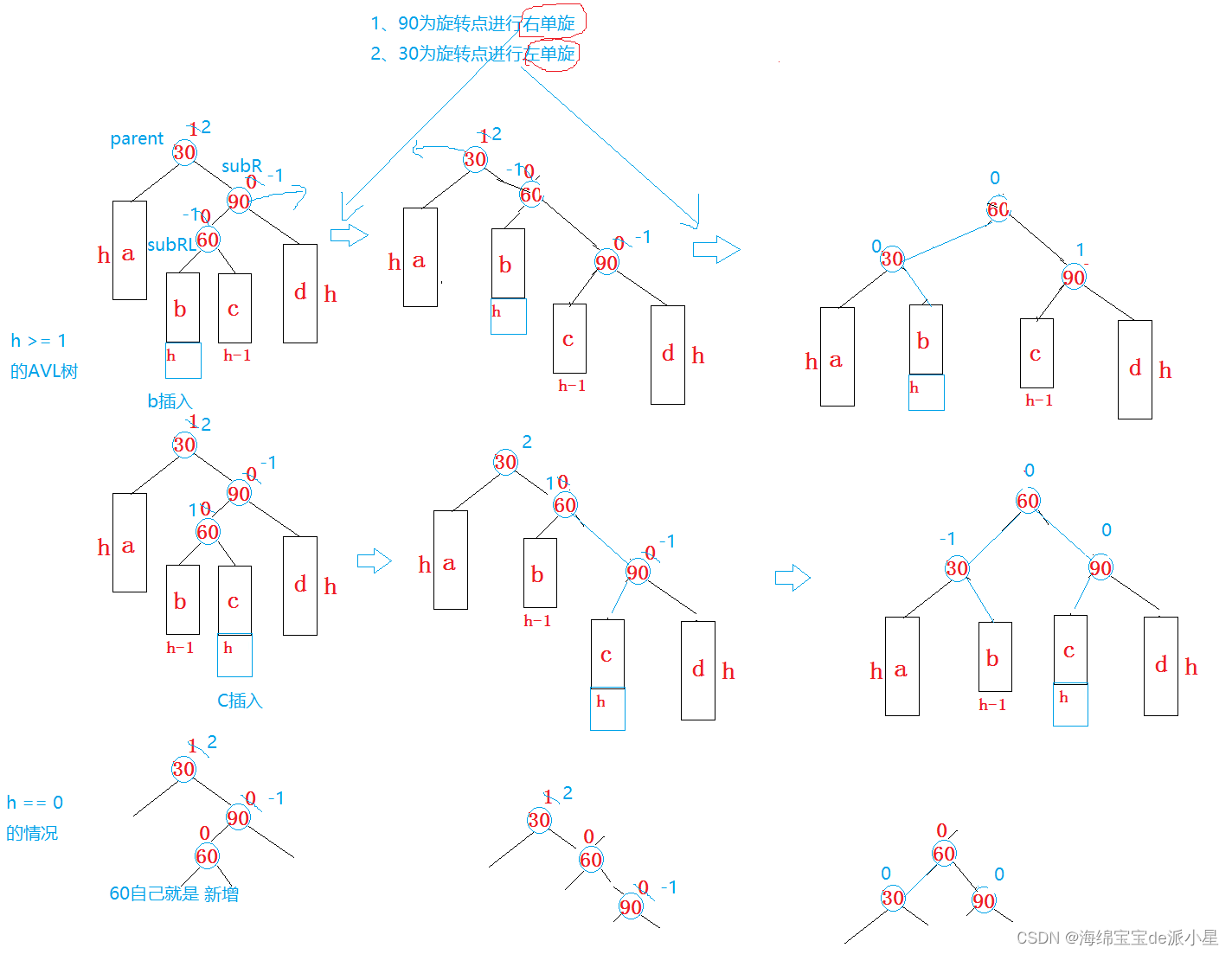
代码实现也有了思路,先左单旋再右单旋,最后修改平衡因子的值即可,而修改平衡因子的值,可以通过subRL的bf值来判断不同的情况,根据不同的情况修改不同的值即可
// 先右单旋再左单旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(subR);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 0){// 自己就是新增的节点parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){// 在左子树进行的插入parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){// 在右子树进行的插入subRL->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else{assert(false);}}4. 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧,引发先左单旋再右单旋
分析方法和前面类似
// 先进行左单旋,再进行右单旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(subL);RotateR(parent);// 更换平衡因子if (bf == 0){subL->_bf = subLR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){// 插入在右子树subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){// 插入在左子树parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;subLR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}AVL树的检查
依据上面的实现可以基本实现AVL树,那如何验证AVL树是否正确?其实验证也很简单,只需要看每个节点的平衡因子是否等于对应的右子树减左子树的值即可
// 用于检查树的高度int TreeHeight(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftheight = TreeHeight(root->_left);int rightheight = TreeHeight(root->_right);return max(leftheight, rightheight) + 1;}// 保持树的封装 进行检查AVL树bool IsBalance(){return _IsBalance(root);}// 进行检查AVL树bool _IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;int leftheight = TreeHeight(root->_left);int rightheight = TreeHeight(root->_right);if (rightheight - leftheight != root->_bf)return false;return abs(rightheight-leftheight)<2 && _IsBalance(root->_left) && _IsBalance(root->_right);}
这样就完成了AVL树的测试
完整实现
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;// 定义AVL树的节点
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(kv), _bf(0){}// 左子树指针 右子树指针 父亲节点指针 节点值 平衡因子AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;pair<K, V> _kv;int _bf;
};// 定义AVL树
template<class K, class V>
class AVLTree
{typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:AVLTree():_root(nullptr){}// 节点的插入// 节点插入的逻辑和搜索树基本一致,只是如果不符合要求需要进行旋转bool Insert(const pair<K, V> kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);if (kv.first > parent->_kv.first){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}// 上面就是二叉搜索树的基本部分,下面更新平衡因子while (parent){// 如果cur是parent的左节点,平衡因子-1,如果是右节点,平衡因子+1if (cur == parent->_left){parent->_bf--;}else{parent->_bf++;}// 判断父节点平衡因子绝对值的情况:// 1. 如果为0,则证明不需要向上更新// 2. 如果为1,则需要向上更新// 3. 如果为2,则需要进行旋转if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){// 开始进行旋转if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}break;}else{// 如果绝对值比2大,说明平衡因子出错了,强制结束assert(false);}}return true;}// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;// 更新节点parent->_right = subRL;parent->_parent = subR;subR->_left = parent;subR->_parent = parentParent;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;// 更新parentParentif (_root == parent){_root = subR;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}}parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}// 先右单旋再左单旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(subR);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 0){// 自己就是新增的节点parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){// 在左子树进行的插入parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){// 在右子树进行的插入subRL->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else{assert(false);}}// 先进行左单旋,再进行右单旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(subL);RotateR(parent);// 更换平衡因子if (bf == 0){subL->_bf = subLR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){// 插入在右子树subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){// 插入在左子树parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;subLR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}// 用于检查树的高度int TreeHeight(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftheight = TreeHeight(root->_left);int rightheight = TreeHeight(root->_right);return max(leftheight, rightheight) + 1;}// 保持树的封装 进行检查AVL树bool IsBalance(){return _IsBalance(root);}// 进行检查AVL树bool _IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;int leftheight = TreeHeight(root->_left);int rightheight = TreeHeight(root->_right);if (rightheight - leftheight != root->_bf)return false;return abs(rightheight-leftheight)<2 && _IsBalance(root->_left) && _IsBalance(root->_right);}private:Node* _root;
};
)




)
)
)











