文章目录
- 4.3 字符串
- 4.3.1 字符串的定义与存储
- 4.3.2 字符串的基本操作(链式存储)
- 1. 结构体
- 2. 初始化
- 3. 判空
- 4. 串尾添加
- 5. 打印
- 6. 串长统计
- 7. 查找
- 8. 复制
- 9. 插入
- 10. 删除
- 11. 串拼接
- 12. 销毁
- 13. 主函数
- 14. 代码整合
4.3 字符串
字符串(String)是由零个或多个字符(char)顺序排列组成的有限序列,简称为串。例如 “good morning”就是由12个字符构成的一个字符串。一般把字符串记作:
S = ′ ′ a 0 a 1 … a n − 1 ′ ′ S=''a_{0} a_{1}…a_{n-1}'' S=′′a0a1…an−1′′
其中S是串名,引号中的字符序列是串值。字符个数是串的长度,长度为0的串被称为空串,因为它不包含任何字符。需要注意的是,空格字符(" ")并不是空串,因为它包含一个字符——空格。
若把某个串称为主串,则主串中任意个连续的字符组成的子序列被称为子串。子串在主串中第一次出现时,其首字符在主串中的序号被称为该子串在主串中的位置。
关于字符串的基础知识亦可参考前文:
【重拾C语言】六、批量数据组织(三)数组初值;字符串、字符数组、字符串数组;类型定义 typedef
【重拾C语言】七、指针(三)指针与字符串(字符串与字符串数组;指针与字符串的遍历、拷贝、比较;反转字符串)
4.3.1 字符串的定义与存储
字符串在许多非数值计算问题中扮演着重要的角色,并在模式匹配、程序编译和数据处理等领域得到广泛应用。在高级程序设计语言中,字符串通常被定义为以特殊字符’\0’(称为空字符或字符串结束符)结尾的字符序列。这个约定使得在处理字符串时可以方便地确定字符串的结束位置。关于字符串的存储方式,主要有两种常见的方式:
-
顺序存储:字符串的字符按照顺序依次存储在连续的内存空间中。这种方式使得字符串的访问和操作效率较高,可以通过索引直接访问任意位置的字符。在顺序存储方式中,字符串的长度可以通过计算字符个数或者遇到’\0’结束符来确定。
-
链式存储:字符串的字符通过链表的方式进行存储。每个节点包含一个字符和指向下一个节点的指针。链式存储方式可以动态地分配内存,适用于长度可变的字符串。但是相比于顺序存储,链式存储方式需要更多的内存空间,并且访问字符需要遍历链表。
选择何种存储方式取决于具体的应用场景和需求。顺序存储适合于需要频繁访问和操作字符串的情况,而链式存储适合于长度可变的字符串或者对内存空间要求较高的情况。具体C语言实现可参照前文:
【数据结构】数组和字符串(十一):字符串的定义与存储(顺序存储、链式存储及其C语言实现)
4.3.2 字符串的基本操作(链式存储)
- 串长统计返回串s的长度;
- 串定位返回字符或子串在母串s中首次出现的位置的指针;
- 串复制将一个串s2复制到另一个串s1中;
- 串插入在指定位置后面插入字符串;
- 串删除是删除一个子串;
- 串拼接将串s2拼接到串s1的尾部;
- ……
【数据结构】线性表(二)单链表及其基本操作(创建、插入、删除、修改、遍历打印)
1. 结构体
typedef struct Node {char data;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;Node* tail;
} LinkedList;Node:表示链表的节点,包含一个字符数据和一个指向下一个节点的指针。LinkedList:表示链表,包含链表的头节点和尾节点。
2. 初始化
initLinkedList函数:用于初始化链表,将头节点和尾节点都设置为NULL。
void initLinkedList(LinkedList* list) {list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}3. 判空
isEmpty函数:判断链表是否为空,即头节点是否为NULL。
bool isEmpty(const LinkedList* list) {return list->head == NULL;
}4. 串尾添加
append函数:向链表末尾添加一个字符节点。
void append(LinkedList* list, char data) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (isEmpty(list)) {list->head = newNode;list->tail = newNode;} else {list->tail->next = newNode;list->tail = newNode;}
}- 如果链表为空,即头节点为
NULL,则将新节点设置为头节点和尾节点。 - 如果链表不为空,即头节点不为
NULL,则将新节点链接到尾节点的后面,并将尾节点更新为新节点。
5. 打印
display函数:遍历链表并打印出所有字符节点的数据。
void display(const LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {printf("%c", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("\n");
}- 函数接受一个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针作为参数,然后从头节点开始遍历链表,打印每个节点的数据。
6. 串长统计
length函数:计算链表的长度,即字符节点的个数。
int length(const LinkedList* list) {int count = 0;Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {count++;current = current->next;}return count;
}- 函数接受一个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针作为参数,然后从头节点开始遍历链表,每遍历一个节点,计数器加1,最后返回计数器的值。
7. 查找
search函数:在链表中搜索目标字符串。
int search(const LinkedList* list, const char* target) {int targetLength = strlen(target);int listLength = length(list);if (targetLength > listLength) {printf("Error: Target string is longer than the source string.\n");return -1;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == target[0]) {Node* temp = current;int i = 0;while (temp != NULL && temp->data == target[i]) {temp = temp->next;i++;if (i == targetLength) {return index;}}}current = current->next;index++;}printf("Error: Target string not found in the source string.\n");return -1;
}- 首先比较目标字符串的长度和链表的长度,如果目标字符串比链表长,说明无法找到目标字符串,函数返回错误。
- 然后从头节点开始遍历链表,找到第一个与目标字符串首字符相同的节点,
- 然后从该节点开始逐个比较字符,直到找到完全匹配的目标字符串或链表遍历结束。
- 如果找到目标字符串,函数返回目标字符串在链表中的起始位置的索引;
- 如果未找到目标字符串,函数返回错误。
8. 复制
copy函数:将源链表中的字符复制到目标链表中。
bool copy(LinkedList* dest, const LinkedList* src) {Node* current = src->head;while (current != NULL) {append(dest, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}- 函数接受两个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针,分别表示源链表和目标链表。 - 通过遍历源链表的每个节点,创建一个新节点并将数据复制过去,然后将新节点添加到目标链表的末尾。
9. 插入
insert函数:在链表的指定位置插入一个字符串。
bool insert(LinkedList* list, const char* insertStr, int pos) {int listLength = length(list);int insertStrLength = strlen(insertStr);if (pos < 0 || pos > listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid insertion position.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {for (int i = 0; i < insertStrLength; i++) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = insertStr[i];newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}- 首先判断插入位置是否合法,即索引是否在有效范围内。然后遍历链表找到插入位置的节点,然后逐个创建新节点并插入到链表中。
10. 删除
delete函数:从链表中删除指定位置和长度的字符。
bool delete(LinkedList* list, int pos, int len) {int listLength = length(list);if (pos < 0 || pos >= listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid deletion position.\n");return false;}if (pos + len > listLength) {printf("Error: Deletion length exceeds the length of the string.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {Node* prev = current;Node* temp = current;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {temp = temp->next;free(prev);prev = temp;}current->next = temp;return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}- 首先判断删除位置是否合法,然后找到删除位置的节点,逐个删除指定长度的节点。
11. 串拼接
concat函数:将第二个链表中的字符追加到第一个链表的末尾。的末尾。
bool concat(LinkedList* list1, const LinkedList* list2) {Node* current = list2->head;while (current != NULL) {append(list1, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}- 遍历第二个链表的每个节点,将节点的数据追加到第一个链表。
12. 销毁
destroy函数:释放链表占用的内存。遍历链表的每个节点,释放节点的内存,并将头节点和尾节点设置为NULL。
void destroy(LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {Node* temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}
- 函数遍历链表的每个节点,释放节点的内存,并将头节点和尾节点设置为
NULL。
13. 主函数
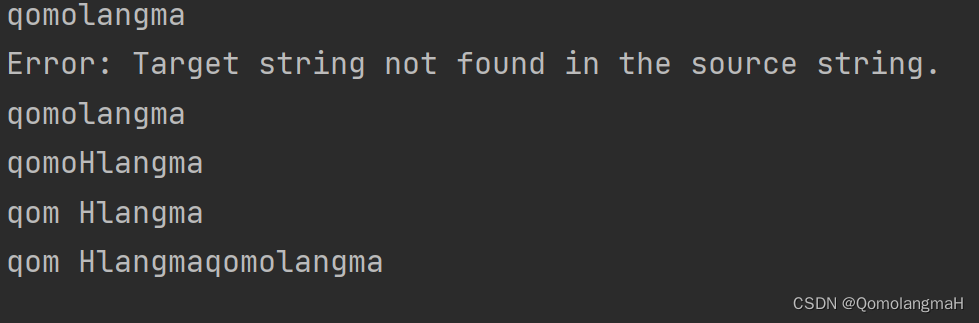
int main() {LinkedList S;initLinkedList(&S);const char target[] = "H";LinkedList copyStr;initLinkedList(©Str);const char insertStr[] = "H";int pos = 3;append(&S, 'q');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'l');append(&S, 'a');append(&S, 'n');append(&S, 'g');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'a');display(&S);int searchIndex = search(&S, target);if (searchIndex != -1) {printf("Target string found at index: %d\n", searchIndex);}copy(©Str, &S);display(©Str);insert(&S, insertStr, pos);display(&S);delete(&S, pos, strlen(insertStr));display(&S);concat(&S, ©Str);display(&S);destroy(&S);destroy(©Str);return 0;
}
14. 代码整合
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>typedef struct Node {char data;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;Node* tail;
} LinkedList;void initLinkedList(LinkedList* list) {list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}bool isEmpty(const LinkedList* list) {return list->head == NULL;
}void append(LinkedList* list, char data) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (isEmpty(list)) {list->head = newNode;list->tail = newNode;} else {list->tail->next = newNode;list->tail = newNode;}
}void display(const LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {printf("%c", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("\n");
}int length(const LinkedList* list) {int count = 0;Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {count++;current = current->next;}return count;
}int search(const LinkedList* list, const char* target) {int targetLength = strlen(target);int listLength = length(list);if (targetLength > listLength) {printf("Error: Target string is longer than the source string.\n");return -1;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == target[0]) {Node* temp = current;int i = 0;while (temp != NULL && temp->data == target[i]) {temp = temp->next;i++;if (i == targetLength) {return index;}}}current = current->next;index++;}printf("Error: Target string not found in the source string.\n");return -1;
}bool copy(LinkedList* dest, const LinkedList* src) {Node* current = src->head;while (current != NULL) {append(dest, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}bool insert(LinkedList* list, const char* insertStr, int pos) {int listLength = length(list);int insertStrLength = strlen(insertStr);if (pos < 0 || pos > listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid insertion position.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {for (int i = 0; i < insertStrLength; i++) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = insertStr[i];newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}bool delete(LinkedList* list, int pos, int len) {int listLength = length(list);if (pos < 0 || pos >= listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid deletion position.\n");return false;}if (pos + len > listLength) {printf("Error: Deletion length exceeds the length of the string.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {Node* prev = current;Node* temp = current;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {temp = temp->next;free(prev);prev = temp;}current->next = temp;return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}bool concat(LinkedList* list1, const LinkedList* list2) {Node* current = list2->head;while (current != NULL) {append(list1, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}void destroy(LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {Node* temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}int main() {LinkedList S;initLinkedList(&S);const char target[] = "H";LinkedList copyStr;initLinkedList(©Str);const char insertStr[] = "H";int pos = 3;append(&S, 'q');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'l');append(&S, 'a');append(&S, 'n');append(&S, 'g');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'a');display(&S);int searchIndex = search(&S, target);if (searchIndex != -1) {printf("Target string found at index: %d\n", searchIndex);}copy(©Str, &S);display(©Str);insert(&S, insertStr, pos);display(&S);delete(&S, pos, strlen(insertStr));display(&S);concat(&S, ©Str);display(&S);destroy(&S);destroy(©Str);return 0;
})


















