为了解决多个进程同时操作一个文件,产生一些情况,通常对文件进行上锁,已解决对共享文件的竞争
对打开文件进行各种操作:
int fcentl(int fd, int cmd, .../*arg*/
如果cmd与锁操作有关,那么fcentl函数的第三个参数就要传入一个结构体
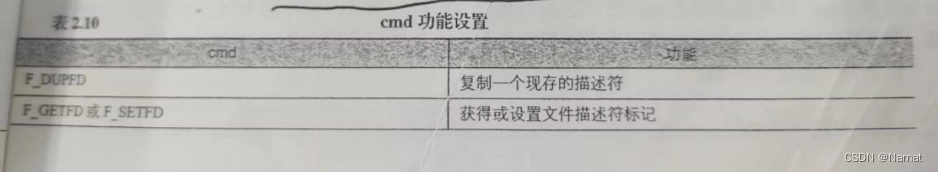
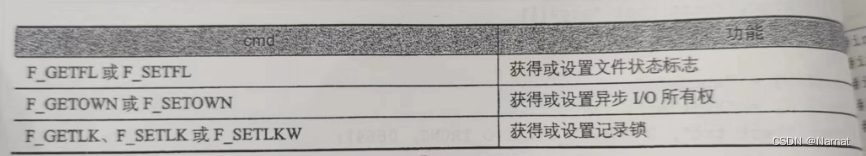
其中结构体如下:
struct flock {...short l_type; /* Type of lock: F_RDLCK,F_WRLCK, F_UNLCK */short l_whence; /* How to interpret l_start:SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR, SEEK_END */off_t l_start; /* Starting offset for lock */off_t l_len; /* Number of bytes to lock */pid_t l_pid; /* PID of process blocking our lock(F_GETLK only) */...};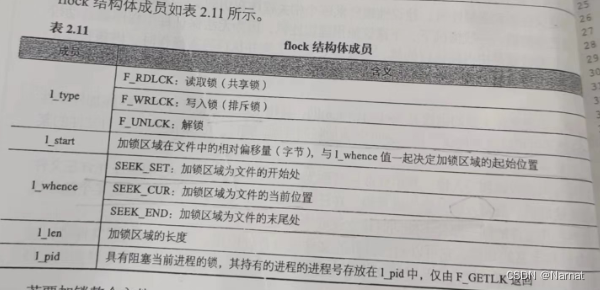

利用fcntl函数解决两个终端同时写访问一个文件产生的竞争问题:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/file.h> int lock_set(int fd, int type){struct flock old_lock, lock;lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; //加锁区域为文件开始处 lock.l_start = 0;//加锁区域在文件位置的相对偏移量 lock.l_len = 0;//加锁区域长度 lock.l_type = type;//锁的类型 lock.l_pid = -1;fcntl(fd, F_GETLK, &lock);//写入if(lock.l_type != F_UNLCK){//若未解锁 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK){//读取锁 printf("Read lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);}else if(lock.l_type == F_WRLCK){printf("Write lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);} } /*上述可能由于不是解锁状态l_type被设置成了相应的锁值下方进行上锁操作时要再次调用type*/ lock.l_type = type;if((fcntl(fd, F_SETLKW, &lock)) < 0){//上锁失败 printf("Lock failed:type = %d\n", lock.l_type);return -1;}switch(lock.l_type){case F_RELCK:printf("Read lock set by %d\n", getpid());//获取当前进程的IDbreak;case F_WRLCK:printf("Write lock set by %d\n", getpid());break;case F_UNLCK:printf("Release lock by %d\n", getpid());//解锁返回1 return 1;break; }return 0;//上锁返回0
}int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){int fd;if((fd = open("test.txt", O_RDWR)) < 0){printf("open error\n");return -1;}lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//设置写入锁getchar();//等待响应 lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);//解锁getchar();close(fd);return 0;
}
为了更好演示,将写访问改成读访问,读访问可以多进程同时进行:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/file.h> int lock_set(int fd, int type){struct flock old_lock, lock;lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; //加锁区域为文件开始处 lock.l_start = 0;//加锁区域在文件位置的相对偏移量 lock.l_len = 0;//加锁区域长度 lock.l_type = type;//锁的类型 lock.l_pid = -1;fcntl(fd, F_GETLK, &lock);//写入if(lock.l_type != F_UNLCK){//若未解锁 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK){//读取锁 printf("Read lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);}else if(lock.l_type == F_WRLCK){printf("Write lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);} } /*上述可能由于不是解锁状态l_type被设置成了相应的锁值下方进行上锁操作时要再次调用type*/ lock.l_type = type;if((fcntl(fd, F_SETLKW, &lock)) < 0){//上锁失败 printf("Lock failed:type = %d\n", lock.l_type);return -1;}switch(lock.l_type){case F_RELCK:printf("Read lock set by %d\n", getpid());//获取当前进程的IDbreak;case F_WRLCK:printf("Write lock set by %d\n", getpid());break;case F_UNLCK:printf("Release lock by %d\n", getpid());//解锁返回1 return 1;break; }return 0;//上锁返回0
}int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){int fd;if((fd = open("test.txt", O_RDWR)) < 0){printf("open error\n");return -1;}lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//设置写入锁getchar();//等待响应 lock_set(fd, F_RDLCK);//解锁getchar();close(fd);return 0;
}
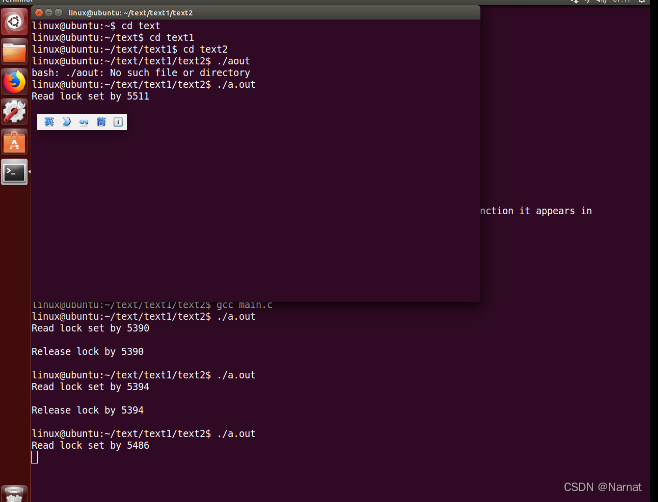
效果:两进程一起访问
c语言strlen与sizeof函数的区别:
char a[32]
a[32] = "abcd";
strlen(a) = 4;
sizeof(a) = 32;
















)


