文章目录
- 释义
- 欧氏距离
- simple——KNN
- sklearn——KNN
释义
近朱者赤近墨者黑----从训练数据集中找出和待预测样本最接近的K个样本
对于分类问题,我们使用了多数表决法来判断目标对象的类别。
对于回归问题,我们使用了平均值法来判断目标对象的数值
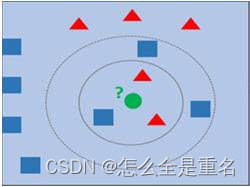
如上图,若k=3,则预测样本为🔺,
k=5,则预测样本为正方形
欧氏距离
一般采用欧式距离进行计算
d = sqrt( (x1-x2)^2 + (y1-y2)²)
simple——KNN
from numpy import *
import operator# 创建数据集和标签
def createDataSet():group = array([[1.0, 1.1], [1.0, 1.0], [0, 0], [0, 0.1]]) # 数据集4行2列的二维数组labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'] # 标签return group, labels# 分类函数
def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): # 1. 距离计算dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]# tile生成和训练样本对应的矩阵,并与训练样本求差diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize, 1)) - dataSet # tile: 列表示复制的行数, 行表示对inx的重复的次数# 取平方sqDiffMat = diffMat ** 2# 将矩阵的每一行相加sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)# 开方distances = sqDistances ** 0.5#使用argsort函数进行排序sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort()# 2. 选择距离最小的k个点classCount = {}for i in range(k):# 找到该样本的类型voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel, 0) + 1sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)return sortedClassCount[0][0]def test():group, labels = createDataSet()print(group)print(labels)print(classify0([0.1, 0.1], group, labels, 3))if __name__ == '__main__':test()
sklearn——KNN
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import *
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn import neighbors, datasetsn_neighbors = 3# 加载鸢尾花数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # 我们只采用前两个feature
y = iris.targeth = .02 # 网格中的步长# 创建彩色的图
cmap_light = ListedColormap(['#FFAAAA', '#AAFFAA', '#AAAAFF'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF'])# 分别以uniform和distance为特征绘图
for weights in ['uniform', 'distance']:# 我们创建了一个knn分类器的实例,并拟合数据。clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors, weights=weights)clf.fit(X, y)# 绘制决策边界。为此,我们将为每个分配一个颜色# 来绘制网格中的点 [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])# 将结果放入一个彩色图中Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)plt.figure()plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap_light)# 绘制训练点plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cmap_bold)plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())plt.title("3-Class classification (k = %i, weights = '%s')"% (n_neighbors, weights))plt.show()
非常棒的学习资料
)




项目环境搭建(项目概况,SSM细节总结))













