目录
- 一、简介
- 二、List 注入使用示例
- 2.1 测试接口类
- 2.2 测试接口实现类1
- 2.3 测试接口实现类2
- 2.4 启动类(测试)
- 2.5 测试结果
- 场景一:
- 场景二:
- 三、CommandLineRunner 使用示例
- 3.1 接口实现类1
- 3.2 接口实现类2
- 3.3 测试结果
- 场景一:
- 场景二:
- 四、@Order失效场景
- 4.1 失效代码示例
- 4.2 执行结果
- 4.3 失效场景补救
- 五、@Order、@Priority底层原理
- 5.1 平平无奇的启动类
- 5.2 神奇的 run() 方法
- 5.3 开始排序的 callRunners() 方法
- 5.4 排序调用图
- 5.5 排序的根源 findOrder() 方法
一、简介
@Order:是 spring-core 包下的一个注解。@Order 作用是定义 Spring IOC 容器中 Bean 的执行顺序。
注意: Spring 的 @Order 注解或者 Ordered 接口,不决定 Bean 的加载顺序和实例化顺序,只决定 Bean 注入到 List 中的顺序。
@Order 注解接受一个整数值作为参数,数值越小表示优先级越高。当存在多个具有 @Order 注解的组件时,Spring Boot将按照数值从小到大的顺序加载它们。
需要注意的是:
- @Order 注解只能用于标记 Spring 容器中的组件,而不适用于标记普通的类。因此,在使用 @Order 注解时,确保你的组件被正确地注册到 Spring 容器中。
- @Order 注解只决定Bean的注入顺序,并不保证实际执行的顺序。例如:在 Web 应用中,Filter 的执行顺序并不受 @Order 注解影响。如果需要确保 Filter 按照顺序执行,可以使用 FilterRegistrationBean 来设置 Filter 的顺序。
二、List 注入使用示例
包结构如下:
2.1 测试接口类
IOrderTest 接口中定义了一个 handle() 方法用于测试。
IOrderTest.java
/*** <p> @Title IOrderTest* <p> @Description @Order注解测试接口** @author ACGkaka* @date 2023/10/17 11:20*/
public interface IOrderTest {/*** 处理*/void handle();
}
2.2 测试接口实现类1
@Order注解测试实现类01 和 @Order注解测试实现类02 实现了 IOrderTest 接口,用于测试 @Order 的生效。
OrderTestImpl01.java
import com.demo.test.IOrderTest;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** <p> @Title OrderTestA* <p> @Description @Order注解测试实现类01** @author ACGkaka* @date 2023/10/17 11:18*/
@Order(1)
@Component
public class OrderTestImpl01 implements IOrderTest {public OrderTestImpl01() {System.out.println("=== OrderTestImpl01 constructor() ==");}@Overridepublic void handle() {System.out.println("=== OrderTestImpl01 handle() ===");}
}
2.3 测试接口实现类2
@Order注解测试实现类01 和 @Order注解测试实现类02 实现了 IOrderTest 接口,用于测试 @Order 的生效。
OrderTestImpl02.java
import com.demo.test.IOrderTest;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** <p> @Title OrderTestImpl02* <p> @Description @Order注解测试实现类02** @author ACGkaka* @date 2023/10/17 11:18*/
@Order(2)
@Component
public class OrderTestImpl02 implements IOrderTest {public OrderTestImpl02() {System.out.println("=== OrderTestImpl02 constructor() ===");}@Overridepublic void handle() {System.out.println("=== OrderTestImpl02 handle() ===");}
}
2.4 启动类(测试)
SpringbootDemoApplication.java
import com.demo.test.IOrderTest;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import java.util.List;@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);}@Beanpublic CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(List<IOrderTest> list) {return args -> {System.out.println("=== CommandLineRunner ===");list.forEach(IOrderTest::handle);};}
}
2.5 测试结果
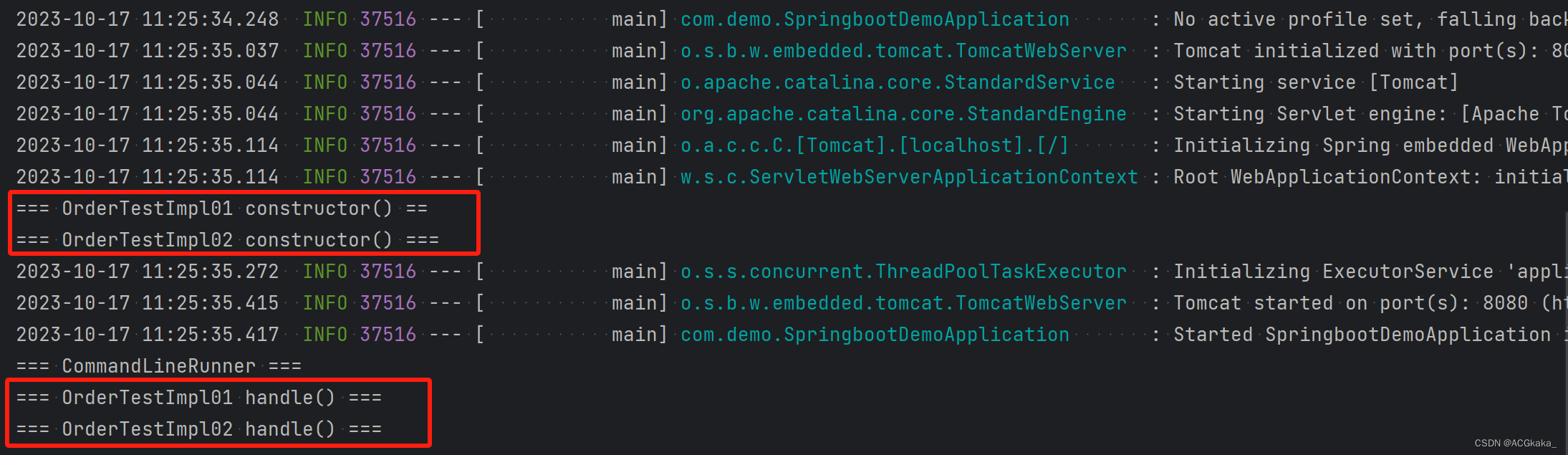
场景一:
@Order(1)注解修饰 OrderTestImpl01.java@Order(2)注解修饰 OrderTestImpl02.java
执行结果如下:
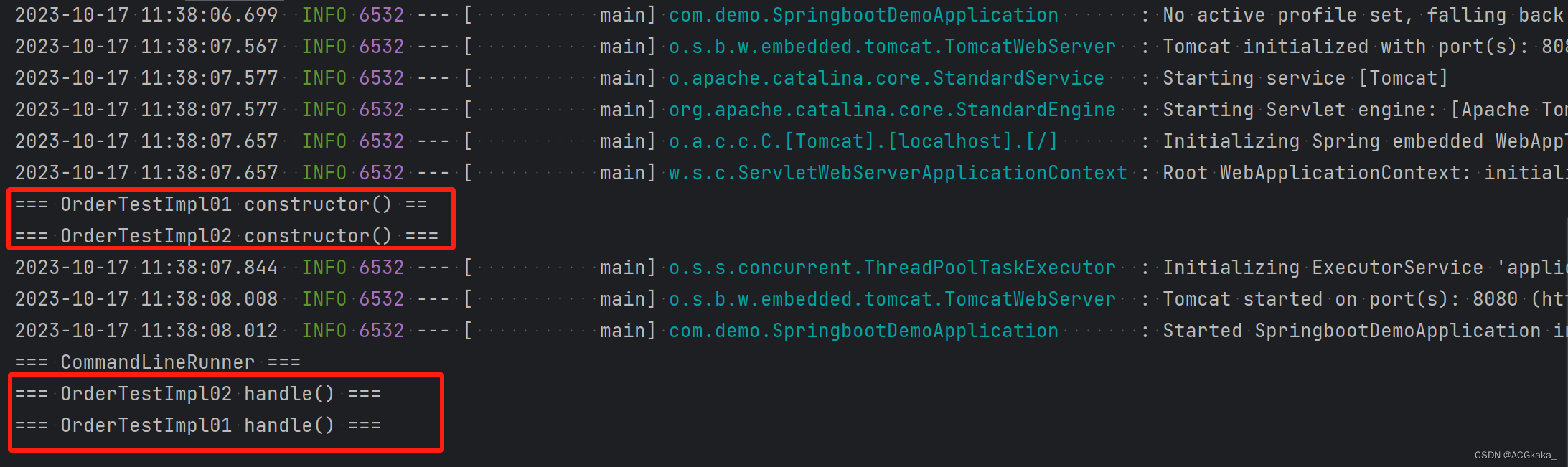
场景二:
@Order(1)注解修饰 OrderTestImpl02.java@Order(2)注解修饰 OrderTestImpl01.java
执行结果如下:
三、CommandLineRunner 使用示例
3.1 接口实现类1
CommandLineRunner01.java
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** <p> @Title CommandLineRunner01* <p> @Description @Order注解测试01** @author ACGkaka* @date 2023/10/17 11:20*/
@Component
@Order(1)
public class CommandLineRunner01 implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) {System.out.println("=== CommandLineRunner01 ===");}
}
3.2 接口实现类2
CommandLineRunner02.java
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** <p> @Title CommandLineRunner02* <p> @Description @Order注解测试02** @author ACGkaka* @date 2023/10/17 11:20*/
@Component
@Order(2)
public class CommandLineRunner02 implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) {System.out.println("=== CommandLineRunner02 ===");}
}
3.3 测试结果
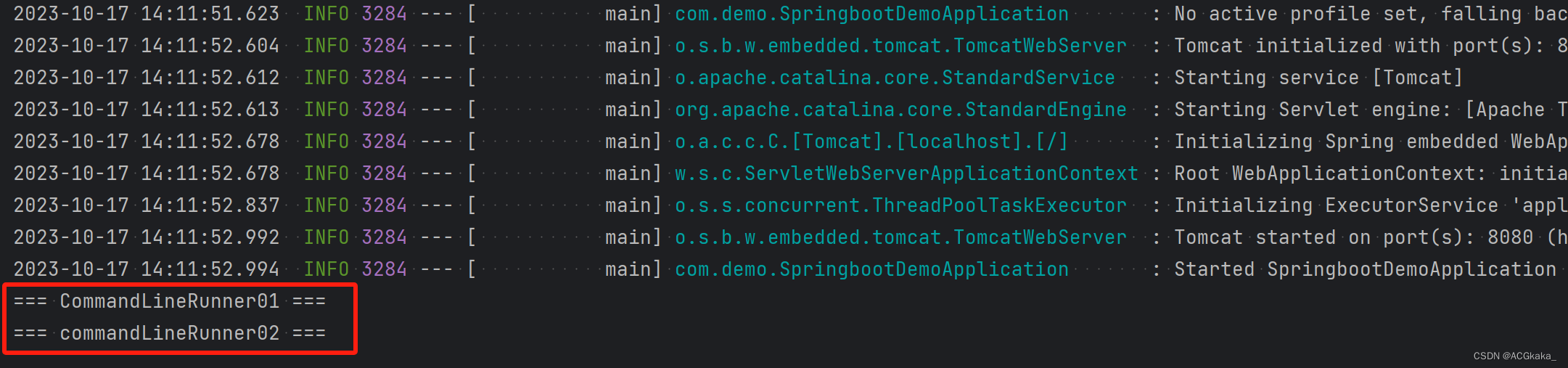
场景一:
@Order(1)注解修饰 CommandLineRunner01.java@Order(2)注解修饰 CommandLineRunner02.java
执行结果如下:
场景二:
@Order(1)注解修饰 CommandLineRunner02.java@Order(2)注解修饰 CommandLineRunner01.java
执行结果如下:
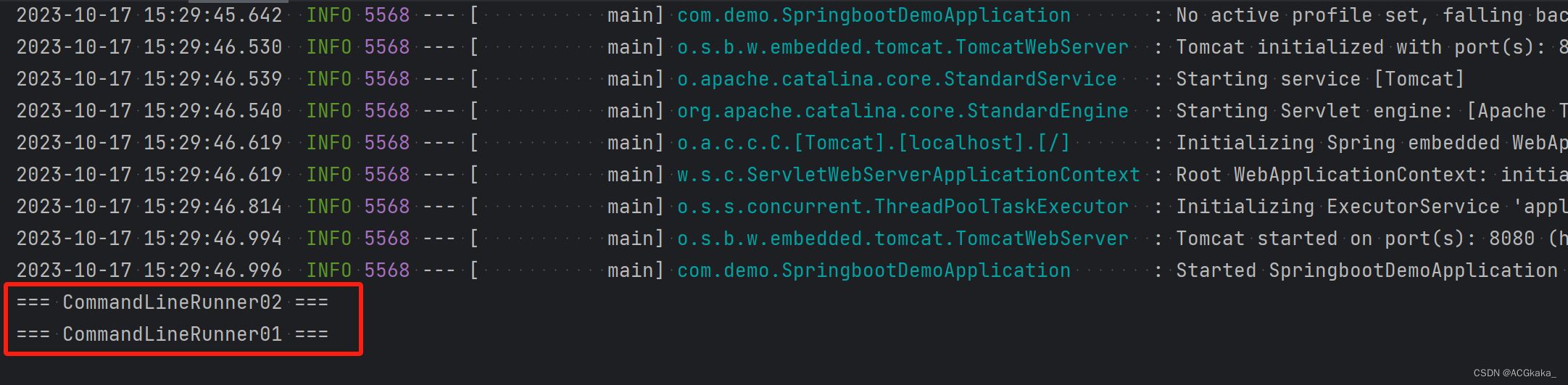
四、@Order失效场景
失效场景: 在
@Configuration里面通过@Bean方式创建 Bean,在上面加 @Order 控制顺序是没有效果的。
4.1 失效代码示例
SpringbootDemoApplication.java
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);}@Order(2)@Beanpublic CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner01() {return args -> System.out.println("=== commandLineRunner01 ===");}@Order(1)@Beanpublic CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner02() {return args -> System.out.println("=== commandLineRunner02 ===");}
}
4.2 执行结果
由下图可知,虽然我们使用 @Order 注解明确声明要先执行 commandLineRunner02,但是并没有生效。
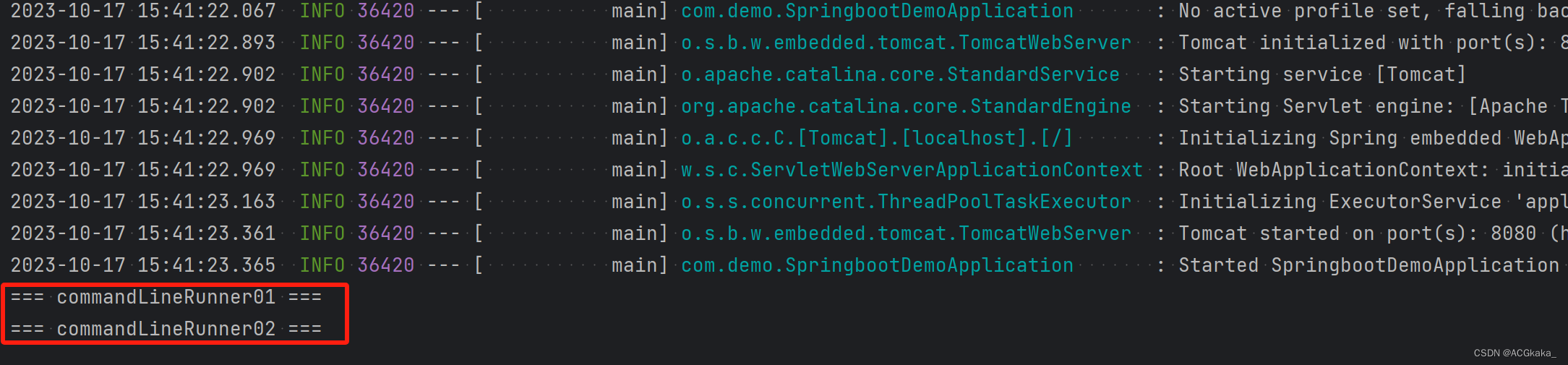
4.3 失效场景补救
在 @Order 注解失效的场景下,可以通过以下方式来控制顺序:
- 方式一: 可以通过具体实现类的方式创建 Bean,用
@Order+@Component注解修饰。 - 方式二: 可以通过 RegistrationBean 方式创建 Bean,用 setOrder 添加顺序。
- 方式三: filter 可以通过 FilterRegistrationBean 创建 filter 的 Bean,用 setOrder 添加顺序。
五、@Order、@Priority底层原理
看完 @Order 注解的时候,可能会疑惑 IOC 容器时如何通过 @Order 注解来控制程序的先后顺序的,接下来我们从源码层面看下,容器是如何加载的。
先说结论:
- @Order 底层是在 Bean 注入 IOC 容器之后执行的,所以无法控制 Bean 的加载顺序。
- @Order 底层是通过 List.sort(Comparator) 实现的,AnnotationAwareOrderComparator 类集成 OrderComparator 类,通过获取注解的 value 值实现了比对逻辑。
5.1 平平无奇的启动类
SpringbootDemoApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);}
}
5.2 神奇的 run() 方法
SpringApplication.run()
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();stopWatch.start();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();configureHeadlessProperty();SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);listeners.starting();try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);context = createApplicationContext();exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);refreshContext(context);afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);stopWatch.stop();if (this.logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);}listeners.started(context);// #### 重点!!!调用具体的执行方法 ###callRunners(context, applicationArguments);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}try {listeners.running(context);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}return context;
}
5.3 开始排序的 callRunners() 方法
SpringApplication.callRunners()
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());// ### 重点!!!按照定义的优先级顺序排序 ###AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);}if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);}}
}
5.4 排序调用图
由于剩下的实现内容调用链比较长,为了看起来更清晰直观,采用顺序图展现出来:
5.5 排序的根源 findOrder() 方法
获取 @Order 注解的 value 值,来进行排序。
OrderUtils.findOrder()
@Nullable
private static Integer findOrder(MergedAnnotations annotations) {MergedAnnotation<Order> orderAnnotation = annotations.get(Order.class);if (orderAnnotation.isPresent()) {// ### 重点!!!获取@Order注解的value值return orderAnnotation.getInt(MergedAnnotation.VALUE);}MergedAnnotation<?> priorityAnnotation = annotations.get(JAVAX_PRIORITY_ANNOTATION);if (priorityAnnotation.isPresent()) {// ### 重点!!!获取@Priority注解的value值return priorityAnnotation.getInt(MergedAnnotation.VALUE);}return null;
}
整理完毕,完结撒花~ 🌻
参考地址:
1.浅谈Spring @Order注解的使用,https://blog.csdn.net/yaomingyang/article/details/86649072
2.深入理解Spring的@Order注解和Ordered接口,https://blog.csdn.net/zkc7441976/article/details/112548075
3.踩坑!@Order失效。。。https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34142184/article/details/126951618





)



(安全解析函数,解析yaml)(防止yaml文件中包含恶意代码))









