
Conference:33rd USENIX Security Symposium
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:网络与信息安全
Year:2024
Num:7
1
Title:
Practical Security Analysis of Zero-Knowledge Proof Circuits
零知识证明电路的实用安全分析
Authors:
Hongbo Wen, University of California, Santa Barbara; Jon Stephens, The University of Texas at Austin and Veridise; Yanju Chen, University of California, Santa Barbara; Kostas Ferles, Veridise; Shankara Pailoor, The University of Texas at Austin and Veridise; Kyle Charbonnet, Ethereum Foundation; Isil Dillig, The University of Texas at Austin and Veridise; Yu Feng, University of California, Santa Barbara, and Veridise
Abstract:
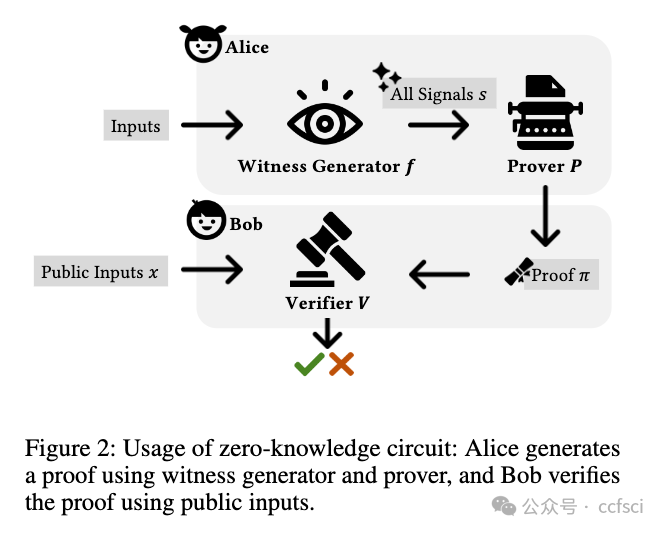
As privacy-sensitive applications based on zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) gain increasing traction, there is a pressing need to detect vulnerabilities in ZKP circuits. This paper studies common vulnerabilities in Circom (the most popular domain-specific language for ZKP circuits) and describes a static analysis framework for detecting these vulnerabilities. Our technique operates over an abstraction called the circuit dependence graph (CDG) that captures key properties of the circuit and allows expressing semantic vulnerability patterns as queries over the CDG abstraction. We have implemented 9 different detectors using this framework and performed an experimental evaluation on over 258 circuits from popular Circom projects on GitHub. According to our evaluation, these detectors can identify vulnerabilities, including previously unknown ones, with high precision and recall.
随着基于零知识证明 (ZKP) 的隐私敏感应用程序越来越受欢迎,迫切需要检测 ZKP 电路中的漏洞。本文研究了 Circom(ZKP 电路最流行的领域特定语言)中的常见漏洞,并描述了用于检测这些漏洞的静态分析框架。我们的技术在称为电路依赖图(CDG)的抽象上运行,它捕获电路的关键属性,并允许将语义漏洞模式表达为对 CDG 抽象的查询。我们使用该框架实现了 9 个不同的检测器,并对 GitHub 上热门 Circcom 项目的超过 258 个电路进行了实验评估。根据我们的评估,这些检测器可以以高精度和召回率识别漏洞,包括以前未知的漏洞。

Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec23winter-prepub-506-wen.pdf
2
Title:
Speculative Denial-of-Service Attacks In Ethereum
以太坊中的投机性拒绝服务攻击
Authors:
Aviv Yaish, The Hebrew University; Kaihua Qin and Liyi Zhou, Imperial College London, UC Berkeley RDI; Aviv Zohar, The Hebrew University; Arthur Gervais, University College London, UC Berkeley RDI
Abstract:
Transaction fees compensate actors for resources expended on transactions and can only be charged from transactions included in blocks. But, the expressiveness of Turing-complete contracts implies that verifying if transactions can be included requires executing them on the current blockchain state.
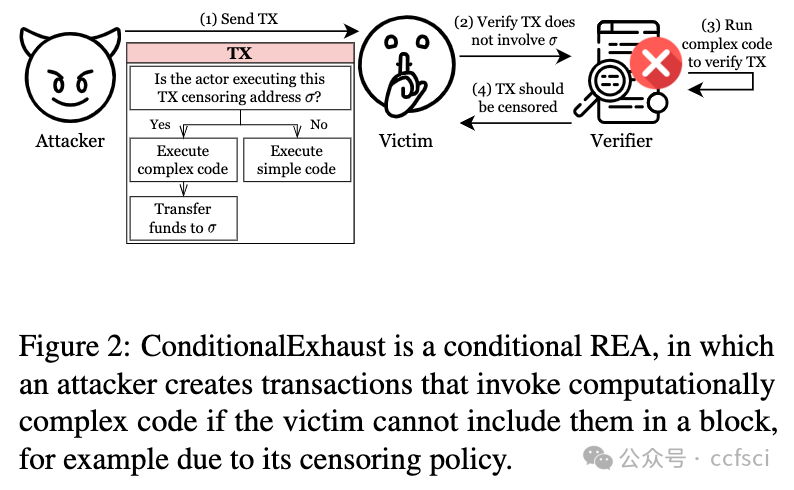
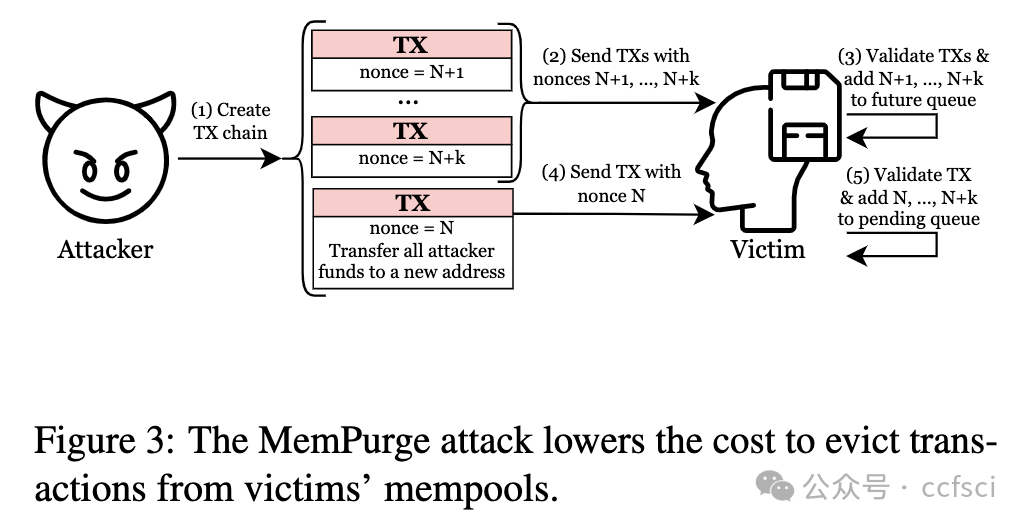
In this work, we show that adversaries can craft malicious transactions that decouple the work imposed on blockchain actors from the compensation offered in return. We introduce three attacks: (i) ConditionalExhaust, a conditional resource-exhaustion attack against blockchain actors. (ii) MemPurge, an attack for evicting transactions from actors' mempools. (iii) GhostTX, an attack on the reputation system used in Ethereum's proposer-builder separation ecosystem.
We evaluate our attacks on an Ethereum testnet and find that by combining ConditionalExhaust and MemPurge, adversaries can simultaneously burden victims' computational resources and clog their mempools to the point where victims are unable to include transactions in blocks. Thus, victims create empty blocks, thereby hurting the system's liveness. The attack's expected cost is $376, but becomes cheaper if adversaries are validators. For other attackers, costs decrease if censorship is prevalent in the network.
ConditionalExhaust and MemPurge are made possible by inherent features of Turing-complete blockchains, and potential mitigations may result in reducing a ledger's scalability.
交易费是对参与者在交易中消耗的资源的补偿,只能从包含在区块中的交易中收取。但是,图灵完备合约的可表达性意味着,要验证交易是否能被包含在内,需要在当前区块链状态下执行这些交易。
在这项工作中,我们展示了对手可以精心设计恶意交易,使强加给区块链参与者的工作与提供的补偿脱钩。我们介绍了三种攻击:(i) ConditionalExhaust,这是一种针对区块链参与者的有条件资源耗尽攻击。(ii) MemPurge,一种将交易从参与者的内存池中驱逐出去的攻击。(iii) GhostTX,一种针对以太坊提议者-构建者分离生态系统中使用的信誉系统的攻击。
我们在以太坊测试网络上评估了我们的攻击,发现通过结合 ConditionalExhaust 和 MemPurge,对手可以同时加重受害者的计算资源负担并堵塞其内存池,以至于受害者无法在区块中包含交易。这样,受害者就会创建空块,从而损害系统的有效性。这种攻击的预期成本是 376 美元,但如果对手是验证者,成本就会降低。对于其他攻击者来说,如果网络中普遍存在审查制度,成本就会降低。
ConditionalExhaust和MemPurge是图灵完备区块链的固有特征,潜在的缓解措施可能会降低分类账的可扩展性。


Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24summer-prepub-32-yaish.pdf
3
Title:
Pixel+ and Pixel++: Compact and Efficient Forward-Secure Multi-Signatures for PoS Blockchain Consensus
Pixel+ 和 Pixel++:用于 PoS 区块链共识的紧凑高效的前向安全多重签名
Authors:
Jianghong Wei, State Key Laboratory of Integrated Service Networks (ISN), Xidian University, and State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing; Guohua Tian, State Key Laboratory of Integrated Service Networks (ISN), Xidian University; Ding Wang, College of Cyber Science, Nankai University; Fuchun Guo and Willy Susilo, School of Computing and Information Technology, University of Wollongong; Xiaofeng Chen, State Key Laboratory of Integrated Service Networks (ISN), Xidian University
Abstract:
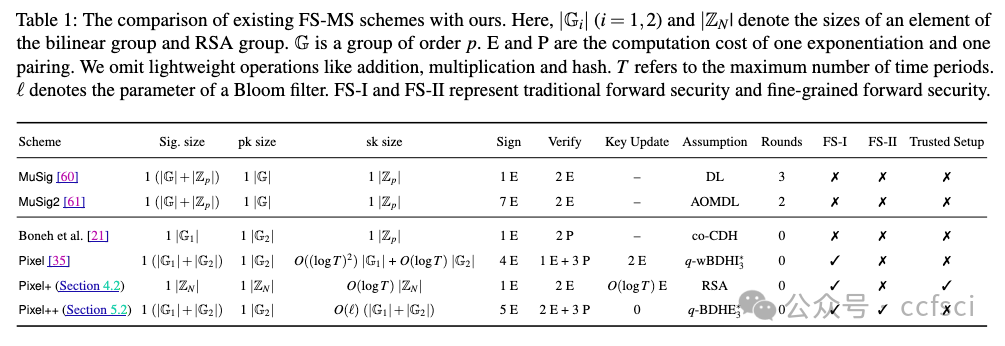
Multi-signature schemes have attracted considerable attention in recent years due to their popular applications in PoS blockchains. However, the use of general multi-signature schemes poses a critical threat to the security of PoS blockchains once signing keys get corrupted. That is, after an adversary obtains enough signing keys, it can break the immutable nature of PoS blockchains by forking the chain and modifying the history from some point in the past. Forward-secure multi-signature (FS-MS) schemes can overcome this issue by periodically updating signing keys. The only FS-MS construction currently available is Drijvers et al's Pixel, which builds on pairing groups and only achieves forward security at the time period level.
In this work, we present new FS-MS constructions that either are free from pairing or capture forward security at the individual message level (i.e., fine-grained forward security). Our first construction Pixel+ works for a maximum number of time periods T. Pixel+ signatures consist of only one group element, and can be verified using two exponentiations. It is the first FS-MS from RSA assumption, and has 3.5x and 22.8x faster signing and verification than Pixel, respectively. Our second FS-MS construction Pixel++ is a pairing-based one. It immediately revokes the signing key's capacity of re-signing the message after creating a signature on this message, rather than at the end of the current time period. Thus, it provides more practical forward security than Pixel. On the other hand, Pixel++ is almost as efficient as Pixel in terms of signing and verification. Both Pixel+ and Pixel++ allow for non-interactive aggregation of signatures from independent signers and are proven to be secure in the random oracle model. In addition, they also support the aggregation of public keys, significantly reducing the storage overhead on PoS blockchains.
We demonstrate how to integrate Pixel+ and Pixel++ into PoS blockchains. As a proof-of-concept, we provide implementations of Pixel+ and Pixel++, and conduct several representative experiments to show that Pixel+ and Pixel++ have good concrete efficiency and are practical.
近年来,多重签名方案因其在 PoS 区块链中的广泛应用而备受关注。然而,一旦签名密钥被破坏,一般多重签名方案的使用就会对 PoS 区块链的安全性构成严重威胁。也就是说,当对手获得足够多的签名密钥后,就可以通过分叉链和修改过去某个时间点的历史记录来破坏 PoS 区块链的不可变性。前向安全多重签名(FS-MS)方案可以通过定期更新签名密钥来克服这一问题。目前唯一可用的 FS-MS 结构是 Drijvers 等人的 Pixel,它建立在配对组的基础上,只能在时间段级别上实现前向安全性。
在这项工作中,我们提出了新的 FS-MS 结构,这些结构要么不需要配对,要么能在单个信息级别上实现前向安全性(即细粒度前向安全性)。Pixel+ 签名仅由一个组元素组成,可使用两次指数运算进行验证。它是第一个基于 RSA 假设的 FS-MS,其签名和验证速度分别是 Pixel 的 3.5 倍和 22.8 倍。我们的第二种 FS-MS 结构 Pixel++ 是一种基于配对的 FS-MS。它可以在对信息创建签名后立即撤销签名密钥重新签名信息的能力,而不是在当前时间段结束时。因此,它比 Pixel 提供了更实用的前向安全性。另一方面,Pixel++ 在签名和验证方面的效率几乎与 Pixel 不相上下。Pixel+ 和 Pixel++ 都允许对来自独立签名者的签名进行非交互式聚合,并已证明在随机甲骨文模型中是安全的。此外,它们还支持公钥聚合,大大减少了 PoS 区块链的存储开销。
我们演示了如何将 Pixel+ 和 Pixel++ 集成到 PoS 区块链中。作为概念验证,我们提供了 Pixel+ 和 Pixel++ 的实现,并进行了几个有代表性的实验,以证明 Pixel+ 和 Pixel++ 具有良好的具体效率和实用性。
Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24fall-prepub-406-wei-jianghong.pdf
4
Title:
LaKey: Efficient Lattice-Based Distributed PRFs Enable Scalable Distributed Key Management
LaKey:基于网格的高效分布式 PRF 可实现可扩展的分布式密钥管理
Authors:
Matthias Geihs, Torus Labs; Hart Montgomery, Linux Foundation
Abstract:
Distributed key management (DKM) services are multi-party services that allow their users to outsource the generation, storage, and usage of cryptographic private keys, while guaranteeing that none of the involved service providers learn the private keys in the clear. This is typically achieved through distributed key generation (DKG) protocols, where the service providers generate the keys on behalf of the users in an interactive protocol, and each of the servers stores a share of each key as the result. However, with traditional DKM systems, the key material stored by each server grows linearly with the number of users.
An alternative approach to DKM is via distributed key derivation (DKD) where the user key shares are derived on-demand from a constant-size (in the number of users) secret-shared master key and the corresponding user's identity, which is achieved by employing a suitable distributed pseudorandom function (dPRF). However, existing suitable dPRFs require on the order of 100 interaction rounds between the servers and are therefore insufficient for settings with high network latency and where users demand real-time interaction.
To resolve the situation, we initiate the study of lattice-based distributed PRFs, with a particular focus on their application to DKD. Concretely, we show that the LWE-based PRF presented by Boneh et al. at CRYPTO'13 can be turned into a distributed PRF suitable for DKD that runs in only 8 online rounds, which is an improvement over the start-of-the-art by an order of magnitude. We further present optimizations of this basic construction. We show a new construction with improved communication efficiency proven secure under the same "standard" assumptions. Then, we present even more efficient constructions, running in as low as 5 online rounds, from non-standard, new lattice-based assumptions. We support our findings by implementing and evaluating our protocol using the MP-SPDZ framework (Keller, CCS '20). Finally, we give a formal definition of our DKD in the UC framework and prove a generic construction (for which our construction qualifies) secure in this model.
分布式密钥管理(DKM)服务是一种多方服务,允许用户外包加密私钥的生成、存储和使用,同时保证所有参与的服务提供商都不会在明面上获知私钥。这通常是通过分布式密钥生成(DKG)协议实现的,即服务提供商在交互式协议中代表用户生成密钥,每个服务器存储每个密钥的一部分。然而,在传统的 DKM 系统中,每个服务器存储的密钥材料会随着用户数量的增加而线性增长。
DKM 的另一种方法是分布式密钥推导(DKD),用户密钥份额按需从恒定大小(以用户数量为单位)的共享密钥主密钥和相应的用户身份中推导出来,通过使用合适的分布式伪随机函数(dPRF)来实现。然而,现有的合适分布式伪随机函数需要服务器之间进行 100 轮交互,因此无法满足高网络延迟和用户要求实时交互的情况。
为了解决这一问题,我们开始研究基于网格的分布式 PRF,并特别关注其在 DKD 中的应用。具体来说,我们展示了 Boneh 等人在 CRYPTO'13 上提出的基于 LWE 的 PRF 可以转化为适用于 DKD 的分布式 PRF,只需 8 轮在线运行,比最先进的技术提高了一个数量级。我们进一步介绍了对这一基本结构的优化。我们展示了一种在相同 “标准 ”假设条件下证明安全的新结构,它的通信效率得到了提高。然后,我们根据非标准的、基于网格的新假设,提出了效率更高的构造,运行时间低至 5 个在线回合。我们通过使用 MP-SPDZ 框架(Keller,CCS '20)实施和评估我们的协议来支持我们的发现。最后,我们给出了 UC 框架中 DKD 的正式定义,并证明了在该模型中安全的通用构造(我们的构造符合该模型)。
Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24fall-prepub-1122-geihs.pdf
5
Title:
Scalable Zero-knowledge Proofs for Non-linear Functions in Machine Learning
机器学习中非线性函数的可扩展零知识证明
Authors:
Meng Hao, Hanxiao Chen, and Hongwei Li, School of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; Chenkai Weng, Northwestern University; Yuan Zhang and Haomiao Yang, School of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; Tianwei Zhang, Nanyang Technological University
Abstract:
Zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs have been recently explored for the integrity of machine learning (ML) inference. However, these protocols suffer from high computational overhead, with the primary bottleneck stemming from the evaluation of non-linear functions. In this paper, we propose the first systematic ZK proof framework for non-linear mathematical functions in ML using the perspective of table lookup. The key challenge is that table lookup cannot be directly applied to non-linear functions in ML since it would suffer from inefficiencies due to the intolerably large table. Therefore, we carefully design several important building blocks, including digital decomposition, comparison, and truncation, such that they can effectively utilize table lookup with a quite small table size while ensuring the soundness of proofs. Based on these building blocks, we implement complex mathematical operations and further construct ZK proofs for current mainstream non-linear functions in ML such as ReLU, sigmoid, and normalization. The extensive experimental evaluation shows that our framework achieves 50∼179× runtime improvement compared to the state-of-the-art work, while maintaining a similar level of communication efficiency.
零知识(ZK)证明最近被用于机器学习(ML)推理的完整性。然而,这些协议的计算开销很大,主要瓶颈来自非线性函数的评估。在本文中,我们从查表的角度提出了第一个针对 ML 中非线性数学函数的系统性 ZK 证明框架。关键的挑战在于,表查询无法直接应用于 ML 中的非线性函数,因为它将因难以容忍的大表而效率低下。因此,我们精心设计了几个重要的构建模块,包括数字分解、比较和截断,使它们能在确保证明正确性的同时,以相当小的表大小有效利用查表。在这些构建模块的基础上,我们实现了复杂的数学运算,并进一步构建了当前 ML 中主流非线性函数的 ZK 证明,如 ReLU、sigmoid 和归一化。广泛的实验评估表明,与最先进的工作相比,我们的框架实现了 50∼179 倍的运行时间改进,同时保持了类似水平的通信效率。
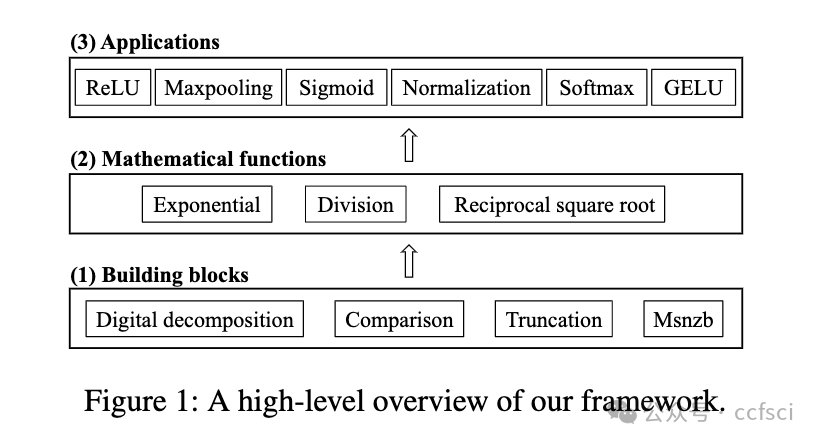
Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24fall-prepub-2279-hao-meng-scalable.pdf
6
Title:
MD-ML: Super Fast Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning for Malicious Security with a Dishonest Majority
MD-ML:针对不诚实多数的恶意安全的超快隐私保护机器学习
Authors:
Boshi Yuan, Shixuan Yang, and Yongxiang Zhang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China; Ning Ding, Dawu Gu, and Shi-Feng Sun, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China; Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Wuxi) Blockchain Advanced Research Center
Abstract:
Privacy-preserving machine learning (PPML) enables the training and inference of models on private data, addressing security concerns in machine learning. PPML based on secure multi-party computation (MPC) has garnered significant attention from both the academic and industrial communities. Nevertheless, only a few PPML works provide malicious security with a dishonest majority. The state of the art by Damgård et al. (SP'19) fails to meet the demand for large models in practice, due to insufficient efficiency. In this work, we propose MD-ML, a framework for Maliciously secure Dishonest majority PPML, with a focus on boosting online efficiency.
MD-ML works for n parties, tolerating corruption of up to n-1 parties. We construct our novel protocols for PPML, including truncation, dot product, matrix multiplication, and comparison. The online communication of our dot product protocol is one single element per party, independent of input length. In addition, the online cost of our multiply-then-truncate protocol is identical to multiplication, which means truncation incurs no additional online cost. These features are achieved for the first time in the literature concerning maliciously secure dishonest majority PPML.
Benchmarking of MD-ML is conducted for SVM and NN including LeNet, AlexNet, and ResNet-18. For NN inference, compared to the state of the art (Damgård et al., SP'19), we are about 3.4—11.0x (LAN) and 9.7—157.7x (WAN) faster in online execution time.
隐私保护机器学习(PPML)可以在私人数据上训练和推理模型,解决机器学习中的安全问题。基于安全多方计算(MPC)的 PPML 引起了学术界和工业界的极大关注。然而,只有少数 PPML 作品提供了大多数不诚实者的恶意安全性。Damgård 等人(SP'19)的研究成果由于效率不足,无法满足大型模型的实际需求。在这项工作中,我们提出了恶意安全不诚实多数 PPML 框架 MD-ML,重点是提高在线效率。
MD-ML 适用于 n 方,最多可容忍 n-1 方的破坏。我们构建了 PPML 的新协议,包括截断、点积、矩阵乘法和比较。我们的点乘协议的在线通信量为每方一个元素,与输入长度无关。此外,我们的乘法-截断协议的在线成本与乘法相同,这意味着截断不会产生额外的在线成本。在有关恶意安全不诚实多数 PPML 的文献中,我们首次实现了这些特性。
MD-ML 的基准测试针对 SVM 和 NN(包括 LeNet、AlexNet 和 ResNet-18)进行。对于 NN 推理,与最先进的技术(Damgård 等人,SP'19)相比,我们的在线执行时间快了约 3.4-11.0 倍(局域网)和 9.7-157.7 倍(广域网)。

Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24fall-prepub-2129-yuan.pdf
7
Title:
Two Shuffles Make a RAM: Improved Constant Overhead Zero Knowledge RAM
两次 Shuffle 组成 RAM:改进的恒定开销零知识 RAM
Authors:
Yibin Yang, Georgia Institute of Technology; David Heath, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Abstract:
We optimize Zero Knowledge (ZK) proofs of statements expressed as RAM programs over arithmetic values. Our arithmetic-circuit-based read/write memory uses only 4 input gates and 6 multiplication gates per memory access. This is an almost 3× total gate improvement over prior state of the art (Delpech de Saint Guilhem et al., SCN'22).
We implemented our memory in the context of ZK proofs based on vector oblivious linear evaluation (VOLE), and we further optimized based on techniques available in the VOLE setting. Our experiments show that (1) our total runtime improves over that of the prior best VOLE-ZK RAM (Franzese et al., CCS'21) by 2-20× and (2) on a typical hardware setup, we can achieve ≈ 600K RAM accesses per second.
We also develop improved read-only memory and set ZK data structures. These are used internally in our read/write memory and improve over prior work.
我们通过算术值优化以 RAM 程序表示的语句的零知识 (ZK) 证明。我们基于算术电路的读/写存储器每次存储器访问仅使用 4 个输入门和 6 个乘法门。与现有技术相比,这几乎是 3 倍的总门改进(Delpech de Saint Guilhem 等人,SCN'22)。
我们在基于矢量不经意线性评估(VOLE)的 ZK 证明的背景下实现了我们的记忆,并根据 VOLE 设置中可用的技术进一步优化。我们的实验表明,(1) 我们的总运行时间比之前最好的 VOLE-ZK RAM(Franzese 等人,CCS'21)提高了 2-20 倍,并且 (2) 在典型的硬件设置上,我们可以实现 ≈ 每秒 600K RAM 访问。
我们还开发了改进的只读存储器并设置了ZK数据结构。这些在我们的读/写存储器内部使用,并比之前的工作有所改进。

Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24summer-prepub-208-yang-yibin.pdf
详情:https://www.usenix.org/conference/usenixsecurity24/summer-accepted-papers

关注ccfsci,持续接收区块链最新论文
洞察区块链技术发展趋势
Follow us to keep receiving the latest blockchain papers
Insight into Blockchain Technology Trends











)


)
)
——继承)


