我们先新建一个Module。
我们的依赖如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.rgf</groupId><artifactId>Spring_mvc_demo</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><packaging>war</packaging><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding></properties><dependencies><!--SpringMVC--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.3.1</version></dependency><!--日志--><dependency><groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId><artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId><version>1.2.3</version></dependency><!--ServletAPI--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>3.1.0</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency><!--Spring和Thymeleaf整合包--><dependency><groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId><artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId><version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version></dependency></dependencies></project>通过此处我们来进行导入web.xml:

导入的web.xml如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><!--配置SpringMVC的前端控制器DispatcherServletSpringMVC的配置文件默认的位置和名称:位置:WEB-INF下名称:<servlet-name>-servlet.xml,当前配置下的配置文件名为SpringMVC-servlet.xmlurl-pattern中/和/*的区别:/:匹配浏览器向服务器发送的所有请求(不包括.jsp)/*:匹配浏览器向服务器发送的所有请求(包括.jsp)--><servlet><servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!--设置servlet的初始化参数--><!--设置SpringMVC配置文件的位置和名称--><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param><!--将DispatcherServlet的初始化时间提前到服务器启动时。(默认为servlet在第一次访问时进行执行--><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><!-- <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>可以写/*,也可以写*.do(为后缀匹配),/无法·匹配jsp的请求的,但是/*可以匹配任意请求--><servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!-- The mappings for the JSP servlet<servlet-mapping><servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name><url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern><url-pattern>*.jspx</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>在tomcat里面的的web.xml已经配置了servlet专门来处理.jsp的请求,即所有的.jsp的请求通过JspServlet来进行处理<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class>-->
</web-app>之后我们来进行创建配置文件:springmvc-config.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!--扫描控制层组件--><context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf.controller"></context:component-scan><!--配置Thymeleaf视图解析器--><bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver"><property name="order" value="1"/><property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/><property name="templateEngine"><!--模板引擎--><bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine"><property name="templateResolver"><!--模板解析器--><bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver"><!--/WEB-INF/templates/index.html--><!--视图前缀+逻辑视图+视图后缀就是我们完整的物理视图,即访问index.html,不用完整路径,即index即可进行访问--><!--视图前缀--><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/><!--视图后缀--><property name="suffix" value=".html"/><property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/><property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" /></bean></property></bean></property></bean>
</beans>我们创建的controller如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;@Controller
public class TestRequestMappingController {}
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller
public class ProtalController {@RequestMapping("/")public String protal(){return "index";}
}
之后根据web.xml的配置文件,我们将该目录创建出来:且该目录下的文件为index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>index.html</h1>
</body>
</html>完成之后,我们来进行配置:
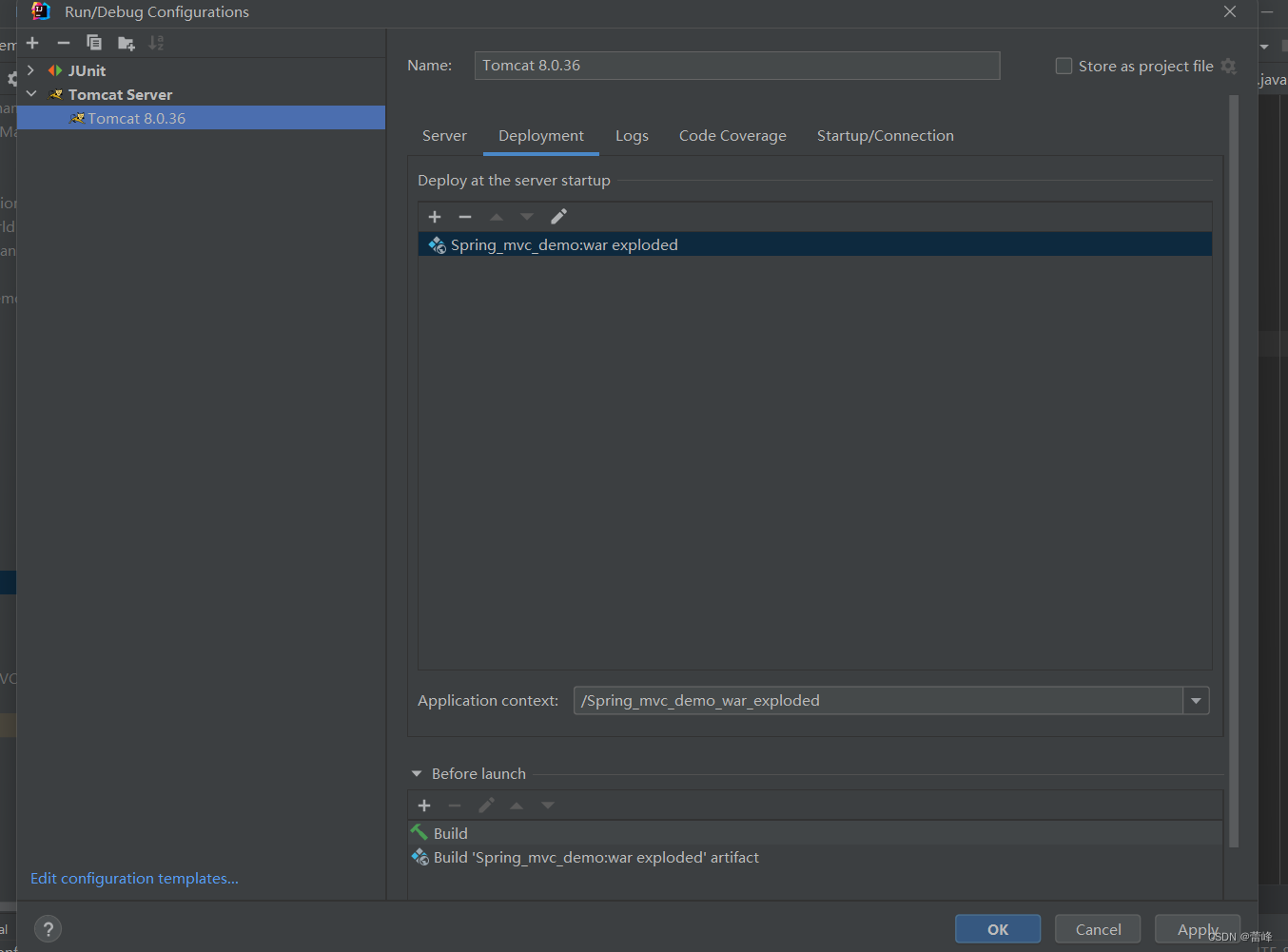
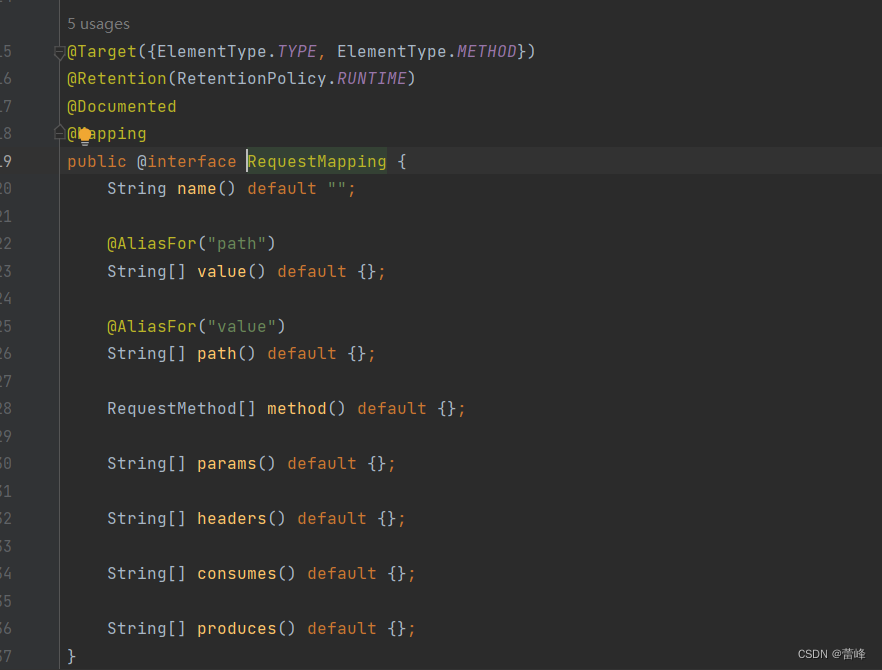
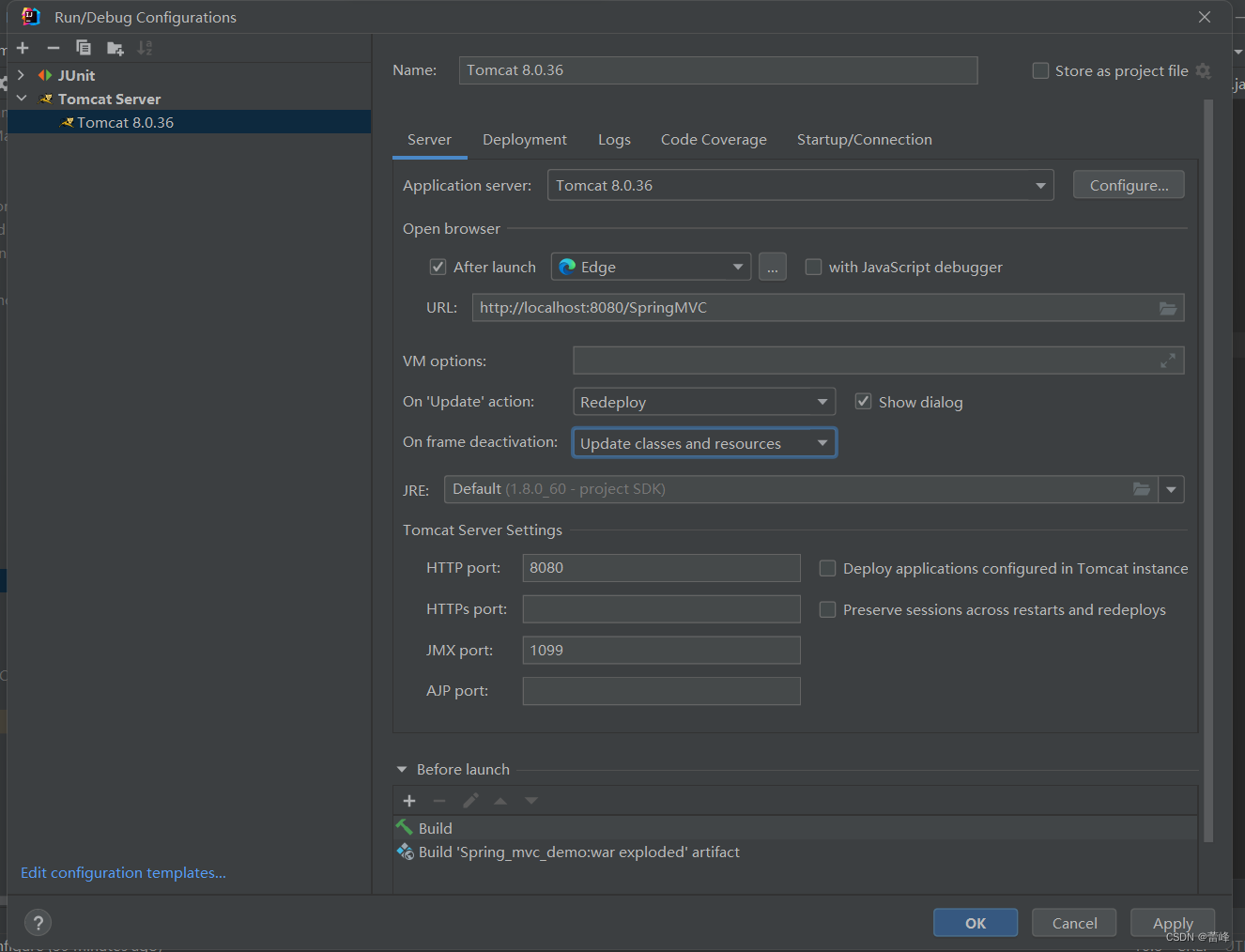 3.1 @RequestMapping注解的功能
3.1 @RequestMapping注解的功能
从注解名称上我们可以看到,@RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。
SpringMVC接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法来处理这个请求。
3.2@RequestMapping注解的位置
@RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
@RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息
@Target:当前注解能够标识的位置
当我们标记到方法的时候:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "success";}}我们可以根据该具体方法,跳转到具体方法标识的具体页面:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>success.html</h1> </body> </html>我们将该注解放到类里面的时候:
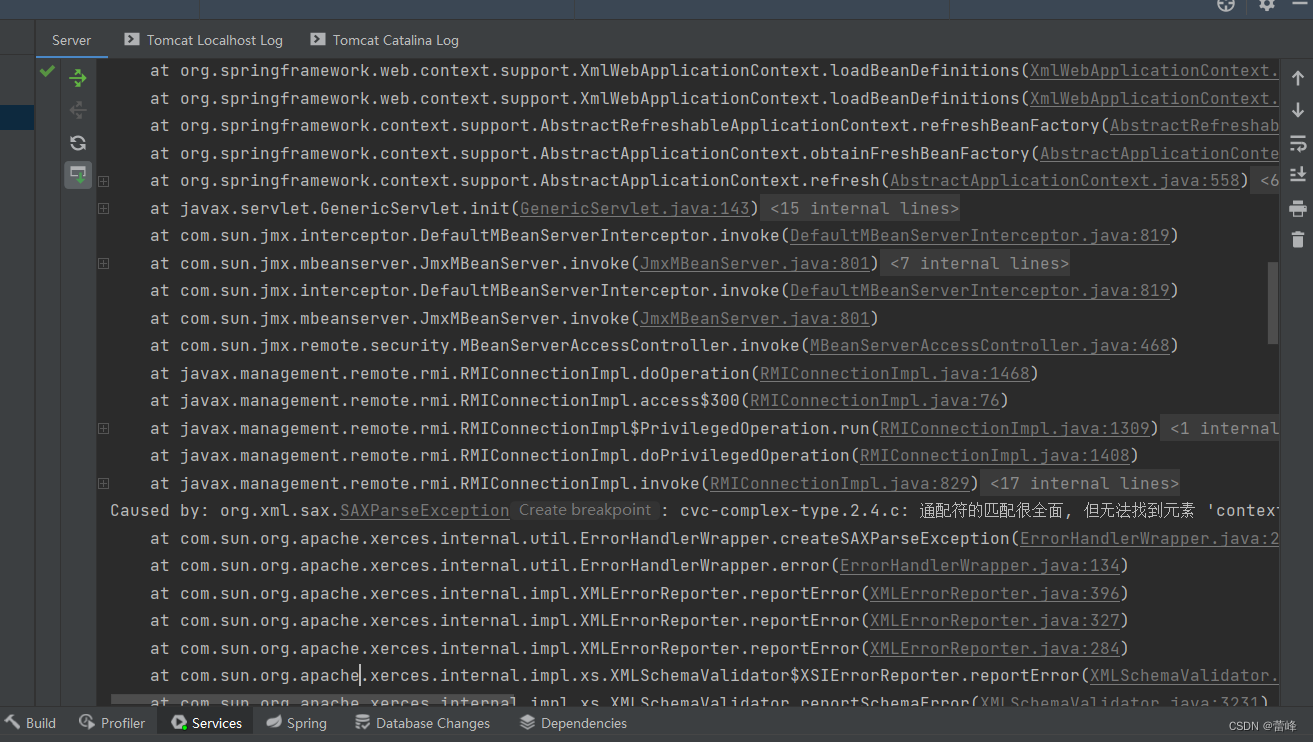
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "success";}}此时我们再进行部署运行的时候,发现它无法进行跳转:
此时的路径为类里面的路径和方法里面的路径进行拼接起来的路径。
当我们在两个控制层下面没有在类的里面采用注解区分相同的路径的方法时则会直接报错
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;/*** @RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "success";} }package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class ProtalController {@RequestMapping("/")public String protal(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "success";} }此时就体现出用@RequestMapping在类里面进行注解的重要性。
3.3@RequestMapping注解的value属性:
我们可以看到value属性是一个数组类型的。我们查看如下所示:
@RequestMapping({"/hello","/abc"})public String hello(){return "success";}此时即为该方法会被多个请求处理
servlet也可以被多个请求处理:
<servlet-mapping><!-- <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>可以写/*,也可以写*.do(为后缀匹配),/无法·匹配jsp的请求的,但是/*可以匹配任意请求--><servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name><url-pattern>/aa</url-pattern><url-pattern>/aaa</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>我们进行测试如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;/*** @RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping({"/hello","/abc"})public String hello(){return "success";} }我们定义该方法的页面为如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>success.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> </body> </html>我们重新部署之后我们点击两者不同的进行如下:
都会进入如下界面:
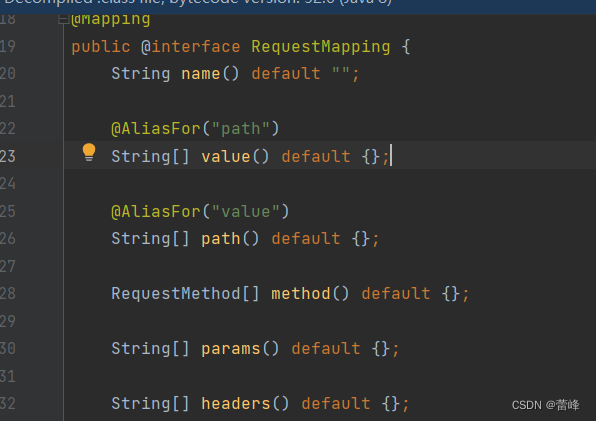
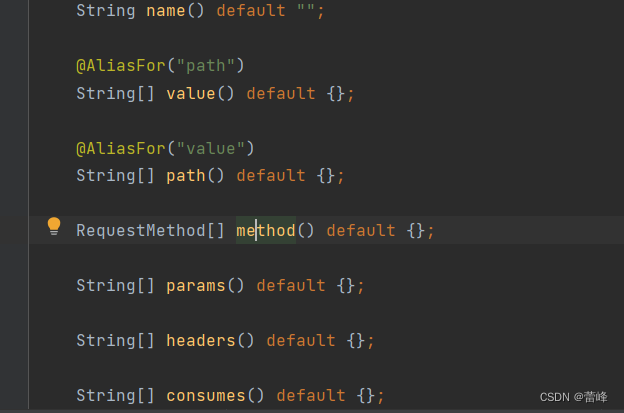
3.4@RequestMapping注解的method属性:
method为请求方式(get请求和post请求) ,且他的类型为RequestMethod[ ]数组。
根据注释,可知他的枚举类型如下所示:
表单提交的时候将method设置为post,ajax里面将请求方式设置为post.
此时设置如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 1.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method = RequestMethod.GET )public String hello(){return "success";} }此时完全匹配。
如果我们将方式改为post则不进行匹配。
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 1.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method = RequestMethod.POST )public String hello(){return "success";} }我们进行修改代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>success.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> <form th:action="@{/hello}"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性"> </form> </body> </html>我们进行点击之后则会直接报错显示405.
我们进行修改如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>success.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> <form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性"> </form> </body> </html>直接复制网址进行访问为get请求方式,如果设置为post请求方式,进行利用复制网址进行访问,则会报错405.
通过service服务(控制台)也可以进行查看报错信息:
我们进行设置如下所示,则会又可以匹配get方式,也可以匹配post方式。‘
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET})public String hello(){return "success";} }
3.5@RequestMapping注解的params属性:
产生的派生注解:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET})public String hello(){return "success";}@GetMappingpublic String helloR(){return "success";}@PostMappingpublic String helloE(){return "success";}@DeleteMappingpublic String hellof(){return "success";}@PutMappingpublic String helloD(){return "success";} }我们进行测试第一种方式如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username"})public String hello(){return "success";} }我们的index.html如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>index.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> <form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性"> </form> <a th:href="@{/hello?username=admin}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第一种)</a><br> <a th:href="@{/hello(username='admin')}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第二种)</a><br> </body> </html>重新运行之后如下所示:
我们进行点击之后会出现如下所示:
会进行跳转该界面。
我们继续进行测试第二种方式如下所示:
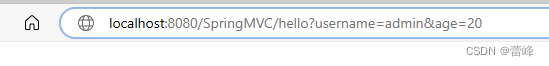
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password"})public String hello(){return "index";} }我们利用此直接进行跳转的时候:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>index.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> <form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性"> </form> <a th:href="@{/hello?username=admin}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第一种)</a><br> <a th:href="@{/hello(username='admin')}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第二种)</a><br> </body> </html>本身未携带,所以不会报错。但是我们直接在网址上进行拼接的时候,如下所示:
拼接上去也会报400错误。!password即为不能携带password.
我们来测试第三种方式:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20"})public String hello(){return "index";} }我们在网址里面进行拼接如下:
则会成功跳转。
我们测试第四种方法:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"})public String hello(){return "index";} }我们继续进行拼接如下所示:
此时重要不进行拼接gender=“男”,则不会进行报错。
总结如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters; */ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"})public String hello(){return "index";} }
3.6@RequestMapping注解的headers属性:
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系
“header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
“!header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
"header=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
"header!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到。
请求头和响应头(他们的键)是不区分大小写的,但是他们的值是区分大小写的
我们进行测试如下所示:
我们发现任意一个页面,点击进去之后,点击network,查看他的请求头信息,即可发现里面有一个referer(即为该页面的来源页面)
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters; * 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-; */ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";} }
3.7@RequestMapping注解使用ant风格的路径
?:表示任意的单个字符
*:表示任意的0个或多个字符(任意个数的任意字符)
**:表示任意层数的任意目录
注意:在使用**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式
我们进行测试如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/a?a/test/ant")public String testAnt(){return "success";} }我们在该index.html里面进行匹配:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>index.html</h1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br> <a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a> <form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性"> </form> <a th:href="@{/hello?username=admin}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第一种)</a><br> <a th:href="@{/hello(username='admin')}">测试@RequestMapping注解的params属性(第二种)</a><br> <a th:href="@{/aaa/test/ant(username='admin')}">测试@RequestMapping注解支持ant风格的路径</a><br> </body> </html>我们进行访问如下所示:
该网址可成功访问到我们的success.html画面。
?代替的是任意字符(不包括其本身)
在一个请求路径中,?是一个路径和我们的请求参数的分割符,?前面是路径,?后面是请求参数。
再测试如下:
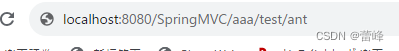
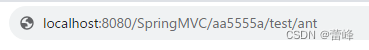
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;* 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-;* 6.SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径* 在@RequestMapping注解的value属性值中设置一些特殊字符* ?:表示任意的单个字符(不包括?)* */ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/a?a/test/ant")public String testAnt(){return "success";}@RequestMapping( "/a*a/test/ant")public String testAnttwo(){return "success";}}我们的访问路径如下所示:
但是?仍然不可以,同时/(路径分隔符)也不可以
我们继续进行如下测试:
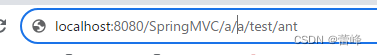
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;* 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-;* 6.SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径* 在@RequestMapping注解的value属性值中设置一些特殊字符* ?:表示任意的单个字符(不包括?)* *:任意个数的任意字符(不包括?和/)* **:任意层数的任意目录,注意使用方式只能将**写在双斜线中,前后不能有任何的其他字符*/ //@RequestMapping("/test") @Controller public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/a?a/test/ant")public String testAnt(){return "success";}@RequestMapping( "/a*a/test/ant")public String testAnttwo(){return "success";}@RequestMapping( "/**/test/ant")public String testAntthree(){return "success";}}我们的访问路径如下所示:
是可以访问成功的。
所以:
?:表示任意的单个字符(不包括?和/)
*:任意个数的任意字符(不包括?和/)
**:任意层数的任意目录,注意使用方式只能将**写在双斜线中,前后不能有任何的其他字符(不包括?)
3.8SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符
原始方式:/deleteUser?id=1
rest方式:/user/delete/1
SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符(xxx)表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>success.html</h1>
<a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a>
<form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性">
</form>
<a th:href="@{/test/rest/1}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性中的占位符</a>
</body>
</html>package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;* 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-;*/
//@RequestMapping("/test")
@Controller
public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/test/rest/1")public String testRest(){return "index";}
}
我们可以通过以上所述进行访问。但是这样子则无法获取传输过去的请求参数。
我们可以这样子进行传输:
package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;* 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-;*/
//@RequestMapping("/test")
@Controller
public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/test/rest/{id}")public String testRest(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){System.out.println("id:"+id);return "index";}
}
我们进行访问如下
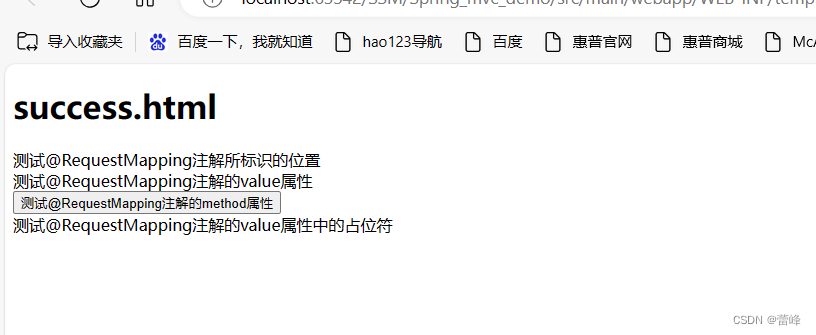
我们点击进行访问之后:
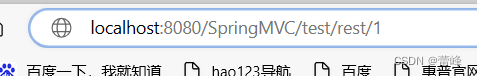
访问成功之后会在控制台看到输出id:1
我们进行添加参数:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>success.html</h1>
<a th:href="@{/hello}">测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/abc}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性</a>
<form th:action="@{/hello}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="测试@RequestMapping注解的method属性">
</form>
<a th:href="@{/test/rest/admin/1}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性中的占位符</a>
</body>
</html>package com.rgf.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** 1.@RequestMapping注解的位置* @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息* @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息* 2.@RequestMapping注解的value属性* 作用:通过请求的请求路径匹配请求* value属性是数组类型,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求路径匹配value属性中的任何一个值* 则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 3.@RequestMapping注解的method属性* 作用:通过请求的请求方式匹配请求* method属性是RequestMethod类型的数组,即当前浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式*则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错:405-Request method 'XXX' not supported* 在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的派生注解:* @GetMapping,@PostMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PutMapping* 派生注解没有method属性,仍然有value属性。* 4.@RequestMapping注解的params属性(value和method匹配其中一个就可以,但是params必须携带且匹配,若为携带,则会报错400,* 意为当前请求的参数与真实的参数不匹配)* 作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的设置* params可以使用四种表达式:* "param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数* "!param":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中一定不能携带param参数* "param=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value* "param!=value":表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中可以不携带param参数,若携带值一定不能为value* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求参数不匹配,此时页面报错:* 400-Parameter conditions "username" not met for actual request parameters;* 5.@RequestMapping注解的headers属性* 作用:通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求头信息满足headers属性的设置* 若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求头信息不匹配,此时页面报错:404-;* 7.@RequestMapping注解使用路径中的占位符* 传统:/deleteUser?id=1* rest:user/delete/1* 需要在@RequestMapping注解的value属性中所设置的路径中,使用{xxx}的方式表示路径中的数据* 在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的值和控制器方法的形参进行绑定*/
//@RequestMapping("/test")
@Controller
public class TestRequestMappingController {//此时控制器方法所匹配的请求的请求路径为/test/hello@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/abc"},method ={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET},params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"},headers={"referer"})public String hello(){return "index";}@RequestMapping("/test/rest/{username}/{id}")public String testRest(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,@PathVariable("username") String username){System.out.println("id:"+id+"username:"+username);return "index";}
}
访问成功之后会在控制台看到输出id:1,username:admin.








![Android LitePal byte[]类型字段不被创建](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/Android LitePal byte[]类型字段不被创建)


)



))








)
