c语言:
memory section:
.bss: uninitialized or zero-initialized global and static variables
.data: initialized global and static variables
.text: Read only, code and const
C语言编译流程:
pre-compiler: #define, #include 【text substitution】
compiler: turn source code into machine code(object file), perform syntax error check
link: link these object files together to create an executable file, resolves references to functions or variables that are defined in other object files【map file里面可以看到】
【C语言关键字 / keyword】
Macro写一个函数: Macro本质就是pre-processor将内容进行文本替换
#define SET_BIT(var, position) var = var | (1<<position)#define MAX(A,B) (A>B)?A:B- short 2bytes
- long 4 bytes
typedef 和 macro哪个好
const的含义: Read only
volatile的含义: tell compiler not to use cache to optimize, always to read from address.
const 和 volatile公用:
uint8_t const volatile * reg_1 = (uint8_t *) 0x10000000;
对固定地址赋值
*(unsigned int *)0xFC880000 = 1;extern: change visible scope
static 修饰
- 全局变量: accessible only within the file
- 局部变量: variables retain their values between function calls
- 函数: accessible only within the file
sizeof (sizeof也是个keyword): 返回的是byte数
sizeof(int)
sizeof(Node) //typedef struct{} Node;
【位操作】
&
|
^ (exclusive or)
~: unsigned int mask = ~(0);
【数据类型】
数组
字符和字符串
end with \0; NULL character
qsort 对数组排序
#include <stdio.h>int compare( const void *a, const void *b)
{return *(const int*)a - *(const int*)b;
}int main()
{int m[] = {1,3,5,2,6};int num = sizeof(m)/sizeof(m[0]);int size = sizeof(m[0]);qsort( m, num, size, compare);printf("0x%x\n", m[0] );printf("0x%x\n", m[1] );printf("0x%x\n", m[2] );printf("0x%x\n", m[3] );printf("0x%x\n", m[4] );return 0;
}注:
1. compare的返回值永远是int, 但是 如果输入数组是char,那么return那行
就要写成 *(const char*)a 【否则不工作】
2. return 那行的 *(const char*)a,星号不要忘了
3. 三个int 变量,啪啪啪写完朝函数里面放就行了
4. qsort是void类型,没有返回值malloc 分配空间
void *malloc(size_t size) //返回的是void型指针char *p;p = (char*) malloc( sizeof(char) * 15 ); //15个元素的空间结构体/union

data alignment: data will be padding
虽然sBa[20],但是仍然看做是2byte的长度,所以结构体还是以 4bytes的长度 来 alignment的
typedef struct
{int Num;short sDate;char cha[2];short sBa[20];
}Test;指针
指针类型:
void: 可以指向任何类型, qsort的函数就有用到。使用的时候要记得 强制类型转换
wild: not been initialized to anything
NULL: a pointer which is pointing to nothing
dangling: A pointer pointing to a memory location that has been deleted (or freed)
没有权限访问该地址,所以*p 直接就报错了
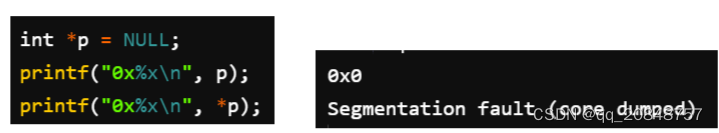
空指针,不指向任何地址。在新建链表的时候会用到

直接对物理地址赋值:
* (int*) 0xFF00CCFF = 1;或者: 【 地址前的 (int*)不要忘了 】
int *p = (int*) 0xFF8800FF;*p = 1指针数组:
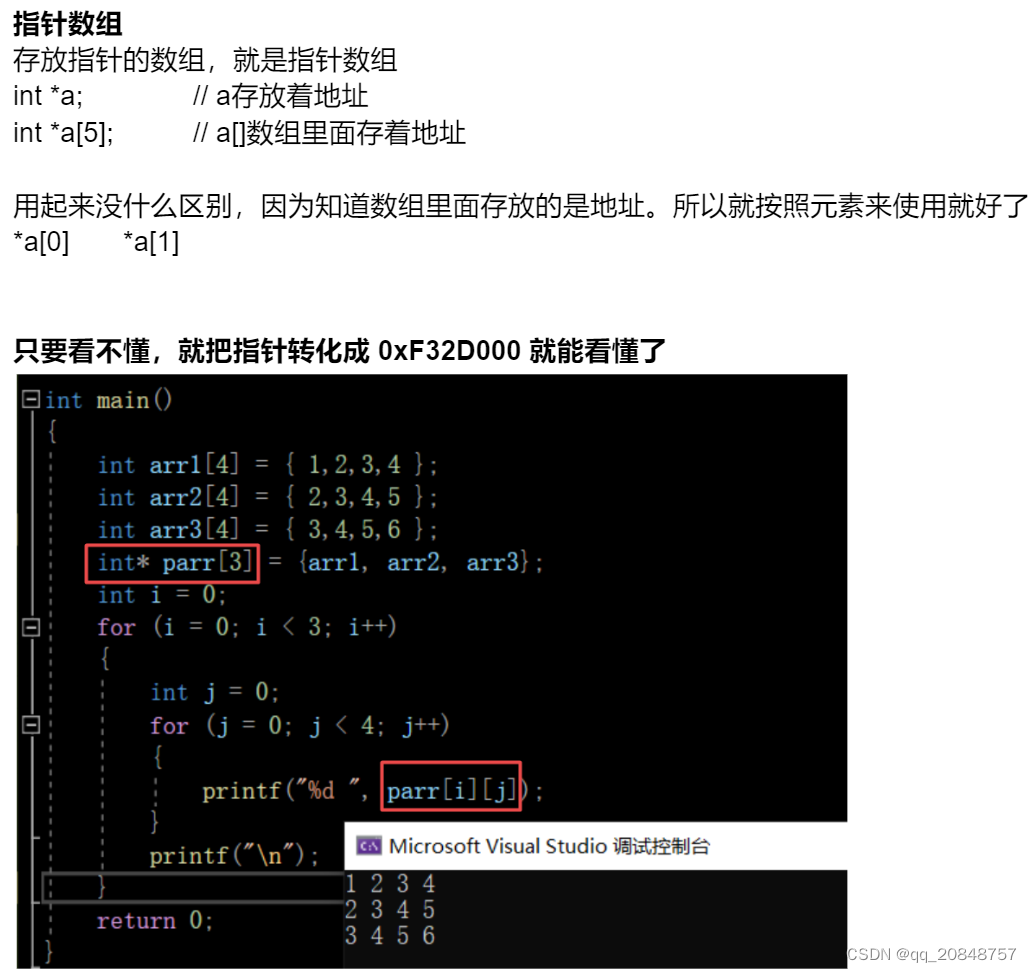
从上图代码可以看出:
二维数组parr[0][0],可以拆开看成 ( parr[0] )[0], 也就是(arrl)[0];函数指针:
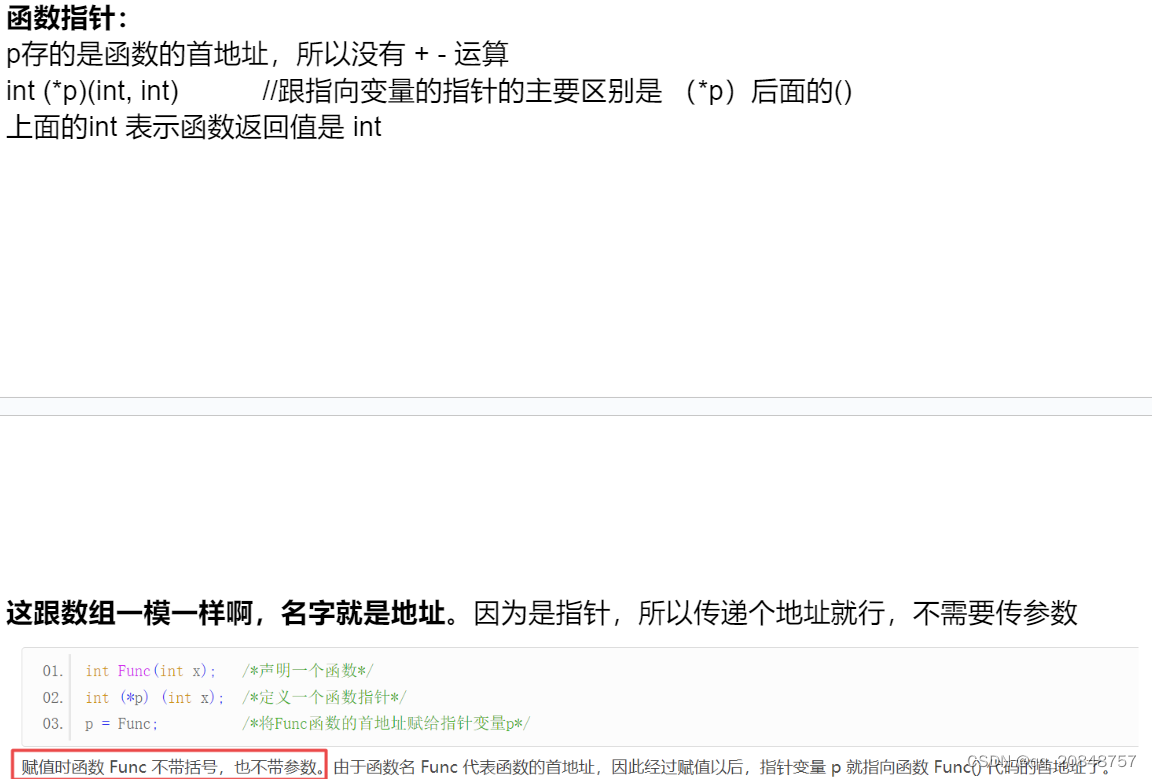
使用很广,中断向量表里面存的就是函数指针
用的时候:
void(*p)(void);或者
void(*0xF32D0000)(1,2);typecasting:
int will be promoted to unsigned int
栈
一个数组,再加一个栈顶指针
队列
链表
【库函数】
strlen(const char* str);void* malloc(size_t size);
void free(void *ptr);void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void*));【恶心的】
auto: default storage class, for local variable 【storage duration is automatic,be created when the program execution enters the block in which it is defined and destroyed when the block exits】
register: only for local variables, store in cpu register instead of RAM 【& cannot be used on register variable】
enum:
bit field:
说白了就是 int A 后面带一个 :n 即可
// 定义
typedef struct
{int a;
}A;typedef struct
{int a_bit0 :1 ;int a_bit1 :1 ;int a_bit2 :1 ;int a_bit3 :1 ;int a_reserved :28 ;
}A_bitfield;//使用A m;
m.a;A_bitfield n;
n.a_bit0;
switch case:
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
i++ / ++i
0xFF
0b011
%s
%d
%f
char 1bit
short 2bit
int: 4 bytes
short vs long:8 bytes
double:
float:
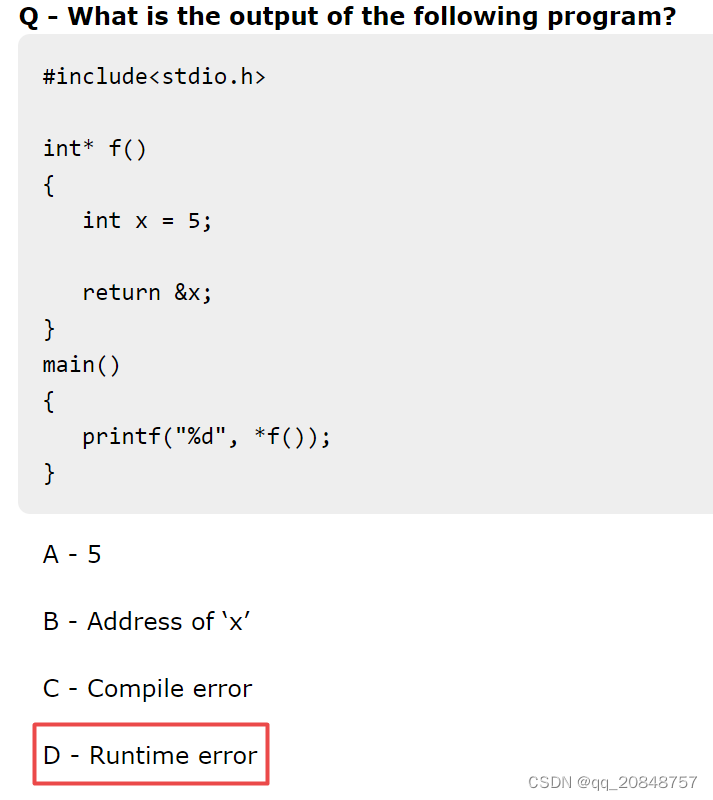
runtime error: X is local variable
OS:
【核心】
basic/extended task:
- basic task: 在running状态下,只有terminate和被更高优先级任务抢占,进入ready状态两种 释放cpu的方式 【不涉及等待共享资源的简单任务】【反正我看到的AUTOSAR project里面都是extended task】
- extended task:在running状态下,有主动释放cpu,进入wait状态的能力【等待共享资源的释放】
deadlock:
前提: 有两个共享的resource A和 B,task 1和2 都需要 A和B 两个资源
task1使用了resource A,然后被task2抢占,task使用了resource B,然后发现resource A不可用,于是进入wait 模式【此时B没有被释放】。 task1拿回cpu控制权继续执行,然后发现 resource B不可用,互相wait
解决: timeout,如果等待时间timeout以后,task需要释放自己的resource
优先级反转:
Priority Inversion
前提:有一个共享的resource 【优先级3>2>1】
优先级1的task 被 优先级3的task抢占,但task3在执行过程中发现share resource不可用【被task1用着呢】,于是释放了cpu【进入wait,任务就绪表置0,触发scheduler】,scheduler根据任务就绪表让task1继续执行,但此时task2又抢占了task1并执行完成,
解决:临时提升低优先级任务的优先级。 task3在因为resource释放cpu的时候,把持有resource的task1优先级临时提升到3,这样task2 就不能抢占他了
【因为basic task中没法处理share resource,所以只有extended task需要考虑deadlock 和优先级反转】
ECU多核之间通讯:
多核间通讯: IOC, spinlock
就一个core,task发现resource 不能用的时候,就只应该立刻释放cpu 【mutex + semaphore】
多核的时候,才有一个core 来while(1),等待另一个core的task运行完release resource的道理【spinlock】
因为spinlock用于多核cpu,其中一个core一直while(1)等待另一个core释放资源,也无所谓 【Spin locks are a low-level synchronization mechanism suitable primarily for use on shared memory multiprocessors. When the calling thread requests a spin lock that is already held by another thread, the calling thread spins in a loop to test if the lock has become available】
进程间通讯:
mutex VS semaphore
都是用来做进程间同步的,区别是mutex必须是进程自己释放,semaphore可以是别的进程释放,而且可以大于1
- mutex: 主要的purpose是protect shared resources
- semaphore: 主要的purpose是notice一个event已经发生了,比如taskA 在等一个semaphore,然后一个传感器触发了ISR,ISR去把semaphore置1了,然后taskA就可以继续执行了,这就是为什么说semaphore可以是别的进程释放
semaphore: 【由计数器和 任务等待表 两部分组成,也就是说每个信号量都有自己的任务等待表】
- 如果信号量的值为0,任务进入wait状态,并在任务等待表上面被标记,然后触发scheduler
- 当其他任务释放了信号量后,会在该信号量的任务等待表中找到最高优先级的任务,并将其从wait转为ready状态,然后触发scheduler
所以scheduler的工作很简单,在任务就绪表里面找最高优先级的任务【有更高的就上下文切换】
- 想让任务wait,并交出cpu控制权很简单:把它在任务就绪表自己的格子中置0,在任务等待表中置1,然后触发scheduler即可
- 想让任务从wait到ready,更简单:把它在任务就绪表自己的格子中置1,在任务等待表中置0,然后触发scheduler即可
说白了extended task,就是task可以【因为共享资源不可用】主动放弃cpu控制权,进入wait状态,让优先级低的先去执行【任务就绪表置0,任务等待表置1】
basic task,task没法自己主动放弃cpu,只能是被动的被其他优先级更高的抢占
任务调度的原理:
scheduler被调用的场景:
- timer ISR调用scheduler【周期性的任务切换】
- task结束,调用scheduler
- extended task因为share resource不可用,放弃cpu进入wait状态,然后触发scheduler
任务就绪表【1张】 + 任务等待表【多张,每个信号量都有自己的1张任务等待表,信号量在被task释放的时候,该task会去该信号量的任务等待表唤醒最高优先级的任务进入任务就绪表,然后触发一次scheduler】
scheduler做的事情:
查找任务就绪表优先级最高的任务,如果需要切换,就context switch切换。否则就继续执行当前任务,开销很小
【杂项】
process/thread
- process has its own dedicated memory space, consume more resource【硬件MPU保护】
- Threads within the same process share the same memory and resources
big/little endian
针对超过一个byte的数据而言。most significant byte在低地址的为big endian
检测方法:
int a = 0x12345678;char *p = (char*)&a; //(char*) 告诉编译器用char类型来解析a地址的数据注:
通过char型指针p变量,获取第一个byte,既可判断inline 函数
a suggestion to the compiler that it should generate code for the function at the call site, instead of generating a separate function call. for better performance
only a suggestion, compiler will make the final decision
include <> 和 “” 的区别
<>: 寻找 system path(编译器的安装目录文件夹)
"": 寻找当前project path(当前工程文件夹),找不到再找system path
上电流程/startup phase
【以下针对嵌入式MCU而言】
单核:
- reset vector
- startup code
- init clock
- memory setup: copy from FLASH to RAM + init stack pointer(stack信息在linker里面定义的 .lsl文件) (.bss .data 会在 RAM运行, .text还是在FLASH运行)
- init peripheral: init GPIO, CAN (如果需要bootloader功能的话)
- system init: 中断向量表初始化,enable 中断
- main()
【linker里面配置了stack的大小,startup phase把stack pointer指向了该位置, 之后main函数入的就是这个栈。只是说操作系统在任务切换的时候,会把cpu register内该task的信息copy到那个task自己的任务控制块里面零时存起来,保护现场。之后再copy回来,就等于恢复现场,可以继续运行了】
【对于操作系统,每个task都要有自己的任务栈,运行的时候,cpu的stack pointer要指过去,是为了方便任务切换。如果所有task公用一个栈,假如task1先入栈运行,然后被优先级更高的task2抢占,入栈到它上面,然后task2运行一半休眠了,那么就没法access到task1的栈内容了。就算你把task2的栈pop出来去存储,也太麻烦了,消耗时间太多】
多核:
- 硬件启动master core0, core0去唤醒slave core1,2,3 。【唤醒的含义是硬件初始化+startOS】 在所以核心的OS start以后,会进行第一次同步。
- 第一次同步后,各个core会去call application startup hook,然后进行第二次同步。从而确保所有core的OS kernel一起开始运行。
- 【第一次同步是OS 初始化完成(OS的stack什么的)【EcuM startupOne】,第二次同步是进程初始化完成(OS-Application,Task的堆栈,控制块初始化等等)【EcuM startupTwo】,然后同时开启时间片进行Task调用】

中断向量表:
中断向量表网站链接:(array of function pointers)
- 一个用来存储各个中断服务函数地址的内存区域
- 中断向量表区间默认是空着的
- 用户在c文件里面创建了ISR函数,那么MCU上电的时候,startup code就要根据用户创建的各个ISR的地址,把这些函数地址都注册到 中断向量表 里面
- 中断向量表在code/FLASH section
Interrupts and exceptions:
-
interrupt: trigger by external event, save context and jump to the ISR
- system exceptions: trigger by cpu (divided by zero, invalid memory access), save context and jumps to an exception handler routine
下图可以看到,Interrupts and exceptions 都在 中断向量表里面
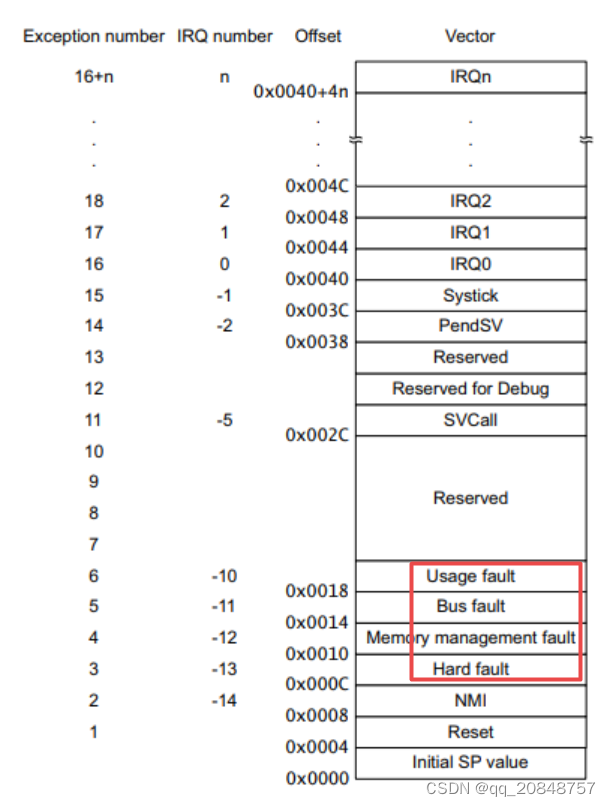
抢占式: (Preemptive)
-
Preemptive OSes are often used in real-time systems where tasks must meet strict deadlines. The OS can guarantee that high-priority tasks will run when required.
-
some preemptive OSes use time slicing, where each task is given a fixed time quantum to run. When the time quantum expires, the task is preempted even if it hasn't finished.
函数入栈流程:
函数入栈流程网站链接:
函数栈从高地址到低地址增长
return address, actual parameters and local variable are pushed into stack【返回地址就是下一行该执行的代码的地址】
ebp, esp stands for base pointer and stack pointer
一道很好的题目
call by value/reference:
- by value: a copy of the actual argument's value is passed to the function, any changes made to the parameter (in the function) do not affect the original argument
- by reference: pointer to the actual argument is passed to the function, It is useful when you want a function to modify the original data
actual and formal parameters:
-
formal: variables or placeholders that are declared as part of a function's definition
- actual: the values passed to a function when it is called
context switch:
save the current status of task into control blocks 【register, task stacks】
trigger by interrupt, pre-emptive multi-task,
reentrant function
- can be safely called simultaneously by multiple threads,
- Reentrant functions use only local data (variables or memory) and do not rely on global or shared data, do not use static variables
#pragma
memory mapping 的时候,用到过
- variable placement:
- code section placement:
原码,反码,补码
正数的原码,反码,补码都一样
负数的原码:和正数一样,除了符号位置1 【问题,正负数原码相加不为0】
反码(ones' complement):直接把正数的原码反过来【问题,正负数反码相加为0xFFFF】
补码(twos' complement):反码+1 【正负数补码相加不为0】
虚拟内存: paged memory
数据结构:
常见错误
的正确用法:
int a[10] = {0}; //记得将所有元素初始化为0 【有些在线编译器很傻逼】num = num <<4; // 记得写num =, 单独的num<<4 不会改变num本身的值unsigned int mask = ~0; //如果要位运算,一定记得是unsigned,要么就直接 (~0)<<8
常用:
int a[] = “abcdefg”;
sizeof(a);
printf(“%s\n”,a);
基本上:
-
数组题,就可以考虑先qsort一下,可能会简单很多
-
数操作,就是从2进制的角度去看, XOR, 一下什么的。 &1111 就是截取, |0000就是删除
-
不知道循环次数的时候, while(n) 就很好用
位操作:
数字题的工具:
-
截取: &1111
-
删除: |0000
-
半加法: XOR
-
取某一个bit: n&1 n = n>>1
-
char型指针可以很方便的操作int型变量的每一个byte
-
二进制字符串转数字: 找到1的位置, n = n| (1<<i)
-
找到的元素,可以用一个数组把下标都存起来,然后再操作
-
不知道循环长度,可以 while() 循环
-
将某一段bit翻转: ^1111
-
找不同: XOR 的结果为1
第5条: 0x5A5A,5A5A 想变成 0xA5A5,A5A5
第8条:

数组操作:
数组题的工具:
-
qsort
-
删除重复的数: XOR
-
有的时候,搞个int型指针,就可以一次操作4个char数组元素
指针:
qsort
链表:
malloc
free
stack:
queue:
递归:
XOR实现加法
#include <stdio.h>int add( int a, int b)
{int sum = a^b;int new = a&b;if( new==0 ){return sum;}else{return add(sum, new<<1);}
}int main()
{printf("%d\n", add(3,21));return 0;
}













)




