摘要
本章将介绍一下auto、for和指针空值,文章末附上入门的所有代码。
目录
摘要
一、auto
二、for
三、指针空值
四、代码
五、思维导图
一、auto
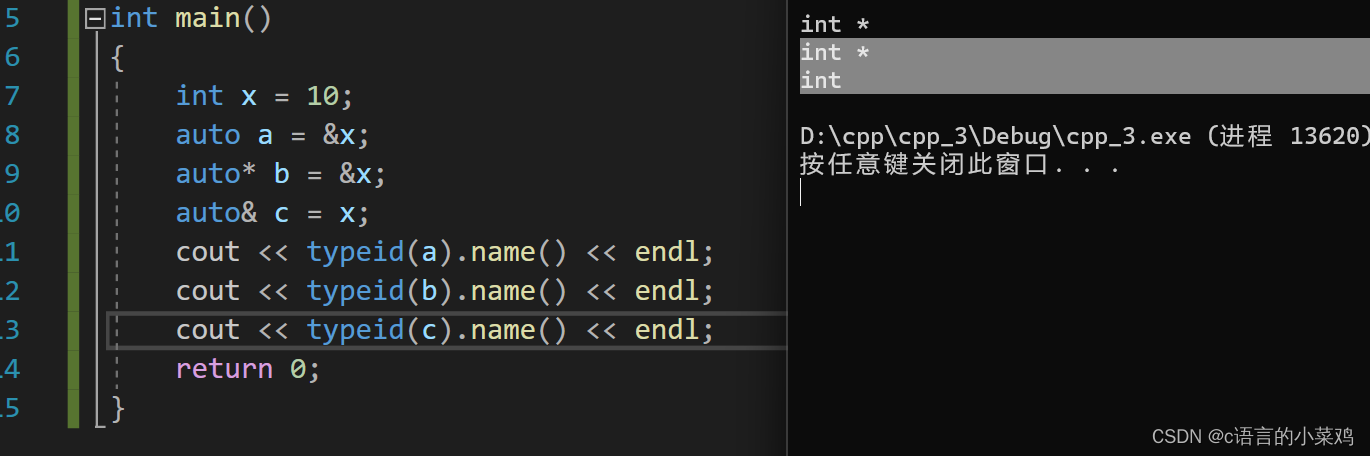
这个关键字是c++提出的,可以自动识别变量的类型,可以看出下方图片,auto自动识别变量类型,a是指针就识别出了指针,a就是指针类型的,b和a一样,但是在auto后面接上*就只可以是指针类型的,同理接上&后就只能是引用了,但是要注意这个关键字后面需要有初始化的变量,不能作为函数的形参和初始化数组。
二、for
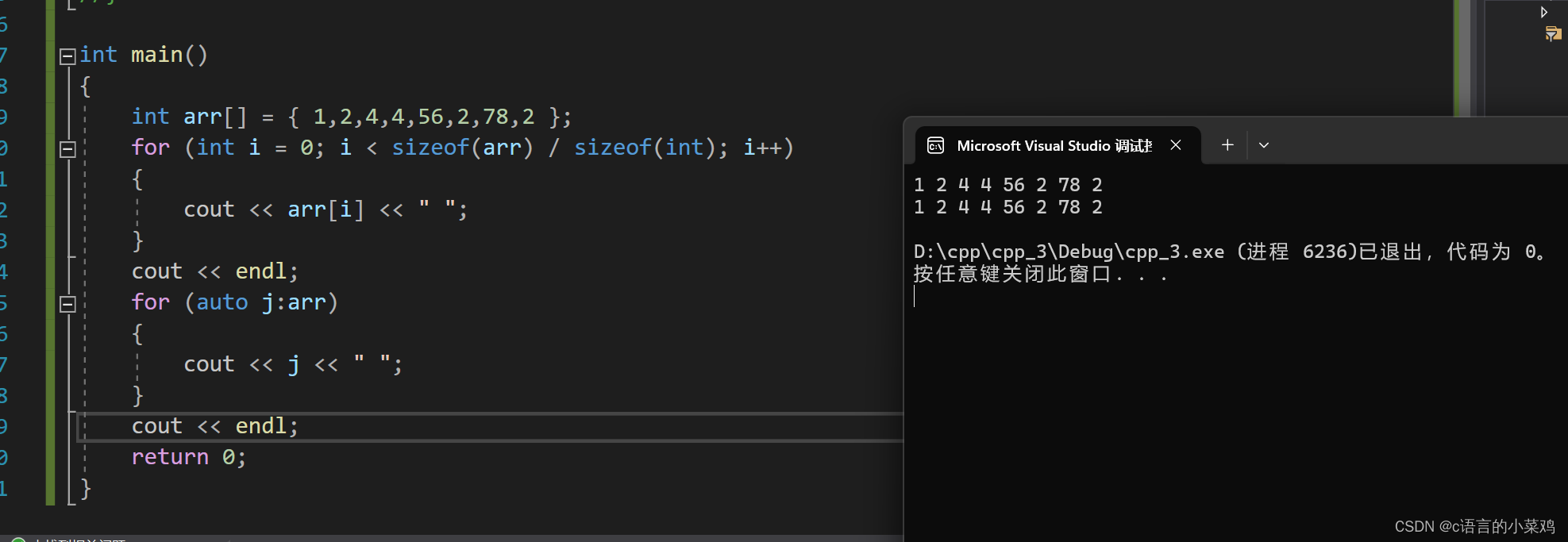
这个是c++在c语言的基础上改编而来的,直接上代码对比吧,如下图这个for就可以配合上面说的auto使用,可以直接用:分割打印,不需要和传统的for一样使用,但是需要注意的是这个for循环迭代的范围必须是确定的 对于数组而言,就是数组中第一个元素和最后一个元素的范围;对于类而言,应该提供 begin和end的方法,begin和end就是for循环迭代的范围。
三、指针空值
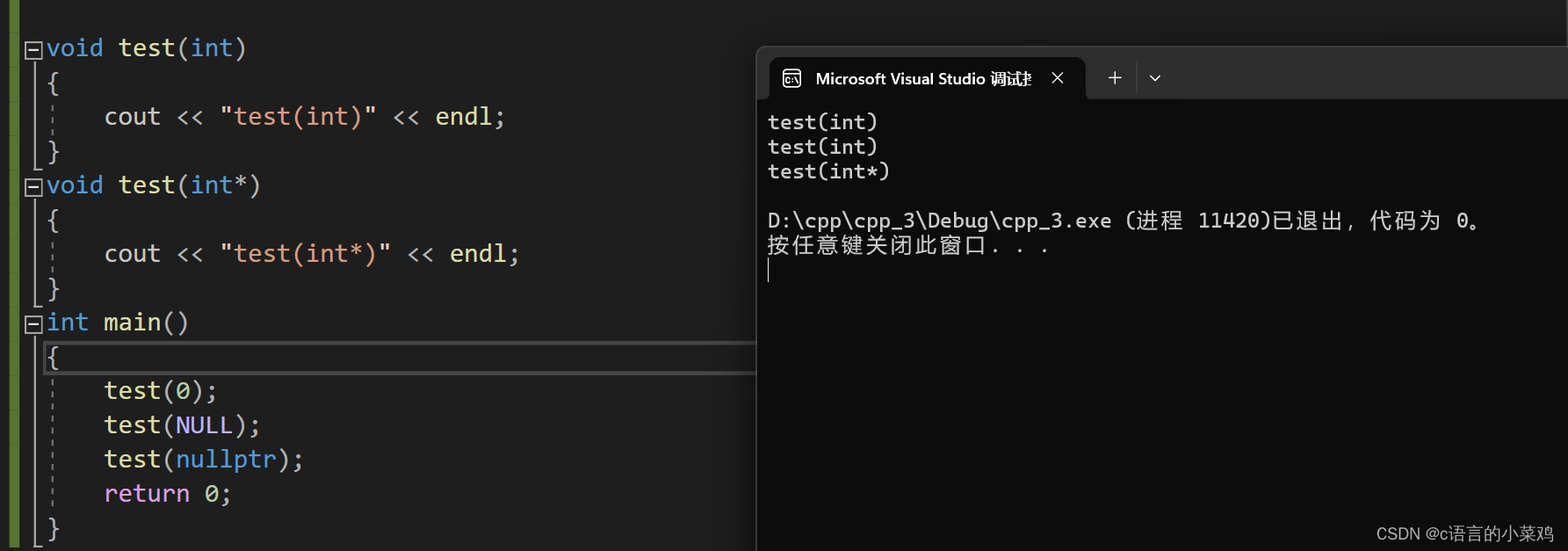
指针空值这个就是在c++创建时有点小BUG就是NULL是0,就是他不是一个指针的值了,在函数重载时匹配的是0,不是指针了,而这时在2011年nullptr作为补丁引入,区别如下图特别明显。
四、代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//int main()
//{
// int x = 10;
// auto a = &x;
// auto* b = &x;
// auto& c = x;
// cout << typeid(a).name() << endl;
// cout << typeid(b).name() << endl;
// cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// int arr[] = { 1,2,4,4,56,2,78,2 };
// for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++)
// {
// cout << arr[i] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// for (auto j:arr)
// {
// cout << j << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}void test(int)
{cout << "test(int)" << endl;
}
void test(int*)
{cout << "test(int*)" << endl;
}
int main()
{test(0);test(NULL);test(nullptr);return 0;
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//int main()
//{
// int a = 0;
// int& b = a;
// int& c = b;
// int& d = a;
// cout << &a << endl;
// cout << &b << endl;
// cout << &c << endl;
// cout << &d << endl;
// return 0;
//}//int& ly(int a,int b)
//{
// static int c;
// c= a + b;
// return c;
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// int ret = ly(1, 2);
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <time.h>
//struct A { int a[10000]; };
//void test1(A a) {}
//void test2(A& a) {}
//void test3()
//{
// A a;
// size_t begin1 = clock();
// for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; ++i)
// test1(a);
// size_t end1 = clock();
// size_t begin2 = clock();
// for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; ++i)
// test2(a);
// size_t end2 = clock();
// cout << end1 - begin1 << endl;
// cout << end2 - begin2 << endl;
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// test3();
// return 0;
//}inline int ADD(int a, int b)
{return a + b;
}inline int ADD1(int a, int b, int c)
{c = a + b;a = a + b;b = a + b;c = a + b;a = a + b;b = a + b;c = a + b;a = a + b;b = a + b;c = a + b;a = a + b;b = a + b;c = a + b;a = a + b;b = a + b;c = a + b;a = a + b;c = a + b;b = a + b;return c;
}
int main()
{int ret = ADD(1, 3);int ret1 = ADD1(1, 3,2);return 0;
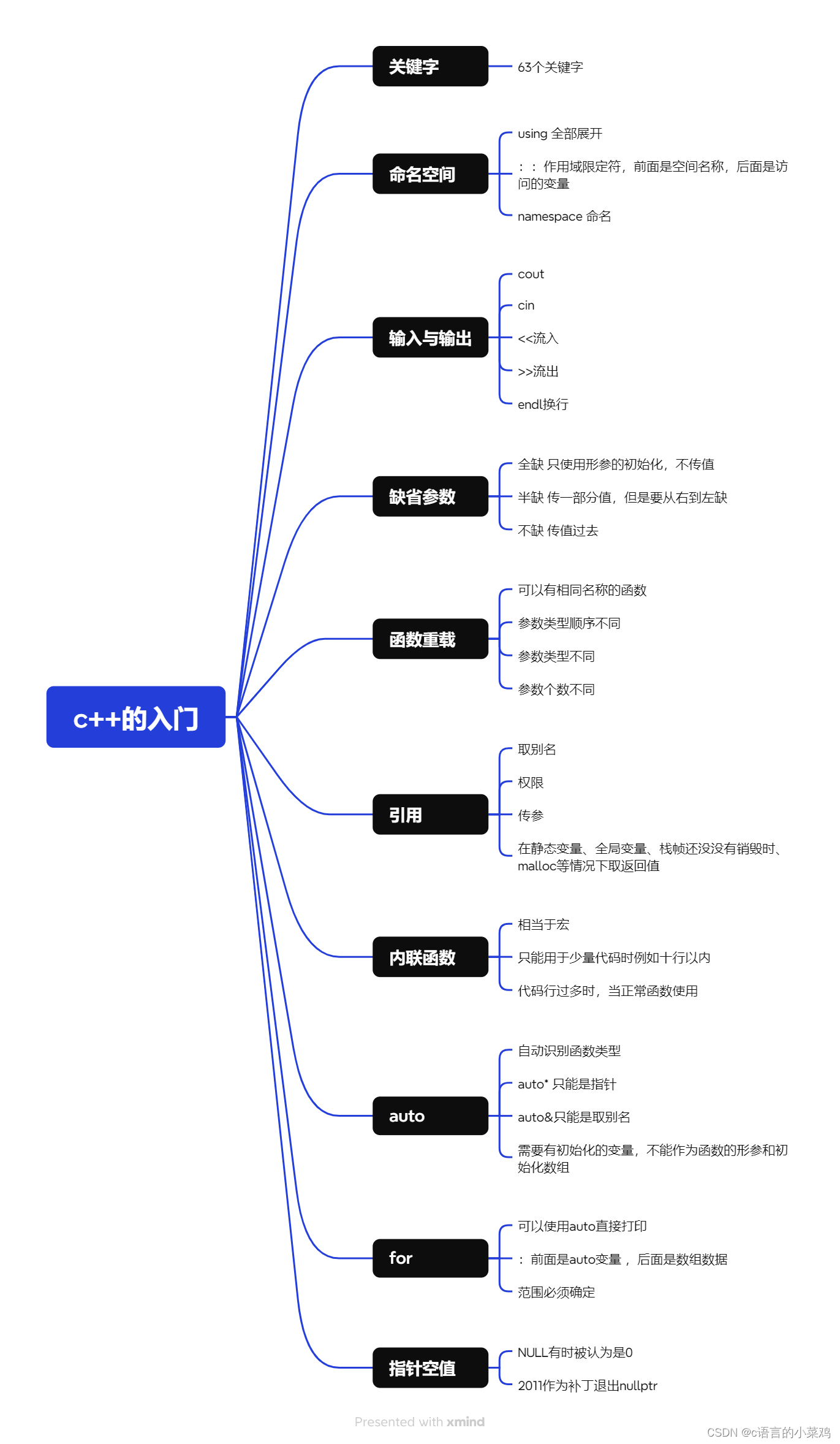
}五、思维导图
和Lambda表达式求List<User>中age最大和最小的年龄)





)

实验室器具有哪些?)


)





)

