1、Linux fork 函数
pid_t fork(void);
pid_t : 对于子进程,返回0
pid_t : 对于父进程进程,返回子进程进程号
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
pipefd[0] 为读取管道
pipefd[1] 为写入管道
返回值:-1失败 0 成功
2、函数实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>int main (int argc, char ** argv){int pipefd[2];int ret = 0;pid_t cpid;char buf;if(argc != 2) {printf("Usage pipe <command> \n");_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);} else {printf("argv[1] = %s \n", argv[1]);}ret = pipe(pipefd);if(ret == -1){perror("fork error \n");} else {printf("create pipe success !\n");}cpid = fork(); if (cpid == -1) {perror("fork error \n");}printf("pid1 = %d \n", getpid());if (cpid == 0) { /*子进程从管道读取 */printf("child pid2 = %d cpid = %d \n", getpid(), cpid);/* 关闭不使用的写管道 */close(pipefd[1]);/*子进程读取管道数据,并输出打印*/while (read(pipefd[0], &buf, 1) > 0){write(STDOUT_FILENO, &buf, 1);}write(STDOUT_FILENO, "\n", 1);/*关闭管道*/close(pipefd[0]);printf("child pid2 = %d cpid = %d \n", getpid(), cpid);_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);} else {printf("parent pid3 = %d cpid = %d \n", getpid(), cpid);/* 关闭不使用的读管道 */close(pipefd[0]);/* 父进程写arg[1]到管道 */write(pipefd[1], argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));close(pipefd[1]);/*等待子进程*/wait(NULL);printf("parent pid3 = %d \n", getpid());exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}return 0;
}
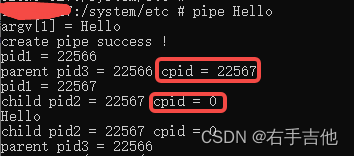
3、代码运行效果
编译二进制文件,运行到手机端


)



自动引入组件和自动生成路由的方法介绍)



)





)


