一、联合查询
1.使用 union 连接两个 select 语句进行联合查询
select 列 1,列 2... from 表名 where 条件 union select 列 1,列 2... from 表名 where 条
件;
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_name,prod_price from products where prod_price <= 5 union select vend_id,prod_id,prod_name,prod_price from products where vend_id=1002 or vend_id=1003;
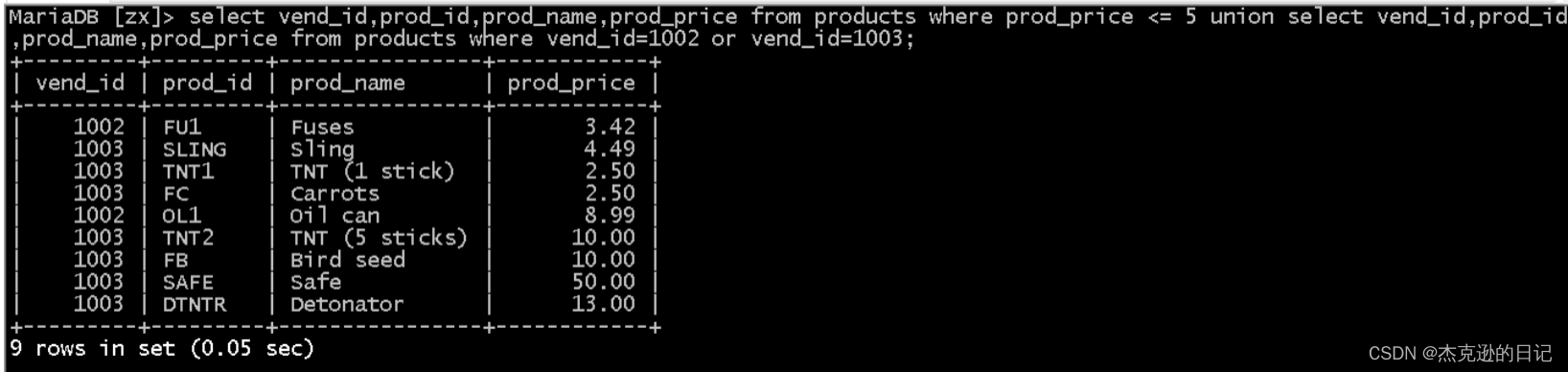
注:1)上述语句等同于
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_name,prod_price from products where prod_price <= 5 or vend_id in (1002,1003);
2)一个 union 必须包含两个或两个以上 select 语句在 union 中的每个查询都必须包含相同的列、表达式或者聚合函数
列数据类型必须是兼容的,他们不必是完全相同的类型,但必须是 MariaDB 能够转换的
union 从查询结果集中自动移除任何重复行,如果要返回所有匹配结果,用 union all代替 union
当使用 union 联合查询时只可以使用一个 order by 子句,并且必须出现在最后一个 select 语句后面
union 也适用于对不同的表进行联合查询
二、全文本搜索
1.限定条件
1)在创建表时需要指定哪些字段为全文本搜索列
2)在创建表时需要指定支持全文本搜索的数据库引擎(Aria)
注:指定的支持全文本搜索的列,MariaDB 会自动给这一列建立索引来提高全文本搜索的查询速度。(字典的目录)
使用 like 操作符配合通配符也可以实现相关关键字的查询。但速度没有全文本搜索快,查询的结果不如全文本搜索的结果智能(全文本搜索可以根据不同单词的排位值显示结果)
2.select 列名 from 表名 where match(列名) against('关键字');
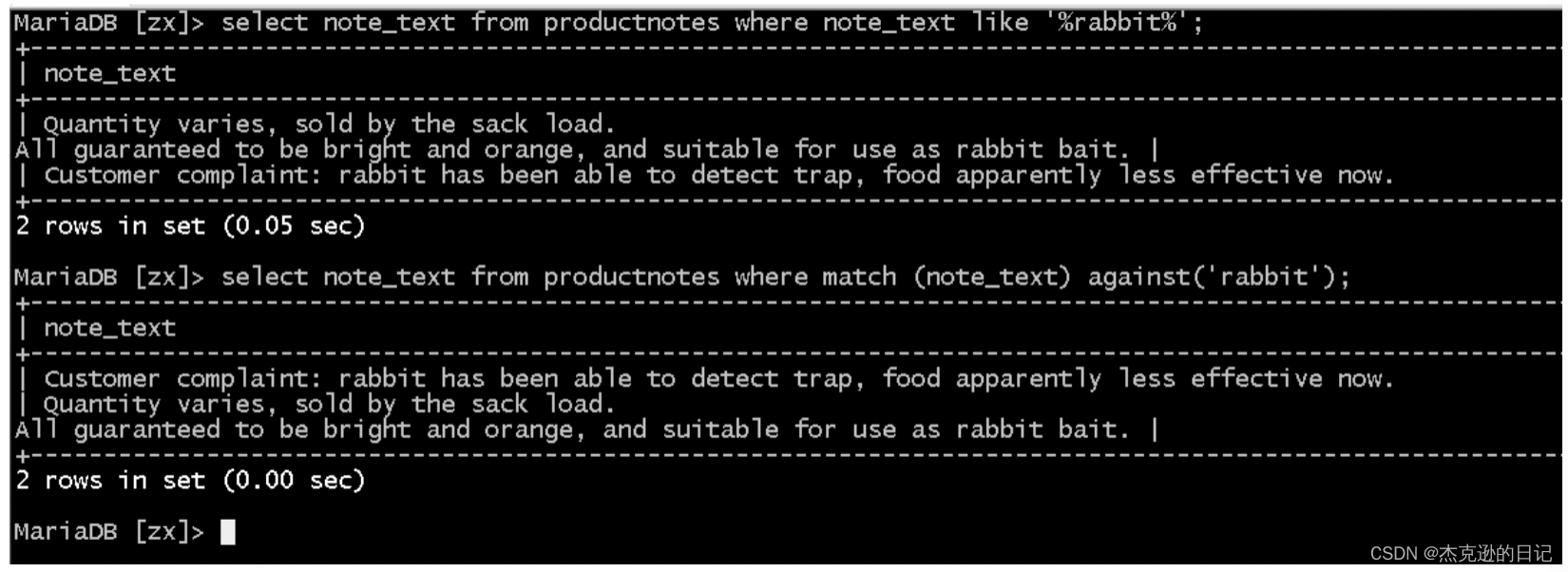
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('rabbit');
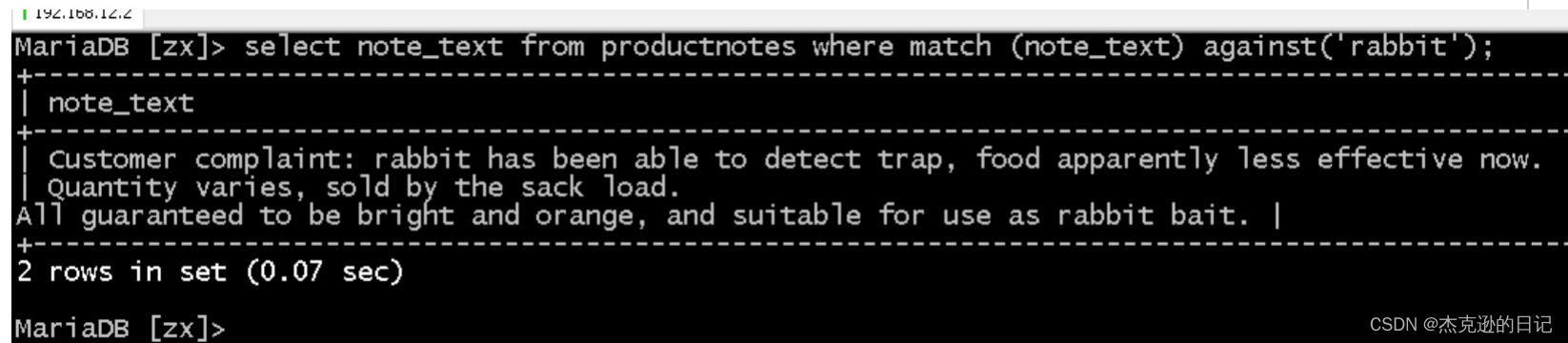
越靠近每段开头,越先显示
注:如果使用 like 操作符查询
select note_text from productnotes where note_text like '%rabbit%';
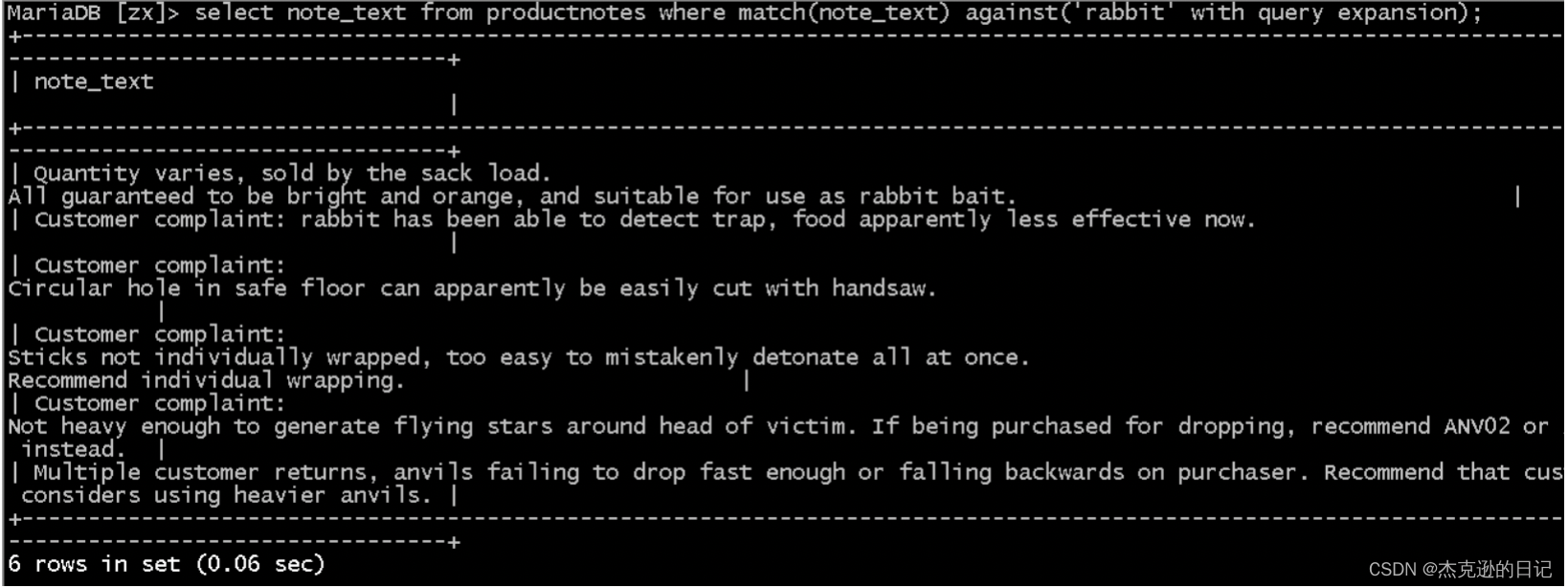
3.扩展查询(把rabbit显示的行 再进行查询)
select 列名 from 表名 where match(列名) against('关键字' with query expansion)
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('rabbit' with query expansion(扩展));
4.布尔文本搜索(必须包含哪个关键字 必须不包含哪些)
select 列名 from 表名 where match(列名) against('关键字' in boolean mode);
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against ('+heavy -rope*' in boolean mode);
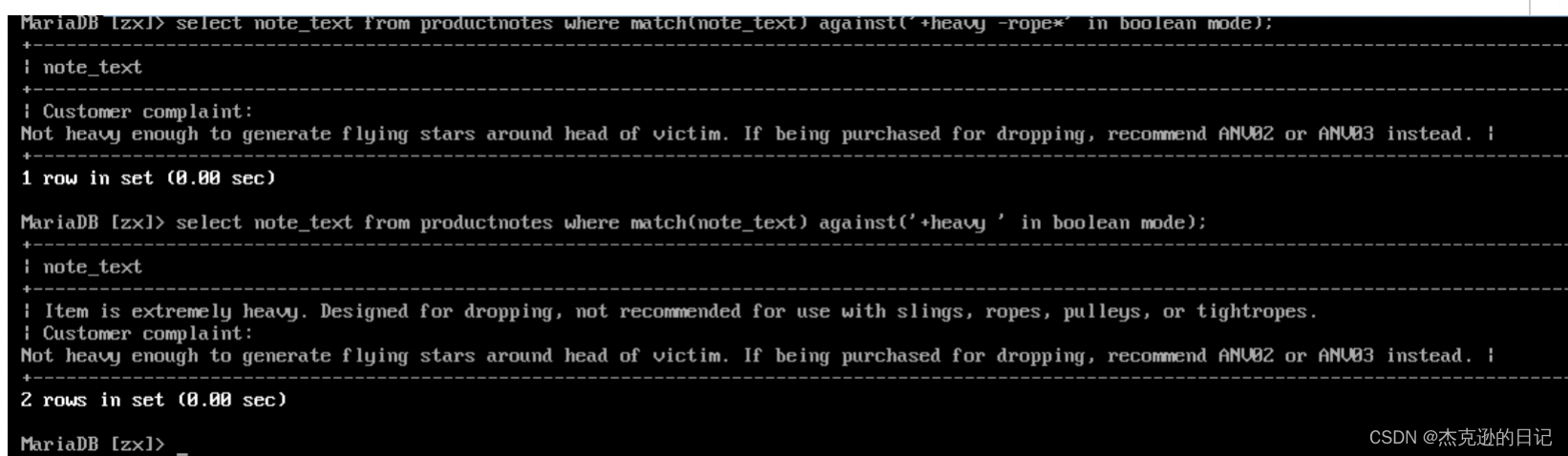
+ 表示必须包含
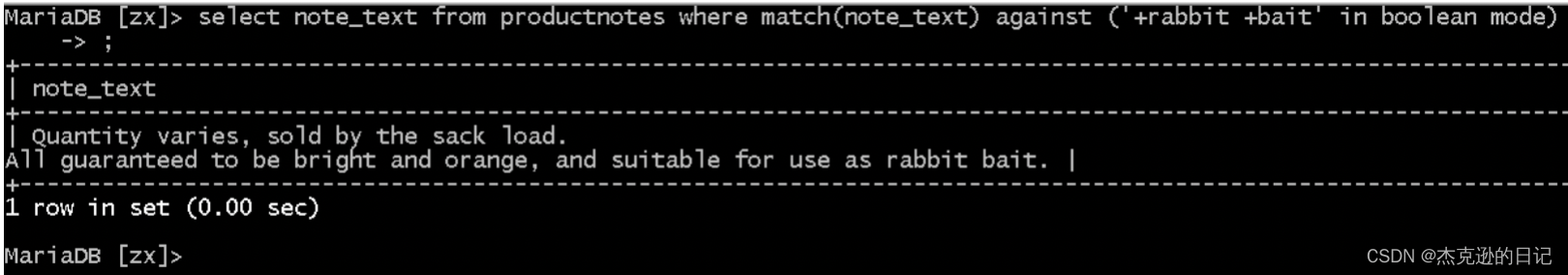
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against ('+rabbit +bait' in boolean mode);
三、连接查询
1.内连接(等值连接)
1)查询所有供货商的 ID,名称及其供应的产品名称和产品价格:
select vendors.vend_id,vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors,products where vendors.vend_id=products.vend_id;
select vendors.vend_id,vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors inner join products on vendors.vend_id=products.vend_id;
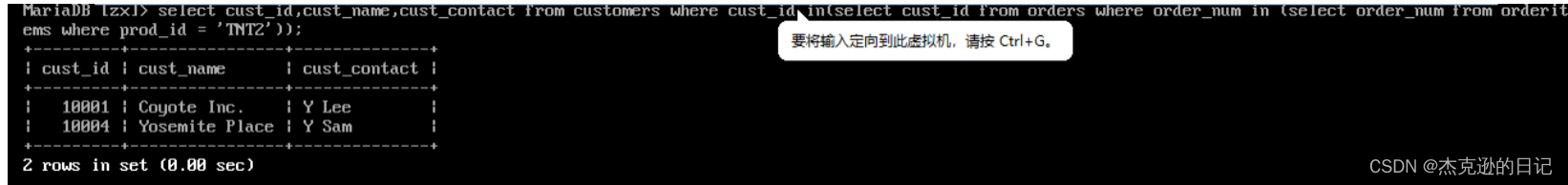
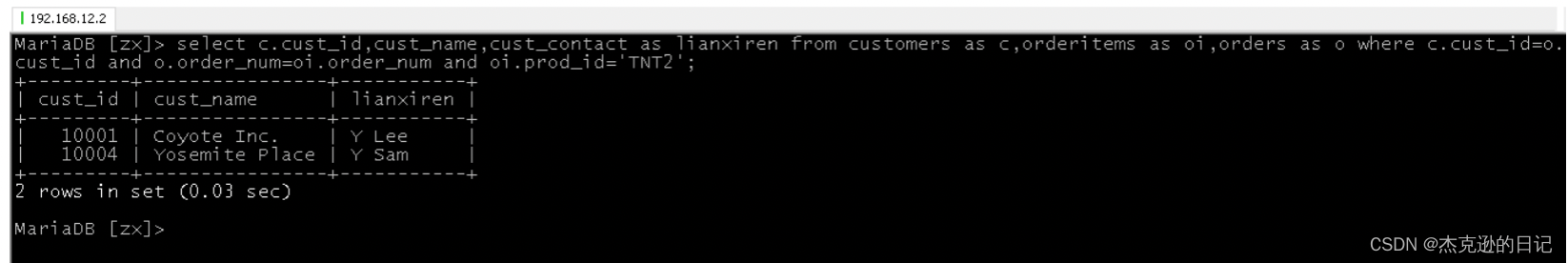
2)查询所有订购了 TNT2 的客户 ID 及客户名称和客户联系人
select cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact from customers where cust_id in (select cust_id from orders where order_num in(select order_num from orderitems where prod_id='TNT2'));
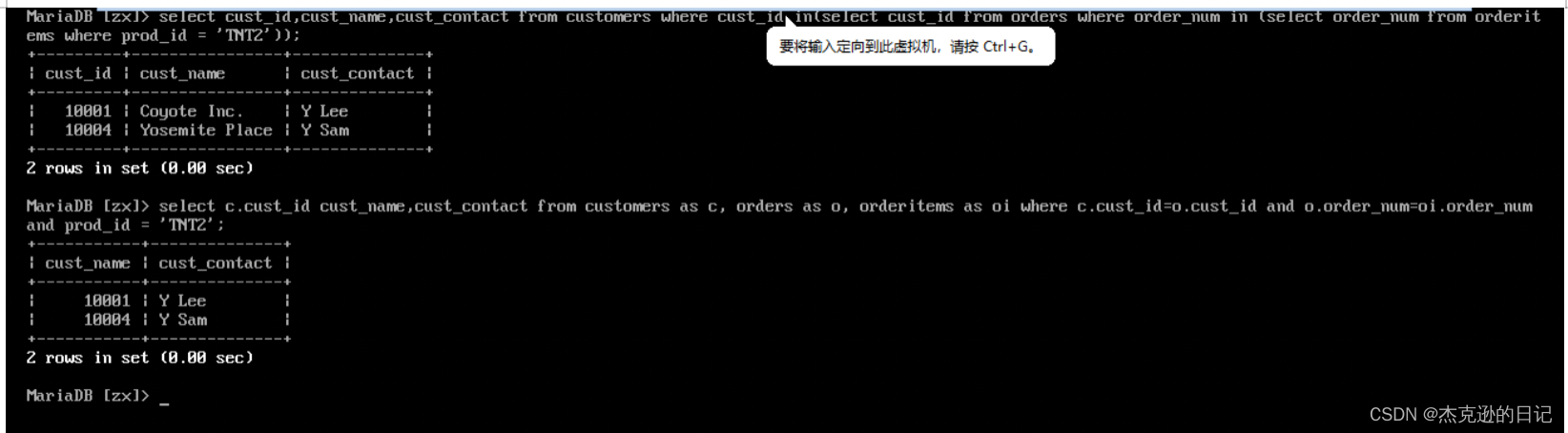
select customers.cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact from customers,orders,orderitems where customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id and orders.order_num=orderitems.order_num and orderitems.prod_id='TNT2';
别名查询:
select c.cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi where c.cust_id=o.cust_id and o.order_num=oi.order_num and oi.prod_id='TNT2';
(查找的是关键字所在行的记录)
(从右往左执行,从内往外执行)
2.交叉连接
在连接查询时不通过 where 子句指定条件,返回的结果集成为笛卡尔乘积
3.对列和表使用别名
select c.cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact from customers as c,orderitems as oi,orders as o where c.cust_id=o.cust_id and o.order_num=oi.order_num and oi.prod_id='TNT2';
4.自连接
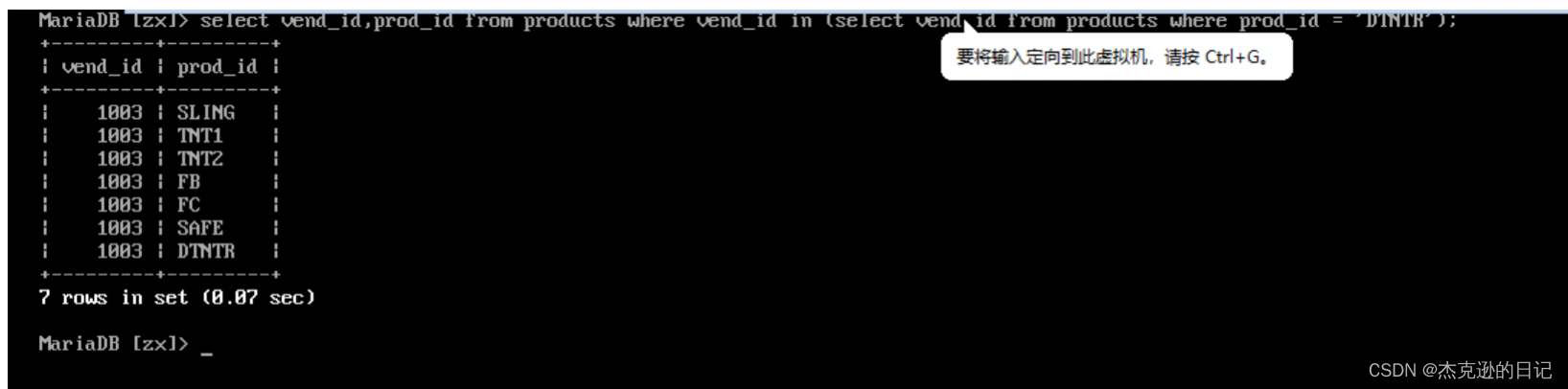
现有一产品被发现存在问题(物品 ID 为 DTNTR),因此要检索该产品供应商生产的所有产品
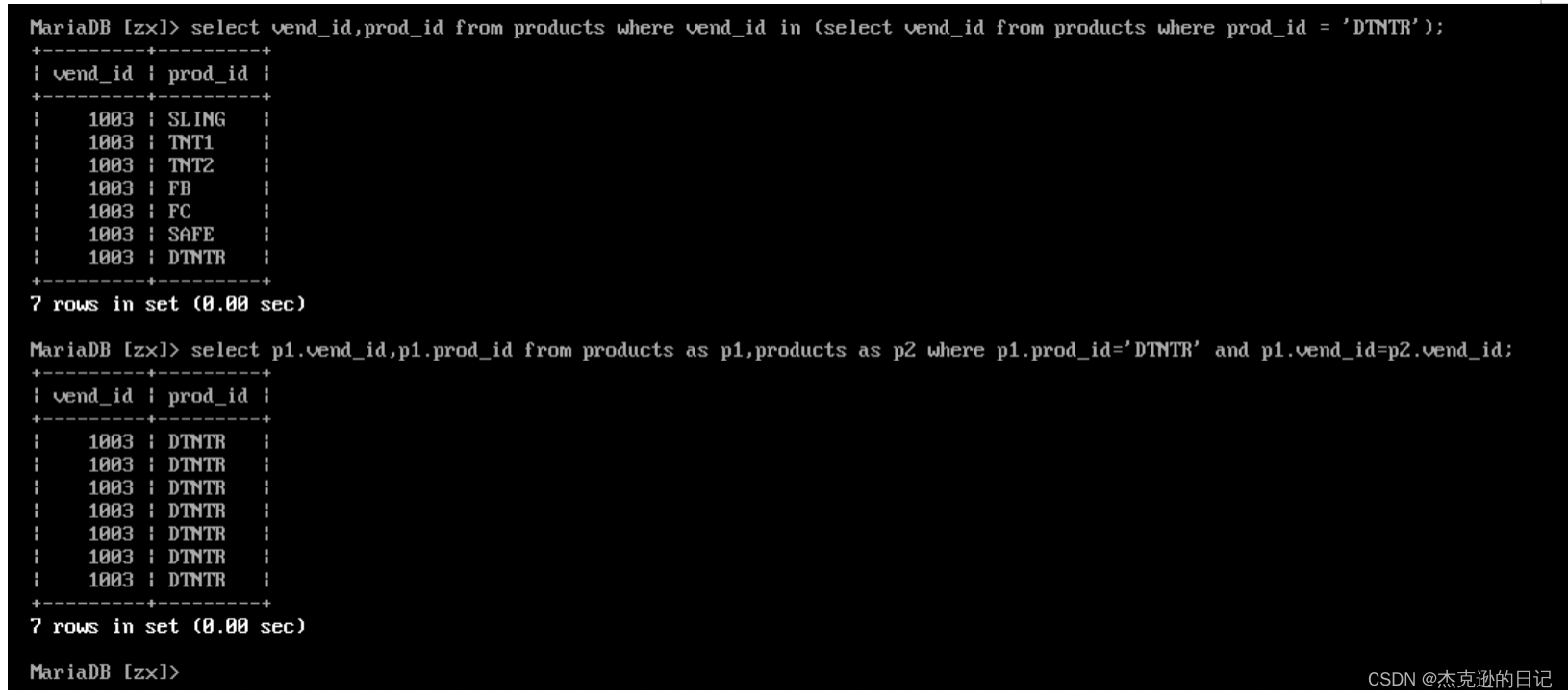
1)子查询
select vend_id,prod_id from products where vend_id in(select vend_id from products where prod_id='DTNTR');
2)自连接
select p1.vend_id,p1.prod_id from products as p1,products as p2 where p1.vend_id=p2.vend_id and p2.prod_id='DTNTR';
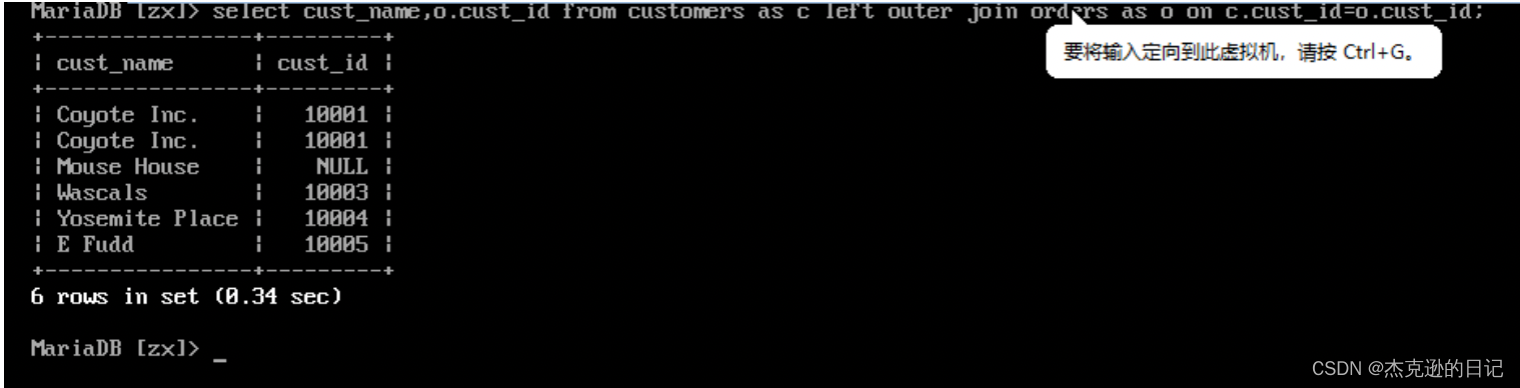
5.外连接
1)左外连接查询所有客户的订单信息(以左边的表为基准)
select c.cust_id,o.order_num from customers as c left outer join orders as o on c.cust_id=o.cust_id;
2)右外连接查询所有订单是哪些客户下的
select c.cust_id,o.order_num from customers as c right outer join orders as o on c.cust_id=o.cust_id;
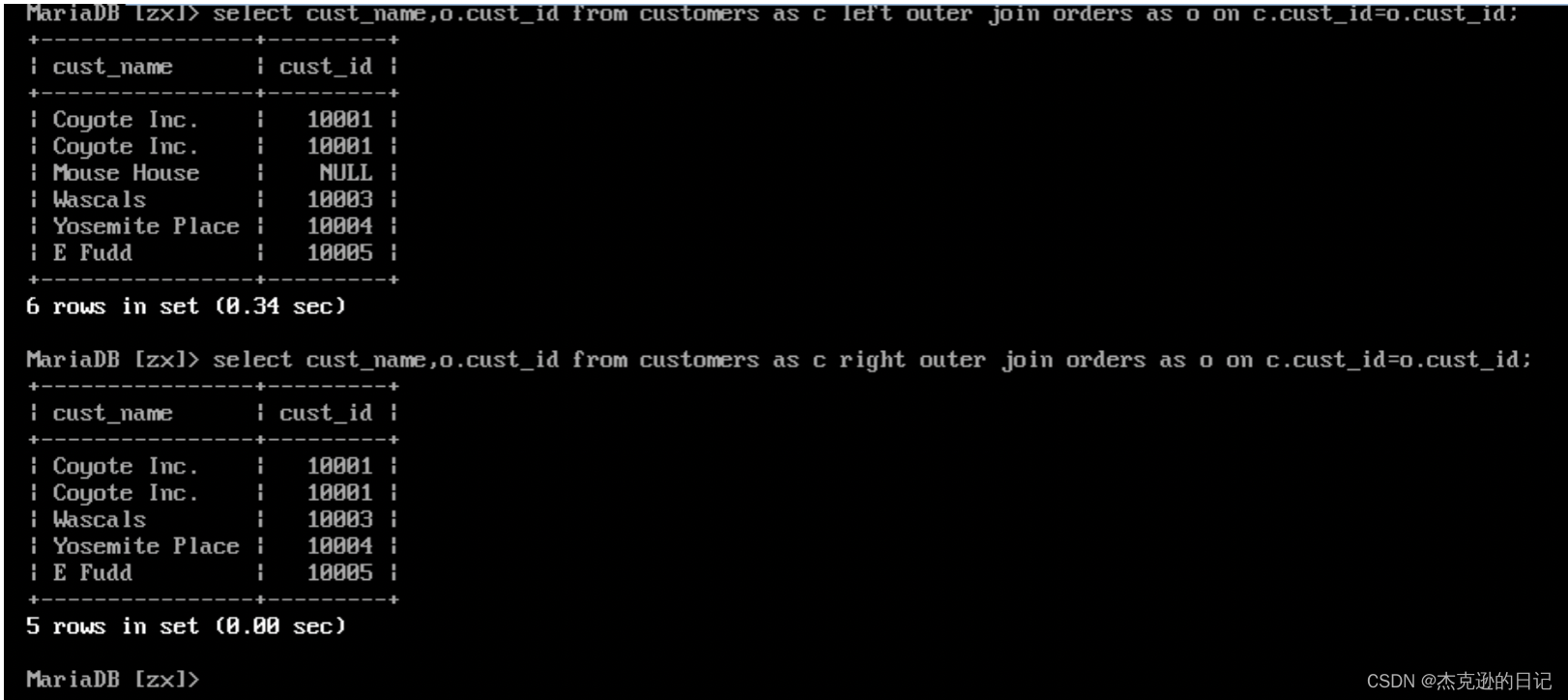
如果是两个表里都有的列 查询的时候要制定是哪个表里的列
四、函数
1.sql 支持的函数类型
1)进行字符串操作的文本函数
2)用来对数值数据算数运算的数值函数
3)用来操作日期和时间以及从这些值中提取特定的组件的日期和时间函数
4)返回和使用 DBMS 相关的信息的系统函数
注:MariaDB 的日期格式:yyyy-mm-dd;也支持两位数年份,将 00-69 视为 2000-2069
2.计算字段
对数据库中存储的数据进行重新的格式化,格式化后的列被称为计算字段
3.拼接字段将值连接起来(通过追加的方式),构成一个单一的更长的值
4.使用 concat()、trim()函数创建拼接字段
要生成供应商报表并且需要列出供应商的位置来作为供应商名称的一部分,即格式为
vend_name(vend_country),并命名为 vend_title
select concat(rtrim(vend_name),'(',rtrim(vend_country),')') as hebing from vendors order by hebing;
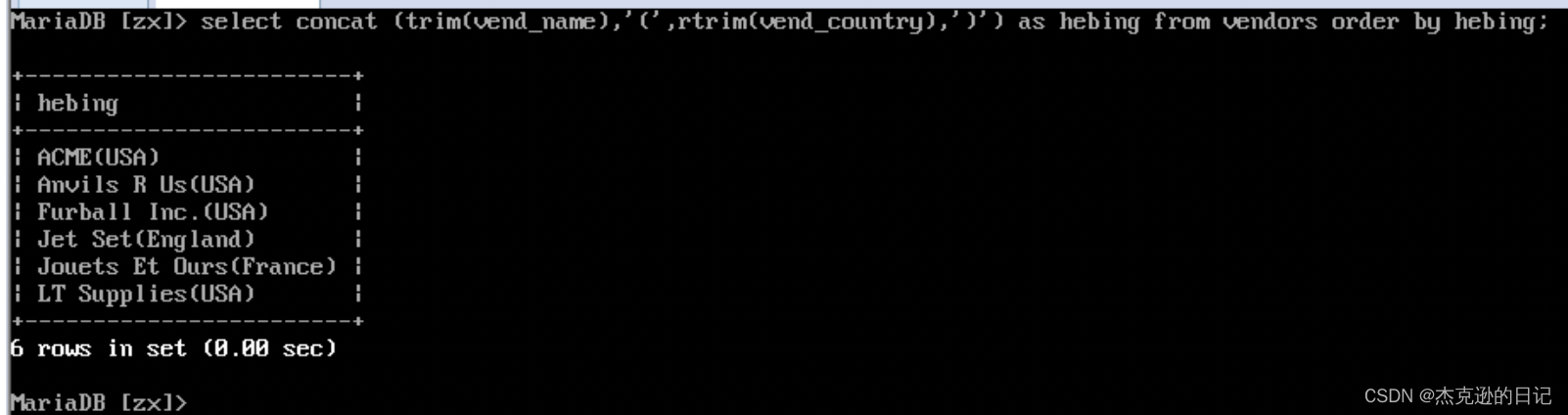
rtrim 去掉右边空格 ltrim 为去掉右侧空格trim 为去掉有左右的空格
5.MariaDB 支持的运算操作符
加:+ 减:- 乘:* 除:/
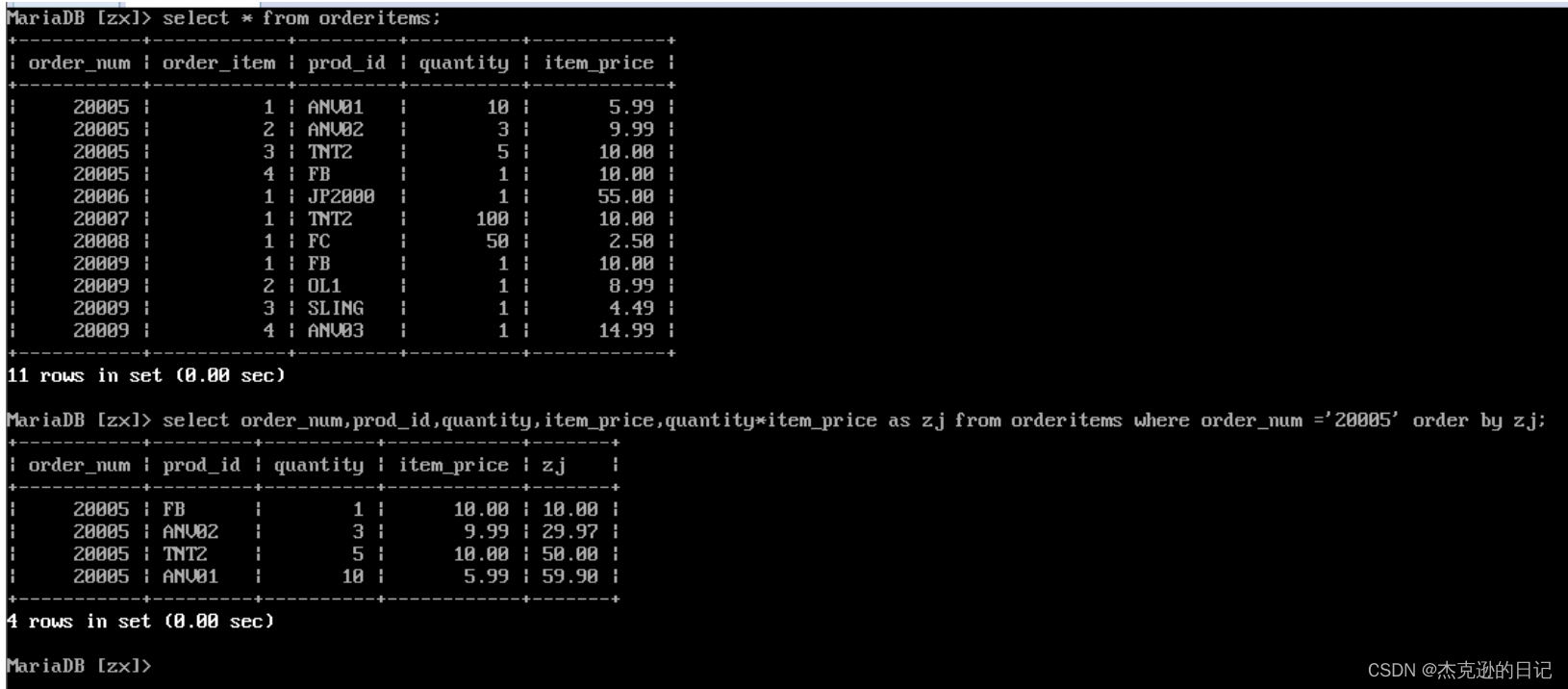
查询 20005 号订单的所有产品 ID、数量、单价、总价
select order_num,prod_id,quantity,item_price,quantity*item_price as zongjia from orderitems where order_num=20005 order by zongjia;
6.调用 upper(),将供应商名称大写(lower小写)
select vend_name,upper(vend_name) as daxie from vendors;
7.调用 soundex(),查询名字发音类似的联系人
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers where soundex(cust_contact) =soundex('Y.Lie');
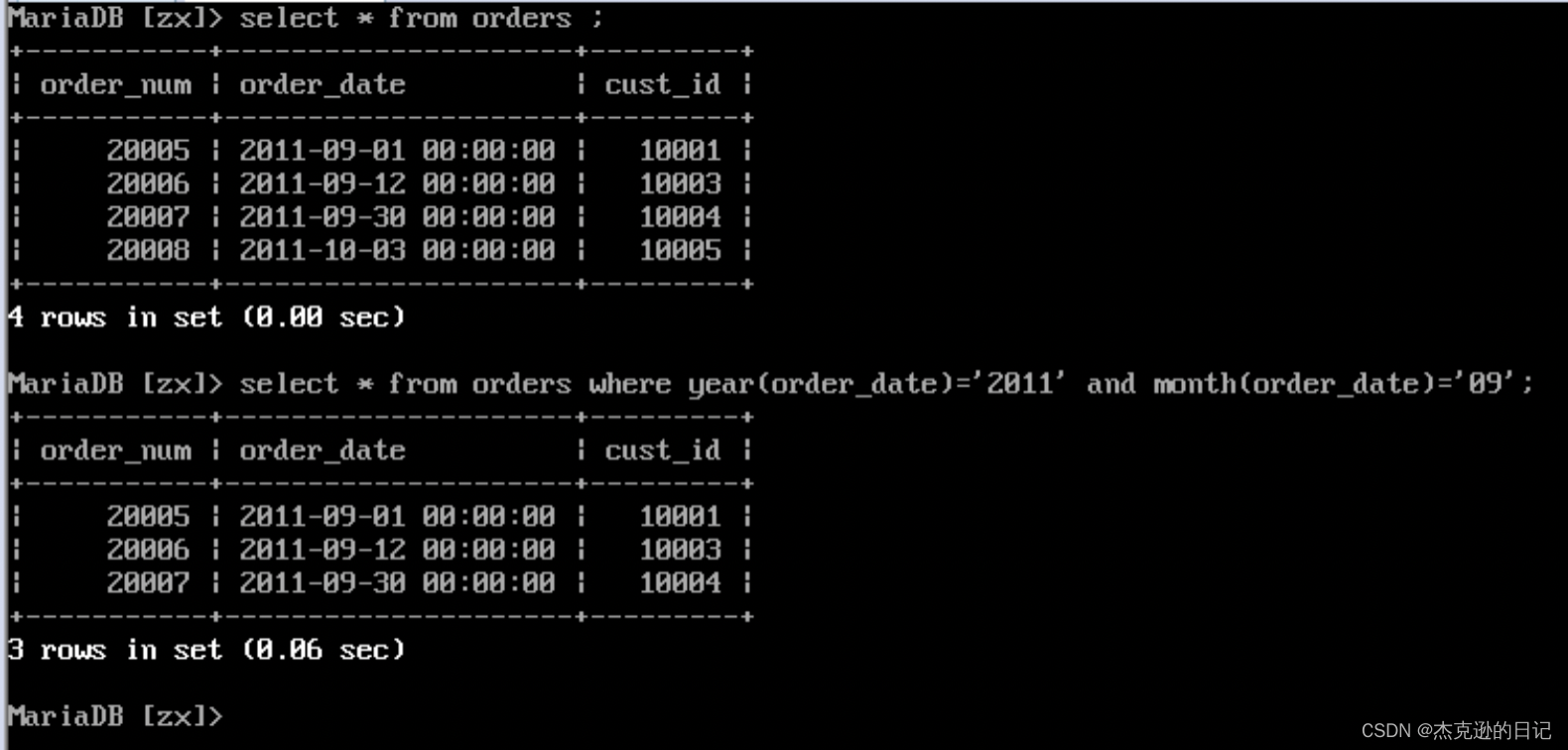
8.调用 date(),查询所有 2011 年 9 月的订单
select * from orders where date(order_date) between '2011-09-01' and '2011-09-30';
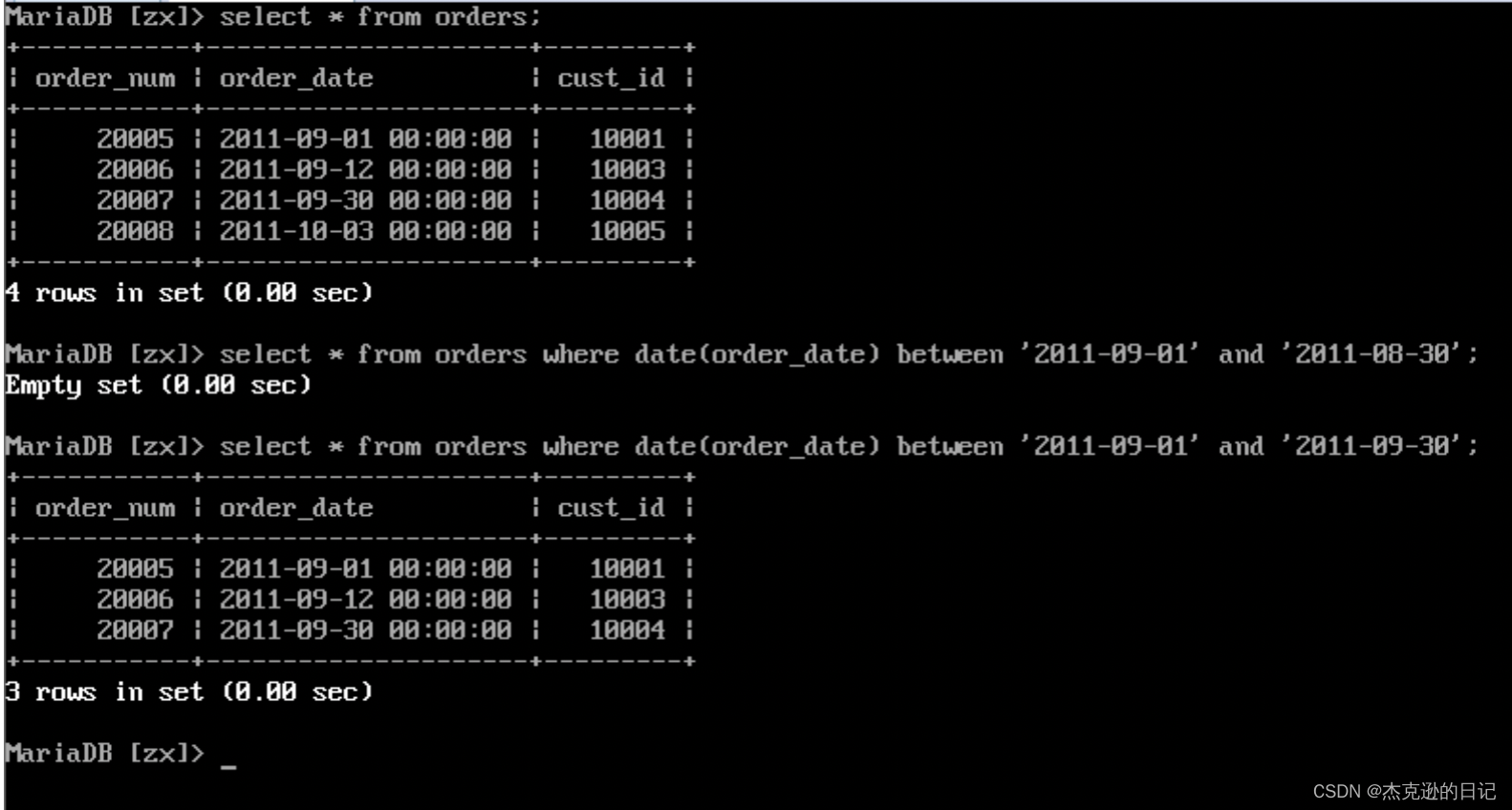
注:可以使用 year()和 month()来实现上述内容
select * from orders where year(order_date)='2011' and month(order_date)='9';
9.聚合函数
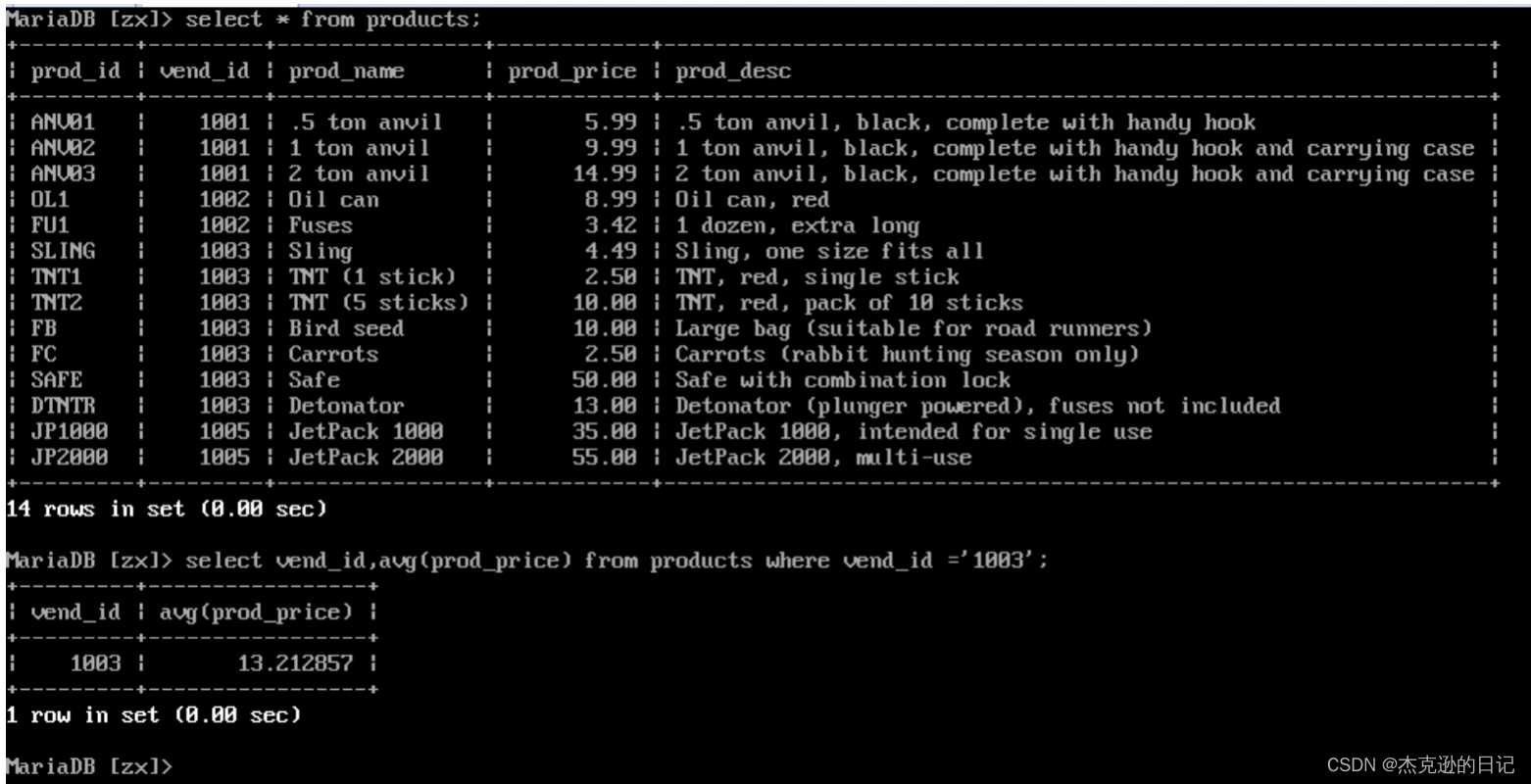
1)查询供应商为 1003 提供的产品的平均值
select vend_id,avg(prod_price) as pingjun from products where vend_id='1003';
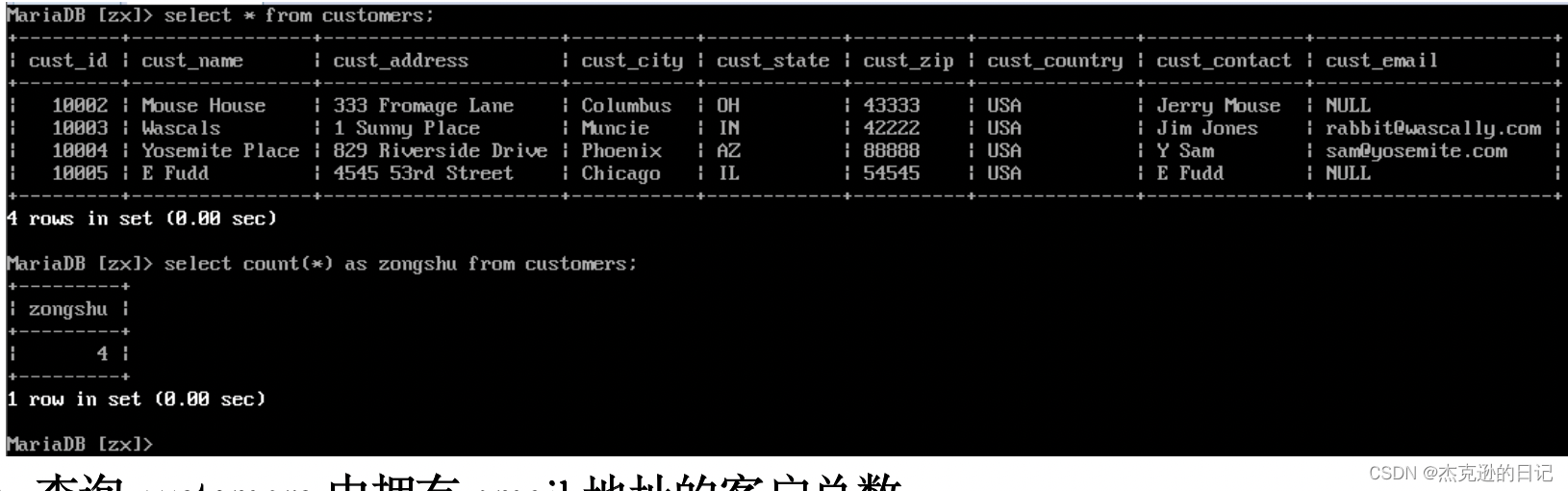
2)查询 customers 中的客户总数
select count(*)(某一列中有几行) as zongshu from customers;
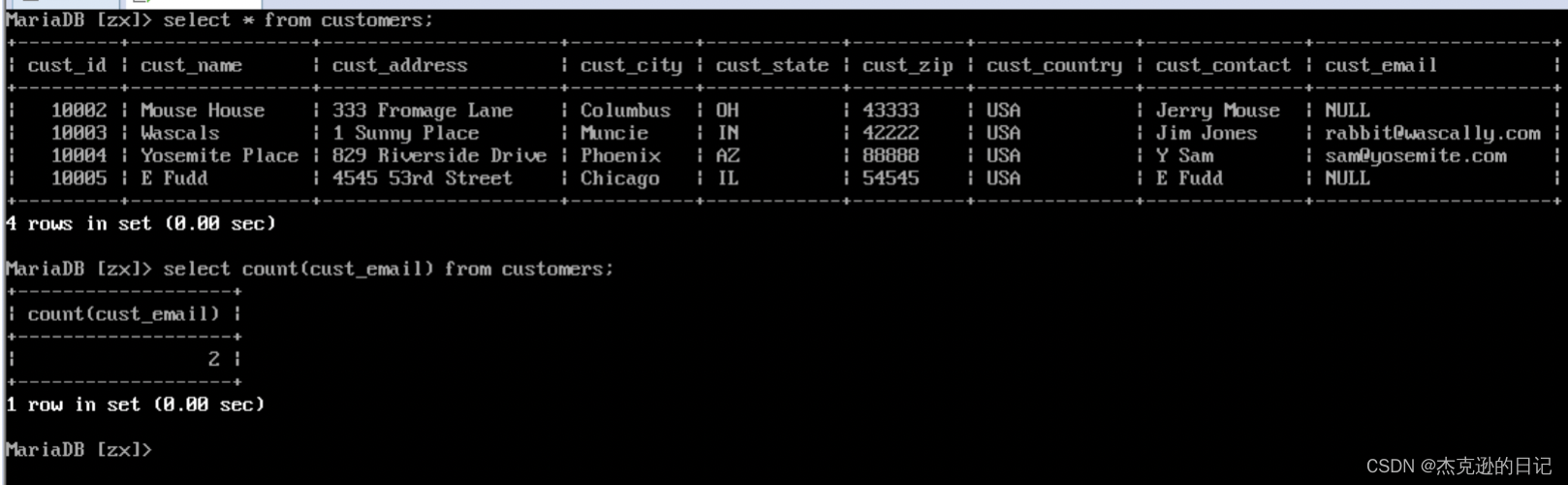
3)查询 customers 中拥有 email 地址的客户总数
select count(cust_email) as zongshu from customers;
4)查询 products 表中产品的最高价和最低价
select max(prod_price) as max_price from products;
select min(prod_price) as min_price from products;
5)计算去掉重复行的平均值
select avg( distinct prod_price) as pingjunzhi from products;
6)组合聚合函数
select count(*) as prod_count,max(prod_price) as price_max,min(prod_price) as price_min,avg(prod_price) as price_avg from products;
10.分组过滤(***)
1)分组:group by 子句
过滤:having 子句(分组之后过滤)
2)查询每个供应商提供的产品数量
select vend_id,count(*/prod_id) as zongshu from products group by vend_id(根据vind_id 分组);
3)查询至少有两个订单的客户
select cust_id,count(*哪一列都可以) as dingdanshu from orders group by cust_id having dingdanshu >= '2';

4)查询拥有产品数大于或等于 2,且产品价格大于或等于 10 的供应商 select vend_id,count(*) as prod_count from products where prod_price >= 10 group by vend_id having prod_count >=2;
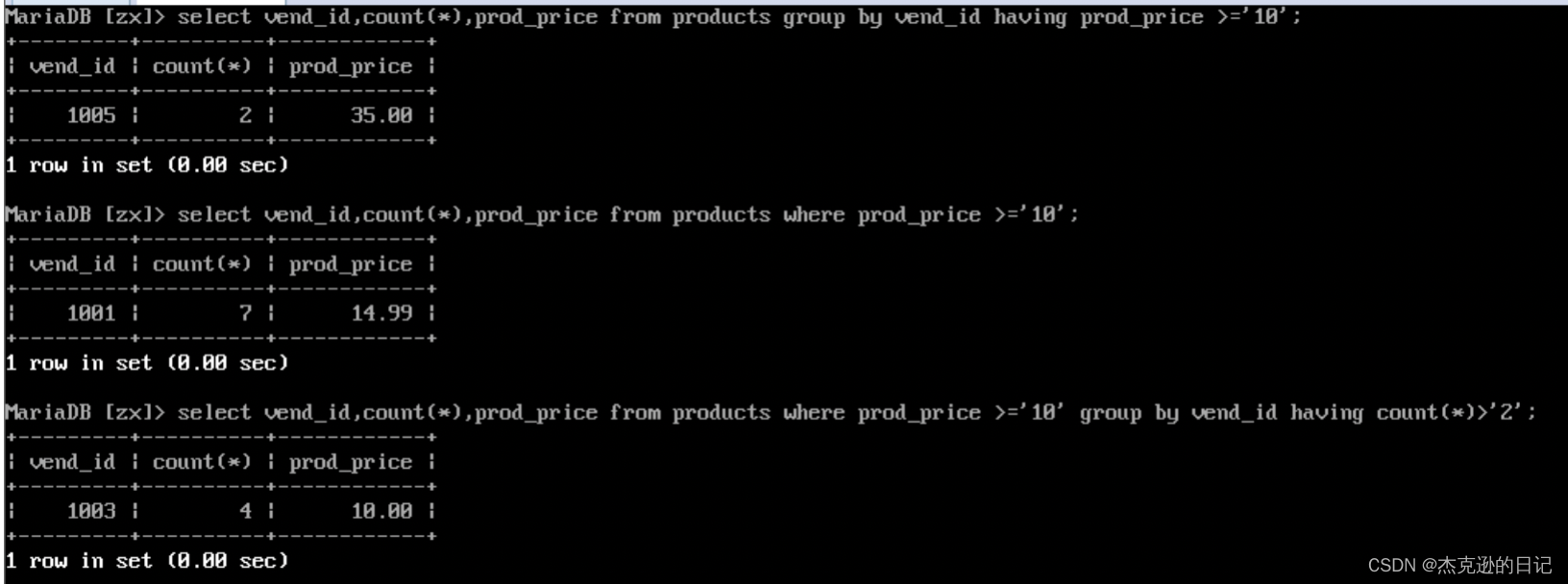
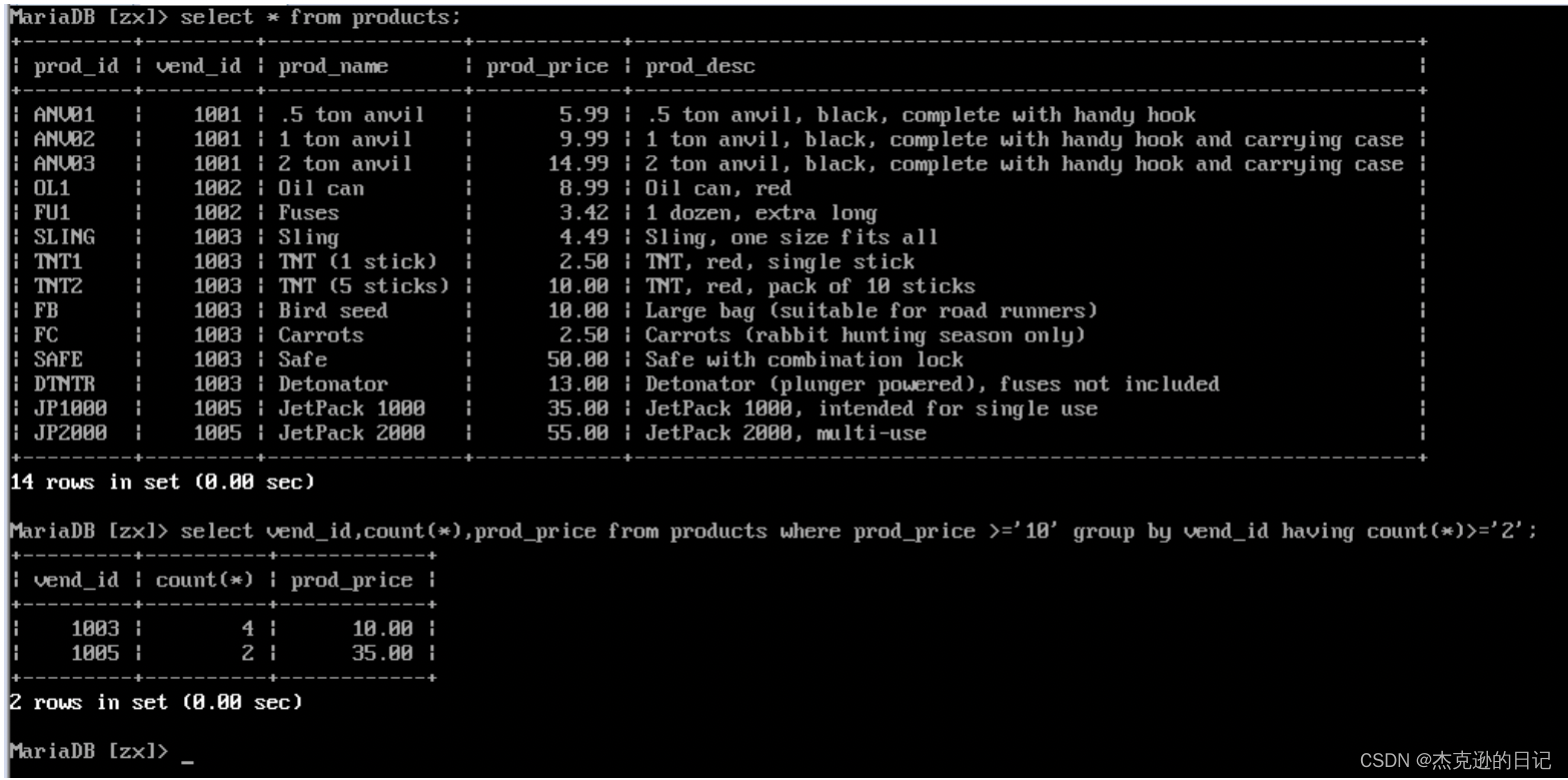
注:where 用于在分组前过滤数据,having 用于在分组后过滤数据
5)查询订单号和所有订单中订单总价大于或者等于 50 的订单
select order_num,sum(quantity*item_price) as order_count from orderitems group by order_num having order_count >= 50;
11.select 语句及其顺序
select ... from ... where ... group by ... having ... order by ... limit;




![[C++][算法基础]模拟堆(堆)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++][算法基础]模拟堆(堆))




)








![[AI in sec]-039 DNS隐蔽信道的检测-特征构建](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[AI in sec]-039 DNS隐蔽信道的检测-特征构建)
