1.删除指定节点数据(非尾节点),要求时间复杂度为O(1)
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
在之前我们将单链表删除指定节点的操作是先遍历找到pos的前一个结点,然后再进行删除,但是现在要求再O(1)时间内完成,这就要想一种新的思路来解决这个问题了。
我们不能去遍历链表,但是我们能找到要删除的节点的下一个节点,这个题的要求是删除那个数据,并不是说要删除这个节点,那么我们就可以将要删除的节点的数据与下一个结点的数据进行调换,这样问题就转换为了删除下一个节点了,怎样处理就很简单了。
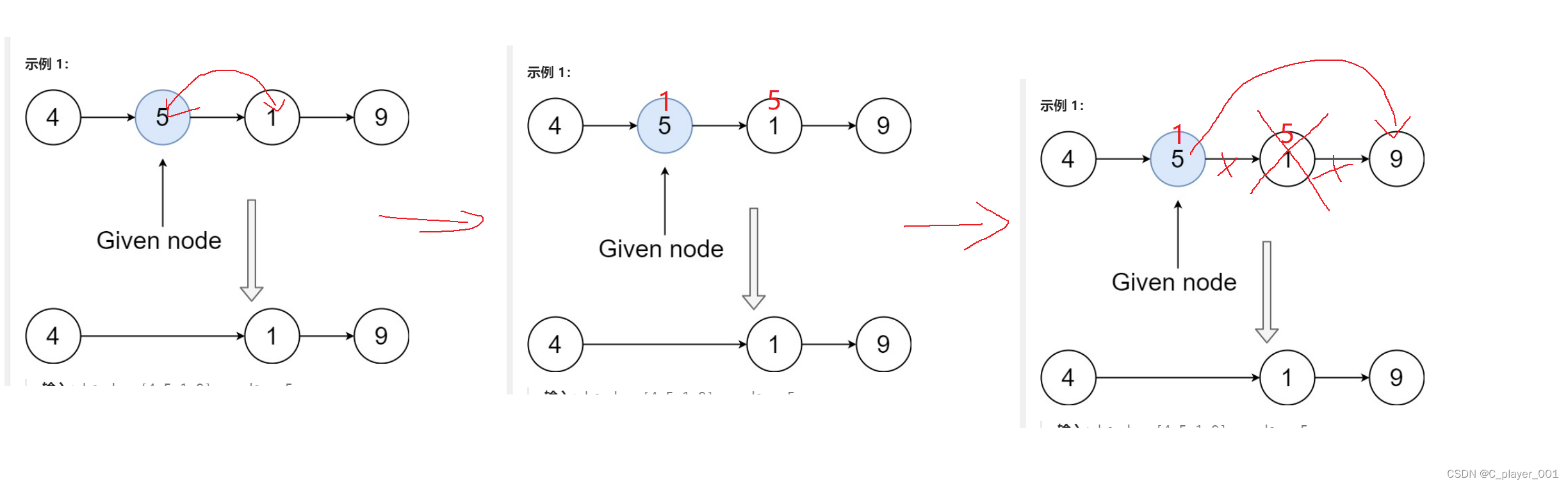
思路有了,而这个题的代码也很简单,那就直接放上答案。
void deleteNode(struct ListNode* node) {struct ListNode* next=node->next;node->val=node->next->val;node->next=node->next->next;free(next);
}2.返回倒数第k个节点
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
看到这个题的第一个思路就是暴力求解,首先遍历一遍链表,统计节点个数 n ,然后第n+1-k个节点就是倒数第 k 个节点 。
int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k){int n=0;struct ListNode* cur=head;while(cur){n++;cur=cur->next;}n=n-k+1;cur=head;while(--n)//第n个节点只要循环n-1次{cur=cur->next;}return cur->val;}
但是这个题还有一这种思路只用遍历一遍链表,我们用快慢指针来解决,首先fast先往后走k步
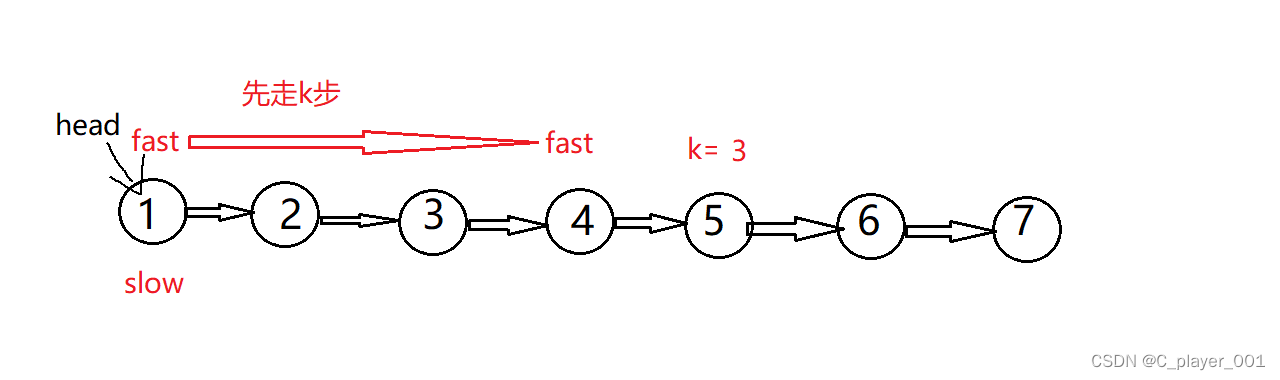
这时slow和fast再同时往后走,当fast为NULL的时候,slow就是倒数第k个节点
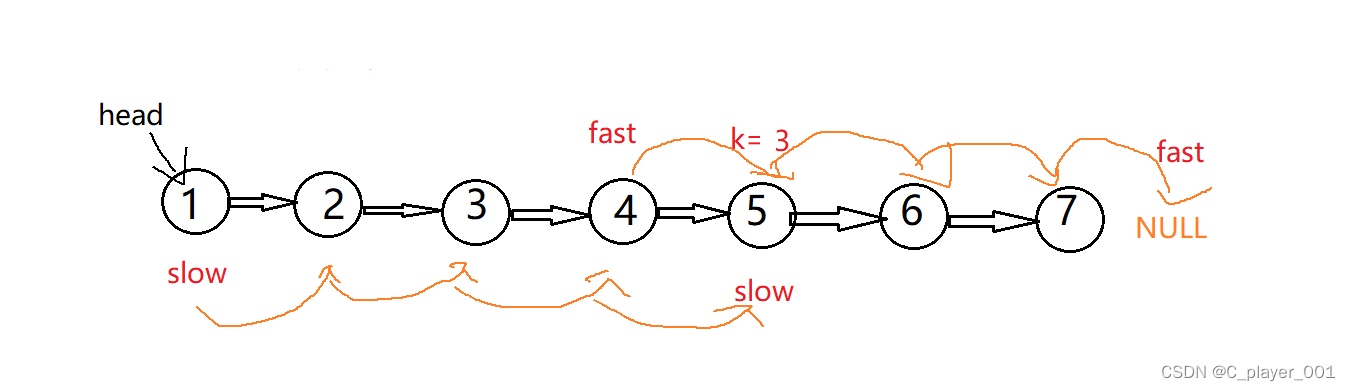
这样实现起来代码也很简单
int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k){struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(k--){fast=fast->next;}while(fast){fast=fast->next;slow=slow->next;}return slow->val;
}
因为题目中明确说明了k是有效的,所以我们就不用判断fast在第一个循环就走到了NULL的情况的。
掌握了上面的题,再来做一个相似的题
删除链表的倒数第N个节点,并返回新的头节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/SLwz0R/
这个题是要删除倒数第N个节点,那我们首先要找到倒数第N+1个节点,修改这个节点的next。
这个题目中给的信息是N<=sz,这就说明有可能删除的是头节点的,所以在fast走完N步之后,要先判断fast是否已经为空,如果fast已经是NULL了,则说明要删除的是头节点。

如果这时候fast不为空,则说明要删的不是头节点,这时候fast再往前走一步,
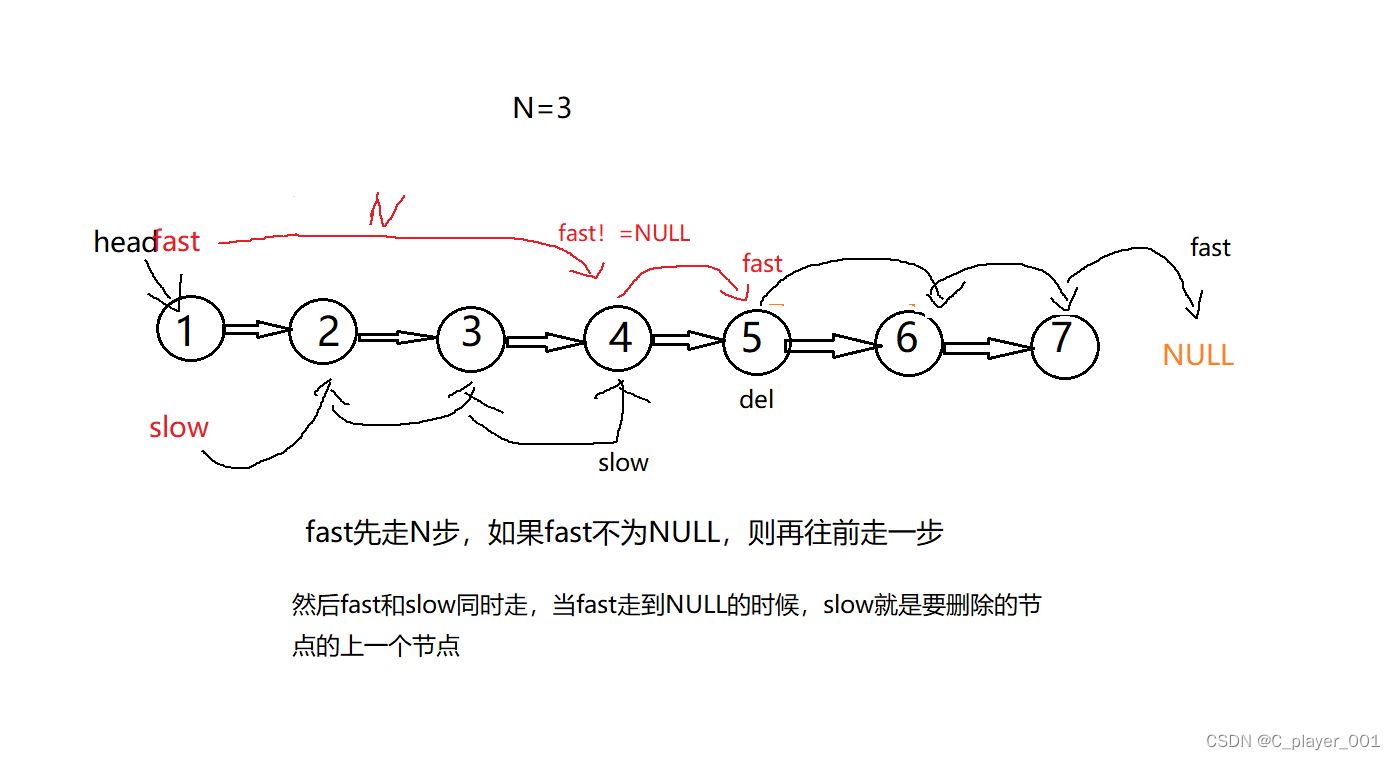
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n){struct ListNode* fast=head;struct ListNode* slow=head;while(n--){fast=fast->next;}if(fast==NULL)//判断要删除的是否是头节点{head=head->next;free(slow);return head;}//不是头节点在快慢指针继续走fast=fast->next;while(fast){fast=fast->next;slow=slow->next;}struct ListNode* del=slow->next;slow->next=del->next;free(del);return head; }3.反转链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
反转链表的思路就是遍历每个节点然后头插,
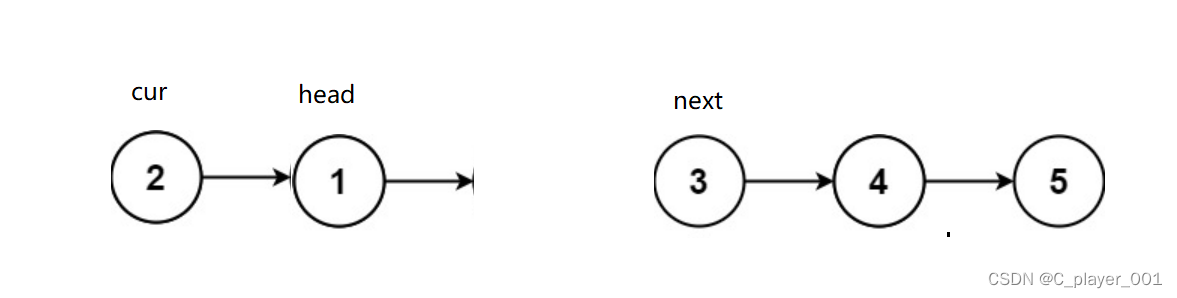
要注意的就是要记录cur的下一个节点的地址。
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* newhead=NULL;struct ListNode* cur=head;struct ListNdoe* next=NULL;while(cur){//记录下一个节点next=cur->next;//头插cur->next=newhead;//换头newhead=cur;//迭代cur=next;}return newhead;
}写完这段代码之后先思考一下空链表的问题,由于我们newhead初始化为NULL,如果是空链表的话,返回时的newhead也是NULLL,所以不会有问题。
4.合并两个升序链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
合并两个升序链表我们很容易想到在之前的数组阶段见过的合并两个升序数组,当时我们使用的是归并排序,在链表中我们同样可以用归并来合并两个链表。首先我们用一个哨兵位的头节点来接收归并后的链表,因为合并升序链表要用到尾插,我们再用一个tail来记录新链表的尾。
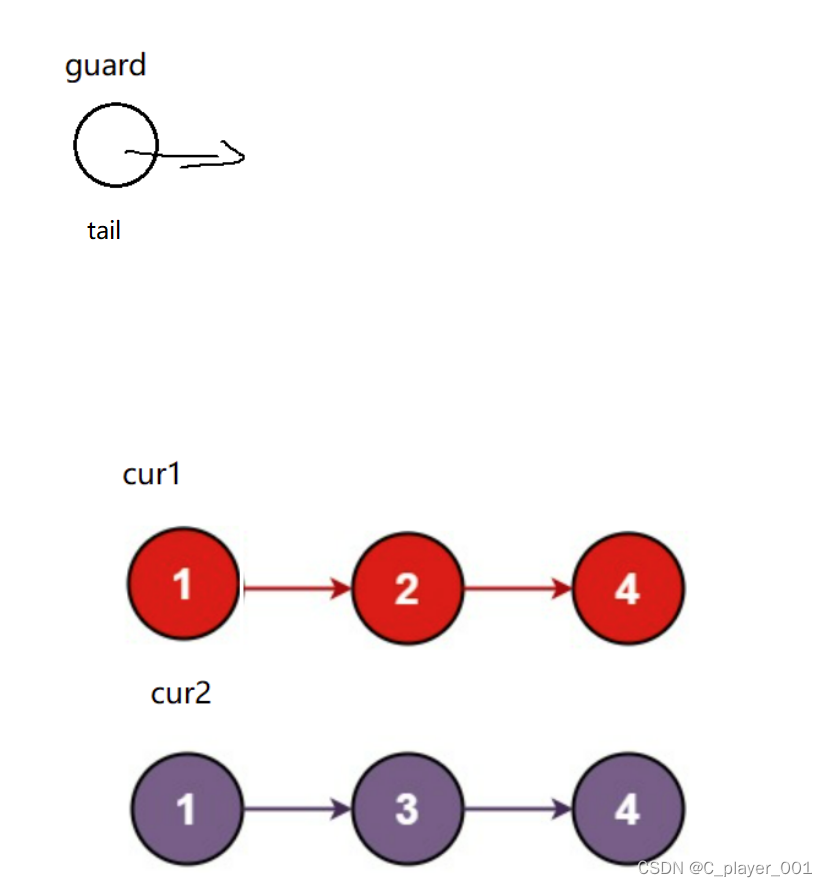
然后我们用两个指针来遍历两个链表,取小的尾插到新链表上去,直到cur1或者cur2指向NULL,之后再将没遍历完的链表插入到新链表后面。
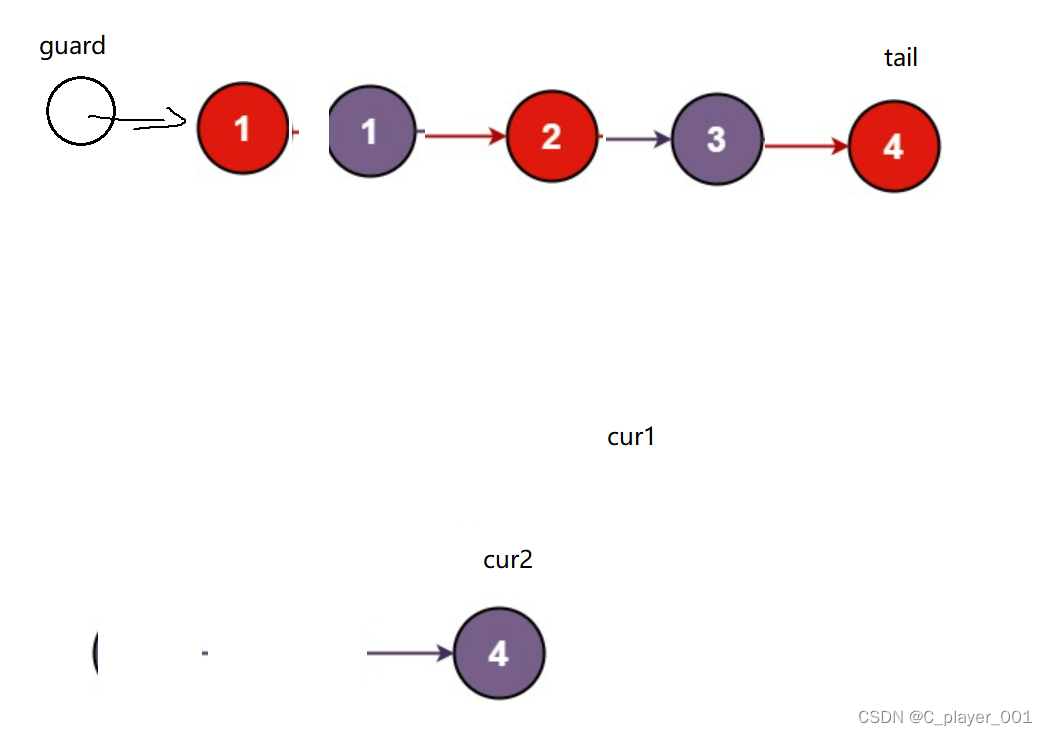
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {struct ListNode* guard=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));guard->next=NULL;struct ListNode* tail=guard;struct ListNode* cur1=list1;struct ListNode* cur2=list2;while(cur1&&cur2){if(cur1->val<=cur2->val){tail->next=cur1;tail=cur1;cur1=cur1->next;}else{tail->next=cur2;tail=cur2;cur2=cur2->next;}}if(cur1)//cur2遍历完了{tail->next=cur1;}else{tail->next=cur2;}struct ListNode* head=guard->next;free(guard);return head;}5.链表相交
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
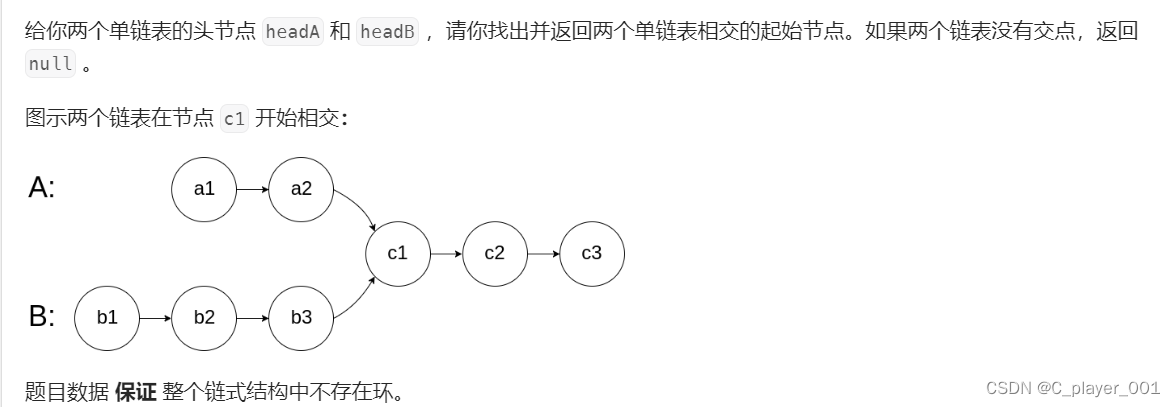
这个题我们首先要判断两个链表是否相交,判断相交不难,因为如果两个链表相交的话,他们的尾节点是相同的,所以我们可以遍历两个链表,判断两个链表的尾节点是否相同。
if(!headA||!headB)//有一个空链表就返回NULLreturn NULL;struct ListNode* cur1=headA;struct ListNode* cur2=headB;while(cur1->next){cur1=cur1->next;}while(cur2->next){cur2=cur2->next;}if(cur1!=cur2)//不相交{return NULL;}else{//找相交节点}我们首先判断一下两个链表是否有空链表,如果有一个是空链表或者都是空链表,则没有相交。
在判断完是否相交之后,如何去找相交的节点呢?
首先我们是可以求出两个链表的节点的个数的,也就是链表的长度,当链表相交之后后半段的长度是相等的,所以两个链表的长度差就差在相交之前的部分。
那么我们是不是可以让长的链表先走 他们的长度差 的步数,如何在两个指针一起走,这样他们相遇的节点就是相交的起始节点。
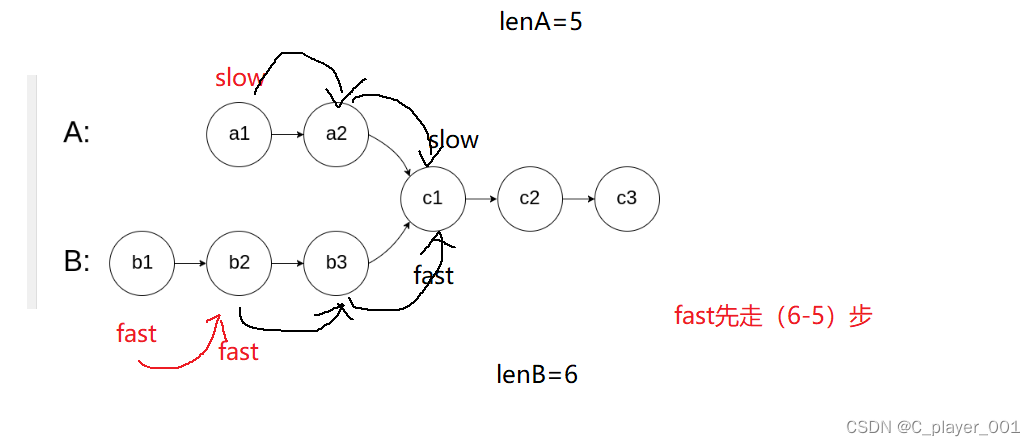
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {if(!headA||!headB)//有一个空链表就返回NULLreturn NULL;struct ListNode* cur1=headA;struct ListNode* cur2=headB;int lenA=0;int lenB=0;while(cur1->next){cur1=cur1->next;lenA++;}while(cur2->next){cur2=cur2->next;lenB++;}if(cur1!=cur2)//不相交{return NULL;}else{//找相交节点struct ListNode* longlist = (lenA>lenB?headA:headB);struct ListNode* shortlist = (lenA>lenB?headB:headA);//求出长度差int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);//长链表先走gap步while(gap--){longlist=longlist->next;}//同时走while(longlist!=shortlist){longlist=longlist->next;shortlist=shortlist->next;}return shortlist;}}











)
)
- 向量整数算术指令)



)
