Leetcode
力扣刷题笔记,记录了几个月来的题目记录,将会继续保持刷题~
2024.01
1768.交替合并字符串
创建字符串不需要声明长度(动态分配内存),push_back()可以加入某个字符,append()一般用于添加字符串,用while循环直到两个字符串都遍历完。
1071.字符串的最大公因子
一般想法就是枚举法,从两个字符串中长度小的开始从后往前比较是否相等,C++中自带辗转相除求最大公因数的函数 gcd()。
class Solution {
public:string gcdOfStrings(string str1, string str2) {//辗转相除法return (str1 + str2 == str2 + str1) ? str1.substr(0, gcd(str1.size(), str2.size())) : "";}
};
2596.检查骑士巡视方案
构建vector类型的indices存放二维棋盘所有格子,array<int,2>表示存放横纵坐标{i, j},语法基础还得熟悉下~
遍历二维棋盘,存放所有格子,故时间和空间复杂度都为O(N2)
class Solution {
public:bool checkValidGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {if (grid[0][0] != 0) return false;int n = grid.size();vector<array<int, 2>> indices(n * n); //array用来接收下标i,jfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {indices[grid[i][j]] = {i ,j};}}for (int i = 1 ; i < indices.size(); i++) {int dx = indices[i][0] - indices[i - 1][0];int dy = indices[i][1] - indices[i - 1][1];if (abs(dx * dy) != 2) return false; //8种情况的规律dx*dy绝对值=2}return true;}
};
198.打家劫舍
动态规划入门题目,四步法
- 定义子问题
- 写出子问题的递推关系
- 确定DP数组的计算顺序
- 空间优化(可选)
从后向前找最大值,自己写的时候像跳台阶、斐波那契数列一样,空间复杂度为O(n),借用空间优化的方法,空间复杂度从O(n)降为O(1) (力扣大佬还是挺多的)
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {int prev = 0;int curr = 0;// 每次循环,计算“偷到当前房子为止的最大金额”for (int i : nums) {// 循环开始时,curr 表示 dp[k-1],prev 表示 dp[k-2]// dp[k] = max{ dp[k-1], dp[k-2] + i }int temp = max(curr, prev + i);prev = curr;curr = temp;// 循环结束时,curr 表示 dp[k],prev 表示 dp[k-1]}return curr;
}213.打家劫舍II
思路:happy:
如果偷 nums[0],那么 nums[1] 和 nums[n−1]不能偷,问题变成从 nums[2]到 nums[n−2] 的非环形版本,调用 198 题的代码解决;
如果不偷 nums[0],那么问题变成从 nums[1]到 nums[n−1]的非环形版本,同样调用 198 题的代码解决。
这两种方案覆盖了所有情况(毕竟 nums[0]只有偷与不偷,没有第三种选择),所以取两种方案的最大值,即为答案。
class Solution {// 198. 打家劫舍int rob1(vector<int> &nums, int start, int end) { // [start,end) 左闭右开int f0 = 0, f1 = 0;for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {int new_f = max(f1, f0 + nums[i]);f0 = f1;f1 = new_f;}return f1;}
public:int rob(vector<int> &nums) {int n = nums.size();return max(nums[0] + rob1(nums, 2, n - 1), rob1(nums, 1, n));}
};337.打家劫舍III
代码随想录之递归三部曲和动规五部曲
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值
这里我们要求一个节点 偷与不偷的两个状态所得到的金钱,那么返回值就是一个长度为2的数组。
别忘了在递归的过程中,系统栈会保存每一层递归的参数。
vector<int> robTree(TreeNode* cur) {
2.确定终止条件
在遍历的过程中,如果遇到空节点的话,很明显,无论偷还是不偷都是0,所以就返回
if (cur == NULL) return vector<int>{0, 0};
这也相当于dp数组的初始化
3.确定遍历顺序
// 下标0:不偷,下标1:偷
vector<int> left = robTree(cur->left); // 左
vector<int> right = robTree(cur->right); // 右
// 中
4.确定单层递归的逻辑
vector<int> left = robTree(cur->left); // 左
vector<int> right = robTree(cur->right); // 右// 偷cur
int val1 = cur->val + left[0] + right[0];
// 不偷cur
int val2 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
return {val2, val1};
5.举例推导dp数组
最后头结点就是 取下标0 和 下标1的最大值就是偷得的最大金钱。
class Solution {
public:int rob(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result = robTree(root);return max(result[0], result[1]);}vector<int> robTree(TreeNode* cur) {if (cur == nullptr) return vector<int>{0, 0};vector<int> left = robTree(cur->left);vector<int> right = robTree(cur->right);int val1 = cur->val + left[0] + right[0];int val2 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);return {val1, val2};}
}
时间复杂度:O(n),每个结点只遍历一次
空间复杂度:O(log n),算上递推系统栈的空间
2591.将钱分给最多的儿童
仔细审题+考虑清楚!!!
给你一个整数 money ,表示你总共有的钱数(单位为美元)和另一个整数 children ,表示你要将钱分配给多少个儿童。
你需要按照如下规则分配:
- 所有的钱都必须被分配。
- 每个儿童至少获得
1美元。 - 没有人获得
4美元。
请你按照上述规则分配金钱,并返回 最多 有多少个儿童获得 恰好 8 美元。如果没有任何分配方案,返回 -1 。
class Solution {
public:int distMoney(int money, int children) {money -= children; // 每人至少 1 美元if (money < 0) return -1;int ans = min(money / 7, children); // 初步分配,让尽量多的人分到 8 美元money -= ans * 7;children -= ans;if (children == 0 && money || // 必须找一个前面分了 8 美元的人,分完剩余的钱children == 1 && money == 3) // 不能有人恰好分到 4 美元--ans;return ans;}
};
146.LRU缓存
class Node {
public:int key, value;Node *prev, *next;Node(int k = 0, int v = 0) : key(k), value(v) {}
};class LRUCache {
private:int capacity;Node *dummy; // 哨兵节点unordered_map<int, Node*> key_to_node;// 删除一个节点(抽出一本书)void remove(Node *x) {x->prev->next = x->next;x->next->prev = x->prev;}// 在链表头添加一个节点(把一本书放在最上面)void push_front(Node *x) {x->prev = dummy;x->next = dummy->next;x->prev->next = x;x->next->prev = x;}Node *get_node(int key) {auto it = key_to_node.find(key);if (it == key_to_node.end()) // 没有这本书return nullptr;auto node = it->second; // 有这本书remove(node); // 把这本书抽出来push_front(node); // 放在最上面return node;}public:LRUCache(int capacity) : capacity(capacity), dummy(new Node()) {dummy->prev = dummy;dummy->next = dummy;}int get(int key) {auto node = get_node(key);return node ? node->value : -1;}void put(int key, int value) {auto node = get_node(key);if (node) { // 有这本书node->value = value; // 更新 valuereturn;}key_to_node[key] = node = new Node(key, value); // 新书push_front(node); // 放在最上面if (key_to_node.size() > capacity) { // 书太多了auto back_node = dummy->prev;key_to_node.erase(back_node->key);remove(back_node); // 去掉最后一本书delete back_node; // 释放内存}}
};/*** Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj->get(key);* obj->put(key,value);*/
151.反转字符串中的单词
双指针解法,快慢指向处理字符串(数组)问题。中等难度,当时做没考虑全😂
class Solution {
public:void reverse(string& s, int start, int end){ //翻转单词,区间写法:左闭右闭 []for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {swap(s[i], s[j]);}}void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {//去除所有空格并在相邻单词之间添加空格, 快慢指针。int slow = 0; //整体思想参考https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.htmlfor (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) { //if (s[i] != ' ') { //遇到非空格就处理,即删除所有空格。if (slow != 0) s[slow++] = ' '; //手动控制空格,给单词之间添加空格。slow != 0说明不是第一个单词,需要在单词前添加空格。while (i < s.size() && s[i] != ' ') { //补上该单词,遇到空格说明单词结束。s[slow++] = s[i++];}}}s.resize(slow); //slow的大小即为去除多余空格后的大小。}string reverseWords(string s) {removeExtraSpaces(s); //去除多余空格,保证单词之间之只有一个空格,且字符串首尾没空格。reverse(s, 0, s.size() - 1);int start = 0; //removeExtraSpaces后保证第一个单词的开始下标一定是0。for (int i = 0; i <= s.size(); ++i) {if (i == s.size() || s[i] == ' ') { //到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。reverse(s, start, i - 1); //翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。start = i + 1; //更新下一个单词的开始下标start}}return s;}
};
334.递增的三元子序列
思路 巧妙!
首先,新建两个变量 small 和 mid ,分别用来保存题目要我们求的长度为 3 的递增子序列的最小值和中间值。
接着,我们遍历数组,每遇到一个数字,我们将它和 small 和 mid 相比,若小于等于 small ,则替换 small;否则,若小于等于 mid,则替换 mid;否则,若大于 mid,则说明我们找到了长度为 3 的递增数组!
上面的求解过程中有个问题:当已经找到了长度为 2 的递增序列,这时又来了一个比 small 还小的数字,为什么可以直接替换 small 呢,这样 small 和 mid 在原数组中并不是按照索引递增的关系呀?
Trick 就在这里了!假如当前的 small 和 mid 为 [3, 5],这时又来了个 1。假如我们不将 small 替换为 1,那么,当下一个数字是 2,后面再接上一个 3 的时候,我们就没有办法发现这个 [1,2,3] 的递增数组了!也就是说,我们替换最小值,是为了后续能够更好地更新中间值!
另外,即使我们更新了 small,这个 small 在 mid 后面,没有严格遵守递增顺序,但它隐含着的真相是,有一个比 small 大比 mid 小的最小值出现在 mid 之前。因此,当后续出现比 mid 大的值的时候,我们一样可以通过当前 small 和 mid 推断的确存在着长度为 3 的递增序列。所以,这样的替换并不会干扰我们后续的计算!
class Solution {
public:bool increasingTriplet(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();if (len < 3) return false;int small = INT_MAX, mid = INT_MAX;for (auto num : nums) {if (num <= small) {small = num;} else if (num <= mid) {mid = num;} else if (num > mid) {return true;}}return false; }
};
443.压缩字符串
思路:利用双指针,一个表示修改后数组长度,另一个表示指向当前数组第一个位置的序号,临界条件是遍历数组时前后元素不一样,后用to_string()将整型数组转换为字符串类型。
class Solution {
public:int compress(vector<char>& chars) {int n = chars.size();//双指针,一个表示修改后数组长度,另一个表示指向的数组第一个位置int len = 0, left = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (i == n - 1 || chars[i] != chars[i + 1]) {chars[len++] = chars[i];int nums = i - left + 1;if (nums > 1) {for (char num : to_string(nums)) {chars[len++] = num;}}left = i + 1;}}return len; }
};
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为字符串长度,我们只需要遍历该字符串一次。
空间复杂度:O(1),我们只需要常数的空间保存若干变量。
392.判断子序列
判断s是否为t的子序列,动态规划求解~
class Solution {
public:bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {int n = s.size(), m = t.size();vector<vector<int> > f(m + 1, vector<int>(26, 0));for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {f[m][i] = m;}for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {if (t[i] == j + 'a')f[i][j] = i;elsef[i][j] = f[i + 1][j];}}int add = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (f[add][s[i] - 'a'] == m) {return false;}add = f[add][s[i] - 'a'] + 1;}return true;}
};1004.最大连续1的个数III
为了获取最大连续1的个数,会将0进行翻转,所以会用滑动窗口,但是大小如何知道,可以结合左右指针动态遍历,判断0的个数是否大于条件中的k,最后再进行取最大值
claas Solution {
public:int longestOnes(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int res = 0, zeros = 0, left = 0;for (int right = 0; right < nums.size(); right++) {if (nums[right] == 0) zeros++;while (zeros > k) { //找到需要定位的leftif (nums[left++] == 0) zeros--;}res = max(res, right - left + 1);}return res;}
}
1207.独一无二的出现次数
仔细读懂题目的意思后,我立刻就想到了map和set,map可以很容易统计不同数字的数量,set可以把相同数量合并,这样直接比较最后set和map的大小就可以,代码如下
class Solution {
public:bool uniqueOccurrences(vector<int>& arr) {map<int,int> mp;for(int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i ++){mp[arr[i]] ++;}set<int> res;for(auto m : mp){res.insert(m.second);}return res.size() == mp.size();}
};- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N为数组的长度,遍历原始数组需要O(N),遍历过程中产生哈希表又需要O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(N)
2390.从字符串中移除星号
模拟栈操作
class Solution {
public:string removeStars(string s) {string res;for (auto c : s) {if (c != '*') res.push_back(c);else res.pop_back();}return res;}
};
- 时间和空间复杂度O(N),若要空间复杂度O(1),即原地操作,则可以使用双指针代替
class Solution {
public:string removeStars(string s) {int n = s.size();int l = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (s[i] != '*') {swap(s[i], s[l++]);} else {l--;}}return s.substr(0, l);}
};
394.字符串解码
class Solution {
public:string decodeString(string s) {string res = "";stack <int> nums;stack <string> strs;int num = 0;int len = s.size();for(int i = 0; i < len; ++ i){if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){num = num * 10 + s[i] - '0';}else if((s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z') ||(s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'Z')){res = res + s[i];}else if(s[i] == '[') //将‘[’前的数字压入nums栈内, 字母字符串压入strs栈内{nums.push(num);num = 0;strs.push(res); res = "";}else //遇到‘]’时,操作与之相配的‘[’之间的字符,使用分配律{int times = nums.top();nums.pop();for(int j = 0; j < times; ++ j)strs.top() += res; //strs.top()是作为一个整体的元素res = strs.top(); //之后若还是字母,就会直接加到res之后,因为它们是同一级的运算;若是左括号,res会被压入strs栈,作为上一层的运算strs.pop();}}return res;}
};
649.Dota2 参议院
队列,R和D一般都会选择消除后面的不同变量,则可以根据序号进行比较(可能涉及多轮比较,故比较完的会放入队列尾部)
class Solution {
public:string predictPartyVictory(string senate) {int n = senate.size();queue<int> radiant, dire; //队列是先进先出(FIFO)for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (senate[i] == 'R') {radiant.push(i);}else {dire.push(i);}}while (!radiant.empty() && !dire.empty()) { //不断比较直到非空if (radiant.front() < dire.front()) {radiant.push(radiant.front() + n);}else {dire.push(dire.front() + n);}radiant.pop();dire.pop();}return !radiant.empty() ? "Radiant" : "Dire";}
};
- 时间复杂度O(N) while和for循环,N为字符串长度,循环并非嵌套,实际上为2*N
- 空间复杂度O(N) 生成辅助队列插入元素,N为原字符串长度
2095.删除链表的中间节点
//官方题解
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteMiddle(ListNode* head) {if (head->next == nullptr) {return nullptr;}ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;ListNode* pre = nullptr;while (fast && fast->next) {fast = fast->next->next;pre = slow;slow = slow->next;}pre->next = pre->next->next;return head;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteMiddle(ListNode* head) {ListNode* tmp = head;int cnt = 0;if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return nullptr;while (tmp != nullptr) {tmp = tmp->next;cnt++;}int mid = cnt / 2;//对于中间位置的结点删除ListNode* p = head;for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) { p = p->next; if (mid < 2) {head->next = head->next->next;break;}//待删除结点的前一个结点if (i == mid - 2) {p->next = p->next->next;} }return head;}
};
对于链表的操作,直接将head进行遍历输出,最后为[],若用tmp,最后输出原链表;所以只有用到指向操作时才会对原来的链表进行变化,上面的p。知识遗忘很正常,需要反复总结哈。
2024.02
872.叶子相似的树
深度优先搜索算法,遍历叶结点,用数组保存数字值,最后比较vector中元素是否相同(只是需要比较所有元素)
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& seq) {if (root == nullptr) return;if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) return seq.push_back(root->val);dfs(root->left, seq);dfs(root->right, seq);}bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {//深度优先搜索,可以获取遍历次数,如何获取末尾值~ (引入数组vector记录元素)vector<int> seq1, seq2;dfs(root1, seq1);dfs(root2, seq2);return seq1 == seq2;}
};
时间复杂度:为O(N1+N2),其中N1与N2为树的结点数量
空间复杂度:为O(L1+L2),L1+L2为叶子数量,递归空间取决于树的高度
同步遍历方法,利用栈来保存辅助元素值,
class Solution {
public:bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {stack<TreeNode*> s1, s2; //栈中保存有左右子树的右节点,为了比较顺序结点异同s1.push(root1), s2.push(root2);while(!s1.empty() && !s2.empty()){TreeNode* node1 = s1.top(); s1.pop();TreeNode* node2 = s2.top(); s2.pop();while (node1->left || node1->right){if (node1->left){if (node1->right) s1.push(node1->right);node1 = node1->left;}elsenode1 = node1->right;}//同样的操作对树2进行一遍while (node2->left || node2->right){if (node2->left){if (node2->right) s2.push(node2->right);node2 = node2->left;}elsenode2 = node2->right;}//此时node1与node2分别指向树1与树2的叶子节点if (node1->val != node2->val) return false;}//到此两种情况://1. 两个栈都空了,并且叶子节点都相等,因此返回true//2. 只有一颗树空了,证明另一棵树一定还有别的叶子节点, 返回false;return s1.empty() && s2.empty();}
};1372.二叉树中的最长交错路径
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:int maxAns;/* 0 => left, 1 => right */void dfs(TreeNode* o, bool dir, int len) {maxAns = max(maxAns, len);if (!dir) {if (o->left) dfs(o->left, 1, len + 1);if (o->right) dfs(o->right, 0, 1);} else {if (o->right) dfs(o->right, 0, len + 1);if (o->left) dfs(o->left, 1, 1);}} int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {if (!root) return 0;maxAns = 0;dfs(root, 0, 0);dfs(root, 1, 0);return maxAns;}
};
1161.最大层内元素和
利用广度优先搜索方法,结合队列(递归也可,一般方法的通用模板可以记下)
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:int maxLevelSum(TreeNode* root) {queue <TreeNode* > que;que.push(root);int max_val = INT_MIN;int a = 1; //记录变化层数int res = 1; //记录返回层数while (!que.empty()) {int t = 0;int num = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {TreeNode* p = que.front();t += p->val;if (p->left) que.push(p->left);if (p->right) que.push(p->right);que.pop();}if (max_val < t) {res = a;max_val = t;}a++;}return res;}
};
1926.迷宫中离入口最近的出口
广度优先搜索算法
class Solution {
public:int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) {// 思路:从入口开始按轮BFS,遇到邻居为“.”则入队,并记录轮数// 结束条件时,邻居为边缘格子,返回轮数// 若BFS结束也没有找到出口,返回-1const int m = maze.size();const int n = maze[0].size();const int dr[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};const int dc[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};queue<pair<int, int>> que;// 初始化int erow = entrance[0], ecol = entrance[1];que.emplace(erow, ecol);maze[erow][ecol] = '-'; // 表示已经搜索过// 按轮BFSint epoch = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int counter = que.size();epoch++;// 一轮for (int k = 0; k < counter; k++) {auto [r, c] = que.front();que.pop();// 邻居找'.'入队for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nr = r + dr[i], nc = c + dc[i];if (nr >= 0 && nr < m && nc >= 0 && nc < n && maze[nr][nc] == '.') {// 是边沿直接返回if (nr == 0 || nr == m - 1 || nc == 0 || nc == n - 1) return epoch;// 不是边沿,入队maze[nr][nc] = '-'; // 表示已经搜过que.emplace(nr, nc); }}}}return -1;}
};
841.钥匙和房间
class Solution {
public:bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {vector<bool> visited(rooms.size(), false);dfs(rooms, 0, visited);//检查是否都访问到了for (int i : visited) {if (i == false) return false;}return true;}void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& rooms, int key, vector<bool>& visited) {if (visited[key]) {return;}visited[key] = true;vector<int> keys = rooms[key];for (int key : keys) {//深度优先搜索遍历dfs(rooms, key, visited);}}
};图的深度优先搜索,
- 时间复杂度:O(n+m),其中n是房间的数量,m是所有房间中的钥匙数量的总数
- 空间复杂度:O(n),n是房间的数量,主要为栈空间的开销
994.腐烂的橘子
class Solution {
public:int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {int min = 0, fresh = 0;queue<pair<int, int>> q; //队列元素对for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) {for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) {if (grid[i][j] == 1) fresh++;else if (grid[i][j] == 2) q.push({i, j});}}vector<pair<int, int>> dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};while (!q.empty()) {int n = q.size();bool rotten = false;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {auto x = q.front();q.pop();for (auto cur : dirs) {int i = x.first + cur.first;int j = x.second + cur.second;if (i >= 0 && i < grid.size() && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].size() && grid[i][j] == 1) {grid[i][j] = 2;q.push({i, j});fresh--;rotten = true;}}}if (rotten) min++;}return fresh ? -1 : min;}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(nm),即进行一次广度优先搜索的时间,其中n=grid.size(),m=grid[0].size()。
- 空间复杂度:O(nm),需要额外记录数据,且队列存放的状态最多nm个。
17.电话号码的字母组合
class Solution {
private:const string letterMap[10] = {"", // 0"", // 1"abc", // 2"def", // 3"ghi", // 4"jkl", // 5"mno", // 6"pqrs", // 7"tuv", // 8"wxyz", // 9};
public:vector<string> result;string s;void backtracking(const string& digits, int index) {if (index == digits.size()) {result.push_back(s);return;}int digit = digits[index] - '0'; // 将index指向的数字转为intstring letters = letterMap[digit]; // 取数字对应的字符集for (int i = 0; i < letters.size(); i++) {s.push_back(letters[i]); // 处理backtracking(digits, index + 1); // 递归,注意index+1,一下层要处理下一个数字了s.pop_back(); // 回溯}}vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {s.clear();result.clear();if (digits.size() == 0) {return result;}backtracking(digits, 0);return result;}
};
Tips:回溯三部曲,1、确定回溯函数参数;2、确定终止条件;3、确定单层遍历逻辑
(1中index表示遍历第一个数字,字符串s用来保存返回字符串(一层层),2中index=digits.size(),3中确定了处理递归回溯操作,作为遍历逻辑)
2023.03
3.无重复字符的最长字串
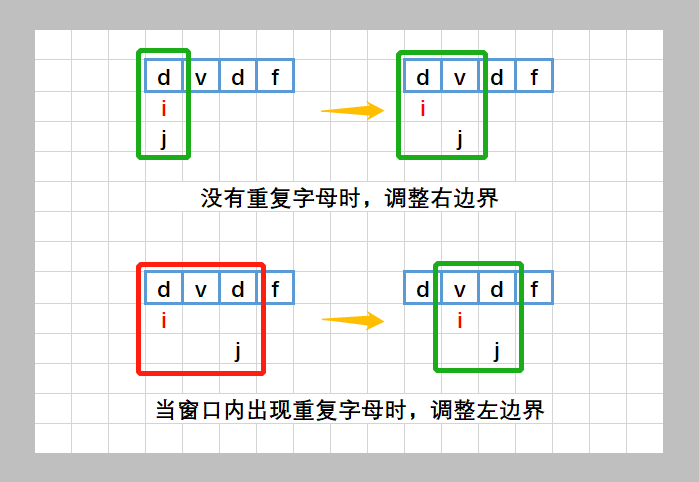
滑动窗口解法:时间和空间复杂度都是O(N)
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {vector<int> m(128, 0);int ans = 0;int i = 0;for (int j = 0; j < s.size(); j++) {i = max(i, m[s[j]]); //重复字母的下一个位置m[s[j]] = j + 1;ans = max(ans, j - i + 1); //无重复的最长字串}return ans;}
正接下题:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {unordered_map<char, int> window;int left = 0, right = 0;int res = 0; // 记录结果while (right < s.size()) {char c = s[right];right++;// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新window[c]++;// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩,是否有重复字母while (window[c] > 1) {char d = s[left];left++;// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新window[d]--;}// 在这里更新答案res = max(res, right - left);}return res;
}
438.找到字符串中所有字母异位词

好诗好诗(手动狗头)
大致框架如下:
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {// 增大窗口window.add(s[right]);right++;while (window needs shrink) {// 缩小窗口window.remove(s[left]);left++;}
} //时间复杂度O(N)
利用以上框架,整体代码如下
vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string t) {unordered_map<char, int> need, window;for (char c : t) need[c]++;int left = 0, right = 0;int valid = 0;vector<int> res; // 记录结果while (right < s.size()) {char c = s[right];right++;// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新if (need.count(c)) {window[c]++;if (window[c] == need[c]) valid++;}// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩while (right - left >= t.size()) {// 当窗口符合条件时,把起始索引加入 resif (valid == need.size())res.push_back(left);char d = s[left];left++;// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新if (need.count(d)) {if (window[d] == need[d])valid--;window[d]--;}}}return res;
}
果然还是有方法的,暴力硬解不是好法子,而且还不一定解决!
239.滑动窗口最大值
hard难度,题意好理解,有效实现不容易
class Solution {
public:vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {MyQueue que;vector<int> res;int n = nums.size();for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {que.push(nums[i]);}for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {res.push_back(que.front());que.pop(nums[i - k]); //移除滑动窗口第一个元素que.push(nums[i]); //加入滑动窗口后一个元素}res.push_back(que.front()); //最后一次放入return res;}private:class MyQueue { //单调队列(从大到小)public:deque<int> que; //使用deque来实现单调队列//每次弹出的时候判断要弹出的数值是否等于队列出口元素的数值,如果相等则弹出//同时pop之前判断队列当前是否为空void pop(int value) {if (!que.empty() && value == que.front()) {que.pop_front();}}//如果push的数值大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列后端的数值弹出,直到push的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值//这样就保持了队列里的数值是单调从大到小的void push(int value) {while (!que.empty() && value > que.back()) {que.pop_back();}que.push_back(value);}//保持当前队列里的最大值 直接返回队列前端也就是front就可以了int front() {return que.front();}};
};
76.最小覆盖子串
class Solution {
public:string minWindow(string s, string t) {unordered_map<char, int> hs, ht;for (auto c : t) ht[c]++;int cnt = 0; //用于记录匹配字符数string res; //最后返回的字符串for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {hs[s[i]]++;if (hs[s[i]] <= ht[s[i]]) {cnt++;}//滑动窗口处理,双指针(j为前端指针,i为后端指针)while (hs[s[j]] > ht[s[j]]) {hs[s[j]]--;j++;}//在满足条件的寻找最短字符串if (cnt == t.size()) {if (res.empty() || i - j + 1 < res.size()) res = s.substr(j, i - j + 1);}}return res;}
};
双指针遍历,严格递增最多移动n次,总的时间复杂度为O(N)。
56.合并区间
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {vector<vector<int>> res;if (intervals.size() == 0) return res; // 区间集合为空直接返回// 排序的参数使用了lambda表达式sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const vector<int> a, const vector<int> b){return a[0] < b[0];});// 第一个区间就可以放进结果集里,后面如果重叠,在result上直接合并res.push_back(intervals[0]);for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); i++) {if (res.back()[1] >= intervals[i][0]) {// 合并区间,只更新右边界就好,因为result.back()的左边界一定是最小值,因为我们按照左边界排序的res.back()[1] = max(res.back()[1], intervals[i][1]);}else res.push_back(intervals[i]);}return res;}
};- 时间复杂度:O(NlogN)
- 空间复杂度:O(logN),排序需要用到的空间开销
238.除自身以外数组的乘积
class Solution {
public:vector<int> productExceptSelf(vector<int>& nums) {int length = nums.size();vector<int> answer(length);// answer[i] 表示索引 i 左侧所有元素的乘积// 因为索引为 '0' 的元素左侧没有元素, 所以 answer[0] = 1answer[0] = 1;for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {answer[i] = nums[i - 1] * answer[i - 1];}// R 为右侧所有元素的乘积// 刚开始右边没有元素,所以 R = 1int R = 1;for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 对于索引 i,左边的乘积为 answer[i],右边的乘积为 Ranswer[i] = answer[i] * R;// R 需要包含右边所有的乘积,所以计算下一个结果时需要将当前值乘到 R 上R *= nums[i];}return answer;}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N指的是数组nums的大小
- 空间复杂度:O(1),输出数组不算进复杂度中,因此我们只需要常数的空间存放变量
41.缺失的第一个正数
难度为困难,不容易想到
置换法,nums[0] = 0+1, nums[1] = 1+1,~
class Solution {
public:int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {swap(nums[nums[i] - 1], nums[i]);}}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (nums[i] != i + 1) {return i + 1; //寻找是否有空缺位置}}return n + 1;}
};时间:O(N),N为数组的长度;空间:O(1)
160.相交链表
方法一:哈希集合
先遍历链表headA,并将链表headA中的结点加入到哈希集合中,然后遍历链表headB,对于遍历到的每个结点,判断该结点是否在哈希集合中
class Solution
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {unorder_set<ListNode *> visited;ListNode *temp = headA;while (temp != nullptr) {visited.insert(temp);temp = temp->next;}temp = headB;while (temp != nullptr) {if (visited.count(temp)) {return temp;}temp = temp->next;}return nullptr;}
};
时间复杂度:O(m+n),其中m和n分别是链表headA和headB的长度,需要遍历两个链表各一次
空间复杂度:O(m),其中m是链表headA的长度,需要使用哈希集合存储链表headA中的全部节点
方法二:双指针
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {if (headA == nullptr && headB == nullptr) return nullptr;ListNode *A = headA, *B = headB;while (A != B) { //a+c+b=a+b+cA = A != nullptr? A->next: headB;B = B != nullptr? B->next: headA;}return A; }
};
时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度为O(1).
141.环形链表
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {//判断是否存在环,双指针ListNode *fast = head;ListNode *slow = head;while (fast != nullptr) {fast = fast->next;if (fast != nullptr) fast = fast->next;if (fast == slow) return true;//存在pos=-1的不合规情况slow = slow->next;}return false;}
};
双指针法
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N是链表中的结点数,当链表中不存在环时,快指针先于慢指针到达链表尾部,链表中的每个结点至多被访问两次;当链表中存在环时,每一轮移动后,快慢指针距离将减小一,而初始距离为环的长度,因此至多移动N轮。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),我们只使用了两个指针的额外空间。
2.两数相加
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(); // 哨兵结点ListNode *cur = dummy;int carry = 0; // 进位while (l1 || l2 || carry) { // 有一个不是空结点,或者还有进位,就继续迭代carry += (l1 ? l1->val : 0) + (l2 ? l2->val : 0); // 结点值和进位相加cur = cur->next = new ListNode(carry % 10); // 每个结点保存一个数位carry /= 10; // 新的进位if (l1) l1 = l1->next; // 下一个结点if (l2) l2 = l2->next; // 下一个结点}return dummy->next; // 哨兵结点地下一个结点就是头结点}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),n为l1长度和l2长度地最大值
- 空间复杂度:O(1),返回值不计入
还有一个递归法,灵茶山艾府666!
class Solution {
public:// l1 和 l2 为当前遍历的节点,carry 为进位ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2, int carry = 0) {if (l1 == nullptr && l2 == nullptr) // 递归边界:l1 和 l2 都是空节点return carry ? new ListNode(carry) : nullptr; // 如果进位了,就额外创建一个节点if (l1 == nullptr) // 如果 l1 是空的,那么此时 l2 一定不是空节点swap(l1, l2); // 交换 l1 与 l2,保证 l1 非空,从而简化代码carry += l1->val + (l2 ? l2->val : 0); // 节点值和进位加在一起l1->val = carry % 10; // 每个节点保存一个数位l1->next = addTwoNumbers(l1->next, (l2 ? l2->next : nullptr), carry / 10); // 进位return l1;}
};
138.随机链表的复制
class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;Node* cur = head;unordered_map<Node*, Node*> map;// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射while(cur != nullptr) {map[cur] = new Node(cur->val);cur = cur->next;}cur = head;// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向while(cur != nullptr) {map[cur]->next = map[cur->next];map[cur]->random = map[cur->random];cur = cur->next;}// 5. 返回新链表的头节点return map[head];}
};
应用哈希表的方法,相比普通链表的构造,多了random指针,类似方法进行遍历
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度O(N):两轮遍历链表,使用O(N)时间
- 空间复杂度O(N):哈希表dic使用线性大小的额外空间
94.二叉树的中序遍历
1、递归法
首先确定递归函数的参数和返回值,其次确定终止条件,最后确定单层递归的逻辑
class Solution {
public:vevtor<int> inorderTraversal (TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;inorder(root, res);return res;}// 确定递归函数的参数和返回值void inorder(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) {// 确定终止条件if (root == nullptr) return;// 确定单层递归的逻辑,中序遍历是左中右inorder(root->left, res);res.push_back(root->val);inorder(root->right, res);}
};
2、迭代法
递归的实现是每一次递归调用都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中,然后递归返回的时候,从栈顶弹出上一次递归的各项参数。
递归,就是在运行的过程中调用自己;迭代法也称辗转法,是一种不断用变量的旧值递推新值的过程,跟迭代法相对应的是直接法(或者称为一次解法),即一次性解决问题。
class Solution {
public:vectot<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;stack<TreeNode*> result;TreeNode* cur = root;while (cur != nullptr || !st.empty()) {if (cur != nullptr) {st.push(cur);cur = cur->left;} else {cur = st.top();st.pop();result.push_back(cur->val);cur = cur->right;}}return result;}
};
200.岛屿数量
关于图论,了解一下就行,笔试大概率遇不到
深度优先搜索:
class Solution {
private:int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; //四个方向void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; //越界了,直接跳过if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { //没有访问过的,同时是陆地visited[nextx][nexty] = true;dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}}}
public:int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {visited[i][j] = true;result++; //遇到没访问过的陆地,+1dfs(grid, visited, i, j);}}}return result;}
};
广度优先搜索:
class Solution {
private:int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; //四个方向void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<pair<int, int>> que;que.push({x, y});visited[x][y] = true; //只要加入队列,立刻标记while (!que.empty()) {pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();int curx = cur.first;int cury = cur.second;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][0];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; //越界了,直接退出if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {que.push({nextx, nexty});visited[nextx][nexty] = true; //只要加入队列立刻标记}}}}
public:int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {visited[i][j] = true;result++; //遇到没访问过的陆地,+1bfs(grid, visited, i, j); //将与其连接的陆地都标记上true}}}return result;}
};
543.二叉树的直径
class Solution {
public:int ans = 0;int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {// 注意路径可能不经过根节点,所以像下面相加的有小问题(ac95%),错了才知道QAQ// if (root->left == nullptr & root->right == nullptr) return 0;// // 二叉树根节点深度改版,左右结点最大深度之和// return dfs(root->left) + dfs(root->right);dfs(root);return ans;}int dfs(TreeNode* cur) {if (cur == nullptr) return -1; //根节点路径为0int l = dfs(cur->left) + 1;int r = dfs(cur->right) + 1;ans = max(ans, l + r);return max(l, r);}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N为二叉树的结点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),最坏情况下,二叉树退化成一条链,递归需要O(N)的栈空间。
102.二叉树的层序遍历
套用层序遍历模板,广度优先搜索BFS
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);vector<vector<int>> result;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();vector<int> vec;// 这里使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为它不断变化for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop(); // 弹出队首元素vec.push_back(node->val);if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}result.push_back(vec);}return result;}
};
递归法,亦可称作深度优先搜索DFS
class Solution {
public:void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth){if (cur == nullptr) return;// 创建不同depth的result[depth]if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>());result[depth].push_back(cur->val);order(cur->left, result, depth + 1);order(cur->right, result, depth + 1);}vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> result;int depth = 0;order(root, result, depth);return result;}
};
时间空间复杂度为O(N),N为二叉树结点数量。
2024.04
105.从前序和中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
private:unordered_map<int, int> index;public:TreeNode* myBuildTree(const vector<int>& preorder, const vector<int>& inorder, int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right) {if (preorder_left > preorder_right) {return nullptr;}// 前序遍历中的第一个节点就是根节点int preorder_root = preorder_left;// 在中序遍历中定位根节点int inorder_root = index[preorder[preorder_root]];// 先把根节点建立出来TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]);// 得到左子树中的节点数目int size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left;// 递归地构造左子树,并连接到根节点// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1 开始的 size_left_subtree」个元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 左边界 开始到 根节点定位-1」的元素root->left = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + 1, preorder_left + size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root - 1);// 递归地构造右子树,并连接到根节点// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1+左子树节点数目 开始到 右边界」的元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 根节点定位+1 到 右边界」的元素root->right = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + size_left_subtree + 1, preorder_right, inorder_root + 1, inorder_right);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {int n = preorder.size();// 构造哈希映射,帮助我们快速定位根节点for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {index[inorder[i]] = i;}return myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);}
};437.路经总和III
非自顶向下方法,任意结点开始(并非都是根节点)
class Solution {
public:int path = 0;int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if (!root) return 0;dfs(root, targetSum);// 递归左子树和右子树pathSum(root->left, targetSum);pathSum(root->right, targetSum);return path;}void dfs(TreeNode* root, long target) {// 递归左右结点if (root == nullptr) return;target -= root->val;if (target == 0) path++;dfs(root->left, target);dfs(root->right, target);}
};
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
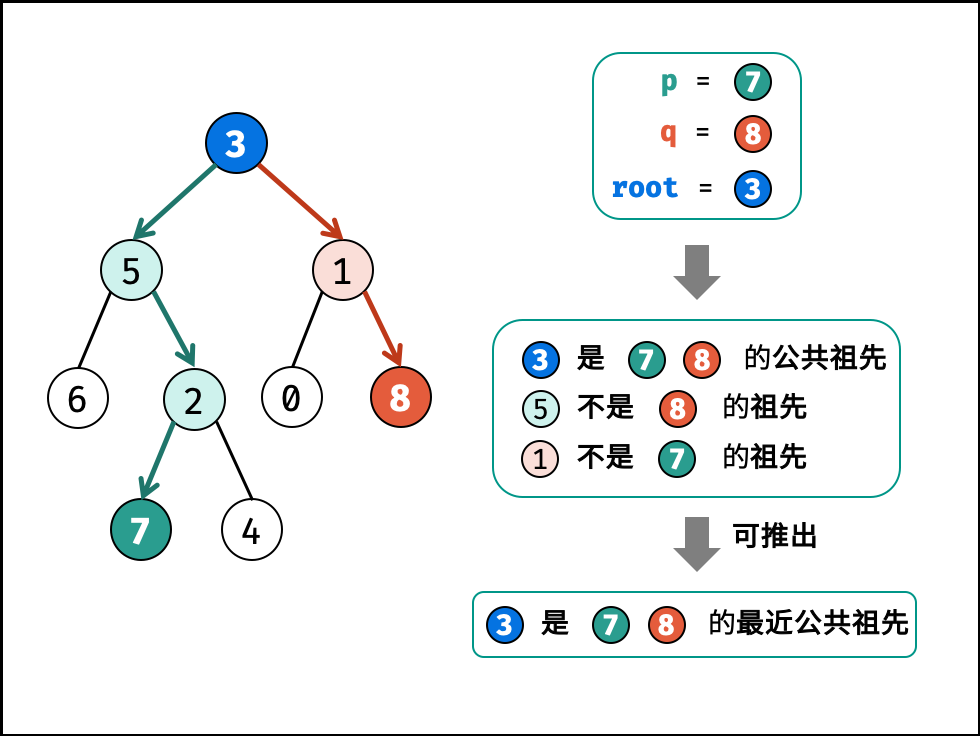
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {// 寻找最近公共祖先,DFS根节点,如何找到最近的,一种情况是root就为p或q或者root为空,此时返回root// 1 终止条件if (root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;// 2 递推工作TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p ,q);// 3 返回值// 情况1,left和right同时为空,此时并不包含p和qif (left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return nullptr;// 情况3,left为空,right不为空,p和q都不在root左子树中,直接返回rightif (left == nullptr) return right;// 情况4与3同理if (right == nullptr) return left;// 情况2,left和right不同时为空,p和q分别位于root两侧,返回rootreturn root;}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度O(N):其中N为二叉树结点树:最差的情况下,需要递归遍历树的所有结点
- 空间复杂度O(N):最差情况下,递归深度达到N,系统使用O(N)大小的额外空间
124.二叉树中的最大路径和
非自顶向下方法(树根节点不一定在路径中)
left,right分别为根节点左右子树最大路径和,注意:如果最大路径和<0,意味着该路径和对总路径和做负贡献,因此不要计入到总路径中,将它设置为0
class Solution {
public:int ans = INT_MIN; // 注意节点值可能为负数,因此要设置为最小值int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {maxPath(root);return ans;}int maxPath(TreeNode* root){ // 以root为路径起始点的最长路径if (!root) return 0;int left = max(maxPath(root->left), 0);int right = max(maxPath(root->right), 0);ans = max(root->val + left + right, ans);return max(left + root->val, right + root->val); // 返回左右子树较长的路径加上根节点值}
};



)





——图解逐步分析底层源码)
小案例银行家应用程序-介绍)
| 即插即用)







